Jharkhand Board JAC Class 10 Science Solutions Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
JAC Board Class 10 Science Solutions Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metals
Jharkhand Board Class 10 Science Metals and Non-metals Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Which of the following pairs will give displacement reactions?
(a) NaCl solution and copper metal
(b) MgCl2 solution and aluminium metal
(c) FeSO4 solution and silver metal
(d) AgNO3 solution and copper metal
Answer:
AgNO3 solution and copper metal
Question 2.
Which of the following methods is suitable for preventing an iron frying pan from rusting?
(a) Applying grease
(b) Applying paint
(c) Applying a coating of zinc
(d) All of the above
Answer:
Applying a coating of zinc
Question 3.
An element reacts with oxygen to give a compound with a high melting point. This compound is also soluble in water. The element is likely to be…
(a) calcium
(b) carbon
(c) silicon
(d) iron
Answer:
calcium
Question 4.
Food cans are coated with tin and not with zinc because …
(a) zinc is costlier than tin.
(b) zinc has a higher melting point than tin.
(c) zinc is more reactive than tin.
(d) zinc is less reactive than tin.
Answer:
zinc is more reactive than tin.
Question 5.
You are given a hammer, a battery, a bulb, wires and a switch.
(a) How could you use them to distinguish between samples of metals and non-metals?
(b) Assess the usefulness of these tests in distinguishing between metals and non-metals.
Answer:
(a) Metals can be hammered Into thin sheets hence, metal possesses property of malleability while non-metals cannot be beaten into thin sheets.
Arrange the battery, bulb, wires and switch in a proper circuit and by passing the electric current, if the bulb glows, then it must be a metal, because metal is a good conductor of electricity. But if the bulb does not glow, then it Is a sample of non-metal, because non-metal is a non-conductor of electricity.
(b) First experiment shows that metal possesses property of malleability and ductility, while second experiment justifies that metals are good conductors of electricity while non-metals are non-conductor of electricity.
![]()
Question 6.
What are amphoteric oxides? Give two examples of amphoteric oxides.
Answer:
Metal oxides which react with both acids and bases to forms salt and water are called amphoteric oxides.
Examples:
- Aluminium oxide (Al2O3)
- Zinc oxide (ZnO)
Aluminium oxide reacts with an acid and a base in the following manner :
Al2O3 + 6HCl → 2AlCl3 + 3H2O
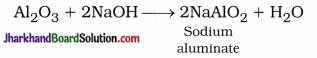
Zinc oxide reacts with an acid and a base in the following manner :
ZnO + 2HCl → ZnCl2 + H2O

Question 7.
Name two metals which will displace hydrogen from dilute acids and two metals which will not.
Answer:
Two metals which displace hydrogen from dilute acids are :
- zinc (Zn) and
- aluminium (Al).
Two metals which cannot displace hydrogen from dilute acids are :
- copper (Cu) and
- mercury (Hg).
Question 8.
In the electrolytic refining of a metal M, What would you take as an anode, the cathode and the electrolyte?
Answer:
In the electrolytic refining, Impure metal (M) is taken as an anode and thin strip of pure metal (M) Is taken as a cathode and solution of soluble salt of metal (M) Is taken as an electrolyte.
Question 9.
Pratyush took sulphur powder on a spatula and heated it. He collected the gas evolved by inverting a test tube over it as shown in figure below:
(a) What will be the action of gas on
(i) dry litmus paper?
(ii) moist litmus paper?
(b) Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction taking place.
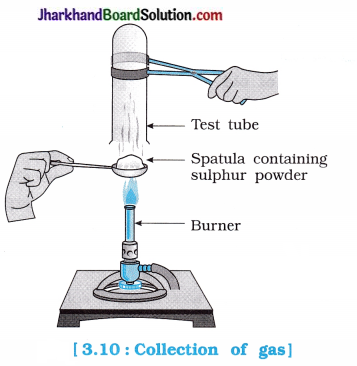
When sulphur powder is heated in air, it forms sulphur dioxide, which is acidic in nature and its aqueous solution is called sulphurous acid (H2SO3).
(a) Action of gas :
- There will be no effect of gas on dry litmus paper.
- Moist blue litmus paper changes its colour to red due to H+ ions present in the aqueous solution of H2SO3 formed from SO2 obtained after burning sulphur.
(b) Balanced chemical equation for the above activity is as given below:
S(s) + O2(g) → SO2(g)
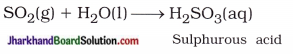
Question 10.
State two ways to prevent the rusting of iron.
Answer:
The rusting of iron can be prevented by painting, oiling, greasing, chrome plating, anodising or by making alloys.
Question 11.
What type of oxides are formed when non¬metals combine with oxygen?
Answer:
Non-metals combines with oxygen to form acidic oxides. For example, SO2, SO3, CO2, Cl2O7, etc.
Question 12.
Give reasons :
(a) Platinum, gold and silver are used to make jewellery.
Answer:
Platinum, gold and silver are used to make jewellery, because these metals possesses lustre. They are malleable and ductile, as a result, jewellery of different shapes can be made. Moreover, these metals do not chemically react with water or air. Due to these properties platinum, gold and silver are used to make jewellery.
(b) Sodium, potassium and lithium are stored under oil.
Answer:
Sodium, potassium and lithium are highly reactive metals. They release hydrogen gas, when they react with air or moisture in air. Hydrogen gas is highly combustible and it catches fire. To prevent accidental fire, lithium, sodium and potassium are stored under oil.
(c) Aluminium is a highly reactive metal, yet it is used to make utensils for cooking.
Answer:
Aluminium is highly reactive metal. It reacts with oxygen of air to form aluminium oxide, which gets deposited as thin layer on the surface of aluminium. This layer acts as protective layer and prevents further reaction of aluminium with oxygen. Moreover it is light in weight and a good conductor of heat. Also, it’s manufacturing cost is very low in comparison to other metals. Therefore, most of the utensils for cooking are made from aluminium.
(d) Carbonate and sulphide ores are usually converted into oxides during the process of extraction.
Answer:
It is easier to obtain a metal from its oxide. Hence, it is essential to convert carbonate and sulphide ores into oxide ores during the extraction of metal. Extraction of metal by reduction of oxide ores is easier than extraction from its carbonate or sulphide ores.
![]()
Question 13.
You must have seen tarnished copper vessels being cleaned with lemon or tamarind juice. Explain why these sour substances are effective in cleaning the vessels.
Answer:
Copper vessels are tarnished and corroded due to formation of copper oxide layer on its surface. The green coating on copper vessels is due to formation of basic copper carbonate. On cleaning with lemon or tamarind juice, the citric acid present in them neutralises the basic copper carbonate and dissolves the layer, there by helps to regain the lustre of copper utensils.
Question 14.
Distinguish between metal and non-metal on the basis of their chemical properties.
Answer:
| Metals | Non-metals |
| 1. They are electro-positive elements. | 1. They are electro-negative elements. |
| 2. Aqueous solutions of metal oxides are basic. | 2. Aqueous solutions of non-metal oxides are acidic. |
| 3. Hydrogen gas is evolved when metals reacts with dilute acid. | 3. When non-metal react with dilute acid hydrogen gas is not evolved. |
| 4. Oxides of metals are basic in nature. For example, Na2O | 4. Oxides of non-metals are acidic in nature. For example, SO2, CO |
| 5. Atoms of metal possess one, two or three electrons in their outermost shell. | 5. Atoms of non-metals possesses more than three electrons in their outermost shell. |
Question 15.
A man went door to door posing as a goldsmith. He promised to bring back the glitter of old and dull gold ornaments. An unsuspecting lady gave a set of gold bangles to him which he dipped in a particular solution. The bangles sparkled like new but their weight was reduced drastically. The lady was upset but after a futile argument the man beat a hasty retreat. Can you play the detective to find out the nature of the solution he had used?
Answer:
That man was using a solution of aqua regia; which is a mixture of concentrated hydrochloric acid and concentrated nitric acid in the ratio of 3 : 1 by volume. Gold dissolves in aqua regia.
Question 16.
Give reason : Why copper is used to make hot water tanks and not steel (an alloy of iron.)?
Answer:
Copper does not react with cold and hot water nor it reacts with steam of water. Hence copper can be used to make hot water tanks.
But, steel is an alloy of an iron and it reacts with steam of water, hence, iron in steel is slowly corroded.
Therefore, copper is used for making hot water tanks and not steel.
Jharkhand Board Class 10 Science Metals and Non-metals InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Give an example of a metal which …
(i) is a liquid at room temperature.
(ii) can be easily cut with a knife.
(iii) is the best conductor of heat.
(iv) is a poor conductor of heat.
Answer:
(i) Mercury is a liquid at room temperature.
(ii) Sodium, potassium can be easily cut with a knife.
(iii) Silver and copper are good conductor of heat.
(iv) Lead is a poor conductor of heat.
Question 2.
Explain the meaning of malleable and ductile.
Answer:
- Malleable : Malleable indicates a tendency of a metal to be brought in sheet form by hammering.
- Ductile: Ductile indicates a tendency of a s metal to be brought in thin wire form.
Question 3.
Why is sodium kept immersed in kerosene oil?
Answer:
Sodium is highly reactive metal. It reacts with oxygen of air at room temperature. This reaction is highly exothermic. Thus, to prevent the reaction of sodium with oxygen, it is kept immersed in kerosene oil.
Question 4.
Write equations for the reactions of (i) Iron with steam.
(ii) Calcium and potassium with water.
Answer:
(i) Iron with steam:
4H2O(g) + 3Fe(s) → Fe3O4(s) + 4H2(g)
(ii) Calcium and potassium with water :

Question 5.
Samples of four metals A, B, C and D were taken and added to the following solution one by one. The results obtained have been tabulated as follows:
| Metal | Iron (II) sulphate | Copper (II) sulphate | Zinc sulphate | Silver nitrate |
| A | No reaction | Displacement | ||
| B | Displacement | No reaction | ||
| C | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction | Displacement |
| D | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction | No reaction |
Use the table above to answer the following questions about metals A, B, C and D:
(1) Which is the most reactive metal?
(2) What would you observe if B is added to a solution of copper (II) sulphate?
(3) Arrange the metals A, B, C and D in the order of decreasing reactivity.
Answer:
(1) Metal B is the most reactive metal.
(2) Blue colour of copper (II) sulphate solution disappears and reddish brown copper metal is < deposited on the metal B.
(3) Decreasing order of reactivity is s B > A > C > D.
![]()
Question 6.
Which gas is produced when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to a reactive metal? Write the chemical reaction when iron reacts with dilute H2SO4.
Answer:
When a reactive metal reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid, it forms hydrogen gas. The reactive metal displaces the hydrogen from acid releasing hydrogen gas.
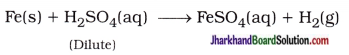
Question 7.
What would you observe when zinc is added to a solution of iron (II) sulphate?
Write the chemical reaction that takes place.
Answer:
Zinc (Zn) is more reactive than iron (Fe). Hence, when it is added to iron (II) sulphate, it displaces the iron metal. As a result, the colour of the solution fades from green to colourless due to formation of zinc sulphate, and the greyish black coloured iron metal gets displaced.
Zn(s) + FeSO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + Fe(s)
Question 8.
Name two metals which displace hydrogen from dilute acid and name two metals which cannot displace hydrogen from dilute acids.
Answer:
Two metals which displace hydrogen from dilute acids are:
- zinc (Zn) and
- aluminium (Al).
Two metals which cannot displace hydrogen from dilute acids are:
- copper (Cu)
- mercury (Hg).
Question 9.
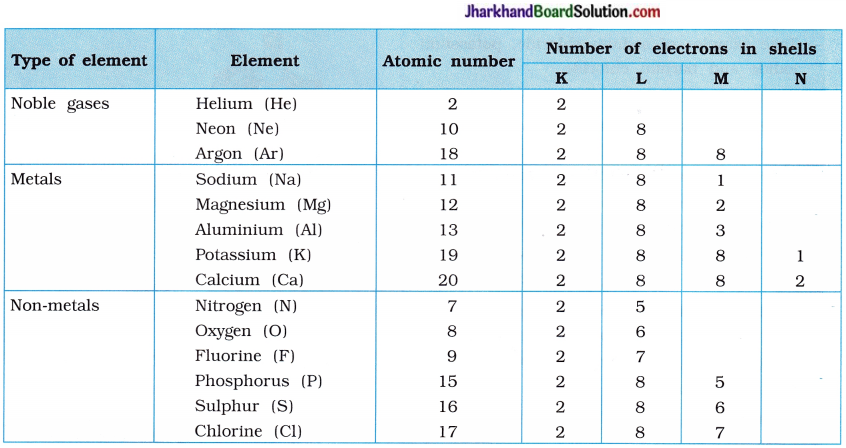
Explain the electronic configuration of noble gases (He, Ne, Ar); metals (Na, Mg, Al, K, Ca) and non-metals (N, O, F, E S, Cl).
Answer:
Electronic Configurations of Some Elements
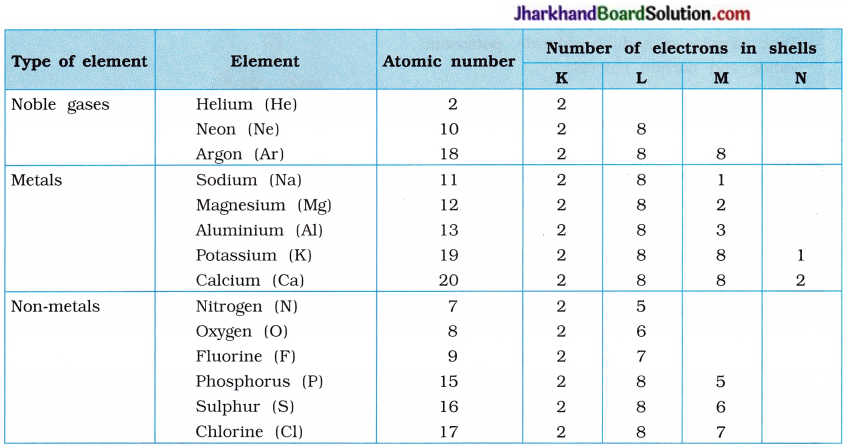
Question 10.
What are ionic compounds or electrovalent compounds? Explain with example.
OR
Explain the formation of sodium chloride (NaCl).
Answer:
The compounds formed by the transfer of electrons from a metal to a non-metal are known as Ionic compounds or electrovalent compounds. Atomic number of sodium is 11. Sodium atom has one electron in its outermost shell (M-shell). Sodium atom loses the electron from its M-shell and forms sodium cation (Na+) and acquires stable complete octet structure of noble gas neon (Ne).
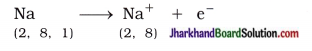
Similarly, atomic number of chlorine is 17. Chlorine atom has seven electrons in its outermost shell (M-shell). Chlorine atom gains one e– which is lost by sodium atom and forms chloride anion (Cl–) and acquires stable complete octet structure of noble gas argon (Ar).
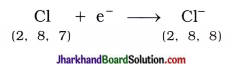
Sodium cation (Na+) and chloride anion (Cl–) being oppositely charged attract each other and are held by strong electrostatic forces of attraction and exists as sodium chloride (NaCl).
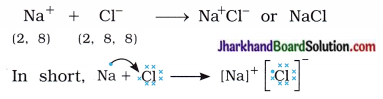
Sodium chloride exists as a group of oppositely charged ions.
Question 11.
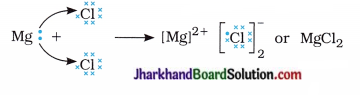
State the formation of magnesium chloride by the transfer of electrons.
Answer:
Atomic number of magnesium is 12. It loses its two electrons from outermost shell and acquires complete octet stable structure.
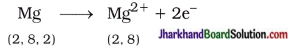
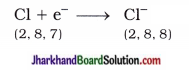
Similarly, atomic number of chlorine is 17. It gains one electron and acquires complete octet stable structure.
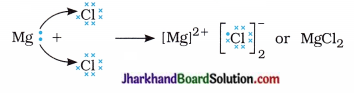
Thus, two electrons lost by magnesium atom are gained by two chlorine atoms (each one gets one electron) and forms magnesium chloride.
Question 12.
Explain the electronic configuration of noble gases (He, Ne, Ar); metals (Na, Mg, Al, K, Ca) and non-metals (N, O, F, P, S, Cl).
Answer:
Electronic Configurations of Some Elements
Question 13.
What are ionic compounds or electrovalent compounds? Explain with example.
OR
Explain the formation of sodium chloride (NaCl).
Answer:
The compounds formed by the transfer of electrons from a metal to a non-metal are known as Ionic compounds or electrovalent compounds. Atomic number of sodium is 11. Sodium atom has one electron in its outermost shell (M-shell). Sodium atom loses the electron from its M-shell and forms sodium cation (Na+) and acquires stable complete octet structure of noble gas neon (Ne).
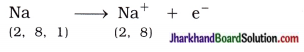
Similarly, atomic number of chlorine is 17. Chlorine atom has seven electrons in its outermost shell (M-shell). Chlorine atom gains one e– which is lost by sodium atom and forms chloride anion (Cl–) and acquires stable complete octet structure of noble gas argon (Ar).
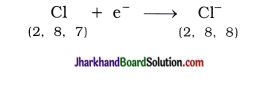
Sodium cation (Na+) and chloride anion (Cl–) being oppositely charged attract each other and are held by strong electrostatic forces of attraction and exists as sodium chloride (NaCl).
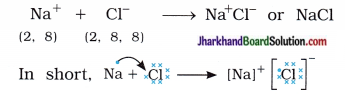
Sodium chloride exists as a group of oppositely charged ions.
Question 14.
State the formation of magnesium chloride by the transfer of electrons.
Answer:
Atomic number of magnesium is 12. It loses its two electrons from outermost shell and acquires complete octet stable structure.
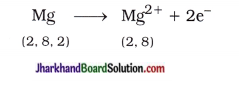
Similarly, atomic number of chlorine is 17. It gains one electron and acquires complete octet stable structure.
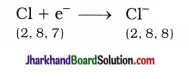
Thus, two electrons lost by magnesium atom are gained by two chlorine atoms (each one gets one electron) and forms magnesium chloride.
Activity 3.1 [T. B. Pg. 37]
Aim : To study the lustrous properties of metals.
Activity:
- Take samples of iron, copper, aluminium and magnesium. Note the appearance of surface of each sample.
- Clean the surface of each sample by rubbing them with sand paper and note their appearance again.
Questions :
Question 1.
How does the surface of samples of metal appear?
Answer:
The surface of samples of metal appear dull.
Question 2.
What happens when the surface of sample of metal is rubbed with sand paper?
Answer:
When the surface of sample of metal is rubbed with sand paper, it appears shiny.
Question 3.
How does the surface of metal appear in their pure form?
Answer:
Metals have shining surface in their pure form.
Question 4.
Name the shining property of metal.
Answer:
The property of shining surface of metal is known as metallic lustre.
Activity 3.2 [T. B. Pg. 37]
Aim : To study the hardness of metals.
Caution : Always handle sodium metal with care.
Activity:
- Take small pieces of iron, copper, aluminium and magnesium.
- Try to cut these metals with a sharp knife and note your observations.
- Hold a piece of sodium metal with a pair of tongs, put it on a watch-glass and try to cut it with a knife.
What do you observe?
Questions:
Question 1.
Can we cut the metals such as an iron, copper, aluminium and magnesium with a knife?
Answer:
No, we can’t cut.
Question 2.
Can sodium metal be cut with a knife?
Answer:
Yes, we can cut sodium metal into pieces.
Question 3.
Which property of metal is seen in the above activity?
Answer:
Metals are hard and their hardness varies from metal to metal.
![]()
Activity 3.3 [T. B. Pg. 38]
Aim : To study that metals are malleable.
Activity:
- Take pieces of iron, zinc, lead and copper?
- Place any one metal on a block of iron and strike it four to five times with a hammer.
- What do you observe?
- Repeat the same with other metals.
- Record the change in the shape of these < metals.
Questions:
Question 1.
Which property of metal is observed in this activity?
Answer:
Metals can be hammered into thin sheets.
Question 2.
What is malleability of metals?
Answer:
The property of metals to be converted into thin sheets when hammered is known as ‘Malleability of metals’.
Question 3.
Name the metals which are most malleable in nature.
Answer:
Gold and silver.
Activity 3.4 [T. B. Pg. 38]
Aim: To study that metals are ductile.
Activity:
Take samples of metals such as iron, copper, aluminium and lead.
Questions:
Question 1.
What is meant by ductility?
Answer:
The ability of metals to be drawn into? thin wires (filaments) is called ductility.
Question 2.
Which metal is most ductile?
Answer:
Gold is most ductile metal.
Question 3.
What is the maximum length of wire which (can be drawn from one gram of gold?
Answer:
2 km length
Question 4.
Why the metals can be given different shapes?
Answer:
Metals can be given different shapes due to their properties like malleability and ductility.
Activity 3.5 [T. B. Pg. 38]
Aim : To show that metals are good conductors of heat and possesses high melting point.
Activity:
- Take an aluminium or copper wire. Clamp this wire on a stand as shown in the figure 3.1.
- Fix a pin to the free end of the wire using wax.
- Heat the wire with a spirit lamp, candle or a burner near the place where it is clamped.
- What do you observe after some time?
- Note your observations.
- Does the metal wire melt?
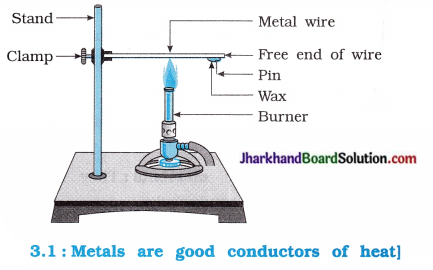
Questions:
Question 1.
What happens to a pin attached to the wire?
Answer:
Due to heating, metal wire expands and the pin is displaced forward. This indicate that heat flows through the wire and melts the wax but wire does not melt.
Question 2.
Which property of metal is observed in the above activity?
Answer:
The above activity shows that metals are good conductors of heat and have high melting point.
Question 3.
Which metal is used as the best conductor of heat?
Answer:
Silver and copper are best conductors of heat.
Question 4.
Which metals are poor conductors of heat?
Answer:
Lead and mercury are poor conductors of heat.
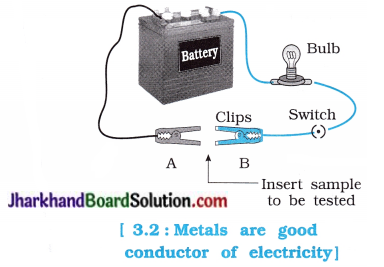
Activity 3.6 [T. B. Pg. 39]
Aim: To study the property of electrical conductivity of metals.
Activity:
- Set up an electric circuit as shown in the figure 3.2.
- Place the metal to be tested in the circuit between terminals A and B as shown.
Questions :
Question 1.
Which property of metal is observed in the above activity?
Answer:
It is observed that metals are good conductors of electricity.
Question 2.
Which coating is used on electric wire?
Answer:
The coating of polyvinyl chloride is formed on electric wire.
Question 3.
Does the bulb glow? What does it indicate?
Answer:
The bulb glows. It indicate that electric current flows through the metal.
Activity 3.7 [T. B. Pg. 39]
Aim : To study the properties of non-metals.
Activity:
- Collect the samples of carbon (coal or graphite), sulphur and iodine.
- Carry out the activities 3.1 to 3.4 and 3.6 with these non-metals and record your observations.
Questions:
Question 1.
State the physical states of non-metals.
Answer:
Non-metals exist in solid, liquid and gaseous states at room temperature.
Question 2.
State the common properties of non-metals based on the above activities.
Answer:
- Non-metals are non-conductors of heat and electricity.
- Boiling points of non-metals are comparatively lower.
- Non-metals do not possess property of malleability and ductility.
Activity 3.8 IT. B. Pg. 40]
Aim: To test the acidity and basicity of oxides.
Activity:
- Take a magnesium ribbon and some sulphur powder.
- Burn the magnesium ribbon. Collect the ashes formed and dissolve it in water.
- Test the resultant solution with red and blue litmus paper.
- Is the product formed on burning magnesium ribbon acidic or basic?
- Now, burn sulphur powder. Place a test tube over the burning sulphur to collect the fumes produced.
- Add some water to the above test tube and shake.
- Test this solution with blue and red litmus paper.
- Is the product formed on burning sulphur acidic or basic?
- Can you write equations for these reactions?
Questions :
Question 1.
What is formed on burning magnesium?
Answer:
Magnesium oxide (MgO) is formed on burning magnesium.
Question 2.
Is the magnesium oxide acidic or basic?
Answer:
Magnesium oxide is basic in nature.
Question 3.
Which product is obtained on burning sulphur?
Answer:
Sulphur dioxide (SO2) is obtained.
Question 4.
Is the product formed on burning sulphur acidic or basic?
Answer:
It is acidic.
Question 5.
Write the equations of chemical reactions which occur in the activity 3.8.
Answer:
- 2Mg(s) + O2(g) → 2MgO(s)
- MgO(s) + H2O(l) → Mg(OH)2(aq)
- S(s) + O2(g) → SO2(g)
- SO2(g) + H2O(l) → H2SO3(aq)
Question 6.
Is the sulphur dioxide acidic or basic?
Answer:
It is an acidic.
Activity 3.9 [T. B. Pg. 41]
Aim: To study the burning of metals in air.
Caution:
- This activity needs the teacher’s assistance.
- It would be better, if students wear goggles for eye protection.
Activity:
- Take samples of metals such as aluminium, copper, iron, lead, magnesium, zinc and? sodium.
- Hold any sample of metal taken above with a pair of tongs and try burning over a flame.
- Repeat the same with the other metal samples.
- Collect the product, if formed.
- Let the products and the metal surface cool down.
- Which metals burn easily?
- What flame colour did you observe when the metal burnt?
- How does the metal surface appear after burning?
- Arrange the metals in the decreasing order of their reactivity towards oxygen.
- Are the products soluble in water?
Questions:
Question 1.
Which metal burns easily in air?
Answer:
Magnesium burns easily in air.
Question 2.
What colour does Na, Mg, Cu and Al impart to the oxidising flame?
Answer:
- Na → Yellow flame
- Mg → Dazzling white flame
- Cu → Greenish blue flame
- Al → White flame
Question 3.
How does the metal surface appear after burning?
Answer:
Silvery white.
Question 4.
What is the solubility of product in water obtained by the reaction of Cu, Fe, Zn, Al with oxygen?
Answer:
The products obtained by the reaction of Cu, Fe, Zn and Al with oxygen are insoluble in water.
Question 5.
Arrange the metals such as Al, Cu, Fe, Pb, Mg, Zn and Na in the decreasing order of their reactivity towards oxygen.
Answer:
Na > Mg > Al > Zn > Fe > Pb > Cu.
Question 6.
Which amongst the given metals forms water soluble product after heating it?
Answer:
Amongst the given metals, only sodium metal on heating forms oxide which is soluble in water.
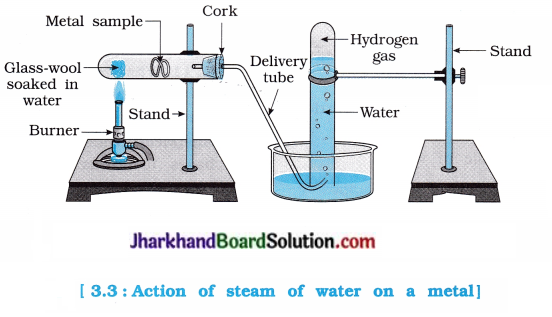
Activity 3.10 [T. B. Pg. 42]
Aim : To study the reaction of water with metals.
Caution :
This activity requires the teacher’s help.
Activity:
- Take samples of metals such as aluminium, copper, iron, lead, magnesium, zinc, calcium, gold, silver, sodium and potassium.
- Put small pieces of the samples separately in beakers half filled with cold water.
- Which metals reacted with cold water? Arrange them in the increasing order of their reactivity with cold water.
- Did any metal produce fire on water?
- Does any metal start floating after some time?
- Put the metals that did not react with cold water in beakers half filled with hot water.
- For the metals that did not react with hot water, arrange the apparatus as shown in the figure 3.3 and observe their reaction with steam.
- Which metals did not react even with steam?
- Arrange the metals in the decreasing order of reactivity with water.
Questions:
Question 1.
Which metals react with cold water?
Answer:
Sodium, potassium and calcium react with cold water.
Question 2.
Which metals produce fire on water?
Answer:
Sodium and potassium produce fire on water.
Question 3.
Which metal floats on water?
Answer:
Calcium and magnesium float on water.
Question 4.
Which metal does not react with cold water, but reacts with hot water?
Answer:
Magnesium does not react with cold water but it reacts with hot water.
Question 5.
Which metal does not react with either cold or hot water but reacts with steam?
Answer:
Aluminium, iron and zinc do not react with cold and hot water, but they react with steam.
![]()
Question 6.
Arrange the given metals (in activity) in the decreasing order of their reactivity with water.
Answer:
Decreasing order of the reactivity of metals with water is given as follows:
K > Na > Ca > Mg > A1 > Zn > Fe
Pb, Cu, Ag and Au does not react with water.
Question 7.
Arrange sodium, potassium and calcium metals in the increasing order of their reactivity with water.
Answer:
Ca < Na < K Question 8. Which metals do not react with cold water and steam? Answer: Pb, Cu, Ag and Au do not react with cold water and steam.
Activity 3.11 [T. B. Pg. 44]
Aim : To study the reaction of metal with an acid.
Activity: Collect the samples of pieces of metals such as magnesium, aluminium, zinc, iron and copper. Put the samples separately in test tubes containing dilute hydrochloric acid. Suspend thermometers in the test tubes. Which metals reacted vigorously with dilute hydrochloric acid? With which metal did you record the highest temperahire? Arrange the metals in the decreasing order of their reactivity with dilute acids.
Questions:
Question 1.
Which metal reacts vigorously with dilute hydrochloric acid?
Answer:
Magnesium metal reacts vigorously with dilute hydrochloric acid.
Question 2.
Which metal does not react with hydrochloric acid?
Answer:
Copper (Cu) metal do not react with hydrochloric acid.
Question 3.
With which metal the rise of temperature is maximum during the reaction?
Answer:
The rise of temperature is maximum in case of magnesium during the reaction.
Question 4.
Arrange the metals Mg, Al, Zn and Fe in the decreasing order of their reactivity towards dilute hydrochloric acid.
Answer:
Mg > Al > Zn > Fe
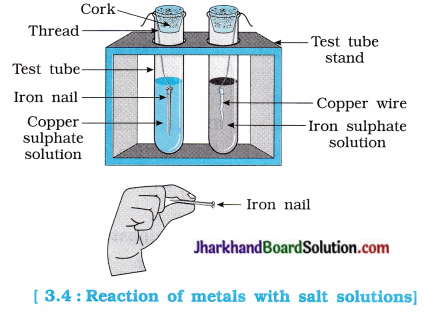
Activity 3.12 [T. B. Pg. 44 – 45]
Aim : To study the reaction of metal with solutions of other metal salts.
Activity:
- Take a clean wire of copper and an iron nail.
- Put the copper wire in a solution of iron sulphate and the iron nail in a solution of copper sulphate taken separately in test tubes (figure 3.4).
- Record your observations after 20 minutes.
- In which test tube did you find that a reaction has occurred?
- On what basis can you say that a reaction has actually taken place?
- Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction that has taken place.
- Name the type of reaction.
Questions:
Question 1.
In which test tube, reaction has occurred? Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction.
Answer:
The following reaction occurred in a test tube containing iron nail dipped in a copper sulphate solution :
Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq) → FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
In this reaction, more reactive Fe displaces less reactive Cu.
Question 2.
On what basis can you say that a reaction has actually taken place?
Answer:
Blue colour of copper sulphate solution turns green during reaction. This change indicates that reaction has occurred.
Question 3.
Name the type of reaction occurring in the above activity.
Answer:
Displacement reaction occurs in the above acitivity.
Question 4.
Why does the reaction not occurred in the test tube containing copper wire dipped in a iron sulphate solution?
Answer:
Because, iron (Fe) is more reactive than copper (Cu); the reaction does not take place.
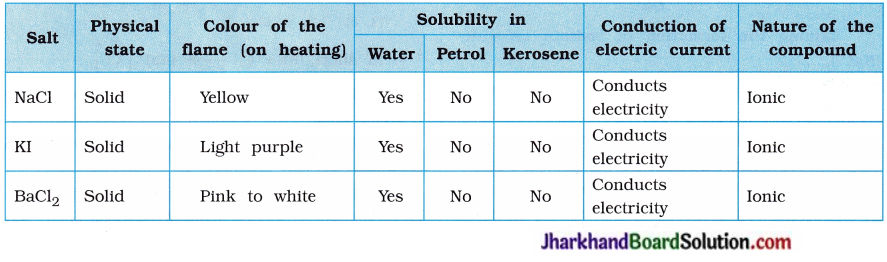
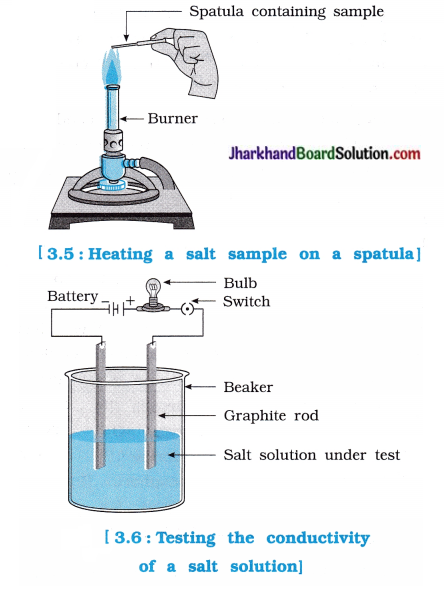
Activity 3.13 [T. B. Pg. 48]
Aim : To study the properties of ionic compounds, s
Activity:
- Take samples of sodium chloride, potassium s iodide and barium chloride.
- What is the physical state of these salts?
- Take a small amount of a sample on a metal ; spatula and heat it directly on the flame (figure 3.5). Repeat with other samples.
- What did you observe? Did the samples s impart any colour to the flame?
- Try to dissolve the samples in water, petrol and kerosene. Are they soluble?
- Make a circuit as shown in figure 3.6 and insert the electrodes into a solution of one salt, s
- What did you observe? Test the other samples too in this manner.
- What is your inference about the nature of these compounds?
Answers of the questions asked in the above activity are given in the following table :