Students must go through these JAC Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds to get a clear insight into all the important concepts.
JAC Board Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds
→ All the living structures (plants and animals) are made-up of (or based on) carbon.
→ The earth’s crust contains 0.02 % carbon in the form of minerals.
→ The reactivity of elements is explained as their tendency to attain a completely filled outermost shell, i.e., attains a noble gas configuration.
![]()
→ Covalent bond : A chemical bond formed between two or more atoms by mutual sharing of valence electrons is known as a covalent bond.
→ There are three allotropes of carbon:
- Diamond
- Graphite and
- Fullerene
→ Catenation: Carbon has the unique ability to form bonds with other atoms of carbon giving rise to large number of molecules. This property of carbon is called catenation.
→ Compounds of carbon, which are linked by only single bonds between the carbon atoms are called saturated compounds while compounds of carbon having double or triple bonds between the carbon atoms are called unsaturated compounds.
→ Unsaturated organic compounds are more reactive than saturated organic compounds.
→ Structural isomers : The organic compounds having the same molecular formula but different structures are known as structural isomers.
→ Hydrocarbons : The compounds containing carbon and hydrogen only are called hydrocarbons. They may be saturated or unsaturated.
→ Saturated hydrocarbons which contain only single bond between carbon atoms are called alkanes. The unsaturated hydrocarbons which contain one or more double bonds between carbon atoms are called alkenes and those containing one or more triple bonds are called alkynes.
→ Functional group : An atom or a group of atoms which imparts specific properties to the compound is called a functional group. Based on functional group the compounds are classified as alcohol, carboxylic acid, etc.
![]()
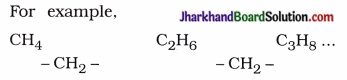
→ Homologous seeries : A series of organic compounds in succession which differ by a definite group (like – CH2 -) is called homologous series.
For example,
→ Oxidising agent: Some substances are capable of adding oxygen to other substances, or remove hydrogen are known as oxidising agents. For example, alkaline potassium permanganate, acidified potassium dichromate.
→ Addition reaction : Unsaturated hydrocarbons adds hydrogen in the presence of catalysts such as palladium or nickel to form saturated hydrocarbons. This reaction is known as addition reaction.
→ Substitution reaction: The reaction in which hydrogen atom of saturated hydrocarbon is replaced by functional group is called a substitution reaction.
→ Esterification: A reaction in which a carboxylic acid and an alcohol react in the presence of acid catalyst forming esters and water is known as an esterification reaction.
![]()
→ Saponification : The reaction of forming alcohol and sodium salt of carboxylic acid from ester is known as saponification.
→ The action of soaps and detergents are based on the presence of both hydrophobic and hydrophilic groups in the molecule which helps in emulsifying the oily dirt.