JAC Board Class 9th Social Science Solutions Civics Chapter 3 Electoral Politics
JAC Class 9th Civics Electoral Politics InText Questions and Answers
Questions of Unni & Munni (Page No. 35)
Question 1.
Do most leaders fulfil their election promises?
Answer:
During elections, most of the leaders make many big promises to the people/voters to win their support and vote. However, after the elections, most of the political leaders forget their promises and do not fulfil their election promises.
Check Your Progress (Page No. 36)
Question 2.
Jagdeep and Navpreet read this story and drew the following conclusions. Can you say which of these are right or wrong (or if the information given in the story is inadequate to call them right or wrong):
1. Elections can lead to changes in the policy of the government.
2. The Governor invited Devi Lai to become the Chief Minister because he was impressed with his speeches.
3. People are unhappy with every ruling party and vote against it in the next election.
4. The party that wins the election forms the government.
5. This election led to a lot of economic development in Haryana.
6. The congress Chief Minister need not have resigned after his party lost elections.
Answer:
- Right,
- Wrong,
- Inadequate information,
- Right,
- Inadequate information,
- Wrong.
Activity (Page No. 36)
Question 1.
Do you know when the last Assembly election was held in your state? Which other elections have taken place in your locality in the last five years? Write down the level of elections (National, Assembly, Panchayat etc.), when were they held and the name and designation (MP, MLA, etc.) of the persons who got elected from your area.
Answer:
Do it yourself.
Questions of Unni & Munni (Page No. 36, 37)
Question 1.
We have seen why democracies need to have elections. But why do rulers in non- democratic countries need to hold elections?
Answer:
Rulers in non-democratic countries hold elections because they need to show that their government and position has been achieved legally and according to the constitutional provisions.
Secondly, they want to show the world that they are not unpopular and they have the support of the people of the country which will improve their image in the sight of the world.

Question 2.
Ah! So, elections are like exams where politicians and parties know if they have passed or failed. But who are the examiners?
Answer:
In this case, the examiners are the voters, who give them marks in the form of votes.
Read the Cartoon (Page No. 38)
Question 1.
Read these two cartoons carefully. Write the message of each of them in your own words.
Have a discussion in class on which of the two is closer to the reality in your own locality. Draw a cartoon to depict what elections do to the relationship between voters and political leaders.
Answer:
- The first cartoon depicts that knowledge, planning, promises of a leader is useless if he has not achieved the essential votes.
- The second cartoon depicts that leaders made a lot of promises during the election campaign and achieved power. But voters are always in the hope that all promises have to be fulfilled by those leades.
- Student discuss yourself in your class.
- Draw the cartoon yourself.
Map based Question (Page No. 39)
Question 1.
Why is the boundary of the Gulbarga Lok Sabha constituency not the same as the district boundary of Gulbarga?
Answer:
The boundary of the Gulbarga Lok Sabha constituency is not the same as the district boundary of Gulbcrga because:
- Whole Karnataka State is divided into Lok Sabha constituencies according to its population
- The population of Gulbarga district is more than that allotted for each Lok Sabha constituency in the state.
Question 2.
Draw a similar map for your own Lok Sabha constituency.
Answer:
Students draw it yourself.

Question 3.
How many Assembly constituencies are there in the Gulbarga Lok Sabha constituency?
Answer:
There are 8 Assembly constituencies in the Gulbarga Lok Sabha constituency.
Question 4.
Is it the same in your own Lok Sabha constituency?
Answer:
Students do it yourself.
Questions of Unni & Munni (Page No. 40)
Question 1.
Like in Panchayats, should we not have at least one-third seats in the parliament and assemblies reserved for women?
Answer:
Since women make half of the population of our society, that’s why we must have at least one-third seats in the parliament and assemblies reserved for women.
Map based Question (Page No. 41)
Question 1.
See the map above (see map on textbook page no. 41) and answer the following questions.
1. What is the number of Lok Sabha constituencies in your state and the neighbouring two states?
Answer:
In Rajasthan, the number of Lok Sabha constituencies is 25. In its neighbouring two states, i.e., Gujarat and Uttar Pradesh, the number of constituencies are 26 and 80 respectively.
2. Which states have more than 30 Lok Sabha constituencies?
Answer:
Bihar (40), Maharashtra (48), Uttar Pradesh (80), West Bengal (42), and Tamil Nadu (39).
3. Why do some states have such a large number of constituencies?
Answer:
The number of constituencies is determined by the area and size of population of a state.
4. Why are some constituencies small in area while others are very big?
Answer:
The size of a constituency depends on its voters. An effort is made to give equal representation to whole of the population.
5. Are the constituencies reserved for the SCs and STs evenly spread all over the entire country or are there more in some areas?
Answer:
No, the constituencies reserved for the SCs and STs are not evenly spread all over the entire country. They are more in those areas where there is increased concentration of SCs, STs population.
Questions of Unni & Munni (Page No. 42)
Question 1.
Why are the candidates required to give a detailed statement of their property?
Answer:
Candidates are required to give a detailed statement of their property at the time of election because the Election Commission makes efforts to control the misuse of money power in elections. The candidate has to give information about his movable and immovable property, loan from financial institutions, tax status and income. With this information, the voters will be able to know more about the candidates and make their correct choice.
Check Your Progress (Page No. 66)
Question 1.
Match the following features of our electoral system with the principles they reflect.
| Principles | Features of election system |
| Universal Adult Franchise | Each constituency has roughly the same population |
| Representation of weaker sections | Everyone who is 18 years of age or older, has a right to vote |
| Open political competition | Anyone can form a party or contest elections |
| One vote one value | Reservation of seats for the SCs and the STs |
Answer:
| Principles | Features of election system |
| Universal Adult Franchise | Everyone who is 18 years of age or older, has a right to vote |
| Representation of weaker sections | Reservation of seats for the SCs and the STs |
| Open political competition | Each constituency has roughly the same population |
| One vote one value | Anyone can form a party or contest elections |
Activity (Page No. 44)
Question 1.
What was the election campaign like in your constituency in the last Lok Sabha elections? Prepare a list of what the candidates and parties said and did.
Answer:
Do it yourself.
Questions of Unni & Munni (Page No. 46)
Question 1.
Why are party agents present in the polling booth and the counting centre?
Answer:
Party agents are present in the polling booth and the counting centre because:
- They ensure that the voting takes place in a fair way.
- They ensure in the counting centre that the counting is done properly without any unfair means.
Check Your Progress (Page No. 46)
Question 1.
Identify the fair and the unfair electoral practices among the following:
1. A minister flags off a new train in his constituency a week before polling day.
2. A candidate promises that she will get a new train for her constituency if she is elected.
3. Supporters of a candidate take the voters to a temple and make them take an oath that they will vote for him.
4. The supporters of a candidate distribute blankets in slums in return for a promise for vote.
Answer:
- Unfair electoral practice,
- Fair electoral practice,
- Unfair electoral practice,
- Unfair electoral practice.
Questions of Unni & Munni (Page No. 47)
Question 1.
Why does the Election Commission have so much powers ? Is this good for democracy?
Answer:
- The Election Commission have so much powers to conduct the free and fair elections and to check the unfair practices during the election.
- Yes, this is good for democracy.
Check Your Progress (Page No. 48)
Question 1.
Read these headlines carefully and identify which powers are used by the Election Commission in each instance to ensure free and fair elections.
1. EC issues notification constituting 14th Lok Sabha.
Answer:
Election Commission takes decisions on every aspect of conduct and control of elections, from the announcement of elections to be declaration of results.
2. EC tightens norms for poll expenses. EC to visit Gujarat again, review poll arrangements.
Answer:
The Election Commission has fixed the amount to be spent by the candidates for each parliamentary and assembly seat. Because some political parties or candidates who have more resources can take advantage of it, the Commission has exercised its authority to conduct fair elections.
3. EC to visit Gujarat again to review poll arrangements.
Answer:
The Election Commission made another visit to review the electoral system in Gujarat due to reports of the possibility of capturing and rigging the polling stations. The commission is exercising its power to conduct free and fair elections.
4. HC asks EC to bar ‘criminal’ netas.
Answer:
Election commission takes decisions on every aspect of conduct and control of elections.
5. EC Shoots down HM advice on poll reforms.
Answer:
The Election Commission is responsible for conducting free and fair elections. The final decisional in this regard is taken by it only. It is free not to accept any suggestion. Therefore it did not accept the election suggestion of the Home Ministry.
6. Photo I-cards not mandatory in Bihar polls.
Answer:
Election Commission takes decision on every aspect of elections and control of elections from the announcement of elections to the declaration of results. It also includes the powers relating to the identification of the voters.
7. EC accepts new Haryana DGP.
Answer:
The Haryana government has transferred the current DGP as per the Commission’s directive. The Commission has used its power to transfer or appoint an impartial office for a fair election here.
8. EC will seek power to censure political ads.
Answer:
At the time of elections, political parties resort to political advertisements to discredit each
other, so the Election Commission, while exercising its power to conduct free and fair elections, allowed only those advertisements which do not accuse others.
9. EC says no immediate plan to ban Exit Polls.
Answer:
Election Commission takes decisions on every aspect of conduct and control of elections, from the announcement of elections to the declaration of results. It also includes power regarding the control of the exit polls.
10. EC orders repoll in 398 more booths.
Answer:
Election Commission takes decisions on every aspect of conduct and control of elections from the announcement of elections and order to repoll to the declaration of results.
11. EC to keep closer eye on hidden poll costs.
Answer:
Election Commission implements election laws and the code of conduct and punishes any candidate or political party that violates it. Thus, every party or candidate can get a fair and equal chance to compete.
Activity (Page No. 49)
Question 1.
Ask the eligible voters in your family whether they voted in the last election to the Lok Sabha or to the state assembly. If they did not, ask them why did they not vote. If they did, ask them which party and candidate they voted for and why. Also ask them whether they had participated in any other election-related activity like attending an election meeting or rally etc.
Answer:
Do it yourself.
Read the Cartoon (Page No. 50 – 51)
Question 1.
The leader is coming out of a press conference: “What was need to say that we have distributed tickets only amongst suitable and winnable family relations ?” Do you think that family politics is confined to only a few states or parties?
Answer:
I think that family politics is confined to not only a few states or parties but it is spread all over India.

Question 2.
Titled ‘Electoral Campaigns’, this cartoon was drawn in the Latin American context. Does this apply to India and to other democracies in the world?
Answer:
Yes, this cartoon applies to India and to other democracies in the world also because each candidate is allowed to spend a definite amount of money on the election campaign.
Question 3.
Is this an accurate picture (Page No. 51) of what happens to the voter before and after elections? Must this always happen in a democracy? Can you think of examples when this did not happen?
Answer:
- Yes, this is an accurate picture of what happens to the voter before and after elections.
- No, this must not be always happen in a democracy.
- No.
Check Your Progress (Page No. 51)
Question 1.
Here are some facts on Indian elections. Comment on each of these to say whether they reflect the strength or the weakness of our electoral system.
1. The Lok-Sabha has 12 percent women members.
Answer:
Reflects the weakness of our electoral system.
2. The Election Commission often refuses to accept the government’s advice about when the elections should be held.
Answer:
Reflects the strength of our electoral system.
3. The 16th Lok Sabha has more than 440 members whose assets are more than Rs. 1 crore.
Answer:
Reflects the weakness of our electoral system.
4. After losing an election the Chief Minister said: “I respect the people’s verdict.”
Answer:
Reflects the strength of our electoral system.
JAC Class 9th Civics Electoral Politics Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Which of the following statements about the reasons for conducting elections are false?
(a) Elections enable people to judge the performance of the government.
(b) People select the representative of their choice in an election.
(c) Elections enable people to evaluate the performance of the judiciary.
(d) People can indicate which policies they prefer.
Answer:
(c) Elections enable people to evaluate the performance of the judiciary.

Question 2.
Which of these is not a good reason to say that Indian elections are democratic?
(a) India has the largest number of voters in the world.
(b) India’s Election Commission is very powerful.
(c) In India, everyone above the age of 18 has a right to vote.
(d) In India, the losing parties accept the electoral verdict.
Answer:
(a) India has the largest number of voters in the world.
Question 3.
Match the following:
| It is necessary to keep the voters’ list up to date because | There is a fair representation of all sections of our society |
| Some constituencies are reserved for SCs and STs so that | Everyone has equal opportunity to elect their representative |
| Everyone has one and only one vote so that | All candidates must have a fair chance of competing in elections |
| Party in power is not allowed to use government vehicles because | Some people may have moved away from the area where they voted last |
Answer:
| (a) It is necessary to keep the voters’ list up to date because | 4. Some people may have moved away from the area where they voted last |
| (b) Some constituencies are reserved for SCs and STs so that | 1. There is a fair representation of all sections of our society |
| (c) Everyone has one and only one vote so that | 2. Everyone has equal opportunity to elect their representative |
| (d) Party in power is not allowed to use government vehicles because | 3. All candidates must have a fair chance of competing in elections |
Question 4.
List all the different election related activities mentioned in the chapter and arrange them in a time sequence, beginning with the first activity and ending with the last. Some of these activities are given below: Releasing election manifestos; counting of votes; making of voters’ list; election campaign; declaration of election results; casting of votes; ordering of re-poll; announcing election schedule; filing nomination.
Answer:
- Making of voter’ list;
- Filing nomination;
- Election campaign;
- Ordering of re-poll;
- Declaraton of election results;

Question 5.
Surekha is an officer in-charge of ensuring free and fair elections in an assembly constituency in a state. Describe what should she focus on for each of the following stages of election:
(a) Election campaign,
(b) Polling day,
(c) Counting day.
Answer:
(a) Election Campaign:
She should ensure that election campaign is totally according to the norms of Election Commission and ends before 48 hours of polling.
(b) Polling day: Polling day should be peaceful without any violence or fake polling or rigging.
(c) Counting day: Counting should be done in fair manner and only genuine candidate, who has actually won, should be declared so.
Question 6.
The table below gives the proportion of different communities among the candidates who won elections to the US Congress. Compare these to the proportion of these communities in the population of the US. Based on this, would you suggest a system of reservation in the US Congress? If yes, why and for which communities? If no, why not?
| Proportion of the Community (in per cent), in the |
| House of representatives | Population of US |
| Blacks | 8 | 13 |
| Hispanics | 5 | 13 |
| Whites | 86 | 70 |
Answer:
Based on the figures given in the table, it is clear that Blacks and hispanics have much less representation than their population in the US Congress. Some seats may be reserved for the blacks and the hispanics in the US Congress. In an open electoral competition, certain weaker sections may not stand a chance to get elected. They may not have the required resources, education and contacts to contest and win elections against others. Those who are influential and resourceful may prevent them from winning election.
Question 7.
Can we draw the following conclusions from the information given in this chapter ? Give two facts to support your position for each of these.
(a) Election Commission of India does not have enough powers to conduct free and fair elections in the country.
(b) There is a high level of popular participation in the elections in our country.
(c) It is very easy for the party in power to win an election.
(d) Many reforms are needed to make our elections completely free and fair.
Answer:
(a) No, this conclusion is not true.
(i) EC can prevent use and misuse of government machinery by party in power.
(ii) Government officers on election duty act under the order of the EC.
(b) Yes, this conclusion is true.
(i) All voters are free to vote.
(ii) Nobody can use force to prevent any voter from voting.
(c) No, this conclusion is not true.
(i) All parties have to follow the same code of conduct.
(ii) Party in power cannot use government machinery.
(d) Yes, this conclusion is true.
(i) Criminals are increasingly appearing as candidates.
(ii) The use of money power is becoming more obvious.

Question 8.
Chinappa was convicted for torturing his wife for dowry. Satbir was held guilty of practicing untouchability. The court did not allow either of them to contest elections. Does this decision go against the principles of democratic elections ?
Answer:
No, this decision does not go against the principles of democratic elections because they are criminals and criminals cannot contest elections.
Question 9.
Here are some reports of electoral malpractices from different parts of the world. Is there anything that these countries can learn from India to improve their elections? What would you suggest in each case?
(a) During an election in Nigeria, the officer in charge of counting votes deliberately increased the votes of one candidate and declared him elected. The court later found out that more than five lakh votes cast for one candidate were counted in favour of another.
(b) Just before elections in Fiji, a pamphlet was distributed warning voters that a vote for former Prime Minister, Mahendra Chaudhry, will lead to bloodshed. This was a threat to voters of Indian Origin.
(c) In the US, each state has its own method of voting, its own procedure of counting and its own authority for conducting elections. Authorities in the state of Florida took many controversial decisions that favoured Mr. Bush in the presidential elections in 2000. But no one could change those decisions.
Answer:
(a) Yes, Nigeria can learn from Indian vote counting system. Nigeria should adopt the method of counting like India’s election system. At the time of counting of votes, agents of all the candidates participating in the elections are present and the votes are counted in front of them. And if there is any doubt, the counting of votes can be done again. In addition to this, the government of Nigeria should also use Electronic Voting Machines (EVM) for voting.
(b) Yes, the people of Fiji can learn from the Indian electoral system. There should be such a powerful agency to deal with such threats, which can take immediate punitive action and voters can vote fairly. There should also be a provision that any party found to be involved in such activities will be debarred from contesting elections.
(c) The United States of America can learn from the Indian electoral system. India has a united system for conducting elections i.e., National Election Commission. Its rules and orders are followed equally throughout the country. This institution is independent and free from government influence. It can prohibit government decisions at the time of elections if they are not in the interest of free and fair elections.

Question 10.
Here are some reports of malpractices in Indian elections, identify what the problem in each case is. What should be done to correct the situation?
(a) Following the announcement of elections, the minister promised to provide financial aid to reopen the closed sugar mill.
(b) Opposition parties alleged that their statements and campaign was not given due attention in Doordarshan and All India Radio.
(c) An inquiry by the Election Commission showed that electoral rolls of a state contain name of 20 lakh fake voters.
(d) The hoodlums of a political party were moving with guns, physically preventing suporters of other political parties to meet the voters and attacking meeting of other parties.
Answer:
(a) The announcement made by the minister other the announcement of the election is a move affecting public opinion that could impede fair elections. This is an open violation of the code of conduct. For this, the Election Commission should issue a show cause notice to the minister, and if it not get the required response, it should declare his declaration invalid and take punitive action against him.
(b) This allegation of the opposition parties hinders the conduct of fair elections. This has not given equal opportunity to the opposition parties to reach out to the public. Therefore, voting may be affected. The Election Commission should get it investigated and if the complaint is found correct, then it should arrange for those parties to also communicate their view on Doordarshan and All India Radio.
(c) This way, there will be no free and fair election because all these voters can vote in favour of one party. This will affect the election results. The Election Commission should dismiss this voters’ list and issue an order to prepare the correct voters’ list. Alongwith this, orders should also be issued to punish the officials who made the wrong voters’ list.
(d) Criminalization of politics cannot lead to free and fair elections. People will not go to participate in elections for fear of criminals, thinking that they will win by illegal voting. The Election Commission should identify such people and related political party and take appropriate action against them. Proper security should be provided to all the candidates and the public should also be motivated to participate in the voting fearlessly.

Question 11.
Ramesh was not in class when this chapter was being taught. He came the next day and repeated what he had heard from his father. Can you tell Ramesh what is wrong with these statements?
(a) Women always vote the way men tell them to. So what is the point of giving them the right to vote?
(b) Party politics creates tension in society. Elections should be decided by consensus, not by competition.
(c) Only graduates should be allowed to stand as condidates for elections.
Answer:
(a) This statement is wrong. Women have an independent vote; they do exercise their vote on their own thinking.
(b) It is wrong. In a system of consensus, mighty and powerful will come to dominate and exploit poor and weaker sections of the society. Open elections creates a guarantee against such an exploitation.
(c) It is wrong. Educational qualifications do make a citizen more knowledgeable and alive towards the social and political situation, but the converse is not true. Every citizen, irrespective of his educational status, should be allowed his civil right to stand for elections.
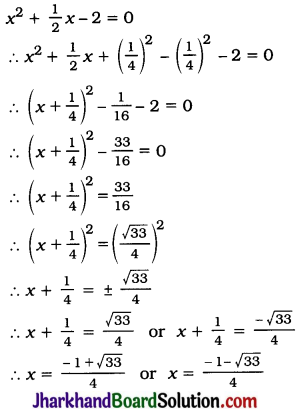
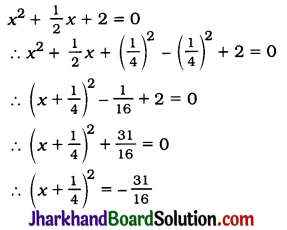
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()