Jharkhand Board JAC Class 10 Science Important Questions Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals Important Questions and Answers.
JAC Board Class 10 Science Important Questions Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
Additional Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Give scientific reasons for the following statements:
(1) Hydrogen gas is not evolved when Al reacts with nitric acid.
Answer:
When Al reacts with nitric acid, hydrogen gas is not evolved because HNO3 is a strong oxidising agent. It oxidises the H2 produced with water and itself is reduced to any of the nitrogen oxide.
(2) Melting points and boiling points of ionic compounds are high.
Answer:
Melting and boiling points : A considerable large amount of energy is required to break the strong inter-ionic attraction. Hence, ionic compounds have high melting and boiling points.
For example,
| Ionic compound | Melting point (K) | Boiling point (K) |
| NaCl | 1074 | 1686 |
| LiCl | 887 | 1600 |
| CaCl2 | 1045 | 1900 |
| CaO | 2850 | 3120 |
| MgCl2 | 981 | 1685 |
(3) Ionic compounds are non-conductor in the solid state, but they conduct electricity in the molten state or in an aqueous solution.
Answer:
Conduction of electricity : The conduction of electricity through a solution involves the movement of charged particles. A solution of an ionic compound in water contains ions, which move to the opposite electrodes, when electricity is passed through the solution.
Ionic compounds in the solid state do not conduct electricity because the movement of ions in the solid is not possible due to their rigid structure. But, ionic compounds conduct electricity in the molten state. Since the electrostatic forces of attraction between the oppositely charged ions are overcome and free ions are obtained due to heat. As a result, these ions move freely and conduct electricity.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain : Roasting and Calcination
Answer:
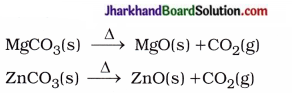
(1) Roasting: In this method, the concen-trated sulphide ore is heated in presence of excess < of air for a long time. So metal sulphides ore oxidised to metal oxides and SO2. This method is known as roasting.

(2) Calcination : The ore containing metal carbonate or metal hydroxide is heated strongly in absence of air to convert it into metal oxide after the removal of volatile impurities and hydrated water. This process is known as calcination.
For example,
Question 3.
Explain : Alloying of gold
Answer:
Pure gold (24 carats) is very soft and s so the jewellery or ornaments made from it do not resist much pressure. Even a little pressure s can change their shape. Moreover they cannot resist much of wear and tear caused by friction. So, gold is alloyed with other metals like copper and silver to make it hard. 22 carat gold means it contains 22 parts of gold and 2 parts copper or silver in 24 parts by weight of an alloy.
Question 4.
Distinguish between :
(1) Metals and non-metals on the basis of their physical properties.
Answer:
| Metals | Non-metals |
| 1. Metals are in solid form. (Exception: mercury and gallium) | 1. Non-metals are in the solid, or gaseous form. |
| 2. They are heavy in weight. | 2. They are light in weight. |
| 3. They | 3. They are bad conductors of heat and electricity. |
| 4. Metals have lustre. | 4. Non-metals do not have lustre. (Exception: Graphite, Silicon, Phosphorus) |
| 5. Generally, they have high melting points. | 5. Generally, they have low melting points. |
| 6. Many metals produce ringing sound. | 6. Non-metals do not produce ringing sound. |
| 7. They can be hammered into thin sheets and drawn into wires. | 7. Non-metals cannot be hammered into sheets nor can be drawn into wires. |
(2) Calcination and roasting
Answer:
| Calcination | Roasting |
| 1. The process in which carbonate ores are changed into oxides by heating strongly in limited air is called calcination. | 1. The process in which sulphide ores are converted into oxides by heating strongly in the presence of excess air is called roasting. |
| 2. CO2 gas is evolved. | 2. SO2gas is evolved. |
 | 3. 2ZnS + 3O2 → 2ZnO + 2SO2 |
Question 5.
Explain :
(a) Why copper is used to make taps, hot water tanks and not any other metal?
(b) What will happen, if iron nails are S’ kept in a solution containing copper sulphate?
(c) Write the balanced chemical equations S> for the following and balance it:
(i) Ca + H2O →
(ii) Al + HCl →
(iii) Fe + H2O →
Answer:
(a) Copper does not react with cold and hot water, nor It reacts with the steam of water. Moreover, it is cheap and easily available, hence, S it is used to make taps and hot water tanks.
(b) Wlien iron nails are kept in a copper sulphate solution, the blue colour of the solution c fades due to displacement of copper by iron.
(c)
- Ca + 2H2O → Ca(OH)2 + H2(g)
- 2Al + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2(g)
- 3Fe + 4H2O → Fe3O4 + 4H2(g)
Question 6.
How will you prove that zinc is more reactive than copper?
Answer:
Take strips of zinc and copper and two test tubes with copper sulphate and zinc sulphate S solution. Add zinc strip in copper sulphate solution and copper strip in zinc sulphate solution.
Observation : In the test tube with zinc strip in copper sulphate solution shows that blue colour of copper sulphate solution fades. The other test tube will not show any change. This proves that zinc is more reactive than copper.
![]()
Question 7.
5 mL each of concentrated HCl and concentrated HNO3 are taken in test tubes labelled as A and B while a mixture of concentrated HCl (15 mL) and concentrated HNO3 (5 mL) is taken in test tube labelled as C. A small piece of metal is placed in each test tube. No change is observed in test tubes A and B, but metal got dissolved in test tube C. What would be the metal?
Answer:
Metal would be silver, gold or platinum.
Question 8.
The electronic configuration of three elements X, Y and Z are as follows:
X → 2, 8 Y → 2, 8, 6 Z → 2, 8, 1
Identify the metal and non-metal.
Answer:
From electronic configuration, X has 10 electrons, Y has 16 electrons and Z has 11 electrons. Hence these elements are
X = 10Ne, Y = 16S and Z = 11Na.
Hence, X and Y are non-metals while Z is a metal.
Question 9.
Arrange the elements Au, Fe, Cu, Mg, Ca, Zn, Ag and K in descending order of their reactivity.
Answer:
Descending order of reactivity:
K > Ca > Mg > Zn > Fe > Cu > Ag > Au.
Objective Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Answer the following questions in short:
(1) What is called metallic lustre?
Answer:
Metals possesses a shining surface in their pure form. This property is called metallic lustre.
(2) State the full form of PVC.
Answer:
The full form of PVC : PolyVinyl Chloride
(3) Give the example of metal and non¬metal existing in liquid state.
Answer:
Liquid metal: Mercury (Hg) and Gallium
(Ga); Liquid non-metal: Bromine (Br)
(4) Which metals will melt, if you keep them on your palm?
Answer:
Gallium (Ga) and Caesium (Cs).
(5) What is an amphoteric oxide?
Answer:
Metal oxide which reacts with both acid as well as base to produce salt and water is S known as an amphoteric oxide.
(6) Which metals react violently with cold water?
Answer:
Sodium and potassium metals react > violently with cold water.
(7) What is an aqua regia?
Answer:
A freshly prepared mixture of concentrated hydrochloric acid and concentrated nitric acid in the ratio of 3 : 1 by volume is called an aqua regia.
(8) State one use of anhydrous calcium chloride.
Answer:
Anhydrous calcium chloride is used as drying agent, because it absorbs moisture from the air.
(9) What is meant by activity or reactivity series?
Answer:
When different metals are arranged in decreasing order of their activities or reactivities then it constitutes a series known as activity or reactivity series.
(10) Why does the noble gases possess little chemical activity?
Answer:
Noble gases possesses completely filled valence shell with 8 electrons. Hence they are chemically inert.
(11) State the reason for conduction of electricity through a solution.
Answer:
The conduction of electricity through a solution is due to the presence of ions which migrate to opposite electrodes and carry electricity.
(12) In which forms are the metals obtained from the earth’s crust?
Answer:
Metals are obtained in the form of oxide, carbonate and sulphide ores from the earth’s crust.
(13) On what factors does the process (method) used to remove the gangue from ores depend?
Answer:
The process (method) used for removing the gangue from the ores depends on the differences between the physical or chemical properties of the gangue and ores.
(14) What type of metals are used as reducing agent in displacement reactions? Mention the examples.
Answer:
Highly reactive metals are used as reducing agent in displacement reactions. For example, sodium, calcium, aluminium, etc.
(15) Name the two allotropes of carbon.
Answer:
Diamond and graphite.
![]()
Question 2.
Define:
(1) Displacement reaction
Answer:
A reaction in which more reactive metal displaces less reactive metal from its compound in solution or in molten form is known as displacement reaction.
(2) Electrovalent compounds
Answer:
The compounds formed by the transfer of electrons from a metal to a non-metal are known as electrovalent compounds. They are ionic compounds.
(3) Ore
Answer:
A mineral containing high percentage of a particular metal and from which metal can be profitably extracted is called an ore.
(4) Roasting
Answer:
The process of strongly heating sulphide ores in the presence of an excess of air and converting them into oxides is called roasting.
(5) Calcination
Answer:
The process of strongly heating carbonate ores in limited air, so that the volatile impurities are removed converting ores into oxides is called calcination.
(6) Anode-mud
Answer:
In electrolytic refining, insoluble impurities such as gold, silver, platinum are settled at the bottom of the anode are known as an anode-mud.
(7) Corrosion
Answer:
Metal gets rusted, when it is exposed to water, air and moisture for long time. This process of rusting is known as metal corrosion.
(8) Alloy
Answer:
The homogenous mixture of two or more metals, or a metal and a non-metal is called an alloy.
Question 3.
Fill in the blanks :
- Iodine is a ………………. but it possesses
- Diamond and graphite are allotropes of ……………….
- Metals forms ………………. oxide.
- The colour of copper (II) oxide is ……………….
- Solder is an alloy of ………………. and ……………….
- The electrical conductivity and melting points of alloys are ………………. than the pure metals.
- The metals at the bottom of the reactivity series are ………………. reactive.
- Ores are usually contaminated with large amount of impurities such as soil, sand, etc. which are called ……………….
- The process of obtaining metal from its compound is ……………….
- Iron (III) oxide is heated with aluminium powder forms iron in the molten state. This process is known as ……………….
Answer:
- non-metal, lustre
- carbon
- basic or amphoteric
- black
- lead, tin
- less
- less
- gangue
- reduction
- Thermit process
Question 4.
State whether the following statements are true or false:
- All metals have similar hardness.
- Silver and copper are good conductors of heat.
- Bromine is a gas.
- Graphite is a non-conductor of heat.
- Li, Na and K can be cut with the knife.
- Non-metallic elements dissolve in water to form acidic oxide.
- Magnesium burns with dazzling blue flame.
- Magnesium is less reactive than sodium.
- Magnesium does not react with cold and hot s water, but it reacts with steam to form metal > oxide and hydrogen gas.
- Gold and platinum do not dissolve in aqua regia.
- Reactivity decreases in order of Mg > Al > Zn.
- Copper reacts with dilute HCl.
- Magnesium chloride possesses two ionic bonds.
- The compounds formed by transfer of electrons are known as ionic compounds; moreover, they are known as electrovalent compounds.
- Electrovalent compounds are kerosene and petrol.
Answer:
- False
- True
- False
- False
- True
- True
- False
- True
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
- True
- False
Question 5.
Choose the correct option from those given below each question:
1. Which of the following is an alloy?
A. Brass
B. Bronze
C. Steel
D. All of the given
Answer:
D. All of the given
2. Height and weight of iron pillar near the s Qutub Minar in Delhi are respectively…
A. 8 metre, 6 tonnes
B. 6 metre, 8 tonnes
C. 6 metre, 6 tonnes
D. 8 metre, 8 tonnes
Answer:
A. 8 metre, 6 tonnes
3. Which of the following metals is highly malleable?
A. Gold
B. Silver
C. A and B both
D. None of these
Answer:
C. A and B both
4. Which of the following is not useful as a good conductor of heat?
A. Silver
B. Copper
C. Lead
D. All of the given
Answer:
C. Lead
![]()
5. Which coating is applied on electric wire?
A. DDT
B. PVC
C. PTFE
D. PAN
Answer:
B. PVC
6. Which metal exists as liquid at room temperature?
A. Mercury
B. Bromine
C. Sodium
D. Calcium
Answer:
A. Mercury
7. Which allotrope of carbon is known as the hardest natural substance?
A. Graphite
B. Diamond
C. Coke
D. Carbon black
Answer:
B. Diamond
8. Most of the metal oxides in water are …
A. Soluble
B. Insoluble
C. Partial soluble
D. Highly soluble
Answer:
B. Insoluble
9. Which layer is formed on Al, when it is exposed to air?
A. Al3O2
B. Al2O3
C. AlO
D. AIN
Answer:
B. Al2O3
10. HNO3 is reduced in …
A. NO
B. NO2
C. N2O
D. All of the given
Answer:
D. All of the given
11. Which of the following reactions is called roasting?
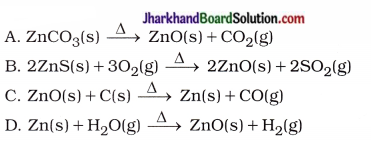
Answer:
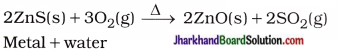
12. During which reaction is dihydrogen gas not produced under normal conditions?
A. Metal + dilute sulphuric acid
B. Metal + dilute hydrochloric acid
C. Metal + dilute nitric acid
D. Metal + water
Answer:
D. Metal + water
13. In which of the following, displacement reaction is possible?
A. Solution of NaCl + coin of copper
B. Solution of MgCl2 + coin of aluminium
C. Solution of FeSO4 + coin of silver
D. Solution of AgNO3 + coin of copper
Answer:
D. Solution of AgNO3 + coin of copper
14. Which of the following reactions is not possible?
A. Zn(s) + CuSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
B. Zn(s) + FeSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Fe(s)
C. Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq) → FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
D. Cu(s) + FeSO4(aq) → CuSO4(aq) + Fe(s)
Answer:
D. Cu(s) + FeSO4(aq) → CuSO4(aq) + Fe(s)
15. Which of the following statements is incorrect?
A. Corrosion of copper takes place by contact with air and water.
B. The melting points and boiling points of metals are low.
C. The method to convert carbonate containing ore to metal oxide is called calcination.
D. The displacement of less active metals from their solution takes place by more active metal.
Answer:
B. The melting points and boiling points of metals are low.
Question 6.
Answer the following questions in one word :
- Metals can be hammered into thin sheets. What does this property called?
- How long thin wire can be drawn from one gram gold?
- Name two metals which are poor conductors of heat.
- How many electrons are present in the outermost shell of fluorine?
- The electron of which shell is removed when sodium cation is formed from sodium atom?
- By which force the anions and cations are held together in ionic compounds?
- Are the melting points and boiling points of ionic compounds high or low?
- Which soluble salts are present in sea-water?
- Which metals are available in free state?
- State the molecular formula of cinnabar.
- Name the metal which can be cut with a knife.
- Name the solution which is used for dissolving gold.
Answer:
- Malleability
- 2 km
- Lead and mercury
- 7 electrons
- M-Shell
- Electrostatic attraction forces
- High
- Sodium chloride and magnesium chloride
- Gold, silver, platinum and copper
- HgS
- Sodium (Na)
- Aqua regia
Question 7.
Mention the formulae, names and physical states of the products in the following reactions :
( 1 ) 2Cu(s) + O2(g) →
( 2 ) 4Al(s) + 3O2(g) →
( 3 ) Al2O3(s) + 6HCl(aq) →
( 4 ) Al2O3(s) + 2NaOH(aq) →
( 5 ) K2O(s) + H2O(l) →
( 6 ) Ca(s) + 2H2O(l) →
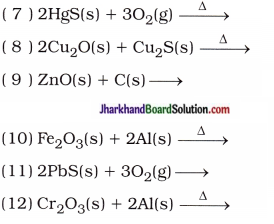
( 13 ) 3Fe(s) + 4H2O(g) →
( 14 ) CO(g) + H2O(g) →
( 15 ) 3NO2(g) + H2O(l) →
Answer:

Value Based Questions With Answers
Question 1.
Arvind delivered a speech in the school assembly on “How to minimise the use of heavy metals?” He told how mercury thermometers when broken and thrown away in the garbage leads to pollution of soil and underground water pollution. He also showed how cadmium and lead also causes dangerous health problems.
- Name two heavy metals which are present in the mobile batteries.
- Name the disease caused due to mercury entering into our food-chain.
- What value of Arvind is seen in the act?
Answer:
- Lead and cadmium are used in the mobile batteries.
- Mercury causes minamata disease.
- Arvind showed the value of concern for nature, aware citizen and responsible behaviour.
Question 2.
A jeweller made jewellery (ornaments) of 22 carat gold and also charged his customers for the rate of 24 carat gold. His business developed due to this act.
- Why can’t we make ornaments of 24 carat gold?
- Name two metals that can be added to make jewellery.
- What value of the jeweller is reflected in this act?
Answer:
- 24 carat gold is soft and pure; and it cannot be moulded in the shape and design given to it while making the jewellery with strength. Hence, it is not advisable to make ornaments of 24 carat gold.
- Copper and silver can be added to gold to make it strong.
- Jeweller has shown the value of dishonesty, unfaithfulness and greediness towards his customers.
![]()
Question 3.
Naman saw his friend riding a cycle which was completely rusted at the edge of the pedal. He advised his friend to weld it and apply a
coating of oil paint over it.
- Why do iron rust?
- Give two remedies to avoid rusting.
- What value of Naman is seen in the above act?
Answer:
- Iron, when exposed to air and moisture, undergoes chemical change to form iron oxide which is reddish brown powder called rust.
- Remedies to avoid rusting are : (i) Apply paint on the surface of iron. (ii) Apply grease or oil coating on iron.
- Naman showed the value of awareness, concern and helpful nature.
Practical Skill Based Questions With Answers
Question 1.
Mention three safety measures essential while performing the reactivity series experiment in s the laboratory.
Answer:
Essential safety measures while performing the experiment of reactivity series are as follows :
- The metal or any other chemicals should not come in contact with skin.
- Do not inhale any fumes or gas released during the experiment.
- One should not taste any chemical or material.
- One should wear goggles, hand gloves and lab coat during the usage of the chemicals.
Question 2.
How will you identify the copper sulphate, iron sulphate and barium sulphate in the laboratory?
Answer:
Above given substances can be identified by their colours. For example, the colour of iron (II) sulphate is green, the colour of iron (III) sulphate is yellowish brown. The s colour of copper (II) sulphate is blue, and the white colour salt is barium sulphate.
Question 3.
Write the name and molecular formula of any three metal salts which are white in colour.
Answer:
- Zinc sulphate (ZnSO4)
- Magnesium sulphate (MgSO4)
- Aluminium sulphate (Al2(SO4)3)
Above metal salts are white in colour.
Question 4.
A student put the spatula of iron in the test tube containing copper sulphate while performing an experiment in the laboratory. What will he observe next day?
Answer:
The student will observe that the blue coloured solution of copper sulphate turns to green and the iron spatula gets the coating of brown colour metal on it, only on the surface which is dipped in the solution.
Question 5.
Three solutions of zinc sulphate, magnesium sulphate and aluminium sulphate are prepared in laboratory by a lab assistant. But he forgot to label the reagent bottles. How will you label these bottles by using the metal reactivity studies?
Answer:
Take three test tubes and add little amount of each solution from the reagent bottle separately. Drop a small piece of magnesium in it. The test tube in which there is no reaction contains magnesium sulphate. Now, to identify the remaining two solutions, take these two solutions in two different test tubes and add a small piece of aluminium metal to them. The test tube in which, there is no reaction contains aluminium sulphate and the other one is zinc sulphate.
Memory Map