Jharkhand Board JAC Class 10 Science Important Questions Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts Important Questions and Answers.
JAC Board Class 10 Science Important Questions Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts
Additional Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Answer the following questions:
(1) How are acids and bases formed and from what?
Answer:
The reaction of oxides of non-metal with water forms an acid.
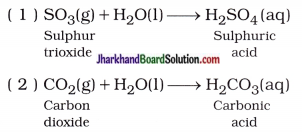
In short, Oxide of non-metal + Water → Acid
The reaction of oxides of metal with water forms a base.
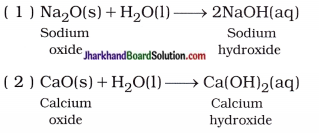
In short, Oxide of metal + Water → Base
(2) Explain : Strong acid and weak acid
Answer:
Strong acid: The mineral acids like hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulphuric acid (H2SO4) and nitric acid
(HNO3) when dissolved in water, they get completely ionised.
The acid which gets ionised completely when dissolved in water is known as strong acid.
For example,
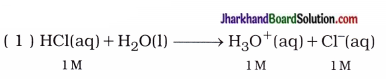
Thus, in 1 M HCl aqueous solution, concentrations of H3O+ and Cl- are 1M.
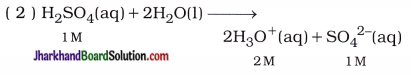
Thus, in 1 M H2SO4 aqueous solution, concentration of H3O+ and SO42- are 2M and 1M respectively, because two moles HsO+ are formed by ionisation of one mole H2SO4.
In the aqueous solution of strong acid, total solute substance is in the form of ions, i.e., the solute substance is ionised to H3O+.
Weak acid: The organic acids like acetic acid (in vinegar), lactic acid (in curd, buttermilk), citric acid (in lemon, orange), tartaric acid (in tamarind), oxalic acid (in tomato) when dissolved S in water they get partially ionised.
The acid which gets ionised partially or incompletely when dissolved in water is known as weak acid.
For example, The concentration of H3O+ is not 1M in 1M CH3COOH aqueous solution but it is very less, (approximately 2 to 3 %).
(3) Explain: Strong acid and weak base
Answer:
Strong base:The base which is ionised ) completely when dissolved in water is called strong base. For example, sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH).
In an aqueous basic solution, total solute substance is in the form OH– ions because of its complete ionisation, i.e., the total solute substance is ionised in the form of OH–.
For example,
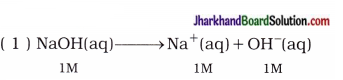
Thus, in 1M NaOH aqueous solution, the concentrations of Na+ and OH– are 1M.
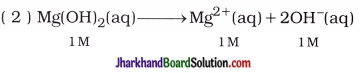
Thus, in 1 M Mg(OH)2 aqueous solution, the concentrations of Mg2+ and OH– are 1M and 2M respectively. Thus, by ionisation of lmole Mg(OH)2, 2 moles OH– are formed.
Weak base:
The base when dissolved in water is ionised or dissociated partially or incompletely is known as weak base. For example, ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH).
In the aqueous solution of weak base, very less amount (approximately 2 to 3%) of solute is ionised to OH–. For example, In aqueous solution of 1M NH4OH, the concentration of OH– is not 1M but it is very less than 1 M.
(4) Explain the chemical properties of acid.
Answer:
For the chemical reaction of acid, H+ s or H3O+ present in its aqueous solution is responsible.
(i) Reaction of acid with metal : By the reaction of acid with metal, a salt of corresponding metal and dihydrogen gas are produced.
For example,
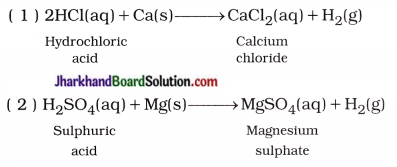
In short,
Acid + Metal → Salt of metal + Dihydrogen gas
(ii) Reaction of acid with base : Salt and water are formed by the reaction of acid with base. This reaction is called neutralisation reaction.
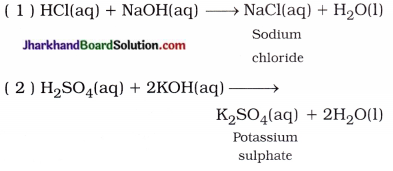
In short, Acid + Base → Salt + Water
(iii) Reaction of acid with metal oxide: The reaction of acid with metal oxide forms salt and water. For example,
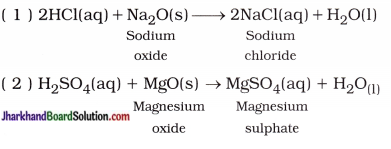
In short, Acid + Metal oxide → Salt + Water
(iv) Reaction of acid with metal carbonate or metal hydrogencarbonate: Most of the acids produce salt, water and carbon dioxide by reaction with metal carbonate or metal hydrogencarbonate.
For example,
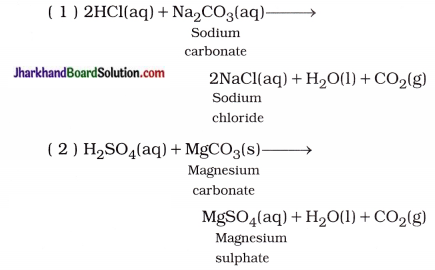
In short, Acid + Metal carbonate / Metal hydrogencarbonate → Salt + Water + CO2(g)
![]()
(5) Explain chemical properties of base.
Answer:
For a chemical reaction of base, OH– present in its aqueous solution is responsible.
(i) Reaction of base with acid : Reaction of a base with an acid forms salt and water. This reaction is called neutralisation.
For example,
- NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)
- 2KOH(aq) + H2SO4(aq) → K2SO4(aq) + 2H2O(l)
In short, Base + Acid → Salt + Water
(ii) Reaction of base with non-metal oxide : Reaction of base with oxides of non-metal forms salt and water.
For example,

In short,
Base + Oxide of non-metal → Salt + Water
(iii) Reaction of a base with some metals : By the reaction of a strong base like sodium hydroxide and potassium hydroxide with certain amphoteric metals (Zn, Al) gives salt and hydrogen gas.
For example,
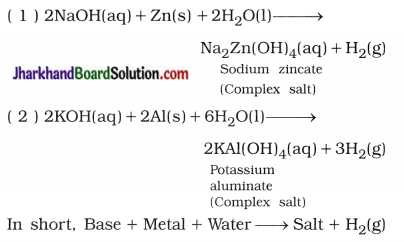
(6) “The aqueous solution of the salt produced by neutralisation of weak acid and strong base possesses basic nature, while aqueous solution of salt produced by neutralisation of weak base and strong acid possesses acidic nature.” Explain.
Answer:
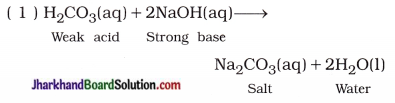
Hence, salt Na2CO3 is formed by the reaction of strong base and weak acid and its aqueous solution contains higher concentration of OH– ions than the concentration of H+ ions. Therefore, solution possesses basic nature.
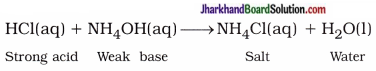
Here, salt NH4Cl is formed by the reaction of strong acid and weak base, and its aqueous solution contains higher concentration of H+(aq) ions than the concentration of OH–(aq) ions. Therefore solution possesses acidic nature.
(7) What is meant chemically by baking soda and baking powder? What happens if baking soda instead of baking powder is added, in making cake?
Answer:
Sodium hydrogencarbonate (NaHCO3) is a baking soda, while baking powder is a mixture of NaHCO3 and tartaric acid. For making cake, if only baking soda is used, then, on heating it produces sodium carbonate and the cake will taste bitter. To avoid this, appropriate amount of tartaric acid is added. Baking soda forms sodium salt of an acid which does not affect the taste of cake.
(8) Compare the acidity of two different acidic solutions A and B having different pH values.
Answer:
The comparison of two different acidic solutions A and B is shown in the table below:
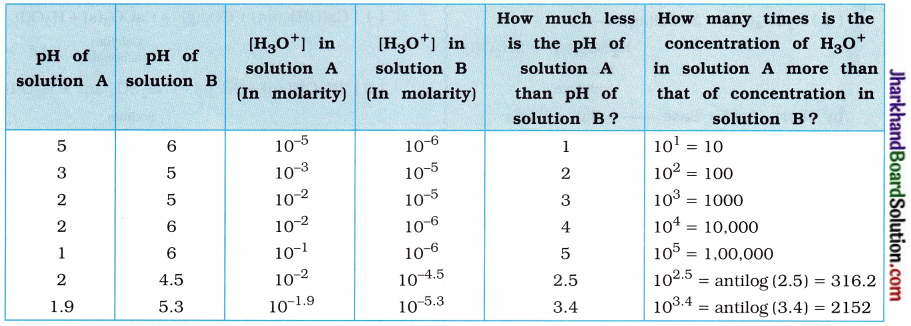
(Thus, it can be said from the above table that if the difference in pH of two acidic aqueous solutions is x, then solution having less pH will possess H3O+ concentration 10x times or antilog x times more acidic.)
Question 2.
Give scientific reasons for the following statements:
(1) An aqueous solution of FeCl3 is acidic.
Answer:
FeCl3 is a salt; when it is dissolved in water, it forms strong acid (HCl) and weak base (Fe(OH)3). Hence, concentration of H+ (aq) s ions is more than the concentration of OH– ions? in the solution. Therefore solution shows acidic behaviour. As a result, an aqueous solution of FeCl3 is acidic in nature.
(2) An aqueous solution of CH3COONa is basic.
Answer:
CH3COONa is a salt, which produces l strong base (NaOH) and weak acid (CH3COOH) in water. Hence, concentration of OH–(aq) is more in comparison with the concentration of H+(aq) s in the solution and hence solution shows basic behaviour. As a result, an aqueous solution of CH3COONa is basic in nature.
(3) An aqueous solution of NaCl is neutral.
Answer:
NaCl is a salt and it produces strong acid (HCl) and strong base (NaOH) in water. Hence, concentration of H+(aq) ions and concentration of OH–(aq) ions are equal in the solution and solution shows neutral behaviour. Therefore an aqueous solution of NaCl is neutral.
(4) Curd and sour substances should not be kept in brass and copper vessels.
Answer:
Curd and sour substances are acidic in nature, which react with brass and copper vessels and form toxic substances; which are harmful to the human body. Therefore, curd and other sour substances should not be kept in brass and copper vessels
(5) Distilled water does not conduct electricity, while rain water does it. Explain.
Answer:
Distilled water is a pure water and it does not contain ions while rain water contains impurities like acid, which provides ions and they help in carrying electricity.
![]()
Question 3.
Solve the following numericals :
(1) Calculate the concentration of OH– ion in an aqueous solution having pH value 8.
Solution:
pH + pOH = 14
∴ pOH = 14 – pH = 14 – 8 = 6
Now, pOH = – log10 [OH–]
∴ log10[OH–] = – pOH
∴ [OH–] = Antilog – pOH
= Antilog – 6.0
= 1 x 10-6M
(2) Calculate the molarity of an aqueous solution prepared by dissolving 2 mol of HC1 in water to form 500 mL solution.
Solution:
Molarity (M) = \(\frac { mole }{ litre }\)
= \(\frac { 2 }{ 0.5 }\)
= 4 M
(3) Calculate the pH of 0.01 M HCl solution.
Solution:
HCl is a strong acid, hence it ionises completely.
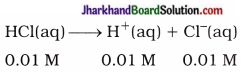
∴ [H+(aq)] = 0.01 M = 1 x 10-2M
Now, pH = – log10 [H+(aq)]
pH = – log10 [1 x 10-2]
= – [2.0000]
∴ pH = 2
(4) 50 mL KOH solution neutralise completely 5 mL HNOa solution. What volume of HNOs is required for complete neutralisation of 15 mL of KOH solution?
Solution:
50 mL KOH solution neutralise 5 mL HNO3 solution
∴ 15mLKOH solution will neutralise,
\(\frac { 15×5 }{ 0.5 }\) = 1.5 mL HNO3 solution.
(5) How many times would be an aqueous solution of pH = 2 be more acidic than aqueous solution of pH = 4?
Solution:
For solution having pH = 4,
PH = – log10[H3O+ ]
∴ – log10[H3O+] = 4
∴ log10[H3O+] = – 4
∴ [H3O+] = 10-4M
Similarly, [H3O+] for solution having pH = 2 = 10-2M.
Now,

Thus, the concentration of [H3O+] in concentrated solution of pH = 2 will be 100 times more than that of pH = 4, i.e., it will be 100 times more acidic.
(6) How many times would be concentrated aqueous solution having pH = 11.9 be more basic as compared to aqueous solution having pH = 8?
Solution:
pOH of basic aqueous solution having pH = 8 will be 14-8 = 6.
∴ [OH–] = 1 x 10-6M
Similarly, pOH of basic aqueous solution having pH 11.9 will be 14 – 11.9 = 2.1.
Now, pOH = – log10[OH–]
2.1 = – log10 [OH–]
– (2.1) = log10[OH–]
∴ log10[OH–] = \(\overline{3}\).9
∴ [OH–] = antilog \(\overline{3}\).9000
= 7.943 x 10-3 M
Now,

Thus, the solution having pH 11.9 will have 7943 times more basicity than solution having pH 8.
Objective Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Answer the following questions in short:
(1) What is the difference of water molecules between gypsum and plaster of paris?
Answer:
There are two molecules of water in gypsum. Plaster of paris contain \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) (half) molecule of water. Thus, the difference of water molecules = 2 – \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) = 1.5 molecules.
(2) What is soda lime? State the importance of lime in it.
Answer:
Mixture of caustic soda (NaOH) and lime (CaO) is called soda lime. In soda lime, lime is useful to absorb moisture during reaction.
(3) How does the soda-acid fire-extinguisher extinguish the fire?
Answer:
Soda-acid fire-extinguisher extinguishes the fire by stopping the contact of air.
(4) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction that occurs during chlor-alkali reaction.
Answer:
2NaCl(aq) + 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + Cl2(g) + H2(g)
(5) Arrange the water, hydrochloric acid and acetic acid in descending order of their acidity.
Answer:
Descending order of acidity:
Hydrochloric acid > Acetic acid > Water
![]()
(6) What is meant by dilution?
Answer:
Mixing of an acid or base with water results in decrease in concentration of acid or base or ions per unit volume. This process is called dilution.
(7) Write the name and molecular formula of product obtained by the reaction of zinc with sodium hydroxide.
Answer:
Sodium zincate – Na2ZnO2.
(8) What are properties of the oxides of metal and non-metal usually?
Answer:
The oxides of metallic elements are basic, while oxides of non-metals are acidic.
(9) Which acid is formed when milk turns into curd?
Answer:
During the formation of curd from milk, lactic acid is formed.
(10) Which ions are responsible for acidic and basic properties of the solution?
Answer:
H+(aq) ions in solution are responsible for acidic properties and OH–aq) ions in solution S are responsible for basic properties of the solution.
(11) Does the solution of urea conduct electricity? Why?
Answer:
The solution of urea does not conduct electricity, because urea does not possess ions in solution.
(12) Give two examples of strong alkali (base).
Answer:
NaOH and KOH
(13) State the nature of saliva before and after the meal.
Answer:
The nature of saliva before meal is basic s but after meal it becomes acidic.
(14) What is an acid rain?
Answer:
When the pH of rain water is less than 5.6, it is called an acid rain.
(15) What pH range is required to a soil for healthy growth and development of plants?
Answer:
The soil with pH in the range of 6.5 to 7.3 is appropriate for healthy growth and development of plants.
(16) Why does red ant bite (sting) cause pain and irritation?
Answer:
Red ant bite (sting) injects formic acid s in our body, which causes pain and irritation.
(17) Two solutions have pH value of 5 and 9 respectively. Which solution will be more basic in nature? Why?
Answer:
Solution with pH value 9 will be more basic, because the concentration of H+ ions in it is less or the concentration of OH– ions is more.
Question 2.
Define :
(1) Olfactory indicator
Answer:
Substances, which changes their odour s (smell) in presence of an acid or a base are known as olfactory indicators.
(2) Neutralisation reaction
Answer:
The reaction between an acid and a base to give a salt and water is known as a neutralisation reaction.
(3) Dilution process
Answer:
The process in which mixing an acid or base with water results in decrease in the concentration of ions (H3O+ or OH–) per unit volume is called dilution process.
(4) pH scale
Answer:
A scale for measuring the concentration of hydrogen ions in a solution is called pH scale.
(5) Family of salts
Answer:
Salts having the same positive or negative radicals are called family of salts.
(6) Rock salt
Answer:
The solid deposits of salts dissolved in sea water in the form of large crystals which turn brown due to impurities are known as rock salt.
Question 3.
Fill in the blanks :
- Neutralisation reaction occur between acid and base forms ………………. and ……………….
- The pH value of acidic solution is lower than ……………….
- An aqueous solution having pH value 4 is less ………………. than an aqueous solution having pH 2.
- Milk of magnesia is used as ……………….
- Molecular formula of gypsum is ……………….
- Butter milk possesses ………………. character.
- The farmers add ………………. to the acidic soil to neutralise it.
- Litmus is a ………………. indicator.
- MgO is a ………………. oxide.
- Generally, ………………. paper is used with universal indicator to measure the pH value of the solution.
- The atmosphere of ………………. planet is made-up of thick white and yellowish clouds of sulphuric acid.
- The stinging hair of nettle leaves injects ………………. into the skin causing burning pain.
Answer:
- salt, water
- 7
- acidic
- an antacid
- CaSO4.2H2O
- acidic
- lime (CaO)
- natural
- basic
- impregnated
- venus
- methanoic acid
![]()
Question 4.
State whether the following statements true or false:
- The molecular formula of sodium zincate is Na2Zn(OH)4.
- An aqueous solution of washing soda possesses acidic nature.
- Bacteria present in the mouth produce base by degradation of food particles left in the mouth after eating.
- The pH value of the blood is greater than 7.
- Orange contains citric acid.
- OH–(aq) ions in the solution are responsible for chemical reaction of base.
- Phenolphthalein is a natural indicator.
- Ca(HCO3)2 is soluble in water.
- Cl2O7 is a basic oxide.
- Solutions of glucose and alcohol do not conduct electricity.
- Hydrogen ions are formed in HCl in presence of water.
- Dissolution of acids and bases in water is an endothermic reaction.
- The p in pH stands for ‘potenz’ in German.
- Salts of strong acids and strong bases are neutral with pH value 7.
- Baking soda is used for faster cooking.
Answer:
- False
- False
- False
- True
- True
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
- True
- False
- True
- True
- True
Question 5.
Choose the correct option from those given below each question:
1. When does tooth decay occur?
A. When the pH of inner part of mouth is lower than 5.5.
B. When the pH of inner part of mouth is higher than 5.5.
C. When the pH of inner part of mouth is 5.5.
D. When the pH of inner part of mouth is 7.0.
Answer:
A. When the pH of inner part of mouth is lower than 5.5.
2. Which of the following solution is most basic?
A. pH = 8.2
B. pH = 9.3
C. pH = 11.5
D. pH = 10.6
Answer:
C. pH = 11.5
Hint: For acidic solution, pH < 7 and pOH > 7.
For basic solution, pH > 7 and pOH < 7.
3. What is the pH value of an aqueous solution of NH4CI?
A. pH = 7
B. pH > 7
C. pH < 7
D. pH = 0
Answer:
C. pH < 7
Hint: An aqueous solution of NH4Cl is acidic. Hence, its pH < 7.
4. Which of the following is a strong acid?
A. Acetic acid
B. Citrus acid
C. Oxalic acid
D. Nitric acid
Answer:
D. Nitric acid
5. The pH values of aqueous solutions A, B, C and D are 1.9, 2.5, 2.1 and 3.0 respectively; then what will be the correct order of their acidic strength?
A. A < C < B < D
B. D < C < B < A
C. D < B < C < A
D. D > C > B > A
Answer:
D. D > C > B > A
Hint : Aqueous solution with lower pH value is more acidic.
6. Which of the following solutions is neutral?
A. Juice of citrus fruits
B. Lemon juice
C. Solution of washing soda
D. An aqueous solution of salt – NaCl
Answer:
D. An aqueous solution of salt – NaCl
7. What will be the value of pH, if blue litmus paper turns red in aqueous solution?
A. Between 0 to 7
B. Between 7 to 14
C. 14
D. 0
Answer:
A. Between 0 to 7
8. The outer layer of the teeth is made-up of…
A. Calcium phosphate
B. Calcium nitrate
C. Potassium phosphate
D. Sodium phosphate
Answer:
A. Calcium phosphate
9. The pH of aqueous solution(s) of which salt is 7?
A. Na2CO3
B. CH3COONa
C. NH4Cl
D. KNO3
Answer:
D. KNO3
Hint: Since KNOs is a salt of strong acid and strong base.
10. CaCl2 + X → CaSO4 + 2NaCl, what is X?
A. Na2SO4
B. CaSO3
C. Na2SO3
D. CaSO2
Answer:
A. Na2SO4
11. Which of the following pair is not appropriate?
A. Citrus fruits – citric acid
B. Curd – lactic acid
C. Sting of red ant – methanoic acid
D. Tomatoes – tartaric acid
Answer:
Tomatoes – tartaric acid
Hint: Tomatoes contains citric acid.
12. Which of the following aqueous solutions contains higher proportion of OH– ions?
A. NaCl
B. Na2SO4
C. CH3COONa
D. Equal in all
Answer:
CH3COONa
Hint:Due to weak acid (CH3COOH) and strong base (NaOH) forms in an aqueous solution of CH3COONa.
13. Which of the following substance does not produce carbon dioxide, when it is treated with dilute acid?
A. Marble
B. Lime stone
C. Lime
D. Baking soda
Answer:
C. Lime
Question 6.
Match the following:
(1)
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Strong acid | p. NaOH |
| 2. Strong base | q. HNO3 |
| 3. Salt | r. NaCl |
| 4. Amphoteric | s. H2O |
Answer:
(1 – q), (2 – p), (3 – r), (4 – s).
(2)
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Sodium carbonate | p. NaNO3 |
| 2. Sodium bicarbonate | q NaNO2 |
| 3. Sodium nitrate | r. Na2CO3 |
| 4. Sodium nitrite | s. NaHCO3 |
Answer:
(1 – r), (2 – s), (3 – p), (4 – q).
(3)
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Melittin | p. Alkaline soil |
| 2. Calcium phosphate | q. Baking soda |
| 3. The value of pH is more than 7.3 | r. A polypeptide containing 26 amino acids |
| 4. Antacid | s. Outer layer of teeth |
Answer:
(1 – r), (2 – s), (3 – p), (4 – q).
Question 7.
Answer the following questions in one word:
- State the chemical formula of caustic potash.
- Write the composition of aqua regia.
- Write the molecular formula of soda ash.
- Which substance reacts with chlorine to form bleaching powder?
- Which acid is present in orange?
- State the pH value of human blood.
- At normal temperature, substance kept in atmosphere loses the water of crystallisation. By which name the substance is known?
- Name the reaction in which base is added in acid.
- What is called a base which is soluble in water?
- State the chemical name of salt which is useful and important raw material of food.
Answer:
- KOH
- 1 part concentrated HNO3 + 3 parts concentrated HCl
- Na2CO3
- Ca(OH)2
- Ascorbic acid
- 7.36 to 7.42 (about 7.4)
- Hydrated salt
- Neutralisation reaction
- Alkali
- Sodium chloride
![]()
Question 8.
Complete the following reactions :
- CaO(s) + H2O(l) →
- 2HNO3(aq) + Ca(OH)2(aq) →
- 2HNO3(aq) + CaO(s) →
- HCl(aq) + NaHCO3(aq) →
- 2NaOH(aq) + H2CO3(aq) →
- CH3COOH(aq) + NaOH(aq) →
- HNO3(aq) + KOH(aq) →
- BaCl2(aq) + H2SO4(aq) →
Answer:
- Ca(OH)2(aq)
- Ca(NOs)2(aq) + 2H2O(l)
- Ca(NO3)2(aq) + H2O(l)
- NaCl(aq) + H2O(l) + CO2(g)
- Na2CO3(aq) + 2H2O(l)
- CH3COONa(aq) + H2O(l)
- KNO3(aq) + H2O(l)
- BaSO4(s) + 2HCl(aq)
Value Based Questions With Answers
Question 1.
Ramesh’s father is a farmer and he is disappointed as he cannot grow any crop on his farmland, because the land has become highly basic in nature. It happens due to paper industry nearby dumping its waste water into canals; that supply water to the farmland.
Ramesh and other youth in the village told the owner of the paper industry about the pollution caused by the paper industry.
- What type of land is suitable for the growth of crops?
- Use of fertilizers also causes change in the pH of soil. How do farmers overcome this problem?
- What values of Ramesh are reflected in the above case?
Answer:
- The farmland should neither be acidic nor basic, it should be neutral for the growth of crops.
- If the soil is acidic then compounds like lime should be added to the soil to neutralise it. If the soil is basic, then the acidic salt is added to neutralise it.
- Ramesh showed the values of aware citizen and group work.
Question 2.
Rita’s mother had severe pain when a honeybee stung her on hand. Rita’s grandmother tried to relieve the pain by rubbing a iron metal on the affected area. But, Rita took the baking powder from the kitchen and applied on her mother’s hand which quickly relieved the pain.
- Why do honeybee stinging causes pain?
- How does baking powder relieve the beesting pain?
- What values of Rita is seen in the above act?
Answer:
- Honeybee sting releases an acid that is injected in body and causes pain.
- Baking powder is basic in nature, it neutralised the acid released in the body by bee-sting and relieves the pain.
- Rita showed the values of prompt, proactive and responsible behaviour.
Question 3.
Bharat’s friend Jaydeep is very fond of coffee. He drinks two cups of coffee everyday in the school and complain the problem of stomach pain very often. Bharat advised him not to drink coffee in the morning.
- What was the cause of stomach pain?
- What would be the pH of stomach juices after consuming coffee?
- What values of Bharat are reflected in the above act?
Answer:
- Two cups of coffee (excess) causes acidity which results into stomach pain.
- The pH of stomach after consuming coffee is 5.
- Bharat showed the values of concern, caring and awareness.
Question 4.
Ashish noticed that his friend always brought sweets in his lunch-box, due to which his tooth decayed. Ashish suggested his friend to eat less sweets in school hours to avoid tooth? decay.
- Why do tooth decay on eating sweets?
- What is the pH of mouth after eating sweets?
- What value of Ashish is seen in the above act?
Answer:
- On eating sweets, the particles of sweets get stuck in the teeth. On the sweet particles bacteria grows and produces acid. This acid causes tooth decay.
- The pH of the mouth after eating sweets lowers and remains in the range of 2 to 6.
- Ashish showed sincerity, responsibility and? care for others.
Practical Skill Based Questions With Answers
Question 1.
In the laboratory, a test tube rack is placed with test tubes containing some acids in it. How will you classify these acids?
Answer:
To classify the acids, we should test their pH and group them as strong or weak acids.
Question 2.
What is the pH of water? Does it change on heating the water? Why?
Answer:
Generally, the pH of pure water is 7 at 25 °C temperature. On heating water, the pH value will change, it decreases, because on heating water molecules will ionise more and as a result concentration of H+ ions and OH– ions increase, which results in decreasing pH. But water remains neutral.
Question 3.
A test was conducted in the laboratory to find the pH of different cold drinks. Draw the observation table to collect the data for this experiment and predict the result for the same.
Answer:
Observation table of collected data :
| Sr. No. | pH of drink-1 | pH of drink-2 | pH of drink-3 | pH of drink-4 |
| 1. | ||||
| 2. | ||||
| 3. |
Prediction:
The pH of the dark cold drink will be higher, as it contains more caffeine which is more acidic and the cold drink which releases more bubbles on opening is highly acidic and will have low pH as the carbonated water is present in it.
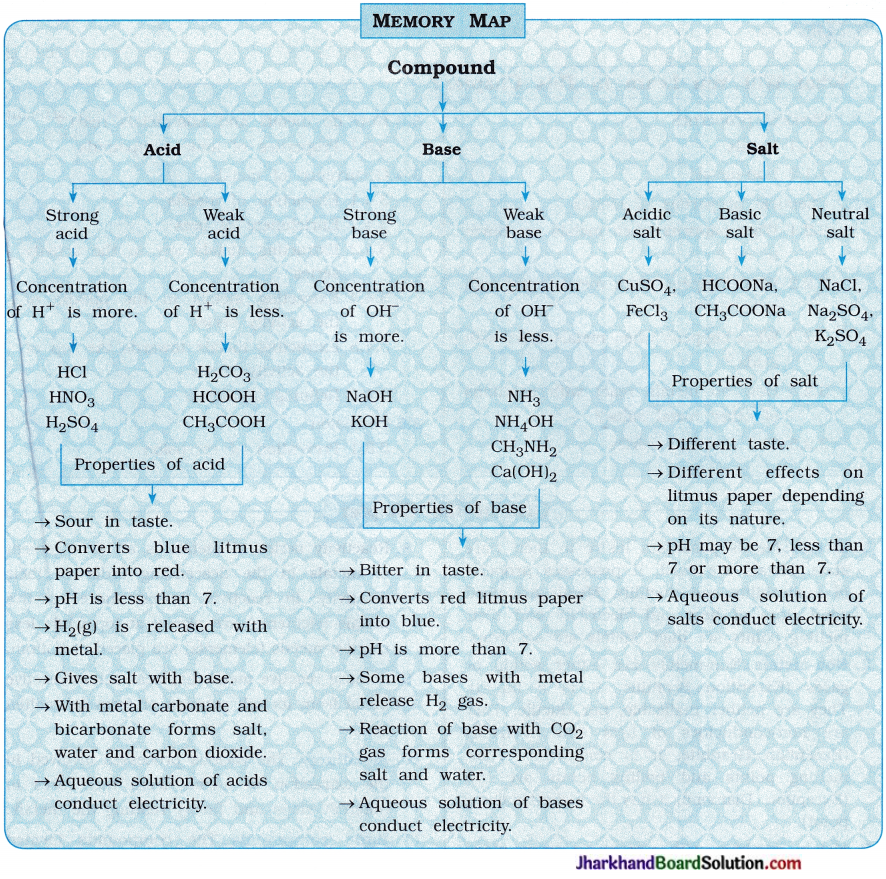
Memory Map