JAC Board Class 10th Social Science Solutions Civics Chapter 2 Federalism
JAC Class 10th Civics Federalism InText Questions and Answers
Page 14
Question 1.
I am confused. What do we call the Indian government? Is it Union, Federal or Central?
Answer:
India is made up of States by ‘holding together,’ so, without any confusion we should call it a federal State and the government at the centre is called the Central government.
Page 15
Question 2.
If federalism works only in big countries, why did Belgium adopt it?
Answer:
Belgium adopted federalism because even though it is a small country, it has diverse population with multilingual groups. .These linguistic groups have their owp intersects which might lead to social conflict. Therefore, it was thought that, possible social conflict and political instability could be avoided by the federal system pf power sharing.
Page 16
Question 3.
Some Nepalese citizens were discussing the proposals on the adoption of federalism in their new Constitution. This is what some of them said:
Khag Raj:
I don’t like federalism. It would lead to reservation of seats for different caste groups as in India.
Sarita: Ours is not a very big country. We don’t needfederalism.
Babu Lai:
I am hopeful that Terai areas will get more autonomy if they get their own state government.
Ram Ganesh:
I like federalism because it will mean that powers that were earlier enjoyed by the king will now be exercised by our elected representatives. If you were participating in this conversation what would be your response to each of these? Which of these reflect a wrong understanding of what federalism is? What makes India a federal country?
Answer:
(i) Response to Khag Raj:
No, It is not true. Different caste groups are given their rights, which they have been kept deprived of for years. Federalism truly serves the purpose when it believes in mutual trust. This is the spirit of democracy.
1.Response to Sarita:
No Sarita, Nepal is also a diverse country consisting of group of people having different interests. For example, Belgium was a small country, but had social conflict. This could only be resolved by making a federation. So a federal system is required that takes care of its people equally.
2. Response to Babu Lai:
No, I do not agree as do not think only about the Terai area. There are other areas as well which need more autonomy. We should contribute to the development of the nation equally.
3. Response to Ram Ganesh:
Yes I agree. When power is concentrated in one hand, it harms the will of the common people. In a democracy, people rule themselves through institution of self-governance. The decentralization of power will ensure due respect to diverse groups and views that exist in the society, and everyone will have a voice in the shaping of public policy.
(ii) Of these Khag Raj and Sarita have a wrong understanding of what federalism is.
(iii) In India there are three levels of government The Central, State and local governments. They have their own jurisdictions. There is a Constitution which declares their powers and duties. There is an apex court under an independent judiciary which can resolve disputes among them. All the State governments have their own sources of income. Income is also shared with the Central government. All these features make India a federal country.
![]()
Question 4.
Isn’t that strange? Did our Constitution makers not know about federalism? Or did they wish to avoid talking about it?
Answer:
It is not strange. Our Constitution makers were aware of the concept of federalism. But, intentionally, they did not talk about it. This was because our democracy was passing through a ascent stage where they had to take steps to consolidate different free princely States.
If they had been given more autonomy, we might have faced many divisions of our country. They supposed that with maturity of democracy, proper changes would be brought in the Constitution to make the nation more federal. So they left this issue to the people and future leaders to decide about.
Page 17
Question 5.
If agriculture and commerce are state subjects, why do we have ministers of agriculture and commerce in the Union cabinet?
Answer:
This is because the States have to deal with each other in commerce and agricultural commodities. There are chances when a State will act arbitrarily. In that condition problems will arise regarding price control, tax, etc. The country has to deal with other nations in these subjects. So, a separate ministry for agriculture and commerce is necessary in the Union Cabinet.
Page 18
Question 6.
Pokharan, the place where India conducted its nuclear tests, lies in Rajasthan. Suppose the Government of Rajasthan was opposed to the Central Government’s nuclear policy could it prevent the Government of India from conducting the nuclear tests?
Answer:
No the government of Rajasthan could not prevent the government of India from conducting the nuclear tests.
Question 7.
Suppose the Government of Sikkim plans to introduce new textbooks in its schools. But the Union Government does not like the style and content of the new textbooks. In that case, does the state government need to take permission from the Union Government before these textbooks can be launched?
Answer:
Yes in this case the government of Sikkim will take permission from the Union government because education is a subject of Concurrent list on which both State and Union governments can make laws and in case of any conflict of law, only the Union law prevails.
![]()
Question 8.
Suppose the Chief Ministers of Andhra Pradesh, Chhattisgarh and Odisha have different policies on how their state police should respond to the naxalites. Can the Prime Minister of India intervene and pass an order that all the Chief Ministers will have to obey?
Answer:
No, police is a State subject on which only the States can make laws.
Page 20
Question 9.
Why Hindi? Why not Bangla or Telugu?
Answer:
The government of India, in its Constitution declares Hindi and English as our official languages. But, being a federal government it cannot impose its will on the people who speak a language other than Hindi. Hindi is the official language but only 40% of its population speaks Hindi. This is the flexibility shown by the Union government that States have their own official languages. We respect the language and culture of each other. So, people are free to speak in the language of their choices. Each State has its official language.
Page 2
Question 10.
Here are two cartoons showing the relationship between Centre and States. Should the State go to the Centre with a begging bowl? How can the leader of a coalition keep the partners of government satisfied?
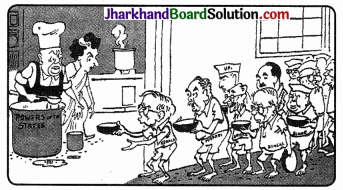
The state plead for more powers

Perils of Running a Coalition Government
Answer:
Yes, the state should go to the centre not with a begging bowl, not for more powers but for some privileges and financial preferences and security. The leader of a coalition keep the partners of government satisfied by giving some or other powers and privileges to every partner according to the proportions of their participation in the government.
Question 11.
Are you suggesting that regionalism is good for our democracy? Are you serious?
Answer:
In no way regionalism can be good for our democracy. In a country like ours, we have multicoloured cultures, languages and traditions, India’s glory lies in its diversity but it does not mean that one region or State is supported and the other is kept deprived. We grow and develop when each region grows and develops. We should develop with the spirit of mutual trust and living together. Hence, I am serious while saying that there is no place for regionalism in our democracy.
Page 25
Question 12.
Prime Minister runs the country. Chief Minister runs the state. Logically, then, the Chairperson of Zila Parishad should run the district. Why does the D.M. or Collector administer the district?
Answer:
The president of Zila Parishad is the political head. All the decisions are made under his leadership. In fact, the DM is the administrative head, who executes the decisions of the Parishad. This is, an example of sharing of power between legislative and executive. So, it is correct that the DM administers the district.
Question 13.
What do these newspaper clippings have to say about efforts of decentralisation in India?

Answer:
- The first clipping of ‘Tamil Nadu’ (TN) shows the misuse of three-tier- system.
- The second clipping on mandatory rule of Nayaya Panchayat
- The third clipping regarding states oppose direct funding reflects to utilize the proper “channels of Decentralisation”.
- The fourth and fifth clipping shows the “Women Empowerment” at the grassroots level.
JAC Class 10th Civics Federalism Textbook Questions and Answers
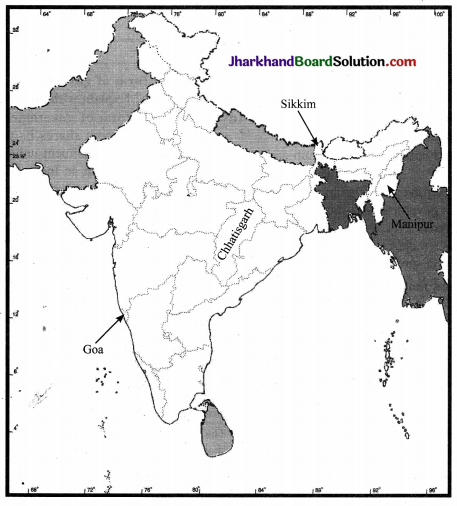
Question 1.
Locate the following States on a blank outline political map of India:
Manipur, Sikkim, Chhattisgarh and Goa.
Answer:
Question 2.
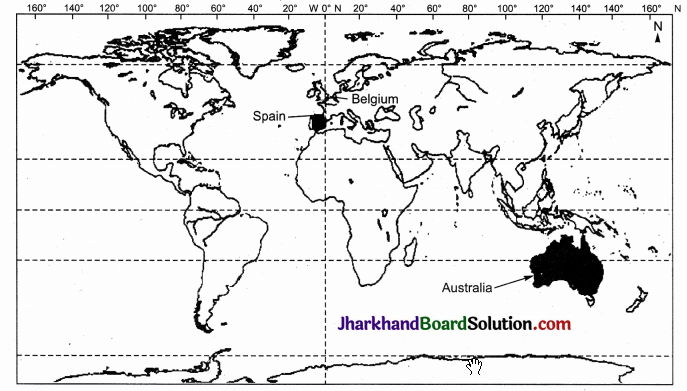
Identify and shade three federal countries (other than India) on a blank outline political map of the world.
Answer:
Federal countries other than India
Question 3.
Point out one feature in the practice of federalism in India that is similar to and one feature that is different from that of Belgium.
Answer:
- Similar Feature: Both Belgium and India have a three-tier government.
- Different Feature: In Belgium there is a community government as the third tier, while we have a local self-government (not based on races/castes) in India as the third tier of the government.
Question 4.
What is the main difference between a federal form of government and a unitary one? Explain with an example.
Answer:
In a federal form of government, the Central government shares its powers with the various constituent units of the country. For example, in India, power is divided between the government at the Centre and the various State governments. In a unitary form of government, all the power is exercised by only one government. For example, in Sri Lanka, the National government has all powers.
![]()
Question 5.
State any two differences between the local government before and after the Constitutional amendment in 1992.
| Local government before the Constitutional amendment in 1992 | Local government after the Constitutional amendment in 1992 |
| (i) Elections were not held regularly. | (i) It is mandatory to hold regular elections to local government bodies. |
| (ii) Local governments did not have any power or resources of their own. | (ii) The State governments are required to share some powers and revenue with local government bodies. |
Question 6.
Fill in the blanks:
1. Since the United States is a………… type of federation.
Answer:
coming together
2. All the constituent States have equal powers and States are……… vis-a-vis the federal government.
Answer:
strong
3. But India is a……… type of federation and some States have more power than others.
Answer:
holding together
4. In India, the ….. government has more powers.
Answer:
Central
Question 7.
Here are three reactions to the language policy followed in India. Give an argument and an example to support any of these positions.
Sangeeta: The policy of accommodation has strengthened national unity.
Arman: Language – based States have divided us by making everyone conscious of their language.
Harish: This policy has only helped to consQuestion lidate the dominance of English over all other languages.
Answer:
The argument by Sangeeta is more appropriate. Language is not just a tool for communication but a part of the culture and mindset which takes hundreds of years to evolve. People are sentimentally attached to their language. The language policy of India is an attempt to instill a sense of respect of others culture and this has definitely helped in strengthening national unity.
Question 8.
The distinguishing feature of a federal government is:
(a) National government gives some powers to the provincial government.
(b) Power is distributed among the legislature executive and judiciary.
(c) Elected officials exercise supreme power in the government.
(d) Governmental power is divided between different levels of government.
Answer:
(d) Governmental power is divided between different levels of government.
Question 9.
A few subjects in various Lists of the Indian Constitution are given here. Group them under the Union, State and Concurrent Lists as provided in the table below.
A. Defence
B. Police
C. Agriculture
D. Education
E. Banking
F. Forests
G. Communications
H. Trade
I. Marriages
Answer:
| Union List | Defence, Banking, Communications |
| State List | Police, Agriculture, Trade |
| Concurrent List | Education, Forests, Marriage |
Question 10.
Examine the following pairs that give the level of government in India and the powers of the government at that level to make laws on the subjects mentioned against each. Which of the following pairs is not correctly matched?
| (a) State Government | State List |
| (b) Central Government | Union List |
| (c) Central and State Governments | Concurrent List |
| (d) Local Governments | Residuary Powers |
Answer:
(d) Local Governments – Residuary Powers
Question 11.
Match List I with List II and select the correct answer using the codes given below the lists:
| List-I | List-II |
| 1. Union of India | A. Prime Minister |
| 2. State | B. Sarpanch |
| 3. Municipal Corporation | C. Governor |
| 4. Gram Panchayat | D. Mayor |
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | |
| (a) | D | A | B | C |
| (b) | B | C | D | A |
| (c) | A | C | D | B |
| (d) | C | D | A | B |
Answer:
(c) A,C,D, and B
Question 12.
Consider the following two statements:
(A). In a federation the powers of the federal and provincial governments are clearly demarcated.
(B). India is a federation because the powers of the Union and State Governments are specified in the Constitution and they have exclusive jurisdiction on their respective subjects.
(C). Sri Lanka is a federation because the country is divided into provinces.
(D). India is no longer a federation because some powers of the States have been devolved to the local government bodies. Which of the statements given above are correct?
(a) A, B and C
(b) A, C and D
(c) A and B only
(d) B and C only
Answer:
(c) A and B only