Jharkhand Board JAC Class 9 English Solutions Grammar Modals Exercises Questions and Answers.
JAC Board Class 9 English Grammar Modals Exercises
Modals अर्थात् modal auxiliaries को पूर्ण रूप से समझने से पहले auxiliaries की परिभाषा व महत्व को जानना अति आवश्यक है।
किसी auxiliary को आमतौर पर एक ‘सहायक क्रिया’ के रूप में जाना जाता है जो किसी क्रिया (मुख्य क्रिया) को एक विशिष्ट अर्थ प्रदान करने के अतिरिक्त, किसी वाक्य की पहचान (काल) स्थापित करती है। सहायक क्रियाएँ मुख्य क्रियाओं के विभिन्न रूपों का निर्माण विभिन्न ग्रकार के वाक्यों व कालों की आवश्यकताओं के लिए करती हैं।
![]()
Kinds of Auxiliaries
Auxiliaries दो प्रकार की होती हैं –
(A) Primary Auxiliaries (प्राथमिक सहायक क्रियाएँ)
(B) Modal Auxiliaries (विधिसूचक सहायक क्रियाएँ)
(A) Primary Auxiliaries
इनमें be, have तथा do (मुख्य क्रियाओं) के विभिन्न रूप – be = is, am, are, was, were, been; have = has, have, had; do=do, does, did आदि न केवल मुख्य क्रियाओं बल्कि सहायक क्रियाओं के रूप में भी प्रयुक्त होती है। Auxiliaries के रूप में ये विभिन्न कालों का निर्धारण करती हैं, जबकि मुख्य क्रियाओं के रूप में ये क्रमशः अवस्था (state), निजता (Possession) तथा कार्य (work) का बोध कराती हैं।
उदाहरण:
(1) Hari is reading a novel. हरी एक उपन्यास पढ़ रहा है। (Auxiliary)
(2) Hina was sleeping. हिना सो रही थी। (Auxiliary)
(3) They were going home. वे घर जा रहे थे। (Auxiliary)
(4) I did not know him. मैं उसे नहीं जानता था। (Auxiliary)
(5) Do you like sweets ? क्या आप मिठाइयाँ पसंद करते हैं? (Auxiliary)
(6) Sheela was weeping. शीला रो रही थी। (Auxiliary)
(7) I have done my work. मैंने अपना कार्य कर लिया है। (Auxiliary)
(8) Rani is my best friend. रानी मेरी सबसे अच्छी सखी है। (Main Verb of State)
(9) Rahul has a car. राहुल के पास एक कार है। (Main Verb of Possession)
(10) She did a work of praise. उसने प्रशंसा का एक कार्य किया। (Main Verb of Action)
![]()
(B) Modal Auxiliaries
‘Modal’ शब्द की उत्पत्ति ‘mode’ शब्द से हुई है जिसका आशय प्रवृत्ति (nature), व्यवहार (behaviour) या मनोस्थिति (mood) से होता है। कुछ ऐसे शब्द — can, could, may, might, shall, should, will, would, must, ought to, need, used to, dare-जो Main verbs के साथ मिलकर सामर्थ्य (capacity), योग्यता (ability), शक्ति (power), अनुमति (permission), सम्भावना (possibility), इच्छ (willingness), धमकी (threat), दृढ़-निश्चय (determination), निषेधाज्ञा (prohibition), अनिवार्यता (compulsion), साहस (courage), आवश्यकता (necessity) जैसे भावों को व्यक्त करने में सक्षम हों, modals या modal auxiliaries कहलाते हैं। Modals का प्रयोग केवल सहायक क्रियाओं (helping verbs) के रूप में ही हो सकता है।
Modal Auxiliaries की विशेषताएँ
1. ये हमेशा मुख्य क्रिया के साथ सहायक की भूमिका में ही प्रयुक्त होती हैं। Modals का प्रयोग निम्न नियमों के अनुसार किया जाता है-
Active Voice : Subject + Modal + Main Verb + Complement.
Passive Voice : Object + Modal + be + Verb III + Complement.
उदाहरण :
- He should obey his parents.
- It may rain today.
- You shall be given the prize.
- I will prove my worth.
2. इन पर कर्ता (Subject) के वचन (Number), लिंग (Gender) का कोई प्रभाव नहीं पड़ता।
उदाहरण :
- He can run fast.
- She can cook well.
- Birds can fly easily.
- It can be advantageous for us.
3. इनके बाद not लगाने से Negative तथा Modal को Subject के पहले रखने से वाक्य Interrogative बन जाता है।
उदाहरण :
- He cannot lift this heavy box.
- What can you do ?
- Would you mind my interrupting you?
- You need not worry about me.
4. एक ही वाक्य में Primary व Modal Auxiliaries का प्रयोग हो सकता है, लेकिन Modal Auxiliary का प्रयोग Primary Auxiliary के पहले होगा।
उदाहरण : I might have gone to the party.
यहाँ might, Modal Auxiliary तथा have Primary Auxiliary है।
![]()
5. Modal Auxiliaries की infinitive form (to + modal, e.g. to will, to could) या present participle (can + ing, could + ing) व past participle नहीं होते।
उदाहरण :
- You must take medicine every day.
- Hari can do this work well.
Note : Ought व used के बाद to V1 (to Infinitive) का प्रयोग किया जाता है।
6. Negative Questions (नकारात्मक प्रश्न) वाले वाक्यों में अधिकतर Modals के साथ n’t का प्रयोग करते हैं ।
उदाहरण :
- You can’t do this job.
- Can’t you lift this weight ?
- Wouldn’t you listen to what she has to say?
- Mustn’t we keep quiet here?
Modal Auxiliaries के Negatives के विभिन्न रूप – इनके निम्न दो रूप हैं –

नोट –
(1) उपर्युक्त संक्षिप्त रूप (Short negative forms या contracted forms) का प्रयोग बोलचाल की भाषा में तथा अनौपचारिक लेखन (informal writing), जैसे – व्यक्तिगत पत्र या मित्र के लिए लिखे पत्र आदि में करते हैं।
(2) can, may, will तथा shall के past forms – could, might, would तथा should होते हैं लेकिन इन past forms से हमेशा वही भावना व्यक्त नहीं होती है जो इनके present forms से होती है। इनके past forms से अनेक अन्य भावों की भी अभिव्यक्ति होती है।
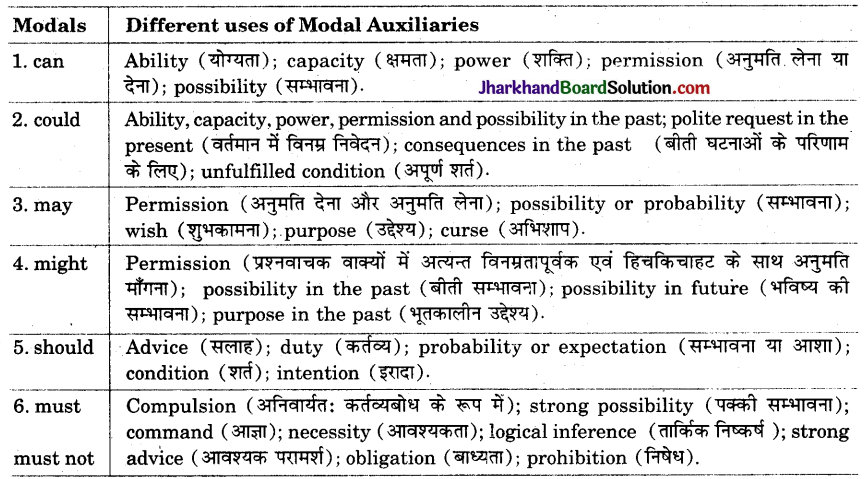
आपके पाठ्यक्रम में ये modals हैं-can, could, may, might, should, must । अतः हम यहाँ इन्ही का वर्णन कर रहे हैं।
![]()
1. Uses Of ‘CAN’
Can का अर्थ है – ‘सकना’ । इसका प्रयोग Present Tense में निम्न भाव प्रकट करने के लिए होता है –
(A) योग्यता (ability), क्षमता (capacity) या शक्ति (power) का भाव प्रकट करने के लिए :
(to express ability, capacity or power)
1. I can teach mathematics.
मैं गणित पढ़ा सकता हूँ। (मुझमें गणित पढ़ाने की योग्यता है।) (ability)
2. A blind man cannot see. एक अंधा आदमी नहीं देख सकता।
(अन्धे आदमी में देखने की क्षमता नहीं होती, अतः नहीं देख सकता है।) ( योग्यता)
3. We can climb this tree. हम इस पेड़ पर चढ़ सकते हैं। (capacity)
(हममें इस पेड़ पर चढ़ने की सामर्थ्य है।) (power, stamina) ( क्षमता )
4. I can lift this heavy box. मैं इस भारी बक्से को उठा सकता हूँ। (strength)
(मुझमें इस भारी बक्से को उठाने की ताकत है।) (शक्ति, सामर्ध्य)
5. I can solve this puzzle. मैं इस पहेली को हल कर सकता हूँ। (intelligence)
(मुझमें इस पहेली को हल करने की बुद्धि है।) ( ताकत)
6. I can befool him. मैं उसे मूर्ख बना सकता हूं। (cleverness)
(मुझमें इतनी चतुराई है।) (बुद्धि)
(B) अनुमति या आदेश देने या लेने का भाव प्रकट करने के लिए :
(be permitted to, be allowed to)
1. You can go now. अब तुम जा सकते हो। (order) (आदेश)
2. Can I use your pen ? क्या मैं आपकी कलम प्रयोग कर सकता हूँ? (permission) (स्वीकृति लेना)
3. Nobody can roam in this prohibited area. (order)
कोई इस प्रतिबंधित क्षेत्र में नहीं घूम सकता। (आदेश)
4. Can’t she enter without permission? (Permission)
क्या वह बिना अनुमति प्रवेश नहीं कर सकती है ? (अनुमति)
Note : can का प्रयोग अनौपचारिक रूप से permission लेने के लिए किया जाता है।
(C) सम्भावना या असम्भावना व्यक्त करने के लिए :
(to express possibility or impossibility)
- Accidents can happen everywhere. दुर्घटनाएँ हर स्थान पर हो सकती हैं।
- ‘The Ramayana’ can be found in the household of every Hindu. (Possibility)
‘रामायण’ प्रत्येक हिन्दू के परिवार में पाई जा सकती है। (सम्भावना)
नोट – किसी बात की सम्भावना जानने के लिए जब प्रश्न किया जाता है तो can का ही प्रयोग किया जाता है, may का नहीं। जैसे –
1. Can this boy be a thief? — क्या यह लड़का एक चोर हो सकता है?
2. Can a crow be white? — क्या कोई कौआ सफेद हो सकता है ?
3. Can the blind see? — क्या नेत्रहीन देख सकते हैं ?
4. Can the lame run? — क्या लंगड़े दौड़ सकते हैं?
![]()
Cannot का प्रयो
वाक्य Negative (नकारात्मक) हो तो can’t या cannot का प्रयोग होगा।
1. I cannot solve this question. (absence of ability)
मैं इस प्रश्न को हल नहीं कर सकता। (योग्यता की कमी)
2. I cannot afford a car. (absence of capability)
मैं कार का खर्च वहन नहीं कर सकता। (क्षमता नहीं, not capable)
3. He cannot lift this box. (not strong, no power)
वह इस बक्से को नही उठा सकता। (शक्ति नही)
4. You can’t park your car here. (not allowed)
तुम अपनी कार को यहाँ खड़ी नहीं कर सकते। (अनुमति नर्ही)
5. This news cannot be true.
यह समाचार सत्य नही्ही हो सकता। (असम्भावना जब कोई बात तार्किक आधार पर गलत हो)
2. Uses Of ‘Could’
Could, can का Past है। could का अर्थ है ‘सका’ या ‘सकता था’। इसका प्रयोग Past Tense में योग्यता (ability), क्षमता (capacity या capability), शक्ति (power), चतुराई (cleverness), बुद्धि (intelligence), संभावना (possibility) आदि व्यक्त करने के लिए होता है।
(A) भूतकाल की योग्यता, क्षमता, शक्ति, ताकत, बुद्धि, चतुराई, अनुमति व सम्भावना व्यक्त करने के लिए अथवा इनका अभाव व्यक्त करने के लिए (to express ability, capacity, power, strength, intelligence, cleverness, permission and possibility in the past or their absence)
1. I could speak English when I was only five years old. (ability of past)
जब मैं मात्र पाँच वर्ष की उम्र का था तब अंग्रेजी बोल सकता था। (भूतकाल की योग्यता)
2. My brother could not send me money last month. (absence of capacity)
मेरा भाई पिछले माह मुझे धन नहीं भेज सका। (क्षमता का अभाव)
3. I could run fast when I was young. (power)
जब मैं युवक था तब तेज दौड़ सकता था। (शक्ति)
4. Umesh could go out whenever he wanted. (permission)
उमेश जब चाहता बाहर जा सकता था। (अनुमति)
(उमेश को अनुमति थी कि जब भी वह चाहे बाहर जा सकता था।)
(B) भूतकाल में सम्भावना के लिए (for possibility in the past)
I could attend the function. मैं उत्सव में सम्मिलित हो सकता था। (possibility) (सम्भावना)
(C) वर्तमान काल में विनम्र निवेदन के लिए (for polite request in the present)
1. Could you lend me your pen ? — क्या तुम मुझे (इसी समय) अपनी कलम उधार दे सकते हो ?
2. Could you tell me the way to the hotel ? — क्या तुम मुझे (इसी समय) होटल का रास्ता बता सकते हो ?
![]()
(D) बीती हुई घटनाओं के लिए (to express incidents in the past)
1. It was so dark that he could see nothing.
इतना अंधेरा था कि वह कुछ भी नही देख सकता था।
2. The fan was so high that Mohan could not touch it.
पंखा इतना ऊँचा था कि मोहन इसे छू नहीं सकता था।
(E) बीते समय की सम्भावना या योग्यता प्रकट करने के लिए (to express past possibility or ability)
कुछ वाक्यों में could + have + Third form of Verb का प्रयोग होता है। इससे यह प्रकट होता है कि काम करने की योग्यता या क्षमता या सम्भावना होते हुए भी भूतकाल में कोई कार्य पूरा न हो सका।
1. She could have passed the examination. (past ability)
वह परीक्षा में पास हो सकती थी। (पर पास हो न सकी) (योग्यता)
2. He couid have caught the train. (past possibility)
वह रेलगाड़ी पकड़ सकता था। (पर पक्ष न सका) (सम्भावना)
(F) काल्पनिक शर्त प्रकट करने के लिए (to express an imaginary condition)
1. If I reached earlier, I could catch the bus.
यदि मैं और जल्दी पहुँच जाऊँ, तो बस पकड़ लूँ। (परन्तु इस वाक्य में भाव यह है कि मैं जल्दी पहुचूँगा नहीं और इसलिए बस नहीं पकड़ सकूँगा।)
2. I could buy a scooter if I had money. यदि मेरे पास धन हो तो मै स्कूटर खरीद लूँ।
(परन्तु वाक्य दर्शाता है कि वक्ता के पास धन नहीं था। वह केवल कल्पना कर रहा है कि यदि धन हो तो स्कूटर खरीद लूँ।)
3. I could solve this problem if I tried. यदि मैं प्रयास करूँ तो मैं इस समस्या को हल कर लूँ। (भाव यही है कि वक्ता प्रयास नहीं करेगा और समस्या हल भी नहीं कर पाएगा। वह केवल कल्पना मात्र कर रहा है।)
(G) Indirect speech में could का प्रयोग (use of ‘could’ in Indirect speech)
जब Reporting Verb, Past Tense में हो तो Reported Speech में दिए गए ‘can’ को ‘could’ में बदलते हैं, जैसे –
1. She said, “I can sing old songs excellently.”
She said that she could sing old songs excellently.
2. Ram said, “I can write a novel.”
Ram said that he could write a novel.
Could not का प्रयोग
भूतकाल की अयोग्यता (inability/disability) को बताने के लिए
He was very weak. He could not walk properly. (absence of ability in past)
![]()
3. Uses of ‘May’
May का अर्थ भी ‘सकना’ होता है। इसका प्रयोग Present Tense में अनुमति लेने या देने, संभावना (possibility), शुभकामना या मनोकामना, आशीर्वाद (blessings) या शाप देने (curse) के लिए किया जाता है।
(A) अनुमति लेने अथवा देने के लिए (for giving or asking permission)
1. May I come in; sir ? क्या मैं अन्दर आ सकता हैँ, श्रीमान् ?
2. You may go home. तुम घर जा सकते हो। (formal permission)
(B) सम्भावना प्रकट करने के लिए (to express possibility) (giving permission)
1. There are clouds in the sky. It may rain tonight. (possibility)
आकाश में बादल हैं। आज रात वर्षा हो सकती है। (सम्भावना)
2. Today is Sunday. He may go home. (possibility)
आज रविवार है। वह घर जा सकता है। (सम्भावना)
3. The news may be true. समाचार सही हो सकता है।
(C) व्यक्तिगत शुभकामना, आशा एवं विश्वास व्यक्त करने के लिए (possibility) (सम्भावना)
(to express personal wish, hope or faith)
1. May you live long ! ईश्वर करे तुम चिरंजीवी रहो ! (wish)
2. May he return home safe ! ईश्वर करे वह घर सुरक्षित लौटे ! (hope)
3. May God bless you with strength and wisdom! — (belessing)
ईश्वर आपको शक्ति व बुद्धिमत्ता प्रदान करे ! — (आशीविद्ध)
4. May all the sinners go to hell ! सभी पापी नर्क में जायें ! — (curse) (शाप)
(D) उड्देश्य प्रकट करने के लिए (to show purpose)
1. Work hard so that you may pass. कठोर परिश्रम करो ताकि तुम सफल हौ सकौ।
2. We eat so that we may live. हम भोजन करते हैं ताकि हम जीवित रह सकें।
(E) जब वाक्य में ‘भले ही’ या ‘चाहे’ का अर्थ ध्वनित होता हो तो उस स्थिति में may का प्रयोग होता है। जैसे-
1. Whatever place she may visit, she cannot forget her home.
भले ही वह कहीं भी चली जाए, वह अपने घर को नहीं भूल सकती।
2. Priya may have learnt English for years, her English is still poor.
चाहे प्रिया वर्षों अंग्रेजी सीख चुकी है, उसकी अंग्रेजी फिर भी कमजोर है।
Note : नकारात्मक वाक्यों के लिए may not का प्रयोग होता है।
![]()
4. Uses Of Might
‘Might’ may का Past Tense Form है। इसका प्रयोग निम्न प्रकार से किया जाता है –
(A) प्रश्नवाचक वाक्यों में विनम्रतापूर्वक एवं हिच्चिचाहटपूर्वक अनुमति माँगने के लिए
1. Might I take your pen ? क्या मैं आपकी कलम ले सकता हूँ ?
2. Might we spend some time here ? क्या हम यहाँ कुछ समय व्यतीत कर सकते हैं ?
नोट –
(a) यद्यपि अनुमति माँगने के लिए वर्तमान काल के प्रश्नवाचक वाक्यों में may का प्रयोग होता है पर might से अत्यन्त विनम्रतापूर्वक एवं हिचकिचाहटपूर्ण अनुमति माँगने का भाव प्रकट होता है। इं वाक्यों से संकोच या संदेह का भाव भी प्रकट होता है।
(b) Indirect speech में ‘may’ के स्थान पर ‘might’ के प्रयोग के अतिरिक्त ‘might’ का प्रयोग अनुमति देने या अनुमति न देने के अर्थ में नहीं किया जाता।
She said to me, “I may help you.” — उसने मुझसे कहा, “मैं तुम्हारी सहायता कर सकती हूँ।”
She told me that she might help me. — उसने मुझे बताया कि वह मेरी सहायता कर सकती थी।
(B) बीती हुई संभावना प्रकट करने के लिए (to express past possibility)
1. Your eldest son might have become a doctor.
तुम्हारा सबसे बड़ा लड़का डॉक्टर हो सकता था (पर हुआ नहीं)।
2. He fell from the roof and broke his leg. He might have died.
वह छत से गिर गया और उसकी टाँग टूट गई। वह मर सकता था (पर मरा नहीं)।
(C) अत्यन्त क्षीण सम्भावना प्रकट करने के लिए (to express remote possibility)
1. Take a taxi. You might catch the train. (remote possibility)
टैक्सी ले लो। तुम्हें गाड़ी मिल सकती है (जिसकी सम्भावना बहुत कम है)।
2. The sky is clear now. It might rain tonight. (remote possibility)
अभी आसमान स्वच्छ है। रात को वर्षा हो सकती है (पर सम्भावना बहुत कम है)।
3. She might reply my letter. (remote possibility)
वह मेरे पत्र का उत्तर दे सकती है (जिसकी सम्भावना बहुत कम है)।
(D) भूतकालीन उद्देश्य प्रकट करने के लिए (to express purpose in the past)
1. He took medicine so that he might get well.
उसने दवा ली ताकि वह अच्छा हो सके।
2. The patriots sacrificed their lives so that we might live honourably.
देशभक्तों ने अपना जीवन इसलिए बलिदान किया ताकि हम सम्मानपूर्वक जी सकें।
Note : वाक्य नकारात्मक हो तो might not का प्रयोग होगा।
![]()
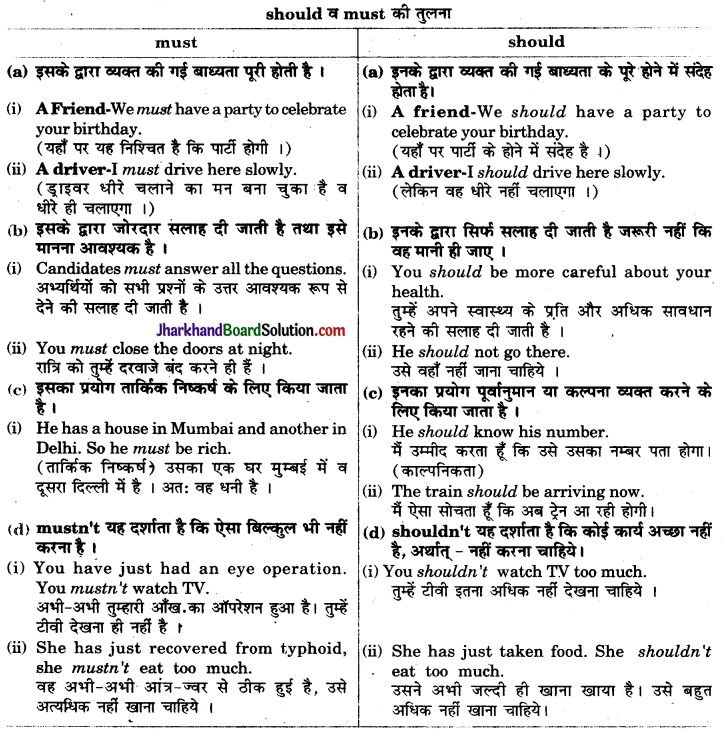
5. Uses Of ‘Should’
Should का अर्थ ‘चाहिये’ होता है। इसका प्रयोग advíce (सलाह), suggestion (सुझाव), duty (कर्त्तव्य), probability or expectation (अनुमान या सम्भावना), conditional (शर्त वाले वाक्य) में lest (ऐसा न हो कि) के बाद होता है। इसका प्रयोग shall के Past के रूप में भी होता है। सामान्यतः परीक्षा में advice व duty के लिए ही इसे पूछा जाता है।
(A) Shall के Past Tense के रूप में (as the past form of ‘shall’)
यदि Reporting Verb का कर्त्ता First Person का है और Reporting Verb, Past Tense में है तो Reported Speech में आये हुए shall को Indirect में परिवर्तित करते हुए should में बदल देते हैं। जैसे –
Direct : I said, “I shall shine in my life.”
मैंने कहा, “मैं अपने जीवन में असाधारण रूप से सफलता अर्जित करूँगी।”
Indirect : I hoped that I should shine in my life.
मैंने आशा की कि मैं अपने जीवन में असाधारण सफलता अर्जित करूँगी।
(B) सलाह या सुझाव (advice or suggestion)
1. We should take a bath daily. हमें प्रतिदिन स्नान करना चाहिए। (advice)
2. That is a dangerous place, he should not go there. (suggestion)
वह एक खतरनाक स्थान है, उसे वहॉँ नहीं जाना चाहिए।
3. They should sell their house in order to pay their debt. (advice/suggestion)
उन्हें अपना कर्जा चुकाने के लिए अपना मकान बेच देना चाहिये।
(C) कर्त्तव्य (duty)
1. We should obey the elders. हमें बड़ों की आज्ञा माननी चाहिए।
2. We should always speak the truth. हमें सदा सत्य बोलना चाहिए।
(D) अनुमान या सम्भावना (probability or expectation)
1. She should reach here soon.( ऐसी संभावना है कि) उसे यहाँ जल्दी ही पहुँचना चाहिए।
2. He should be at the theatre. (ऐसा अनुमान है कि) वह नाट्यशाला में मौजूद है।
(E) शर्त if के अर्थ में (in the sense of ‘if’ showing condition)
1. Should it rain, we shall not go home.
(Should it rain = If it rains) यदि वर्षा हुई तो हम घर नहीं जायेंगे।
2. Should it rain, there will be no match. यदि वर्षा हुई तो मैच नहीं होगा।
(F) Lest के बाद should का प्रयोग (use of ‘should’ after ‘lest’)
भविष्य में होने वाली किसी घटना की चिन्ता व्यक्त करने के लिए lest (कहीं ऐसा न हो कि) के साथ should का प्रयोग होता है। जैसे –
1. Walk carefully lest you should fall. संभलकर चलो कहीं ऐसा न हो कि तुम गिर जाओ।
2. Work hard lest you should fail. कठिन परिश्रम करो कहीं ऐसा न हो कि तुम अनुत्तीर्ण हो जाओ।
![]()
6. Uses Of ‘Much’
Must का तात्पर्य है ‘निश्चित रूप से चाहिये’। इस Modal का प्रयोग अनिवार्यता (compulsion), आवश्यकता (necessity), बाध्यता (persuation), प्रबल सम्भावना (strong possibility), आवश्यक सलाह/परामर्श (strong advice), तर्कसंगत निष्कर्ष (logical inference) आदि को व्यक्त करने के लिए किया जाता है।
(A) अनिवार्यता (compulsion)
We must reach school in time to avoid punishment.
हमें सजा से बचने के लिए समय पर विद्यालय पहुँचना चाहिए।
(B) प्रबंल संभावना (strong possibility)
1. He must be a dacoit. वह डाकू होना चाहिये ( निश्चित रूप से)।
2. He has three cars. He must be a rich man.
उसके पास तीन कारें हैं। (निश्चित रूप से) वह धनी व्यक्ति होना चाहिए।
(C) आज्ञा व्यक्त करने के लिए (to express command)
1. You must stay where you are. तुम्हें वर्हीं रुकना चाहिए जहाँ तुम हो। (आज्ञा)
2. She must attend all her classes. उसे अपनी सारी कक्षाओं में शामिल होना है।
(D) आवश्यकता व्यक्त करने के लिए (to express necessity)
We must work hard to pass. उत्तीर्ण होने के लिए हमें आवश्यक रूय से कठोर परिश्रम करना चाहिए।
(E) आवश्यक परामर्श के लिए (to express strong advice)
You must close all the doors in the night.
तुम्हें (परामर्श दिया जाता है कि) रात्रि में सभी दरवाजे बन्द करने चाहिए।
(F) तर्कसंगत निष्कर्ष के लिए (to express logical inference) Hari is an intelligent boy. He must get first division.
Use of ‘must not’
(A) प्रतिबन्ध (Prohibition) के लिए must not का प्रयोग होता है। जैसेWe must not park our vehicles at public places.
हमें सार्वजनिक स्थानों पर अपने वाहन खड़े नहीं करने चाहिए।
(B) आदेश तथा चेतावनी के साथ नकारात्मक सलाह व्यक्त करने के लिए
(to express order, negative advice with warnings)
You must not overtake from the left.
आप बायें से दूसरे वाहनों से आगे नहीं निकल सकते।
![]()
Chart of Modals
 Note : यद्यपि निम्न तीन Modals आपकी कक्षा IX के पाठ्यक्रम में नहीं हैं। फिर भी ये तीनों दैनिक जीवन में बहुत उपयोगी है। अतः इन्हें दे रहे हैं।
Note : यद्यपि निम्न तीन Modals आपकी कक्षा IX के पाठ्यक्रम में नहीं हैं। फिर भी ये तीनों दैनिक जीवन में बहुत उपयोगी है। अतः इन्हें दे रहे हैं।
(A) Uses On ‘Will’
व्यक्तिगत तौर पर नियन्त्रित किया जा सकने वाला कोई तत्व जब वाक्य में उपस्थित नहीं होता तो वाक्य में will का प्रयोग सिर्फ pure future दर्शाता है, जैसे-
1. Tomorrow will be Monday. कल सोमवार होगा।
2. The work will take ten days. इस कार्य में 10 दिन लगेंगे।
(A) सामान्य निर्देश (general instruction)
All the members of this club will attend the meeting.
इस क्लब के सभी सदस्य सभा में शामिल होंगे।
(B) निवेदन (polite request)
Will you please help me ? क्या आप कृपया मेरी सहायता करेंगे ?
(C) संभावना (possibility)
It will be a storm. ऐसी संभावना है fि तूफान आएगा।
(D) आदत (habit) या किसी ऐसी बात को दिखाने के लिए जिसकी, बिना किसी परिवर्तन के, सदैव अपेक्षा की जा सकती है।
1. He will talk only nonsense. उसकी बातें बिना अक्ल की ही होंगी।
2. Accidents will happen. दुर्घटनाएँ तो होंगी ही।
(E) Won’t you का प्रयोग आमन्त्रण (invitation) के लिए किया जाता है।
1. Won’t you stay a little longer? कुछ देर और ठहर जाओ।
2. Won’t you have a cup of coffee? एक कप कॉफी लो।
नोट – आधुनिक अंग्रेजी में I तथा w e के साथ future time व्यक्त करने के लिए shall के स्थान पर will का भी प्रयोग किया जाने लगा है। पर Interrogative Sentences में I और w e के साथ shall का ही प्रयोग होता है, will का नहीं । जैसे – Shall I go to Agra ?
(इस वाक्य में will का प्रयोग नहीं होगा।)
I, we के साथ will का प्रयोग निम्न भाव प्रकट करता है:
(A) वायदा (promise)
1. I will accompany you to Jaipur. मैं (वायदा करता हूँ कि) तुम्हारे साथ जयपुर जाऊँगा।
2. We will help you. हम (वायदा करते हैं कि) तुम्हारी सहायता करेंगे।
(B) दृढ़ निश्चय (determination)
We will fight against injustice. हम (निश्चित रूप से) अन्याय के विरुद्ध लड़ेंगे।
(C) धमकी (threat) या चेतावनी (warning)
1. I will arrest you. मैं (धमकी देता हूँ कि) तुम्हें गिरफ्तार कर लूँगा।
2. I will punish you if you do this work again.
यदि तुम इस कार्य को पुनः करते हो तो मैं (चेतावनी देता हूँ कि) तुम्हें दण्ड दूँगा।
(D) इच्छा या सहमति (willingness)
1. I will join the army after two years. (मेरी इच्छा है कि) मैं दो वर्ष बाद सेना में शामिल होऊँगा।
2. We will provide you every possible help. हम आपको हर सम्भव सहायता प्रदान करेंगे।
Note : वाक्य नकारात्मक (Negative) हो तो will not या won’t का प्रयोग होगा।
![]()
(B) Uses Of’ ‘Shall’
First Person के Pronouns (I व we) के साथ shall का प्रयोग केवल Simple Future को प्रकट करता है । उस समय shall केवल एक Auxiliary Verb (सहायक क्रिया) का कार्य करता है उदाहरण : I shall be fifty next birthday. अगले जन्मदिन पर मैं पचास का हो जाऊँगा।
Second Person (you), Third Person (he, she, it, name, they व it) तथा एकवचन संज्ञाओं के साथ shall लगाने पर यह shall Modal Auxiliary का कार्य करेगा तथा निम्न भावों को प्रकट करेगा –
(A) वायदा (promise)
You shall get a prize for your extraordinary bravery. (promise, वायदा)
(वायदा किया जाता है कि) तुम्हारी इस असाधारण बहादुरी के लिए तुमको इनाम मिलेगा।
(B) आज्ञा (command) या धमकी (threat)
1. He shall not attend the class without completing his home work. (command, आज्ञा)
वह अपना गृह कार्य पूर्ण किये बिना कक्षा में उपस्थित नहीं होगा।
(उसको कक्षा में उपस्थित होने की आज्ञा नहीं दी जायेगी।)
2. He shall be punished if he doesn’t behave himself. (threat, धमकी)
(अगर वह अच्छा व्यवहार नहीं करेगा तो उसे दण्डित किया जाएगा।)
(C) कानूनी नोटिसों या कार्यालंयों की व्यवस्था/अधिनियम व्यक्त करने में
(in legal notices or official regulations)
Trespassers shall be punished. बिना अनुमति के घुसने वाले दण्डित किये जायेंगे। (कानूनी चेतावनी)
(D) प्रस्ताव करने अथवा परामर्श/निर्देश प्राप्त करने में
(in offering or seeking advice/instructions)
1. Shall I call in the doctor for you ? क्या मैं आपके लिए चिकित्सक बुलवाऊँ? (प्रस्ताव करने हेतु)
2. Where shall I wait for you ? मैं तुम्हारा इंतजार कहाँ करूँ? (निर्देश प्राप्त करने में)
3. What books shall I consult for the test? (सलाह लेने में)
मैं परीक्षा के लिए कौन-सी किताबों का अध्ययन करूँ?
(E) पक्का इरादा (determination)
You shall help her.
(मैंने इरादा कर लिया है कि मैं तुमसे उसकी मदद करवाऊँगा।)
Note : वाक्य नकारात्मक होने पर shall not या shan’t का प्रयोग होगा।
![]()
(C) Uses Of ‘Would’
Will का Past Tense Form would है । परन्तु इसका प्रयोग polite request ( विनम्र निवेदन), past happenings ( भूतकालीन घटनाओं ), intention (इरादा ज्ञात करने ), others’ wishes (दूसरों की इच्छाओं) आदि हेतु होता है ।
Note : वाक्य Negative होने पर would not का प्रयोग होगा ।
(A) वर्तमान काल में विनम्र निवेदन के रूप में (for polite request in the present)
1. Would you lend me your pen ?
क्या आप मुझे (इसी समय) अपनी कलम उधार देंगे ?
2. Would you tell me the way to the hotel ?
क्या आप मुझे (इसी समय) होटल का रास्ता बतायेंगे ?
नोट-वर्तमान काल में आग्रह करने के लिए will के स्थान पर would के प्रयोग से अधिक नम्रता का भाव प्रदर्शित होता है।
(B) भूतकाल में होने वाली घटनाओं के लिए या भूतकालिन आदत बताने के लिए (for the happenings in the past)
1. Sometimes my father would get angry with me. कभी-कभी मेरे पिता मुझसे क्रोधित हो जाते थे ।
2. On Saturdays, Sohan would usually run home to his mother.
शनिवार को बहुधा सोहन अपनी.माँ के पास घर भाग जाता था ।
(C) किसी व्यक्ति की इच्छा या सहमति ज्ञात करने के लिए
1. Would you like to have some tea ? क्या आप थोड़ी चाय लेना चाहेंगे ?
2. Would you share my joys ? क्या आप मेरे आनन्द बॉटेंगे ?
(D) इरादा प्रकट करने के लिए (to express intention)
I would obey you even if I die. मैं आपकी आज्ञा मानूँगा चाहे मैं मर ही जाऊँ।
(E) प्रश्नवाचक वाक्यों में नम्रतापूर्वक प्रस्ताव, अनुमति तथा इच्छा व्यक्त करने के लिए
(to express polite offer, permission and wish in Interrogatives)
1. Would you like our house ? क्या आप हमारा घर पसंद करेंगे ? (polite offer)
2. Would you mind if I smoke ? यदि मैं धूम्रपान करूँ तो क्या आपको बुरा लगेगा ? (permission)
3. Would that I had become a Minister! काश ! मैं मन्त्री बन जाता । (desire)
(F) बीती सम्भावना प्रकट करने के लिए (to express past possibility)
Sheela would be about sixty when she died.
जब शीला की मृत्यु हुई तब वह लगभग साठ वर्ष की रही होगी ।
Exercise 1.
Fill in the blanks with can or can’t : रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति can या can’t से करो-
1. He …………… play football very well.
2. But he …………… play cricket.
3. This cake is delicious, you …………… cook it easily.
4. Mum, …………… I go out tonight ?
5. No, you …………….
6. I’m sure you …………… do this exercise alone: it’s very easy.
7. This is too difficult ! I …………… do it.
8. …………… your uncle speak Chinese ?
9. Yes, he …………….
10. My uncle is trilingual. He …………… speak French, English and Chinese.
(trilingual = तीन भाषाओं को बोलने वाला।)
Answers:
1. can
2. can’t
3. can
4. can
5. can’t
6. can
7. can’t
8. Can
9. can
10. can
![]()
Exercise 2.
Fill in the blanks with can, could, may or might:
रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति can, could, may या might से करो-
1. ……………. you please pass me that book over there ?
2. When he was young, he …………… dance all night long.
3. ………….. you speak Chinese ?
4. You at least come with us and meet our new neighbour.
5. She ……………. drive safely.
6. In that country citizens
7. Now-a-days, people ………….. travel very easily all over India. now make suggestions openly, it is a new democracy.
9. I don’t know yet, but I …………… come with you after all.
10. She ……………. be in the library.
Answers:
1. Could
2. could
3. Can
4. might
5. can
6. can
7. can
8. Could
9. might
10. may.
![]()
Exercise 3.
Complete the following sentences by should or must:
should या must से निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को पूरा करो-
1. When you play badminton, you …………. watch shuttle-cock.
2. It is very late, we ………………. go home now.
3. I am cooking food so my hands are dirty. I
4. I …………. see him now.
5. If you have time, you …….go to Science Museum at Jaipur.
6. He needs a change so he ………… go away for a few days.
7. He ………… pass the exam. He has been studying very, hard.
8. I have no time to wait. You ………….. answer at once.
9. The film has been a big success. It …………. be a very good film.
10. In this condition what …………….. I do?
Answers:
1. should
2. must
3. must
4. must
5. should
6. should
7. must
8 . must
9. must
10. should
Exercise 4.
Fill in the blanks with should, shouldn’t or mustn’t:
रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति should, shouldn’t या mustn’t से करो-
1. A- I always feel tired of my hard work.
B. You ………….. work so hard.
2. The dentist has told Ravina that she eat any more chocolates. Her teeth are in bad condition.
3. What are you doing here ? ………… you be at the meeting at Kota ?
4. He …………. tell it to his brother. It is confidential.
5. You ………….. make so much noise. They will ask us to leave otherwise.
6. She ………………… stay in bed unless she is ill.
7. She oversleep or she will miss her train.
8. You are a patient of diabetes. You …………. control your diet.
9. Time is money. We …………. waste time on unnecessary discussions.
10. You are quite well now ………… You
Answers:
1. shouldn’t
2. mustn’t
3. Shouldn’t
4. mustn’t
5. mustn’t
6. should
7. mustn’t
8. should
9. shouldn’t
10. should.
![]()
Exercise 5.
Use one of the modal verbs given in brackets to fill each gap:
प्रत्येक रिक्त स्थान को भरने के लिए कोष्ठकों में दी गई modal verbs में से एक का प्रयोग करो ।
1. They …………… (can’t/may) still be out.
2. With luck, tomorrow …………… (can’t/could) be a sunny day.
3. You …………… (can/might) be right but I’m going to check anyway.
4. The exam ……………. (can’t/might) be easy. You never know.
5. I …………….(can’t/might) go to the party but I’m not sure yet.
6. She …………….. (can’t/could) steal things from shops. She is rich and famous.
Answers:
1. can’t
2. could
3. might
4. might
5. might
6. can’t.
Exercise 6.
Use one of the modal verbs given in brackets to fill each gap:
प्रत्येक रिक्त स्थान को भरने के लिए कोष्ठकों में दी गई modal verbs में से एक का प्रयोग करो-
1. She looks pretty sick. I think she
2. You’ve been driving all day. You ……………. be exhausted. (must/should)
3. You …………… smoke so much. It’s bad for your health. (can’t/shouldn’t)
4. Hey! I’m lost. you help me ? (Should/Can)
5. You have such a beautiful voice. You sing for us. (should/can)
6. I know he speaks five languages, but he speak Arabic ? (should/can)
7. I believe that you failed your test. (can’t/shouldn’t)
Answers:
1. should
2. must
3. shouldn’t
4. Can
5. should
6. can
7. can’t.
![]()
Exercise 7.
Use one of the modal verbs given in brackets to fill each gap.
प्रत्येक रिक्त स्थान को भरने के लिए कोष्ठकों में दी गई modal verbs में से एक का प्रयोग करो-
1. You leave now, if you wish. (may/might)
2. …………… you open the window a bit, please ? (Could/May)
3. He …………… be Marathi, judging by his accent. (may/could)
4. ……………. I play the piano ? (Could/May)
5. Listen, please. You …………… speak during this exam. (may not/might not)
6. You be hungry after your long walk. (must/should)
7. It was so hot that I sleep. (can’t/couldn’t)
Answers:
1. may
2. Could
3. could
4. May
5. may not
6. must
7. couldn’t.
Exercise 8.
Fill in the blanks with appropriate modals:
उपयुक्त modals से रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति करो-
1. It is growing dark. We ……………
2. It is very hot today. You …………….go out.
3. You are a worthy citizen. You ……………. fight against injustice.
4. There is no one in the office. You ………….. stay here till someone comes.
5. The day of the wedding is drawing nearer. You …………. buy necessary things.
6. Run fast lest you ……………. miss the train.
7. He has many cars. He ……………. be a very rich man.
Answers:
1. must
2 . shouldn’t
3 . should
4 . must
5 . must
6 . should
7. must.
![]()
Exercise 9.
(Based on the Textbook)
Fill in the blanks with the suitable modals given in the brackets :
कोष्ठक मे दिए modals में से उपयुक्त modal से रिक्त स्थान की पूर्ति कीजिए :
1. [can, could, shall, would, must]
(i) She had been hoping they………. take the teacher away altogether.
(ii) How ……… a man be a teacher?
(iii) ……… I read the book some more with you after school?
(iv) Work hard and you ……… make it.
Answers:
(i) would, (ii) could, (iii) Can, (iv) shall.
2. [can, could, would, cannot]
(i) My speech is clear because I ……… hear till I was eleven.
(ii) They see that there is nowhere that they ………….
(iii) If she can do it, I…………….
(iv) Few had thought that it ……… one day be revived.
Answers:
(i) could, (ii) cannot, (iii) can, (iv) would.
3. [can, could, should, would, must]
(i) Ali Bux would play the shehnai and Bismillah ……… sit captivated for hours on end.
(ii) If you are a good girl you ……… come down and take off father’s boots.
(iii) You ……… be taught once and for all not to touch what does not belong to you.
(iv) Soon Evelyn discovered that she ………. sense certain notes in different parts of her body.
Answers:
(i) would, (ii) can, (iii) must, (iv) could.
![]()
4. [would, could, must, can, should]
(i) I ……… always keep that attractive smile on my face.
(ii). If I made some silly mistake and needed to run away she after me and catch me.
(iii) Half a century later, I ………. still feel the surge of pride in earning my own money for the first time.
(iv) Of course, I found George’s and Harris’s eighteen times over, but I not find my own.
Answers:
(i) would, (ii) should, (iii) can, (iv) could.
5. [would, could, should, can, may]
(i) The new teacher……… not stomach a Hindu priest’s son sitting with a Muslim boy.
(ii) Lakshmana Sastry told the teacher that he……… no spread the poison of social inequality.
(iii) I said I pack.
(iv) I ……..not sit still and see another man slaving and walking.
Answers:
(i) could, (ii) should, (iii) would, (iv) can
6. [shall, should, would, can, could]
(i) In fact, I ……… say mine was a very secure childhood.
(ii) They did that just to show you what they……… do.
(iii) Stand still, ……….not you!
(iv) What time ………. I wake you fellows?
Answers:
(i) would, (ii) could, (iii) can, (iv) shall.
![]()
7. [should, would, can, may, will]
(i) Bruno ……… move his arms and legs a little although he cannot stand yet.
(ii) If my boss agrees, you ……… have him back.
(iii) ……… you please give him back to me?
(iv) I consider what route I take back home.
Answers:
(i) can, (ii) may, (iii) Will, (iv) should.