Jharkhand Board JAC Class 10 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Our Environment Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
JAC Board Class 10 Science Solutions Chapter 15 Our Environment
Jharkhand Board Class 10 Science Our Environment Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Which of the following groups contain only biodegradable items?
A. Grass, flowers and leather
B. Grass, wood and plastic
C. Fruit peels, cake and lime juice
D. Cake, wood and grass
Answer:
Grass, flowers and leather; Fruit peels, cake and lime juice; Cake, wood and grass.
Question 2.
Which of the following constitute a food chain?
A. Grass, wheat and mango
B. Grass, goat and human
C. Goat, cow and elephant
D. Grass, fish and goat
Answer:
Grass, goat and human
Question 3.
Which of the following are environment-friendly practices?
A. Carrying cloth-bags to put purchases in while shopping
B. Switching off unnecessary lights and fans
C. Walking to school instead of getting your mother to drop you on her scooter.
D. All of the above
Answer:
All of the above
![]()
Question 4.
What will happen if we kill all the organisms in one trophic level?
Answer:
If we kill all the organisms in one trophic level then organisms of next trophic level will not get food (chemical energy) and the entire food chain gets disturbed. All the organisms which are dependent on these are died.
On the other hand, the organisms at the lower trophic level will increase in abundance. Due to this, ecosystem will be in imbalance.
Question 5.
Will the impact of removing all the organisms in a trophic level be different for different trophic levels? Can the organisms of any trophic level be removed without causing any damage to the ecosystem?
Answer:
The impact of removing all the organisms in a trophic level will be different for different trophic levels. Removal of producers will affect all the organisms of successive trophic levels. It will be a threat the survival. The removal of organisms at higher trophic level will lead to increase in organisms of lower trophic level. Removal of organisms of any trophic level will cause the damage to the ecosystem.
Question 6.
What is biological magnification? Will the levels of this magnification be different at different level of the ecosystem?
Answer:
Successively increasing concentration of some substance (e.g., pesticides) at various trophic levels of a food chain of organisms is known as biological magnification.
The level of biological magnification will be different at different trophic levels of the ecosystem. Maximum concentration will be at the third and fourth trophic level and concentration of chemical will be less at lower trophic levels.

Question 7.
What are the problems caused by the non-biodegradable wastes that we generate?
Answer:
The problems caused by the generated non-biodegradable wastes are as follows :
- It causes biological magnification.
- They keep on accumulating in nature causing pollution.
- They prevent growth of vegetation when dumped underground.
- They may be inert and simply persist in the environment for a long time and may harm various members of the ecosystem.
- There is imbalance of the food chains causing problems in ecosystem.
Question 8.
If all the wastes we generate is biodegradable, will this have no impact on the environment?
Answer:
If all the waste we generate is biodegradable and if properly allowed it to decompose, then it will have no impact on the environment. They should be properly managed.
![]()
Question 9.
Why is damage to the ozone layer a cause for concern? What steps are being taken to limit this damage?
Answer:
Ozone layer absorbs ultraviolet radiation of the sun which is very harmful to living organisms.
Damage to the ozone layer is a cause for concern because depletion of ozone layer allows harmful ultraviolet radiation to reach to the surface of earth, which may lead to skin cancer, cataract, etc.
To reduce the damage to the ozone layer, use of chlorofluorocarbons has been minimised. In 1987, the UNEP-United Nations Environment Programme has passed an agreement to freeze CFC production at 1986 levels. This will protect the ozone layer and subsequent effects of radiation.
Jharkhand Board Class 10 Science Our Environment InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What are trophic levels? Give an example of a food chain and state the different trophic levels in it.
Answer:
Successive levels of nourishment in the food chain are known as trophic levels.
- It shows transfer of energy in an ecosystem.
- Food chain is a sequential list of prey-predator

Question 2.
What is the role of decomposers in the ecosystem?
Answer:
Decomposers feed on the excretory substances as well as dead bodies of plants and animals.
Bacteria and fungi are decomposers.
- They breakdown the complex organic substances into simple inorganic substances.
- Such simple inorganic substances are used up by the plants again.
- So, they play an important role in cyclic pathway of the elements.
Question 3.
Why are some substances bio¬degradable and some non-biodegradable?
Answer:
Some substances such as paper, vegetables, peels, etc. are acted upon by decomposers and get converted into simple form are called biodegradable. Biodegradable substances are natural substances.
Some synthetic substances such as plastic, polythene, etc. cannot be degraded by microbial activity are called non-biodegradable.
Question 4.
Give any two ways in which biodegradable substances would affect the environment.
Answer:
- Biodegradable substances get degraded by microbial activity releasing simple component back to nature. These components help to sustain the life of other organisms.
- Diming the biodegradation certain gases may be released in atmosphere causing pollution.
Question 5.
Give any two ways in which non-biodegradable substances would affect the environment.
Answer:
- Non-biodegradable substances such as pesticides cause soil and water polluton. It may cause biological magnification.
- Non-biodegradable substances block the functions of an ecosystem, i.e., transfer of energy and elements may stop.
Question 6.
What is ozone and how does it affect any ecosystem?
Answer:
Ozone is a molecule formed by three atoms of oxygen in the presence of UV (Ultraviolet) rays. Ozone performs an essential function at the higher levels of the atmosphere. However, at ground level it is a deadly poison. Ozone absorbs shorter wavelength UV rays from the sun. Thus it protects the living system on earth.
![]()
Question 7.
How can you help in reducing the problem of waste disposal? Give any two methods.
Answer:
We can help in reducing the problem of waste disposal by following methods :
- Biodegradable domestic wastes such as left-over food, fruit and vegetable peels, dry leaves and other wastes of gardens, etc. can be hurried in a pit. They are converted into compost and used as manure.
- Waste materials such as tin, cans, paper, glass, metallic articles are recycled. Through the process of recycling such materials are reused to form new products.
Activity 15.1 [T. B. Pg. 256-257]
To make an aquarium.
Materials:
Large jar of glass, water, pebbles, fish food, aerator (oxygen pump), small fishes, aquatic plant
Procedure:
- Take a large jar of glass. Keep some pebbles in it.
- Fill the jar with water.
- Add few aquatic plants such as algae in the jar.
- Add few small fishes in it.
- Arrange oxygen pump in such a way that we can provide oxygen in the jar.
- Provide fish food regularly which is available in the market.
- Add few small aquatic animals other than fishes in the jar.
Questions :
Question 1.
How can an aquarium become self-sustaining system by adding a few aquatic plants and animals?
Answer:
Aquatic plants performs photosynthesis. They are producers on which animals depend for their nutrition. Plants release oxygen during photosynthesis. Oxygen is utilised by animals in respiration and release carbon dioxide in the water. Carbon dioxide is available to plants for photosynthesis. Thus, aquarium becomes self-sustaining system.
Question 2.
Can we leave the aquarium as such after it is set up?
Answer:
No, we cannot leave the aquarium as it is because metabolic wastes are released in water make it polluted. Therefore, finally change of water is needed.
Question 3.
Why does aquarium have to be cleaned once in a while?
Answer:
Metabolic wastes produced by aquatic organisms make the water polluted. So, it should be cleaned once in a while.
Question 4.
Do we need to clean lakes or ponds in the same manner? Why or why not?
Answer:
Yes, because sometimes excretory wastes accelerate the growth of algae. The lake or pond gets covered with algal growth. Some toxic substances are released and dissolved 02 in water body will be depleted. This will lead to death of all aquatic life and such ecosystem may destructed.
Activity 15.2 [T. B. Pg. 257]
To find more about aquarium.
Material:
An aquarium
Questions:
Question 1.
While creating an aquarium did you take care not to put an aquatic animal which would eat others? What would have happened otherwise?
Answer:
Yes, while creating an aquarium care was taken predator aquatic animals were not used. Otherwise such predators can feed on other organisms and destroy. All small aquatic animals will be consumed by carnivores which later would all die.
Question 2.
Write the aquatic organisms in order of who eats whom and form a chain of at least three steps.
Answer:
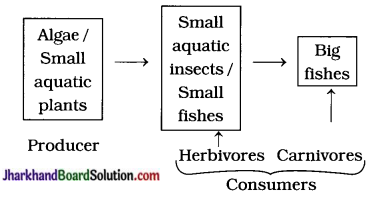
Question 3.
Would you consider any one group of organisms to be of primary importance? Why or why not?
Answer:
Yes, plants (producers) should be given primary importance because they form first trophic level and all the consumers directly or indirectly depend on plants for their food (energy) requirement.
Question 4.
Explain the components of an ecosystem.
OR
Explain the groups of organisms based on their role in an ecosystem.
Answer:
Each ecosystem consists of two main components:
(1) Abiotic components : All the non-living constituents of an ecosystem are included in the abiotic components.
Abiotic components are the physical factors like temperature, rainfall, wind, soil, light, minerals, etc.
(2) Biotic components : All living organisms of an ecosystem are included in the biotic components.
Organisms can be grouped as producers, consumers and decomposers according to their food habit. Their mode of sustenance forms the trophic relationship in the environment.
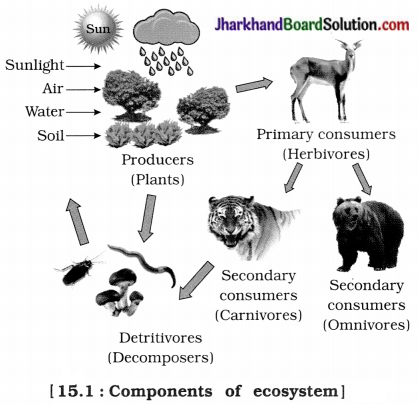
(i) Producers : Those organisms which can make organic compounds like sugar and starch from inorganic substances using solar energy in presence of chlorophyll are called producers.
Example: Certain bacteria, various kinds of algae and all green plants.
(ii) Consumers : Those organisms which consume the food produced either directly from
producers or indirectly by feeding on other consumers are called consumers.
Example: Non-chlorophyllous and heterotrophic organisms.
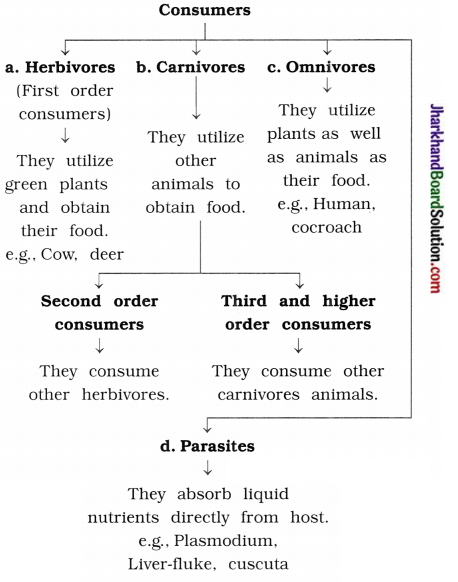
Consumers can be divided into four categories.
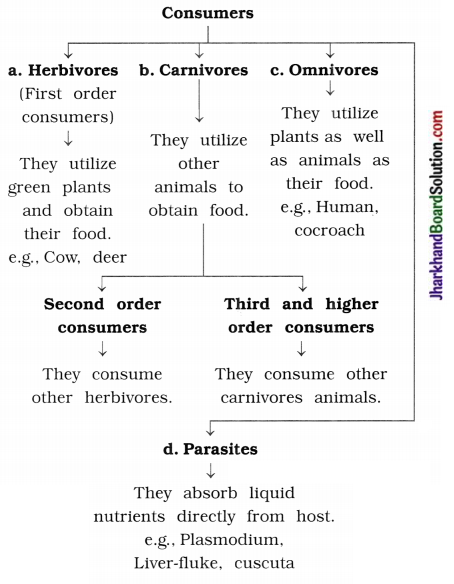
(iii) Decomposers : The microorganisms which breakdown the complex organic substances into simple inorganic substances are called decomposers.
Example: Certain bacteria and fungi, breakdown the dead remains and waste products of organisms.
Question 5.
Write a short note on : Consumers
Answer:
Consumers : Those organisms which consume the food produced either directly from producers or indirectly by feeding on other consumers are called consumers.
Example: Non-chlorophyllous and heterotrophic organisms.
Consumers can be divided into four categories
Activity 15.3 [T. B. Pg. 260]
Newspaper reports about pesticides level in ready-made food items are often seen these days and some states have banned these products.
Questions :
Question 1.
What would be the source of pesticides in ready-made food items?
Answer:
Pesticides are non-biodegradable substances. They are excessively used for controlling the pest in crop field. They enter in food items through food chain.
Question 2.
Could pesticides get into our bodies from food products other than ready-made food?
Answer:
Yes, pesticides can get into our bodies from the food grains, vegetables, fruits, milk, etc. that contain residues of pesticides.
![]()
Question 3.
What methods could be applied to reduce our intake of pesticides?
Answer:
- Pesticides in the crop fields should be s judiciously used.
- Monitoring of pesticides level in agricultural products should be tested at regular interval.
Question 4.
Why some states have banned on some ready-made food products?
Answer:
Some states have banned on some ready-made food products because the level of pesticides is high in it, thus causing hazard to our health.
Activity 15.4 [T. B. Pg. 261]
To find harmful chemicals for ozone layer.
Materials:
Library, internet, newspaper reports
Questions:
Question 1.
Which chemicals are responsible for the depletion of the ozone layer?
Answer:
Ozone depleting substances such as chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs), hydrofluoro-carbons (HFCs) and oxides of nitrogen are resonsible for depletion of the ozone layer.
Question 2.
Find out if the regulations to control the emission of ozone depleting chemicals have succeeded in reducing the damage to the ozone layer. Has the size of the hole in the ozone layer changed in recent years?
Answer:
In 1987, the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP), succeeded in forging an agreement to freeze CFC production at half of the 1986 levels.
Yes, by reducing the continuous use of ozone depleting chemicals, the size of the hole in the ozone layer has reduced in recent years.
Activity 15.5 [T. B. Pg. 261]
Collect waste materials from your home. (kitchen wastes, waste paper, torn clothes and its pieces, empty cartons, milk packets, empty bottles, its lid, used tea leaves, empty medicine bottles/strips/bubble packs, broken footwear, etc.)
- Bury these materials in a pit near your home.
- Keep these moist by spraying water on it.
- Fill the pit with moist clay and cover the waste.
- Dig the pit and observe at 15-day intervals.
Questions:
Question 1.
What are the materials that remain unchanged over long periods of time?
Answer:
The materials that remain unchanged over long periods of time are empty medicine bottles, bubble packs, milk packets, broken plastic footwear.
Question 2.
What are the materials which change their form and structure over time?
Answer:
The materials that change their form and structure are food, vegetable peels, used tea leaves, empty cartons, waste paper, torn clothes, broken leather footwear.
Question 3.
What are the materials that change the faster?
Answer:
The materials that are changed faster are vegetable peels, used tea leaves, spoilt food, etc.
Activity 15.6 [T. B. Pg. 262]
To find more about biodegradable and non-biodegradabie substances.
Questions:
Question 1.
How long are various non-biodegradable substances expected last in our environment?
Answer:
Non-biodegradable substances such as plastic wastes can be acted upon by physical factors such as heat and pressure. But under the ambient conditions found in our environment, non-biodegradable wastes persist for a long time.
Question 2.
Find out whether biodegradable plastic do or do not harm the environment.
Answer:
Polymer fabrics and dental implants are examples of biodegradable plastics. Biodegradable plastics do not cause any harm to the environment.
Activity 15.7 [T. B. Pg. 263]
To find about the disposal of waste generated at home,
Questions
Question 1.
Find out what happens to the waste generated at home? Is there a system in place to collect this waste?
Answer:
The waste generated at home is collected in dustbins daily. The municipal corporation of our city has set up a system to remove such garbage on daily basis. Large collection containers are set up at specific sites to collect the household waste.
In some areas, municipal corporation has set up a system to collect household waste from door to door.
Question 2.
Find out how the local body (panchayat, municipal corporation, resident welfare association) deals with the waste.
Are there mechanisms in place to treat the biodegradable and non-biodegradable wastes separately?
Answer:
Biodegradable and non-biodegradable wastes are separated at the source. In some villages, biogas plants have been established to use biodegradable waste to generate biogas and manure.
In cities, municipal corporation collects waste and finally send to specific vacant site on the extreme edge of the city and dump it there.
Biodegradable wastes should not be burnt as burning causes air pollution. They are converted into manure by composting. Non-biodegradable wastes such as plastics, glass, metals are collected separately and send to respective recycling units.
Question 3.
Calculate how much waste is generated at home in a day. How much of this waste is biodegradable?
Answer:
Large amount of waste is generated at home in a day. Most of it is biodegradable. Some of it is non-biodegradable.
Question 4.
Calculate how much waste is generated in a classroom in a day. How much of this waste is biodegradable?
Answer:
In a classroom, large amount of waste which is mostly biodegradable waste generated.
Question 5.
Suggest the ways of dealing with the waste.
Answer:
Biodegradable wastes should be burried in a pit. After few days they change into manure / compost due to action of decomposers. It can be used in garden.
Activity 15.8 [T. B. Pg. 263]
To find about how the sewage is treated.
Questions:
Question 1.
Find out how the sewage in your locality is treated. Are there mechanisms in place to ensure that local water bodies are not polluted by untreated sewage?
Answer:
We have underground drainage system in our city. The interconnected drainage lines take away sewage to distantly place where sewage treatment plant is located. Here it is treated.
Sewage is not allowed to pollute the local water bodies. It is first treated in sewage treatment plant, during this the treated water is disinfected through chlorination, water is then used for irrigation.
Question 2.
Find out how the local industries in your locality treat their wastes.
Are there mechanisms in place to ensure that the soil and water are not polluted by this water?
Answer:
Local industries are legaly bound to treat their industrial waste before releasing/discarding them in local water bodies.
But, these industries do not follow the rules and the norms set for them. Due to it, the industrial wastes that come out from industries have still pollutants and pollute our water bodies.
Activity 15.9 [T. B. Pg. 264]
To find out hazardous materials in disposed electronic items.
Materials:
Internet, books from library.
Questions:
Question 1.
What hazardous materials have to be dealt with while disposing the electronic items? How would these materials affect the environment?
Answer:
When we dispose off electronic wastes, the hazardous materials in them include plastics and electronic chips made of silicon. Such materials are non-biodegradable and will remain unchanged for a long time in the environment.
Question 2.
How are plastics recycled? Does the recycling process have any impact on the environment?
Answer:
Plastic wastes are isolated from garbage and sent to recycling unit. Plastics are melted in the unit and then remoulded to form various plastic items for reuse.
The recycling process reduces plastic wastes from the environment. Recently, plastic wastes are being used to construct polymer plastic road.