Jharkhand Board JAC Class 10 Science Important Questions Chapter 6 Life Processes Important Questions and Answers.
JAC Board Class 10 Science Important Questions Chapter 6 Life Processes
Additional Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Distinguish between :
(1) Gastric juice and Bile
Answer:
| Gastric juice | Bile |
| 1. It is a mixture of secretions from gastric glands located in the inner wall of the stomach. | 1. It is secreted from the liver cells. |
| 2. It is not stored anywhere in stomach. | 2. It is stored in the sac-called gall bladder. |
| 3. It is secreted from the gastric glands in stomach and acts in the stomach itself. | 3. It is secreted from the liver cells and acts in the duodenum (small intestine). |
| 4. It is an acidic digestive juice. | 4. It is an alkaline digestive juice. |
| 5. It contains dil. HCl, enzyme pepsin and mucus. | 5. It does not contain any enzyme. |
(2) Herbivores animals and Carnivores animals
Answer:
| Herbivores animals | Carnivores animals |
| 1. These animals take in only plant material as food. | 1. These animals take in only animal flesh and bones as well as blood as their food. |
| 2. Their small intestine is relatively much longer than in carnivores. | 2. Their small intestine is relatively much shorter than in herbivores. |
| 3. They are consumers of the first order. | 3. They are consumers of the second and third order. |
| 4. The digestion of cellulose of the plant cells is quite complex and takes time. | 4. The digestion of flesh of the animals is quite easy and rapid. |
| 5. Example: rabbit, cow, buffalo, goat, etc. | 5. Example: tiger, lion, leopard, wolf, etc. |
(3) Respiration in plants and Respiration in animals
Answer:
| Respiration in plants | Respiration in animals |
| 1. In plants, exchange of gases is carried out individually by different organs (roots, stem and leaves in the process of respiration.) | 1. In animals, exchange of gases is carried out by some definite parts or organs of the body, meant for respiration. |
| 2. The flow of respiratory gases from one part of the body to the other, is a slow process. | 2. The flow of respiratory gases from one part of the body to the other, is a rapid process. |
| 3. The respiration in plants is slow. | 3. The respiration in animals is quite rapid. |
| 4. In anaerobic respiration in plants the end product is ethanol and CO2. | 4. In anaerobic respiration in animals the end product is lactic acid. |
(4) Xylem tissue and Phloem tissue
Answer:
| Xylem tissue | Phloem tissue |
| 1. It transports water and mineral Ions absorbed by the roots to different parts of the plant. | 1. It transports organic products of photosynthesis from the leaves to different parts of the plant. |
| 2. The principal conducting elements of xylem are tracheids and tracheae (vessels). | 2. The principal conducting elements of phloem are sieve cells and sieve tubes with companion cells. |
| 3. The conduction occurs only in upward direction. | 3. The conduction occurs in both upward and downward directions. |
| 4. It conducts only water and mineral ions. | 4. Along with the sugars it conducts amino acids, plant hormones and several other substances. |
| 5. For conduction of water In the xylem, the suction force due to transpiration is the principal force. | 5. For conduction of organic food substances the energy required is obtained from ATP. |
(5) Conduction of water in plants and Translocation of food in plants
Answer:
| Conduction of water in plants | Translocation of food in plants |
| 1. It occurs through the xylem tissue. | 1. It occurs through the phloem tissue. |
| 2. It occurs from the roots to the stem, leaves and flowers. | 2. It occurs from the leaves to different parts of the plant. |
| 3. It occurs only from below upwards. | 3. It occurs from above downwards as well from below upwards. |
| 4. A continuous water column is formed in the plant from root upwards which is pulled up due to suction force. | 4. No food column is formed but the difference of pressure causes translocation which requires energy from ATP. |
(6) Atria and Ventricles
Answer:
| Atria | Ventricles |
| 1. The upper two chambers of the heart are atria. | 1. The lower two chambers of the heart are ventricles. |
| 2. They are relatively thin-walled. | 2. They are quite thick-walled. |
| 3. Atria receive blood from different parts of the body and is poured in the ventricles. | 3. Ventricles receive blood from the auricles and force the blood towards different parts of the body. |
| 4. In atrium, the blood pressure is relatively low. | 4. In ventricles, the blood pressure is quite high. |
(7) Artery and Vein
Answer:
| Artery | Vein |
| 1. The blood vessel that carries blood from the heart to different organs is called an artery. | 1. The blood vessel that carries blood from any organ towards the heart is called a vein. |
| 2. In artery, the blood flows under higher pressure. | 2. In vein, the blood flows under somewhat low pressure. |
| 3. The wall of the artery is relatively thick and elastic. | 3. The wall of the vein is relatively thin and less elastic. |
| 4. The artery divides into several arterioles and numerous fine blood capillaries in the organs and tissues. | 4. In the organs and tissues, the veins are formed by the union of numerous blood capillaries and several venules. |
| 5. Arteries carry oxygenated blood (exception -Pulmonary artery). | 5. Veins carry deoxygenated blood (exception -Pulmonary vein). |
(8) Blood and Lymph
Answer:
| Blood | Lymph |
| 1. It is red coloured fluid connective tissue. | 1. It is a colourless liquid connective tissue. |
| 2. It contains liquid blood plasma and freely floating blood corpuscles. | 2. It contains a certain amount of blood plasma, proteins and some blood cells (except red blood corpuscles). |
| 3. It flows in the heart, arteries, veins and blood capillaries. | 3. It flows in the intercellular spaces, larger lymph capillaries and in lymph ducts. |
| 4. It is an independent liquid connective tissue. | 4. It arises by the diffusion from the thin walls of the blood capillaries and after circulation in the body, it is poured back in the blood. |
(9) Breathing and Respiration
Answer:
| Breathing | Respiration |
| 1. It is a physical / mechanical process. | 1. It is a physiological process. |
| 2. It occurs through the respiratory organs aided by accessory respiratory organs. | 2. It occurs in each and every living cell of the body. |
| 3. The mechanism of breathing is not necessarily found in all the living organisms. | 3. The process of respiration occurs invariably in each and every living cell of all the living organisms. |
| 4. It includes the physical processes of inhalation or inspiration expelled (taking in of atmospheric air) and exhalation or expiration (throwing out air contaihing CO2, into the atmosphere). | 4. It includes the physiological (biochemical) processes of glycolysis and Krebs cycle and also oxidative phosphorylation. |
| 5. There are no subtypes of breathing. | 5. Aerobic and anaerobic respiration are the two different types of respiration. |
| 6. Energy is utilized in this process. | 6. Energy is released in this process. |
Question 2.
Give scientific reasons for the following statements:
(1) Proper transportation (conducting) system is necessary in higher plants.
Answer:
The green leaves of plants obtain CO2 from the atmosphere and synthesize carbohydrates. The plants, through their roots, absorb water and other raw mineral elements essential for the constitution of the body, from the soil.
In higher plants the distance between the roots and the leaves being more, the water, mineral elements and the products of photosynthesis cannot be sent to all the different parts of the plant body, merely by diffusion from cell to cell. Therefore, in order to distribute all these substances rapidly and timely, a proper transportation (conducting) system is necessary in higher plants.
(2) In very tall plants, the suction force created due to transpiration is the main conducting force for water and mineral ions through the xylem.
Answer:
The xylem tissue in all the organs of a plant remains connected to each other and forms a continuous path for the flow of water, etc. Thus, a continuous water column is formed therein.
Mere root pressure, created in small herbs, is not sufficient to push water and minerals to the great height of very tall plants. The plants adopt another way to reach the target of fulfilling the water requirement. Evaporation of water molecules in the form of vapour occurs through stomata.
Due to that a suction force arises in the cells of leaves. This suction force comes into being from the cells of the leaves and is gradually experienced in the xylem of roots. As a result, the water column in the xylem rises up. Hence in very tall plants, the suction force created due to transpiration is the main conducting force for water and mineral ions through the xylem.
(3) Translocation in the phloem takes place in both upward and downward directions.
Answer:
The phloem transports amino acids, various plant hormones and other organic substances in addition to the products of photosynthesis.
Carbohydrates are synthesized in the leaves due to photosynthesis. These carbohydrates are transported to the roots and stem through phloem. The plant hormones synthesized in shoot apex flow downwards through the phloem and the plant hormones synthesized in the root apex and the food reserve stored in roots are transported upwards through the phloem. Thus, the translocation in the phloem takes place in both, upward and downward directions.
(4) The right side chambers of the heart have deoxygenated blood and left side chambers have oxygenated blood in them.
Answer:
The four-chambered heart, in man, is formed of two atria and two ventricles. All the four chambers of the heart are separated from each other by septa.
Deoxygenated blood from different organs of the body (except lungs) is brought through s superior and inferior vena cava and poured in the right atrium and then into the right ventricle, Similarly oxygenated blood from the two lungs is brought through pulmonary veins and poured in the left atrium and then into the left ventricle.
The four-chambered heart prevents the mixing of oxygenated blood with deoxygenated blood. Hence, the right side chambers of the heart have deoxygenated blood and the left side chambers have oxygenated blood in them.
(5) Lymph separates from the blood and remixes with the blood.
Answer:
The lymph oozes out through the pores in thin walls of the blood capillaries, as a fluid from the blood flowing through the capillaries. It flows very slowly in the intercellular spaces between the tissue cells. The intercellular spaces have no walls of their own and are called lymph capillaries.
These lymph capillaries meet and join with each other to form larger ones which finally open in a vein to pour its contents. Thus, lymph, as a colourless watery fluid collects in a large lymph vessels that finally open in particular veins S in the body to pour its contents back in blood.
(6) The wall of the artery is thick and elastic while that of vein is relatively thin.
Answer:
The arteries carry blood from the heart towards different organs. When the ventricles contract, the blood is pushed in the arteries under high pressure. In order to withstand this pressure, the arteries must have thick and elastic walls. The veins receive blood from different organs and carry it to the heart. The blood in the veins flows at relatively low pressure. Hence, the wall of the veins is relatively thin and less elastic.
(7) The organisms possessing chlorophyll are autotrophs.
Answer:
The organisms, possessing chlorophyll, can trap and utilize the solar energy to synthesize their own food using CO2 and water. This process of trapping the solar energy for synthesis of ones own food is called photosynthesis and the mode of nutrition of such organisms is called autotrophic. In photosynthesis, the food synthesized is the simplest hexose sugar-glucose, which is utilized for obtaining energy. The surplus glucose is stored as reserve food in the form of starch. Hence, the organisms possessing chlorophyll are autotrophs.
(8) The stomata in leaves keep on opening and closing.
Answer:
On one or both the surfaces of the leaves of flowering plants, there are numerous stomata as minute pores. Each of these pores is guarded by a pair of guard cells. The opening and closing of the stomata is controlled by these guard cells, which contain chloroplasts.
When water enters the guard cells, the latter swell and cause the opening of stomata and when the guard cells lose water, the guard cells contract and cause the closing of stomata. Thus, the stomata in leaves keep on opening and closing due to entry and exit of water in the guard cells.
(9) The parasitic mode of nutrition is harmful for the host organism.
Answer:
In parasitic nutrition, one organism depends fully for obtaining its nutritional needs, directly on other living organism. The latter is called a host from whom the parasite directly obtains food. The parasitic organism keeps close contact with the host and sucks or absorbs nutrients from its body. The host goes on becoming weaker physically and physiological. The health of host thus is affected. Thus, the parasitic mode of nutrition is harmful for the host organism.
(10) HCl (Hydrochloric acid) is an important constituent of gastric juice.
Answer:
For the chemical digestion of food in stomach, the stomach secretes gastric juice from its gastric glands. HCl is one of the constituents of gastric juice.
HCl destroys the bacteria and other micro¬organisms entering along with the ingested food and thereby prevent the decay of food in stomach. HCl provides acidic medium for the action of gastric enzyme. HCl converts inactive enzyme pepsinogen into an active enzyme pepsin. Pepsin acts in acidic medium on proteins and starts their digestion and convert them into preoteoses and peptones. Thus, HCl is an important constituent of gastric juice.
(11) The length of small intestine of herbivorous is relatively much longer than that of carnivorous.
Answer:
The length of small intestine is different in different animals and that depends upon the nature of food taken by the animal. The carnivorous eat flesh. The digestion of flesh as food is quite easy and rapid and there is very small amount of roughage.
Hence these animals have short small intestine. The herbivorous eat grass and other vegetation. The cellulose of the plant cells is a complex substance and its complete digestion needs more space and time and hence longer small intestine and longer large intestine. Hence, the length of small intestine of herbivorous is relatively much longer than that of carnivorous.
(12) Bile is an important digestive juice though it does not contain any digestive enzymes.
Answer:
Bile is a greenish yellow alkaline digestive juice secreted from the liver cells. Bile contains bile salts, certain bile pigments but does not contain any digestive enzymes.
The bile salts turn the acidic food from stomach, alkaline and thereby provide alkaline medium for further reactions in intestine. Pancreatic enzymes and intestinal enzymes need alkaline medium. Bile salts emulsify the large fat globules into a very large number of very minute fat droplets and thereby greatly increase the exposed surface area of fat for the rapid action of lipases. Hence bile is an important digestive juice though it does not contain any digestive enzymes.
(13) Respiration is important to keep the organism in living state.
Answer:
The living cells of the body need energy for performing various vital functions. The energy is obtained by the biological oxidation of organic nutrients in the cell.
The process of breakdown of food sources for cellular needs either using oxygen or without oxygen is called respiration. The energy, so released is for continuation of various functions and thereby ‘ maintaining the living state of the organism. Thus, respiration is essential for life.
Question 3.
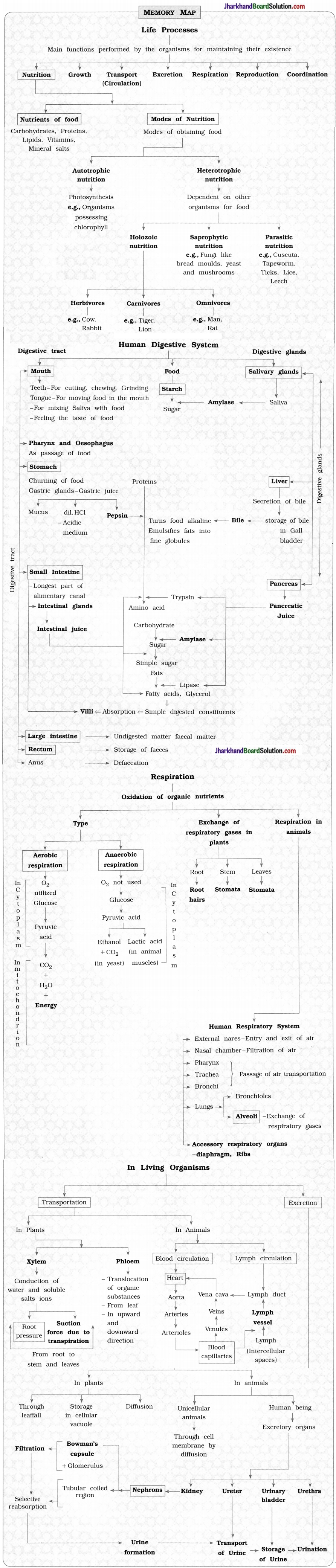
Carefully observe the given diagram and answer the questions related with it:
Questions :
- Identify label x and state any two process that occur through it.
- Identify label y and state the name of process and equation that occurs in it.
- Identify label z and which situation you think for the given diagram?
- What you think about transportation during day from label x in given diagram?
Answer:
- x – stomatal pore, exchange of gases and transpiration occur through it.
- y – chloroplast, photosynthesis process occurs in it.
- z – guard cells, the guard cells swell when water flows into them, causing the stomatal pore to open.
- During the day when stomata are open, the transpiration pull becomes the major driving force in the movement of water in xylem.
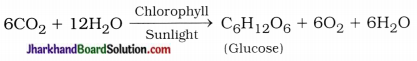
Questions :
- Identify x and state the name of enzyme secreted in it and a medium required for its action.
- Which juice is secreted from y? Where does it show its action and state the name of process which occurs by it?
- State the name of specific finger-likc projections located in z and its functions.
- Which other finger-like projection do you know and where can you observe it?
Answer:
- x – stomach, name of enzyme is pepsin and acidic medium is required for its action.
Bile juice secreted from y. It shows its action in small intestine and emulsification (breakdown of fat globules) process occurred by it. - Specific finger-like projections in the walls of z are villi. It increases surface area for absorption of food.
- We know other finger-like projections are pseudopodia. We can observe it on the cell surface of amoeba.
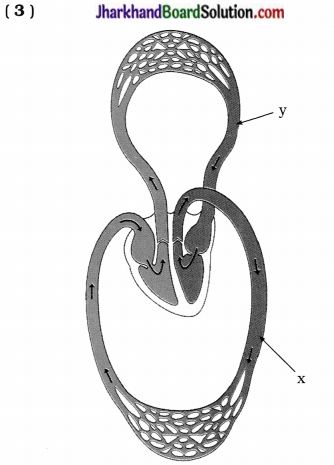
Questions :
- Which type of blood circulation you see in this diagram, what it means?
- Which type of blood flows through x? Which one is exceptional for this?
- Which type of blood flows through y? Why?
- How our body gets highly efficient supply of oxygen?
Answer:
- Double circulation. It means blood goes through the heart twice during each cycle.
- Oxygenated blood flows through x. Pulmonary artery is exceptional because it transports deoxygenated blood.
- Oxygenated blood flows through y. Because it carries blood from lungs to heart and in lungs blood becomes oxygenated.
- The separation of the right side and the left side of the heart is useful to keep oxygenated and deoxygenated blood from mixing.
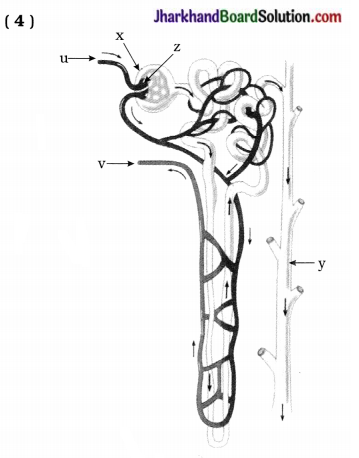
Questions:
- Which structure is shown in the above diagram? Which nitrogenous wastes is removed from blood by this structure?
- Identify x and mention its shape and function.
- Identify y and z.
- Compare the blood flowing through u and v blood vessles.
Answer:
- Structure of nephron shown in the diagram. Nitrogenous wastes such as urea and uric acid are removed from blood by it.
- x – Bowman’s capsule. It is cup-shaped and collects the filtrate.
- y – collecting duct, z – glomerulus.
- u – It transports oxygenated blood containing more nitrogenous wastes, v – It transports deoxygenated blood with lesser nitrogenous wastes due to filtration.
Objective Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Answer the following questions in short:
(1) Which inorganic substances are used as raw materials by autotrophic organisms?
Answer:
Water and CO2 are the inorganic substances used as raw material for the synthesis s of organic food by autotrophic organisms.
(2) What is the mode of nutrition in fungi?
Answer:
The fungi show heterotrophic nutrition, in which breakdown the food material outside the body and then absorb it.
(3) Name one organism each, having saprophytic, parasitic and holozoic modes of nutrition.
Answer:
| Mode of nutrition | Name of organism |
| Saprophytic | Most of fungi |
| Parasitic | Tapeworm, Ascaris |
| Holozoic | Amoeba, Human |
(4 ) In addition to carbon dioxide and water, state two other conditions necessary for the process of photosynthesis.
Answer:
Presence of chlorophyll in the cells and <: the presence of sunlight are also necessary, in addition to CO2 and water, for photosynthesis.
(5) Why there is a controversy about whether viruses are truly alive or not?
Answer:
There is a controversy about whether viruses are truly alive or not, because viruses do not show any molecular movement in them unless they infect specific host cell.
(6) Why are molecular movements needed for life?
Answer:
Molecular movements are needed for life because all the structures of living cells are made up of molecules and they must move molecules around all the time.
(7) On what the survival of heterotrophs depend? Give example of heterotrophic organisms?
Answer:
The survival of heterotrophs depends directly or indirectly on autotrophs.
Example of heterotrophic organisms : Animals and fungi.
(8) Which form of carbohydrate is stored in green plants and in human beings?
Answer:
Carbohydrates in the form of starch is stored in green plants while in human beings it is stored as glycogen.
(9) How desert plants perform process of photosynthesis?
Answer:
Desert plants take up carbon dioxide at night and prepare an intermediate which is acted upon by the energy absorbed by the chlorophyll during the day.
(10) Where does the exchange of gases occur in plants other than stomatal pores?
Answer:
The exchange of gases occurs across the surface of stems, roots and leaves other than in stomatal pores of plants.
(11) What is the function of guard cells?
Answer:
The opening and closing of the stomatal pore is a function of the guard cells.
(12) What is the essentiality of nitrogen element?
Answer:
Nitrogen is an essential element in the synthesis of protein and other compounds.
(13) Give the name of organisms that use parasitic nutritive strategy.
Answer:
The name of organisms that use parasitic nutritive strategy are cuscuta, ticks, lice, leech, tapeworm, etc.
(14) How a food vacuole is formed in amoeba?
Answer:
Amoeba takes in food using temporary finger-like extensions called pseudopodia of the cell surface which fuse over the food particle forming a food vacuole.
(15) What is peristaltic movement?
Answer:
The rhythmic movement shown by the contractions of the muscles of lining of alimentary canal which push the food only in one direction is called peristaltic movement.
(16) What causes acidity in adults?
Answer:
Acidity is caused due to excess secretion of hydrochloric acid in stomach.
(17) State the name of enzyme involved in digestion of protein and its location.
Answer:
| Name of enzyme involved in digestion of protein | Location |
| (1) Pepsin | Gastric juice |
| (2) Trypsin | Pancreatic juice |
(18) In which type of respiration more energy is released?
Answer:
In aerobic respiration more energy is released.
(19) Which part of root is involved in the exchange of respiratory gases?
Answer:
The root hairs, formed from the epidermal cells of the root, are involved in the exchange of respiratory gases.
(20) Name the respiratory organ of fish.
Answer:
The fish possesses pharyngeal gills as respiratory organs.
(21) In which pathway of breakdown of glucose CO2 is not produced?
Answer:
Anaerobic respiration in our muscle cells
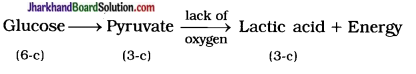
(22) Why the air passage does not collapse in our body?
Answer:
Rings of cartilage are present in the trachea so that the air passage does not collapse in our body.
(23) What are the characteristics of respiratory surface?
Answer:
Respiratory surface is very fine, delicate, moist and contains an extensive network of blood vessels and it remains in contact with atmosphere.
(24) Why the lungs always contain a residual volume of air?
Answer:
Thle lungs always contain a residual volume of air so that there is sufficient time for oxygen to be absorbed and for carbon dioxide to be released.
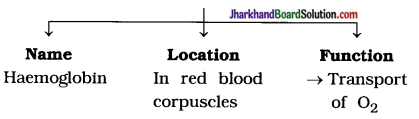
(25) Give the name, location and function of respiratory pigment in human beings.
Answer:
In human beings, respiratory pigment
(26) What is called single circulation?
Answer:
Blood goes only once through the heart in the fish body during the once circulation.
(27) What is the function of blood capillaries?
Answer:
Exchange of material between blood and the surrounding cells takes place across the thin wall of blood capillaries.
(28) What is the significance of lymph?
Answer:
Lymph carries digested and absorbed fat from small intestine and drains excess fluid from intercellular space back into the blood.
(29) Who forms conducting tubes in higher plants? What are transported through it?
Answer:
Xylem and phloem forms conducting tubes in higher plants. Xylem transports water and minerals, phloem transports products of photosynthesis.
(30) How sunction is created in xylem? What is it significance?
Answer:
Evaporation of water molecules from the cells of a leaf creates a sunction in xylem. It pulls water from the xylem cells.
(31) State any two points of importance of transpiration in plants?
Answer:
Importance of transpiration in plants:
- It helps in the absorption and upward movement of water and minerals dissolved in it from roots to the leaves.
- It helps in temperature regulation.
(32) State the name of forces important for the movement of water in the xylem during day and at night respectively?
Answer:
Transpiration pull during day and root pressure at night are important forces for the movement of water in the xylem.
(33) Which substances are transported through phloem?
Answer:
Sucrose, amino acids and other substances are transported through phloem.
(34) Which component of phloem shows translocation of food? In which direction does s it take place?
Answer:
The translocation of food takes place in the sieve tubes with the help of adjacent companion cells of phloem and in both upward and downward directions.
(35) Explain translocation of sugar in the spring season in plants.
Answer:
In the spring season, sugar stored in root or stem tissue is translocated to the buds which need energy to grow.
(36) Which substances are selectively reabsorbed from initial filtrate in the tubular part of nephron?
Answer:
Glucose, amino acids, salts and a major amount of water are selectively reabsorbed from initial filtrate in the tubular part of nephron.
(37) Until when urine is stored in the urinary bladder?
Answer:
Urine is stored in the urinary bladder until the pressure of the expanded bladder leads to the urge to pass it out through the urethra.
(38) Why we can usually control the urge to urinate?
Answer:
We can usually control the urge to urinate because the bladder can store urine and it is under voluntary nervous control.
(39) State name and location of any three structures which are richly supplied with blood vessels.
Answer:
| Structure | Location |
| (1) Villi | Wall of intestine |
| (2) Alveoli | Terminale of bronchioles in lungs |
| (3) Nephron | In the kidneys |
Question 2.
Define : OR Explain the terms :
(1) Nutrition
Answer:
A process of transfer of a source of energy from outside the body of the organism to the inside is called nutrition.
(2) Photosynthesis
Answer:
A process of synthesis of simple form of carbohydrate, i.e. glucose with the use of solar energy, water and carbon dioxide in presence of chlorophyll is called photosynthesis.
(3) Autotrophs
Answer:
Those organisms which utilise simple inorganic sources in the form of carbon dioxide and water and synthesise complex food are called autotrophs.
(4) Heterotrophs
Answer:
Those organism which utilise complex food material prepared by other organisms are called heterotrophs.
(5) Digestion
Answer:
A process by which complex food components are transformed into simple, soluble and absorbable form with the help of enzymes is called digestion.
(6) Respiration
Answer:
A process of breakdown of food source such as glucose, in presence or in absence of oxygen inside the living cell to provide energy for cellular need is called respiration.
(7) Breathing
Answer:
A process of inhalation and exhalation is called breathing.
(8) Transpiration
Answer:
A process of loss of water in the form of vapour from the aerial parts of the plant is known as transpiration.
(9) Excretion
Answer:
The biological process involved in removal of nitrogenous metabolic wastes from the body is called excretion.
Question 3.
Fill in the blanks :
- The substance, used in cellular respiration, is ………………..
- The effect of ……………….. in transport of water is more important at night.
- Carbohydrate is synthesized by the reduction of COa in the process of ………………..
- The secretions from the liver and pancreas are poured in the ………………..
- Human beings show ……………….. mode of nutrition.
- The enzyme ……………….. digests starch and converts it into maltose.
- Pepsin is an enzyme that can act only in ……………….. medium.
- The digestion of food particle in Amoeba occurs in ………………..
- The ……………….. in the wall of small intestine greatly increase the surface area for absorption.
- The conversion of glucose into ……………….. during the first phase of the respiratory process occurs in the cytoplasm.
- The conduction of the photosynthetic products is called ………………..
- The ……………….. increases when the sucrose is transported through the phloem tissue.
- The suction force created due to ……………….. is the main force for the conduction of water in the xylem.
- The artery emerging from the left ventricle is called ………………..
- There is always ……………….. blood in the right auricle.
- As compared to blood the lymph contains ……………….. proteins.
- The exchange of materials between the blood and tissue cells of the body takes place through ………………..
- The terminal end of the excretory unit opens in the ………………..
- The wall of the arteries are thick and ………………..
- ……………….. During photosynthesis, ……………….. is evolved as by-product.
Answer:
- glucose
- root pressure
- photosynthesis
- small intestine
- heterotrophic
- amylase
- acidic
- food vacuole
- vIlli
- pyruvate
- translocauon
- osmotic pressure
- transpiraüon
- aorta
- deoxygenated
- less
- capillaries
- collectIng duct
- elastic
- oxygen
Question 4.
State whether the following statements are true or false:
- Euglena is an autotrophic animal.
- In human body the carbohydrates are stored in the form of glycogen.
- In photosynthesis the carbon dioxide is oxidized to form carbohydrates.
- The control and regulation of the opening and closing of stomata is done by the chloroplasts.
- Liver and pancreas produce digestive juices which help in digestion in small intestine.
- The liver secretes acidic bile.
- The cellulose in the cells of grass, can be digested by herbivores animals.
- The inner wall of the stomach possesses tubular glands which secrete gastric juice.
- Cuscuta is a plant, harmful for the host plant.
- The rate of breathing in terrestrial animals is much faster than that seen in aquatic animals.
- Cilia help in ingestion of food in paramoecium.
- The enzymes pepsin and trypsin digest carbohydrates and fats respectively.
- An artificial kidney is a device to remove nitrogenous wastes from the blood through dialysis.
- The bronchus ends in the alveolus.
- The diaphragm bends (moves) downwards at the time of expiration.
- The blood flows from the heart to other organs under pressure.
- In unicellular animals, the excretory substances are removed by diffusion in the surrounding water.
- The blood vessels absorb fat through the villi of the ileum.
- In certain plants, the useless waste substances are stored in cellular vacuoles.
- The wall of the blood capillaries is bilayered and thick.
- The body temperature is maintained by using energy in animals of classes Mammalia and Aves.
- The pulmonary arteries cany oxygenated blood.
- In plants, the conduction of water is in both upward and downward directions.
- The phloem tissue transports carbohydrate, amino acids and plant hormones.
- Blood is a red coloured, non-living liquid connective tissue.
Answer:
- True
- True
- False
- False
- True
- False
- True
- True
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
- False
- False
- True
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
- False
- False
- True
- False
Question 5.
Match the following:
(1)
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Algae | p. Saprophytic nutrition |
| 2. Cuscuta | q. Holozoic nutrition |
| 3. Fungi | r. Autotrophic nutrition |
| 4. Amoeba | s. Parasitic nutrition |
Answer:
(1 – r), (2 – s), (3 – p), (4 – q).
(2)
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Salivary glands | p. Beginning of protein digestion |
| 2. Liver | q. Enzyme trypsin |
| 3. Pancreas | r. Alkaline bile |
| 4. Stomach | s. Secretion of amylase |
Answer:
(1 – s), (2 – r). (3 – q). (4 – p).
(3)
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Amoeba | p. Omnivores |
| 2. Paramoecium | q. Gills |
| 3. Human being | r. Pseudopodia |
| 4. Fish | s. Cilia |
Answer:
(1 – r), (2 – s), (3 – p), (4 – q).
(4)
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Villi | p. Exchange of gases |
| 2. Cartilagenous ring | q. Absorption |
| 3. Alveolus | r. Helps in breathing |
| 4. Diaphragm | s. Trachea |
Answer:
(1 – r), (2 – s), (3 – p), (4 – q).
(5)
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Phloem | p. Urine formation |
| 2. Excretory unit | q. Upward and downward conduction |
| 3. Pulmonary vein | r. Deoxygenated blood |
| 4. Renal vein | s. Oxygenated blood |
Answer:
(1 – q), (2 – p), (3 – s), (4 – r).
(6)
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Human heart | p. Cup-shaped |
| 2. Human kidney | q. Four-chambered |
| 3. Nephron | r. Bean-shaped |
| 4. Bowman’s capsule | s. Long-coiled tubule |
Answer:
(1 – q), (2 – r), (3 – s), (4 – p).
(7)
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Villi | p. Right auricle |
| 2. Bowman’s capsule | q. Less protein |
| 3. Lymph | r. Glomerulus |
| 4. Vena cava | s. Small intestine |
Answer:
(1 – s), (2 – r), (3 – q). (4 – p).
(8)
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Chloroplast | p. Stomatal pore |
| 2. Mitochondria | q. Digestion |
| 3. Guard cells | r. Reduction of CO<sub>2</sub> |
| 4. Food vacuole | s. Breakdown of pyruvate using O<sub>2</sub> |
Answer:
(1 – r), (2 – s), (3 – p), (4 – q).
(9)
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Photosynthesis | p. Temperature regulation |
| 2. Respiration | q. Energy stored |
| 3. Transpiration | r. Sucrose |
| 4. Translocation | s. Energy released |
Answer:
(1 – q), (2 – s), (3 – p), (4 – r).
Question 6.
Chart – diagram based questions:
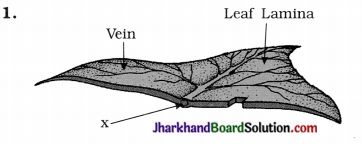
Identify x in diagram and state which system of plant does it indicate.
Answer:
x-phloem, xylem vascular bundle, it indicates transportation system of plant.
2.
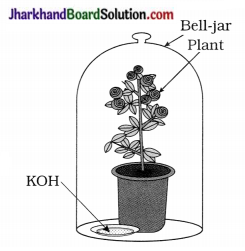
Why starch test is negative in any leaf of plant? What you conclude?
Answer:
Starch test is negative in any leaf of plant s because CO2 is not available as the plant is in bell-jar in which KOH absorbed CO2.
CO2 is a raw material essential for s photosynthesis.

State the lable x and y in given diagram and also mention which life process do they indicate.
Answer:
x – pseudopodia, y – food vacuole
Life process : nutrition in amoeba
4. Fill the blanks in given table with reference to digestion process in human:
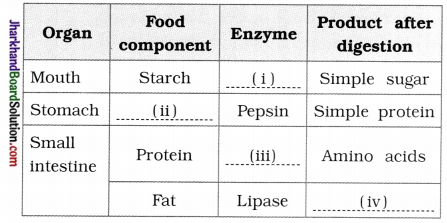
Answer:
- Amylase
- Protein
- Trypsin
- Fatty acid and glycerol
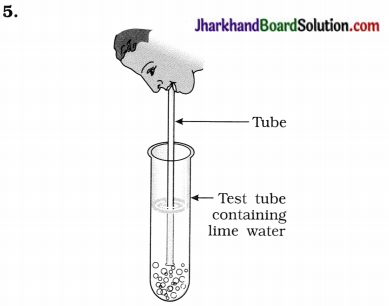
What change occurs in the solution in test tube? What is responsible for such change?
Answer:
The lime water in test tube turns milky.
We breath out CO2 which is responsible for lime water to turn milky.
6. Fill the blanks in given chart:
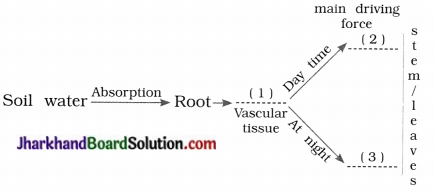
Answer:
- Xylem
- Transpiration pull
- Root pressure
7.
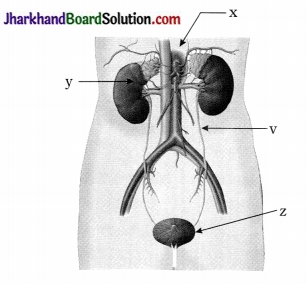
Observe the diagram and indicate which parts shows function of storage of urine and filtration of blood?
Answer:
y – kidney – filtration of blood
z – urinary bladder – storage of urine
Question 7.
Select the correct alternative from those given below each question:
1. Which of the following organism breaks down food material outside of body?
A. Mushroom
B. Cuscuta
C. Leech
D. Lice
Answer:
A. Mushroom
2. Where does the digestion of protein start in human being?
A. Mouth
B. Stomach
C. Small intestine
D. Colon
Answer:
B. Stomach
3. Which of the following type has longest small intestine?
A. Tiger
B. Human
C. Cow
D. Rat
Answer:
C. Cow
4. Which one of the following organisms can live without oxygen or air?
A. Amoeba
B. Leech
C. Green plant
D. Yeast
Answer:
D. Yeast
5. Which is the exact site for gaseous exchange s in human beings?
A. Brochus
B. Alveoli
C. Villi
D. Skin
Answer:
B. Alveoli
6. What is the product from glucose in the first phase of respiration?
A. Ethanol
B. Lactic acid
C. Pyruvic acid
D. CO2
Answer:
C. Pyruvic acid
7. What is the ultimate purpose of digestion?
A. Transportation
B. Absorption
C. Respiration
D. Assimilation
Answer:
B. Absorption
8. Which cells surround the pore of the stomata?
A. Epidermal cells
B. Companion cells
C. Sieve cells
D. Guard cells
Answer:
D. Guard cells
9. Which organ stores bile?
A. Liver
B. Pancreas
C. Small intestine
D. Gall bladder
Answer:
D. Gall bladder
10. The enzyme acting in acidic medium is ………………..
A. amylase
B. pepsin
C. trypsin
D. both B and C
Answer:
B. pepsin
11. In plants, photosynthetic products are transported through ………………..
A. vessel and sieve tube
B. tracheid and vessel
C. sieve tube and companion cell
D. sieve tube and tracheid
Answer:
C. sieve tube and companion cell
12. In which part of the body blood is oxygenated?
A. Heart
B. Liver
C. Kidney
D. Lungs
Answer:
D. Lungs
13. At which part the actual process of filtration of blood takes place in kidney?
A. Bowman’s capsule
B. Collecting duct
C. Tubular part of nephron
D. Capillaries of nephron
Answer:
A. Bowman’s capsule
14. From which part of the human heart only oxygenated blood always flows?
A. Both atria
B. Both ventricles
C. Left atrium and left ventricle
D. Right atrium and right ventricle
Answer:
C. Left atrium and left ventricle
15. As compared to blood, the lymph contains ………………..
A. fewer RBCs
B. less amount of water
C. less amount of metabolic waste
D. less amount of proteins
Answer:
D. less amount of proteins
16. Which of the following brings oxygenated blood into left atrium in heart?
A. Pulmonary vein
B. Pulmonary artery
C. Vena cava
D. Aorta
Answer:
A. Pulmonary vein
17. What happens in the process of photo-synthesis?
A. Transformation of solar energy into functional energy
B. Transformation of solar energy into chemical energy
C. Transformation of chemical energy into functional energy
D. Transformation of functional energy into chemical energy
Answer:
B. Transformation of solar energy into chemical energy
18. Which is the main force for the conduction of water through the xylem in plants?
A. Absorption of water through roots
B. Absorption of ions through roots
C. Sufficient availability of water from the soil
D. Suction due to transpiration
Answer:
D. Suction due to transpiration
19. Which of the following alternative shows the correct path of oxygenated blood flow in human beings?
A. Lungs → Pulmonary veins → Left auricle → Left ventricle → Various organs of the body
B. Lungs Pulmonary artery → Left auricle → Left ventricle → Various organs of the body
C. Lungs → Pulmonary artery → Right auricle → Right ventricle → Various organs of the body
D. Various organs of the body Right auricle → Right ventricle → Pulmonary artery → Lungs
Answer:
A. Lungs → Pulmonary veins → Left auricle → Left ventricle → Various organs of the body
20. Select the correct pair :
A. Stomata – transpiration
B. Translocation – glucose
C. Villi – egestion of feaces
D. Trachea – cartilaginous rings
Answer:
A. Stomata – transpiration
D. Trachea – cartilaginous rings
21. Which process is important for osmoregulation?
A. Nutrition
B. Circulation
C. Breathing
D. Excretion
Answer:
D. Excretion
22. Which one is the false statement for arteries?
A. Arteries carry blood from the heart towards other organs.
B. In arteries the blood flows under high pressure.
C. All arteries carry oxygenated blood.
D. The arterial walls are thick and elastic.
Answer:
C. All arteries carry oxygenated blood.
23. Resin and gum are the substances of plants.
A. excretory
B. nutritive
C. constitutional
D. reserve
Answer:
A. excretory
24. Which is the circulatory pathway of blood in the human heart?
A. Right auricle → Left auricle → Lungs → Right ventricle → Left ventricle → Different organs
B. Right auricle → Right ventricle → Lungs → Left auricle → Left ventricle → Different organs
C. Right auricle → Right ventricle Different organs → Left auricles Left ventricle → Lungs
D. Right auricle → Left auricle → Different organs → Right ventricle → Left ventricle → Lungs
Answer:
B. Right auricle → Right ventricle → Lungs → Left auricle → Left ventricle → Different organs
25. Which substance does not get reabsorbed in nephron during urine formation?
A. Glucose
B. Urea
C. Amino acid
D. Uric acid
Answer:
B. Urea, Uric acid
26. In which of following process. ATP is used?
A. Translocation of food
B. To maintain body temperature in human
C. Respiration
D. Simple diffusion in human
Answer:
Translocation of food, To maintain body temperature in human
27. Statement A: The rate of breathing is much faster in fishes.
Reason R : The blood goes only once through the heart in the fish during one cycle of passage through the body.
Which is the correct option for Statement A and Reason R?
A. Both A and R correct and R is explanation of A.
B. Both A and R correct but R is not explanation of A.
C. A is correct, R is incorrect.
D. A is incorrect, R is correct.
E. Both A and R incorrect.
Answer:
A. Both A and R correct and R is explanation of A.
28. Statement A : ATP is the energy currency for cellular processes.
Reason R: Complete oxidation of pyruvate in presence of oxygen occurs in mitochondria.
Which is the correct option for Statement A and Reason R?
A. Both A and R correct and R is explanation of A.
B. Both A and R correct but R is not explanation of A.
C. A is correct, R is incorrect.
D. A is incorrect, R is correct.
E. Both A and R incorrect.
Answer:
B. Both A and R correct but R is not explanation of A.
29. Which animals tolerate some mixing of oxygenated and deoxygenated blood streams?
A. Fishes
B. Birds
C. Mammals
D. Amphibians
Answer:
D. Amphibians
30. The diagram is labelled, which part secretes digestive juice?
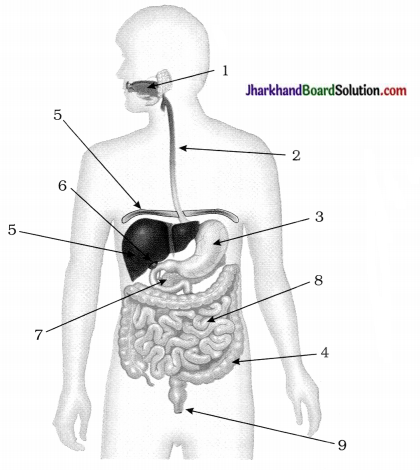
A. 1, 3, 5, 7
B. 2, 4. 6, 8
C. 2, 3, 5, 8
D. 1, 4, 6, 8
Answer:
A. 1, 3, 5, 7
Question 8.
Answer as directed : (Miscellaneous)
(1) Which pigment has a very high affinity for oxygen? Where is it present in human body?
Answer:
Haemoglobin in red blood cells
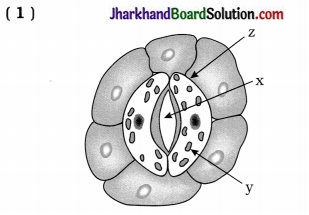
(2) State the equation of photosynthesis.
Answer:
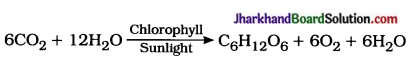
(3) Name of instrument used to measure blood pressure.
Answer:
Sphygmomanometer
(4) About which organism there is a controversy regarding whether it is a living being or non-living entity?
Answer:
Viruses
(5) Give the full form of ATP.
Answer:
Adenosine TriPhosphate
(6) Identify me : I am a cup-shaped structure with glomerulus and I carry out filtration.
Answer:
Bowman’s capsule
(7) Find mismatched pair :
1. One cell thick – blood capillary
2. Ring of cartilage – trachea
3. Phloem tissue – transport of sucrose
4. Platelet cells – transport of respiratory gases
Answer:
4. Platelet cells – transport of respiratory gases
(8) State the normal blood pressure of human.
Answer:
Systolic pressure 120 mm Hg and diastolic pressure 80 mm Hg
(9) Identify me : A component of gastric juice protect the inner lining of the stomach from the action of hydrochloric acid under normal condition.
Answer:
Mucus
(10) Sketch the respiratory pathway which does not produce CO2.
Answer:
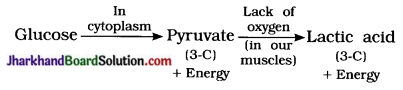
(11) Which of the following organisms show parasitic nutritive strategy?
Lion, lice, bread mould, cuscuta, leech, yeast, tick
Answer:
lice, cuscuta, leech, tick
(12) Find mismatched pair:
1. Paramoecium – Fermentation
2. Peristaltic movement – All along the gut
3. Emulsifying action – Bile
4. Trachea – Windpipe
Answer:
1. Paramoecium – Fermentation
(13) Which treatment do you suggest to a patient whose both kidneys have stopped functioning?
Answer:
Hemodialysis
(14) Transpiration helps to create osmotic pressure for translocation of sucrose. State whether s this sentence true or false.
Answer:
False
Value Based Questions With Answers
Question 1.
Your younger brother complains about pain in teeth. You often notice that he frequently eats chocolates and pastries. Even he likes to eat sweets.
Questions:
- What do you think about the pain in teeth?
- Which advise will you give to your brother?
- What will happen if this problem is untreated?
Answer:
- Sugar content is very high in chocolates, pastries and sweets. Bacteria act on sugars and produce acidic substances. Acids soften? the enamel, i.e.. cause dental caries or tooth decay. Masses of bacterial cells together with food particles stick to the teeth to form dental plaque. This is responsible for pain in teeth.
- Brushing the teeth after eating, will remove plaque.
- If this problem is untreated, microorganisms may invade the gums causing inflammation and infection
Question 2.
Your uncle often complains about indigestion of after having oily food. He consults a doctor and? is diagnosed with stone in gall bladder. Doctor advised him to remove gall bladder surgically.
Questions:
- What is the function of gall bladder?
- Which process initiates the digestion of oils?
- After surgery, which type of food should be given to uncle?
Answer:
- Gall bladder stores bile juice.
- Emulsification (i.e.. bile salts breakdown large 5 oil globules into fine small droplets) process initiate the digestion of oils.
- After surgery, food with low fat content, i.e., less oil, ghee, butter, etc. is advisable.
Question 3.
Your neighbour is a chain-smoker. He often suffers from cough and lung infection. His relatives often tell him to leave smoking.
Questions:
- How inhaled air is filtered in the upper part of respiratory tract?
- Which is the effect of smoking on the upper part of respiratory tract?
- Why do you call smoking as injurious to health?
Answer:
- The upper part of respiratory tract is provided with small hair-like structures called cilia, which help to remove germs, dust and other harmful particles from inhaled air.
- Smoking destroys hair like cilia due to which germs, dust, smoke and other harmful chemicals enter lungs and causes harm.
- Smoking reduces the breathing efficiency of lungs, may cause various infection and even lung cancer. So, called it is injurious to health. Cigarette contains nicotine which can cause cancer to the respiratory organs.
Question 4.
Your subject teacher arranges a visit to a hospital, where you can observe haemodialysis.
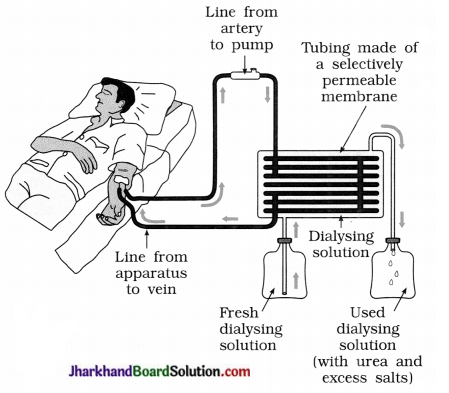
Questions :
- Which conditions may lead to kidney failure?
- What is the use of artificial kidney?
- Explain how artificial kidneys work?
Answer:
- Several factors such as infections, injury or restricted blood flow to kidney reduce the activity of kidneys. This leads to accumulation of toxic nitrogenous substances, gradually may lead to kidney failure.
- An artificial kidney is a device to remove s nitrogenous waste products from the blood through dialysis.
- Artificial kidneys contain a number of tubes with a semi-permeable lining, suspended in a tank filled with dialysing fluid. This fluid has same osmotic pressure as blood but nitrogenous wastes are absent.
As shown in diagram, patient’s blood is passed through tubes. During this, nitrogenous waste products from blood pass into dialysing fluid by diffusion. The purified blood is pumped back into the patient’s vein.
Practical Skill Based Questions With Answers
Question 1.
Observe experiment arranged in your school laboratory as shown in figure.
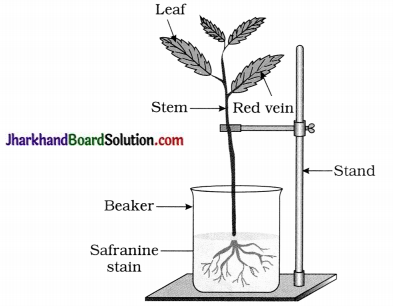
Questions :
- State the colour of the stem and veins of the leaves.
- Does the volume of solution in the beaker get reduced? Why?
- In the T.S. of stem, which part is observed to be reddish in colour? Why?
- State your inference.
Answer:
- Reddish
- Yes, because plant absorbed solution from beaker through its roots.
- Xylem tissue becomes reddish in colour in T.S. of stem because water moves up through xylem.
- Water and minerals absorbed by root move in upward direction through xylem vessels.
Question 2.
Take a potted plant.
- Insert one of its branches in a large, thin and transparent plastic/polythene bag and tie the bag at its open end with the branch.
- Add adequate amount of water to the clay in the pot, and keep the pot exposed to sunlight for a few hours.
- Observe the inner side of the bag after a few hours.
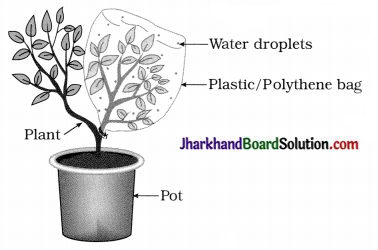
Questions :
- Why are small droplets of water seen on the inner surface of the plastic/polythene bag?
- State the role played by sunlight in the formation of water droplets.
- State the passage of flow of water droplets through the potted plant.
Answer:
- Loss of water vapour from leaves condense and show water droplets.
- Sunlight is responsible for transpiration. Water is lost in the form of vapour, which creates suction and transpiration pull in upward direction.
- Soil root xylem → stem-xylem → leaf xylem → stomata → water vapour
Question 3.
Place two fingers of your right hand on the left wrist and feel the pulse beats.
- Count the number of pulse beats felt by your right hand fingers in exactly one minute.
- Repeat the counting of pulse beats twice or thrice for accuracy. Find out the mean of all readings.
- Now run fast for a short distance for about one or two minutes, or climb the steps of a staircase quite rapidly twice or thrice.
- And thereafter, again measure your pulse s beats.
Questions:
- State the normal pulse rate.
- State the relation of pulse rate with the rate of heart beats.
- State the number of pulse beats after a little running or climbing the staircase.
- What is the change found in the pulse rate after running, as compared to the normal pulse rate? Why?
Answer:
- 60- 100
- The pulse rate is similar to heart beats.
- 120 to 130 times in a minute.
- Pulse rate increases after riming because body requires more oxygen and to fullfil it, heart beats increase.
Memory Map: