JAC Board Class 10th English Grammar Modals
JAC Class 10th English Grammar Modals Textbook Questions and Answers
Modal:
Auxiliary verbs are used together with a main verb to show its tense or to form a negative or
question. Auxiliary verbs are also called helping verbs.
These are classified into two types – Primary Auxiliaries and Modal Auxiliaries.
Be, have and do are Primary Auxiliaries. They change their forms according to the number and person of the subject.
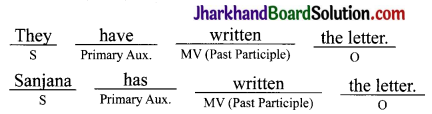
Note: MV means main verb.
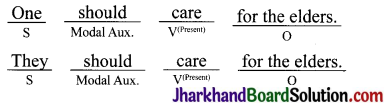
Modal Auxiliaries are used to show possibility, ability, permission and obligation. They do not change their forms according to the number and person of the subject. They are always followed
![]()
Uses Of Primary Auxiliary Verbs (Be, Have, Do)
Use of Be:
or to be verb includes is, am, are, was, were. These are paired with a main verb to create a complete verb phrase. Different be forms tell about different tenses of the main verbs and also the number of the subject in a sentence.
Examples:
The kite is flying in the sky.
Children are playing hide and seek.
The new cutlery was placed on the dining table.
The letters were distributed by the postman.
Use of Have:
Have as an auxiliary verb is always paired with a main verb. It includes has and had. These are used to form the perfect tense form of present, past and future.
Examples:
Jessica has bought a new cardigan for winter.
Raj and his friends have never been to a beach.
They had completed their assignment before the last date of submission.
to ask a question politely.
Example: Could I take one more chocolate?
to show weak possibility.
Example: We could go outside for dinner.
to express a suggestion or an offer.
Example: I could book a cab for you.
![]()
Use of Must:
Must is used-
to express necessity.
Example: One must respect one’s elders.
to recommend something strongly.
Example: You must exercise to keep yourself fit.
to show certainty.
Example: We are going in the right direction and the clinic must be on the next street.
Use of Ought to:
Ought to is used to express moral responsibility or duty.
Example:
Siblings ought to take care of each other.
Note: ‘Ought’ is always followed by the infinitive ‘to’.
Use of Used to:
Used to is used to express a past habit.
Example:
I used to cycle a lot during my childhood days.
Note: While using ‘used to’ in interrogative sentences, we use ‘use to’.
Example:
Did he use to smoke?
![]()
Use of Need:
Need is used mainly in negative and interrogative sentences. As a modal, it is followed by an infinitive without ‘to’.
In negative sentences, it is used to say that something is not necessary
Examples:
You need not buy an extra pair of shoes.
People now need not pay parking charges in malls.
In interrogative sentences, it is used in the beginning to ask if something is necessary.
Examples:
Need I come along with you at parent-teacher meeting?
Need he answer all the questions?
Use of Dare:
Dare is used in negative and interrogative sentences. Like need, it is also followed by an infinitive without ‘to’.
In negative sentences, it is used to show that one does not have courage enough to do a work.
Examples:
I dare not go to school late.
He dares not speak loudly in front of his teacher.
In interrogative sentences, it is used to warn or threaten someone from preventing him to do a work.
Examples:
Dare you disconnect the call when I am talking?
Dare he shout at me?
Use of Have to/Had to:
Have to is used to express obligation and necessity in the present while had to is used to do so in the past.
Examples:
You have to call at the reception desk at 4 pm.
Kanika had to finish the work in a hurry.
![]()
Exercise (Solved)
A. Answer any ten of the questions given below by choosing the most appropriate modals from the given option. [10 x 1 = 10]
1. Students ……………. study hard to score well in the final examinations.
(a) may
(b) need to
(c) would
(d) have to
Answer:
(d) have to
2. Rahul ……………….. start preparing for the entrance of India’s top universities.
(a) can
(b) should
(c) ought to
(d) should hase
Answer:
(b) should
3. Ayesha ……………….. not read French when she was only five years old.
(a) can
(b) should
(c) would
(d) could
Answer:
(d) could
4. Ahana ……………….. to be courteous and well-mannered to work with others.
(a) should
(b) must
(c) need
(d) has to
Answer:
(c) need
![]()
5. ……………….. is used for the moral duty or obligation.
(a) Should
(b) Must
(c) Have to
(d) Ought to
Answer:
(d) Ought to
6. ……………….. I talk to mv parents, please? Itas urgent.
(a) Could
(b) Do
(c) Can
(d) Should
Answer:
(a) Could
7. I and mv brother ……………….. exercise regularly in the early morning.
(a) should
(b) ought to
(c) used to
(d) will
Answer:
(c) used to
8. You ……………….. be loyal to our country.
(a) dare
(b) can
(c) could
(d) Ought to
Answer:
(d) Ought to
9. ……………….. you please help nie to learn this debate?
(a) Can
(b) Could
(c) Will
(d) Would
Answer:
(b) Could
![]()
10. You ……………….. leave your important documents ¡n the
(a) won’t
(b) mustn’t
(c) shouldn’t
(d) couldn’t
Answer:
(c) shouldn’t
11. You ……………….. take your rain coat. It Is not raining.
(a) shouldn’t
(b) mustn’t
(c) haven’t
(d) needn’t
Answer:
(d) needn’t
12. ……………….. are used for future expression.
(a) Shall
(b) Will
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) Ought to
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
B. Answer any ten of the questions given below by choosing the most appropriate modals from the given option. [10 x 1 = 10]
1. ……………….. I check the examination papers?
(a) Shall
(b) llave
(c) Will
(d) Should
Answer:
(a) Shall
2. You ……………….. silent your mobile phone when you are doing something important.
(a) have to
(b) ought to
(c) need to
(d) used to
Answer:
(b) ought to
3. If you score well in your examination, you ……………….. get a reward.
(a) shall
(b) must
(c) have to
(d) will
Answer:
(d) will
4. ……………….. I learn Spanish language?
(a) Could
(b) Shall
(b) Can
(d) Should
Answer:
(d) Should
![]()
5. Drivers ……………….. stop is’heii the traffic lights arc red.
(a) should
(b) have to
(c) may
(d) must
Answer:
(d) must
6. ……………….. sou mind accompanying nie to the airport today, please?
(a) Should
(b) Could
(c) Would
(d) Will
Answer:
(a) Should
7. Must Is used to express:
(a) Possibility, assumption, obligation, and disapproval
(b) Obligation, persuade, need and past
(c) Obligation, possibility, necessity and duty
(d) Obligation, duty, necessity and compulsion
Answer:
(d) Obligation, duty, necessity and compulsion
8. He ……………….. not oppose his father.
(a) ought
(b) shall
(c) dare
(d) will
Answer:
(c) dare
9. ……………….. I leave and play for a while?
(a) Should
(b) Could
(c) May
(d) Would
Answer:
(c) May
10. The construction work of our home ……………….. be finished by the end this month.
(a) might
(b) should
(c) have to
(d) doesn’t
Answer:
(c) have to
11. You ……………….. not smoke in the hospital.
(a) have
(b) should
(c) could
(d) must
Answer:
(d) must
![]()
12. I made a few purchases. The first item that I ……………….. was cupboard.
(a) must
(b) have
(c) have to get
(d) had to have
Answer:
(d) had to have