JAC Board Class 9th Science Important Questions Chapter 6 Tissues
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Which are the two types of tissues?
(a) Meristematic and temporary
(b) Meristematic and permanent
(c) Meristems and temporary
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Meristematic and permanent
Question 2.
Parenchyma is a type of
(a) complex tissue
(b) simple tissue
(c) xylem
(d) phloem
Answer:
(b) simple tissue
Question 3.
Transpiration and exchange of gases are functions of
(a) stomata
(b) xylem
(c) both (a) and (b)
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) stomata
Question 4.
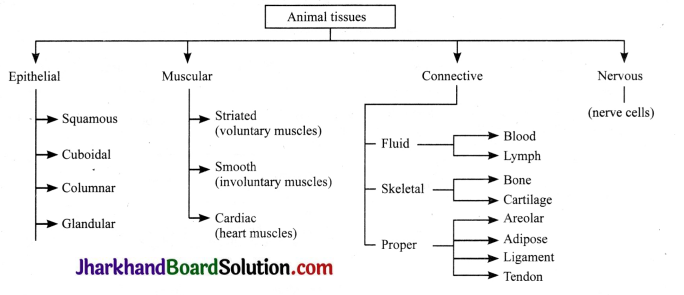
Which are the four types of animal tissues?
(a) Epithelial, squamous, muscular, connective
(b) Epithelial, cardiac
(c) Connective, nervous
(d) Cuboidal, columnar
Answer:
(c) Connective, nervous
![]()
Question 5.
Which of the myelin sheath?
(a) Blood
(b) Cartilage
(c) Tendon
(d) Neuron
Answer:
(d) Neuron
Question 6.
A group of cells alike in form, function and origin are called
(a) tissue
(b) organ
(c) organelle
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) tissue
Question 7.
Which of the following tissues is composed of mainly dead cells?
(a) Phloem
(b) Epidermis
(c) Xylem
(d) Endodermis
Answer:
(c) Xylem
Question 8.
Phloem in the plants performs the function of
(a) conduction of food
(b) conduction of water
(c) providing support
(d) photosynthesis
Answer:
(a) conduction of food
Question 9.
Which of the following tissues forms glands?
(a) Epithelial
(b) Connective
(c) Nervous
(d) Muscle
Answer:
(a) Epithelial
Question 10.
The end of a long bone is connected to another bone by
(a) ligament
(b) tendon
(c) cartilage
(d) nuclei
Answer:
(a) ligament
Question 11.
Which of the following cells are living cells?
(a) Fibres
(b) Vessels
(c) Collenchyma
(d) all of these
Answer:
(c) Collenchyma
Question 12.
How many guard cells enclose a stoma?
(a) One
(b) Two
(c) Three
(d) Four
Answer:
(b) Two
Question 13.
Which of the following cells helps sieve tubes to translocate food?
(a) Xylem parenchyma
(b) Phloem parenchyma
(c) Phloem fibre
(d) Companion cell
Answer:
(d) Companion cell
Question 14.
A neuron consists of
(a) cell body
(b) dendrites
(c) axon
(d) all of these
Answer:
(d) all of these
Question 15.
Nerve cell does not contain
(a) nerve endings
(b) tendons
(c) axon
(d) dendrites
Answer:
(b) tendons
Analysing & Evaluating Questions
Question 16.
While doing work and running, you move your organs like hands, legs et(c) Which among the following is correct?
(a) Smooth muscles contract and pull the ligament to move the bones.
(b) Smooth muscles contract and pull the tendons to move the bones.
(c) Skeletal muscles contract and pull the ligament to move the bones.
(d) Skeletal muscles contract and pull the tendon to move the bones.
Answer:
(d) Skeletal muscles contract and pull the tendon to move the bones.
![]()
Question 17.
A nail is inserted in the trunk of a tree at a height of 1 metre from the ground level. After 3 years the nail will.
(a) move downwards.
(b) move upwards.
(c) remain at the same position.
(d) move sideways.
Answer:
(c) remain at the same position.
Question 18.
You are asked to observe the permanent slides of parenchyma and sclerenchyma tissues. You will identify the slide containing sclerenchyma tissue by locating.
(a) thickened cell walls
(b) size of the cells
(c) position of nucleus
(d) size of nucleus
Answer:
(a) thickened cell walls
Assertion Reason Questions
Directions: In the following questions, the Assertions and the Reasons have been put forward. Read the statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following:
(A) Both the assertion and the reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(B) The assertion and the reason are correct but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(C) The assertion is true but the reason is false.
(D) Both the statements are false.
1. Assertion: Meristematic tissues are found in the growing tips of roots and shoots of a plant.
Reason: Meristematic tissues are composed of cells having the ability of cell division.
Answer:
(A) Both the assertion and the reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
2. Assertion: Outer protective layer of plants is made up of epidermal tissues.
Reason: Epidermal tissue is always composed of dead cells.
Answer:
(C) The assertion is true but the reason is false.
3. Assertion: Xylem shows unidirectional transport of materials.
Reason: Tracheids and vessels of xylem consist of dead cells.
Answer:
(B) The assertion and the reason are correct but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
4. Assertion: Ligament is a fibrous connective tissue.
Reason: Ligament connects muscle with skin.
Answer:
(C) The assertion is true but the reason is false.
5. Assertion: Peristalsis of food pipe is an involuntary action.
Reason: Food pipe is made up of smooth muscles.
Answer:
(A) Both the assertion and the reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name the three types of meristematic tissues.
Answer:
Apical, lateral and intercalary tissues.
Question 2.
Where is apical meristem found?
Answer:
It is present at the growing tips of stem and root it increases the length of the stem and roots.
Question 3.
Name the two types of plant tissues.
Answer:
Meristematic tissue and permanent tissue.
Question 4.
Define tracheids.
Answer:
A tracheid is a tubular cell in a vascular plant that carries water and minerals from the roots to the rest of the plant. lt also provides structural support.
![]()
Question 5.
Write the names of various types of blood cells.
Answer:
There are three types of blood cells: RBCs, WBCs, and Platelets.
Question 6.
What are guard cells?
Answer:
Each stoma is bounded by a pair of specialised kidney-shaped epidermal cells called guard cells.
Question 7.
Write the main function of meristematic tissue.
Answer:
The main function of meristematic tissue is to form new cells continuously for increasing cell number, length and the girth of the plant.
Question 8.
Define simple permanent tissue.
Answer:
It consists of one type of cells which look like one another.
Question 9.
Give three types of simple permanent plant tissues.
Answer:
(a) Parenchyma
(b) Collenchyma
(c) Sclerenchyma
Question 10.
What are the main functions of vascular tissues in plants?
Answer:
Vascular tissues transport:
- Water and dissolved minerals from roots to various parts of the plant (xylem).
- Prepared food material from leaves to different plant parts (Phloem).
Question 11.
Define vascular bundles.
Answer:
In plants, complex tissues xylem and phloem, together constitute a structure called vascular bundle. Their main function is transportation of water, minerals and food materials within plant body.
Question 12.
Define xylem.
Answer:
Xylem is a complex plant tissue which transports water and dissolved minerals from roots to all other plant parts.
Question 13.
What are muscular tissues?
Answer:
These are specialised tissues which are composed of contractile, fibre – like cells. These tissues are responsible for movement in our body.
Question 14.
What are the main functions of muscular tissue?
Answer:
The main function of muscular tissue is the movement of the body or limbs which is brought about by contraction and relaxation of contractile proteins present in muscle cells.
Question 15.
Which type of muscles is the stomach wall made up of?
Answer:
Smooth or non – striated muscles. They are involuntary muscles.
Question 16.
What are the two main features of connective tissue?
Answer:
Main features:
- Cells are loosely spaced and are embedded in matrix.
- Matrix may be jelly – like, fluid, dense or rigid.
Question 17.
Which cell may be longest in the body of an animal?
Answer:
Neuron (nerve cell) which may be up to 1m long (in special cases).
Analysing & Evaluating Questions
Question 18.
If the tip of sugarcane plant is removed from the field, even then it keeps on growing in length. Explain why?
Answer:
The sugaracane plant keeps growing due to the presence of intercalary meristem which is responsible for increase in intemodal length.
Question 19.
If a potted plant is covered with a glass jar, water vapours appear on the inner wall of glass jar. Explain why?
Answer:
Plants lose water through the aerial parts by the process known as transpiration. If the potted pant is covered with a glass jar, the water vapours cannot escape outside and stick to the cooler inner walls of glass jar due to condensation.
Question 20.
Water hyacinth floats on water surface. Explain.
Answer:
In aquatic plants like water hyacinth, a type of parenchyma tissue called aerenchyma is present. It develops air spaces in these plants to provide them buoyancy so that they can float easily on the surface of water.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Differentiate between bone and cartilage.
Answer:
| Bone | Cartilage |
| (a) It is hard. | (a) It is soft. |
| (b) Matrix has an inflexible material. | (b) Matrix has a flexible material. |
| (c) Matrix always contains calcium salts. | (c) Calcium salt may or may not be present in the matrix. |
| (d) Bones have rich blood supply. | (d) Cartilages do not have rich blood supply. |
Question 2.
What are the functions of areolar tissue?
Answer:
Functions of areolar tissue are as follows:
- It fills the space inside the organs, thus acts as a packing tissue between the organs.
- It supports many delicate organs in the body.
- It plays role in repair of tissues.
Question 3.
Write differences between xylem and phloem.
Answer:
| Xylem | Phloem |
| (a) It contains mainly dead elements. | (a) It consists of mainly living elements. |
| (b) It conducts water and minerals. | (b) It conducts food. |
| (c) It provides mechanical strength to the plant. | (c) It does not provide mechanical strength to the plant. |
Question 4.
Why does epidermal tissue have no intercellular space?
Answer:
Epidermis is formed of single continuous layered cells. It covers without any intercellular space and protects all parts of the plant. Small pores called stomata are present on the leaf, and help in the exchange of gases and water. Epidermal cells on the aerial parts of the plant secrete waxy, water resistant layers on their outer surface. It checks the loss of water, mechanical injury and invasion by parasitic fungi. Roots commonly bear long hair like parts that increase the total absorptive surface area of water absorption.
Question 5.
Write the functions of different types of cells of xylem.
Answer:
Xylem consists of tracheids, vessels, xylem parenchyma and xylem fibres. Tracheids and vessels allow the transport of water and minerals. Xylem parenchyma stores food and helps in the sideways conduction of water. Xylem fibres are supportive in function.
Question 6.
State the difference between bone and blood.
Answer:
| Bone | Blood |
| (a) It is a hard tissue. | (a) It is a liquid tissue. |
| (b) It consists of osteocytes. | (b) It consists of plasma, RBC, WBC and blood platelets. |
| (c) It helps in movement and support of the body. | (c) It helps in the transport of substances. |
Question 7.
What are the characteristic features of meristematic cells?
Answer:
Meristematic cells have:
- Thin cell walls.
- Abundant or dense cytoplasm and single large nucleus.
- Spherical, oval, polygonal or rectangular shape.
- No intercellular spaces between them.
- Either no vacuole at all or a few vacuoles.
Question 8.
How many types of meristems are present in plants, on the basis of position? Show diagrammatically.
Answer:
On the basis of location of meristem, it is classified into three types:
- Apical meristem: It is present at the tip of stem, root and their branches.
- Intercalary meristem: It is found at the leaf base, above the nodes (i.e, at the base of intemodes like in grasses) or below the nodes (i.e., at the uppermost region of intemodes like in mint). Apical meristem
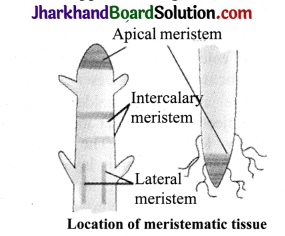
- Lateral meristem: Vascular cambium and cork cambium are examples of lateral meristem. Vascular cambium is found in vascular bundles, while cork cambium is found underneath the bark of trees. Both of these cause increase in girth of plants.
Question 9.
What are permanent tissues?
Answer:
The cells of meristematic tissue lose the ability to divide and get differentiated into specialised cells. These differentiated cells form different types of tissues which are known as permanent tissues. Some examples of permanent tissues are parenchyma, sclerenchyma, etc.
![]()
Question 10.
Give the main functions of parenchyma The main functions of parenchyma are as follows:
Answer:
- Chlorenchyma contains chloroplast which helps in photosynthesis.
- Parenchyma cell stores food in the form of starch, proteins, oils and fats.
- It helps in floating of aquatic plants due to presence of aerenchyma tissue.
- Idioplasmic cell secretes resins, latex, tannin, oils, etc.
- Parenchyma of xylem and phloem helps in transport of nutrition and water.
- Parenchyma tissue provides mechanical support.
Question 11.
Define the structure of sclerenchyma Write its major functions.
Answer:
Sclerenchyma (scleras – hard) is the chief mechanical tissue of plants. It is a permanent tissue. The cells are made up of sclerenchymatous tissue. The cells are usually long, narrow, pointed at both ends and uniformly thickened by the deposition of lignin without any space in between the cells. The walls are often very highly thickened so that the lumen or cell cavity is nearly obliterated. They are usually provided with simple pits which may be oblique or straight.
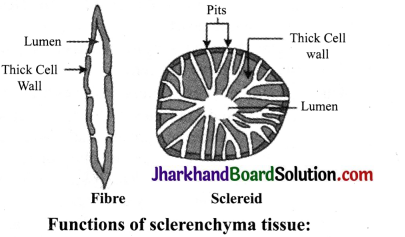
- Sclerenchyma is made up of dead and lignified cells which provide support to plants.
- It provides hardness to stony fruits such as nuts, coconut, almonds, etc.
Question 12.
What are the main functions of collenchyma?
Answer:
The main function of collenchyma is to provide mechanical support, tensile strength, elasticity and flexibility to stem, leaf stalks and leaves.
Question 13.
What are the four main functions of epithelial tissues?
Answer:
Epithelial tissue covers the body surface and forms the lining for most internal cavities. The major function of epithelial tissue includes protection, secretion, absorption and filtration. The skin is an organ made up of epithelial tissue which protects the body from dirt, dust, bacteria and other microbes that may be harmful.
Question 14.
Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles.
Answer:
Voluntary muscles are those which are directly under control of our conscious will, e.g., skeletal muscle. They work or move on our command. Involuntary muscles are not directly under command of our will. We cannot stop contraction or restart contraction of the stomach, intestine or heart muscles. They are of two types cardiac and smooth muscles. Smooth muscles are found in stomach, intestine, and iris of eyes, in ureter and in the bronchi of lungs. Another type of involuntary muscles, i.e, cardiac muscles are found in heart.
Question 15.
Name three types of muscle tissues and give functions of each.
Answer:
The three types of muscle tissues are:
- Striated muscles: These muscles show alternate light and dark bands or striations. They are voluntary muscles and present in skeletal tissues, help in movement of body and bones.
- Smooth muscles: These are involuntary muscles; control the movement of food in alimentary canal, contraction and relaxation of blood vessels are present in iris, uterus, etc.
- Cardiac muscles: These muscles are present in heart, help in the rhythmic contraction and relaxation of heart throughout the life.
Question 16.
What are the two main components of blood? Why is blood considered a type of connective tissue?
Answer:
Blood has two main components:
- Fluid (liquid) matrix called plasma.
- Suspended red blood cells (RBCs), white blood cells (WBCs) and platelets.
- Blood is considered as a connective tissue because it has the same origin as the other connective tissues have.
- It flows to different parts of the body and thus connects different parts of the body with one another to exchange materials and gases.
Analysing & Evaluating Questions
Question 17.
Animals of colder regions and fishes of cold water have thicker layer of subcutaneous fat. Describe why?
Answer:
The animals of colder regions are subject to more heat loss due to very low temperature. The subcutaneous fat under the dermis layer of the skin forms an insulating layer against the extremely cold environment and also acts as a food store.
Question 18.
Due to excessive workout, an athlete was suffering from fatigue. He was suggested to take rest for some time and then again join the practice.
(a) Why did the athlete feel tired after excessive workout?
(b) Why was he asked to take rest and then join the practice again?
Answer:
(a) The skeletal muscles of our limbs are responsible for body movement. These muscles have power and contract very fast. The excessive activity and lack of oxygen supply to the muscles makes them tired soon. This results in the accumulation of lactic acid in the muscles which keeps them in the state of inactivity and tiredness.
(b) While he is on rest, the body regains the oxygen supply to the muscle cells. The lactic acid deposited in the muscles is then transported by blood to the liver, where it is converted to glycogen (a carbohydrate).
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Give the flow chart of plant tissues.
Answer:
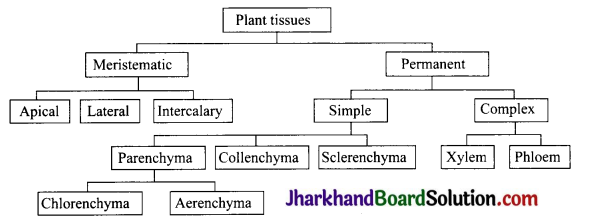
Question 2.
What is connective tissue? Explain its types.
Answer:
A connective tissue consists of different types of cells. The different types of connective tissues are as follows:
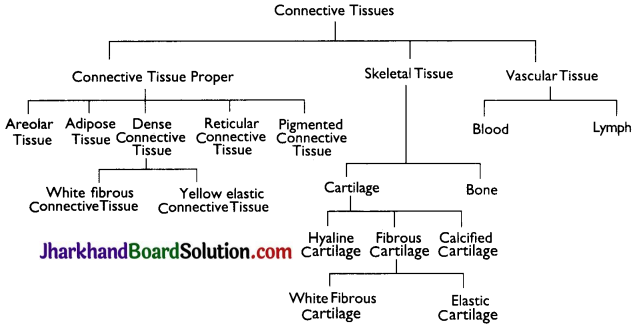
1. Blood: It has a fluid matrix called plasma in which RBCs, WBCs and platelets are suspended, Blood transports gases, digested food, hormones and waste materials to different body parts.
2. Bone: This connective tissue forms the framework that supports the body. It also anchors the muscles and supports the main organs of the body
3. Ligament: This connective tissue connects the two bones. This is very elastic having considerable strength.
4. Tendon: It connects muscles to bones. It is a fibrous tissue with great strength but limited flexibility.
5. Cartilage: It has widely spaced cells. It smoothens bone surfaces at joints and is also present in the nose, ear, trachea and larynx.
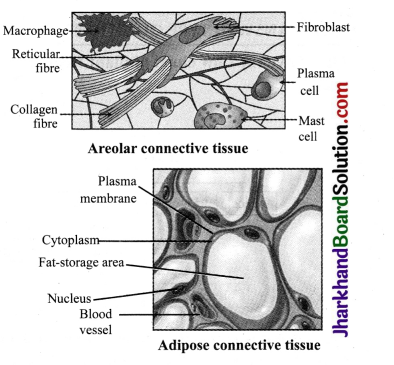
6. Areolar tissue: It is a connective tissue which consists of matrix, several types of cells, collagen and elastin fibres. It is found between the skin and muscles, around blood vessels and nerves and in the bone marrow. It fills space inside the organs, supports internal organs and helps in repair of the tissues.
7. Adipose tissue: It consists of cells (adipocytes) which are filled with fat globules. These cells remain scattered in a matrix. It is found below the skin and between internal organs. It stores fats and acts as an insulator.
Question 3.
Show the types of animal tissues through flow chart.
Question 3.
Why is epidermis considered a protective tissue?
Epidermis is considered a protective tissue because its prime purpose is to form a physical barrier between the outside and inside of the body. These tissues are usually present in the outermost layer of the plant body such as leaves, stem and roots. It is one cell thick and covered with cutin and protects the underlying tissues present in the plant body. As roots and stems grow older with time, tissues at the periphery become cork cells. Cork cells are dead, have no intercellular spaces and the cell walls are heavily thickened by the deposition of suberin. They prevent loss of water.
![]()
Question 5.
Describe the complex tissue of plants.
Answer:
Complex permanent tissue is composed of two or more than two types of cells and contributes to a common function. It is also known as vascular tissue Xylem and phloem are the two complex tissues.
- ylem: Xylem is composed of four types of cells tracheids, vessels, xylem fibres and xylem parenchyma Most of these cells are dead. Tracheids and vessels help in water transportation, parenchyma cells are mainly supportive in function.
- Phloem: Phloem is made up of four types of elements sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem fibres and phloem parenchyma It helps in the transportation of food in both the directions, i.e., from leaves to roots and to other parts of the plant.
Question 6.
Observe the diagrams and answer the questions given below.
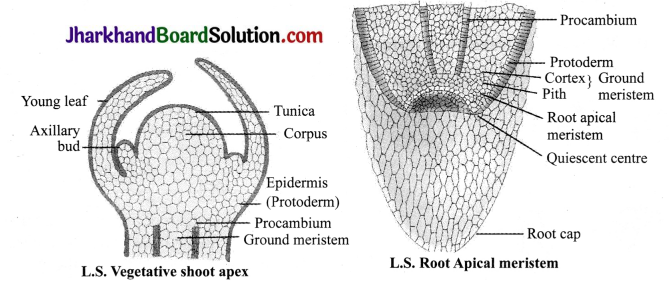
(a) What kind of cells are there in shoot apex and root apex?
(b) What are the main characteristics of these cells?
Answer:
(a) Meristematic cells.
(b) Cells have big nucleus and dense cytoplasm. These cells lack intercellular spaces and vacuoles.
Question 7.
Describe the characteristics of parenchyma What are its major modifications?
Answer:
Characteristics of parenchyma tissue:
- Living tissue.
- Shape spherical, oval, rectangular, polygonal, elongated or irregular in shape.
- Cell wall a thin wall made up of cellulose, hemicellulose and pectin.
- Young parenchymatous cells are loosely arranged.
- Intercellular space is present.
- Cells store reserve food material.
- Parenchyma is found in all parts of plant such as cortex, pith, palisade, mesophyll, flower, seed, etc.
- It is also found in vascular tissues.
Two modifications of parenchyma are chlorenchyma and aerenchyma.
- Chlorenchyma: Sometimes cells of the parenchyma contain chlorophyll and perform photosynthesis. This kind of parenchyma is known as chlorenchyma.
- Aerenchyma: In aquatic plants, parenchyma contains big air spaces in between them. Such a parenchyma tissue is known as aerenchyma
Analysing & Evaluating Questions
Question 8.
Bharti was asked to identify the following blood cells as erythrocytes, thrombocytes and types of leucocytes.
(a) On what basis was she able to identify erythrocytes?
(b) Which cells are shown by the labels B, C and D?
(c) What are the functions of E and F?
(d) Write any characteristic feature of G.
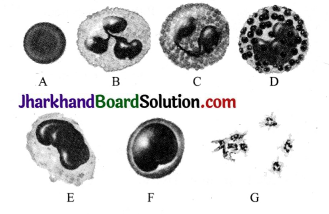
Answer:
(a) Erythrocytes or red blood cells are biconcave, disc – shaped and without nucleus.
(b) B, C and D represent neutrophils, eosinophils and basophils, respectively. These are types of leucocytes called granulocytes.
(c) E – Monocytes engulf bacteria and cellular debris at the injured site on the body. F – Lymphocytes produce antibodies and provide immunity.
(d) G – Blood platelets are colourless, non – nucleated, small or round – shaped cells. They play role in blood coagulation.
Activity 1
- Take two glass jars and fill them with water.
- Now, take two onion bulbs and place one on each jar, as shown in the given figure.
- Observe the growth of roots in both the bulbs for a few days.
- Measure the length of roots on day 1, 2 and 3.

On day 4, cut the root tips of the onion bulb in jar 2 by about 1 cm. After this, observe the growth of roots in both the jars and measure their lengths each day for five more days and record the observations in table, as shown below. Growth of roots in onion bulb:
| Length | Day 1 | Day 2 | Day 3 | Day 4 | Day 5 |
| Jar 1 | |||||
| Jar 2 |
Observations
- Onion in Jar 1 has longer roots because they keep on growing due to the presence of root tips.
- Roots stop growing in onion in Jar 2 as their root tips are removed.
- The tips stop growing in Jar 2 after we cut them because the apical meristem which causes increase in length of roots is removed.
Activity 2
- Take a plant stem and with the help of your teacher, cut very thin slices or sections of it.
- Now, stain the slices with safranin. Place one neatly cut section on a slide, and put a drop of glycerine.
- Cover with a cover – slip and observe under the microscope. Observe the various types of cells and their arrangement and compare them.
Observations
- All cells are not similar in structure; we see a variety of cells with different shapes and sizes.
- We can see at least 8 – 10 different types of cells in the slide.
- There are varieties of cells so that each group of cells does a specific role in the overall growth of plant.
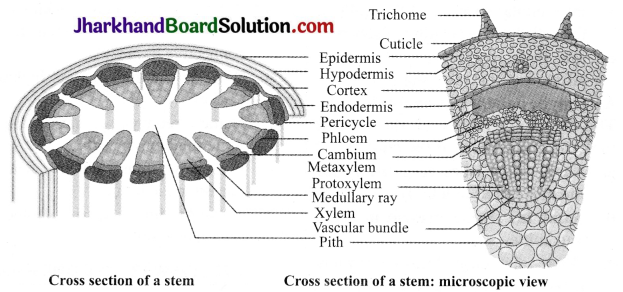
Activity 3
- Take a freshly plucked leaf of Rhoeo.
- Stretch and break it by applying pressure.
- While breaking it, keep it stretched gently so that some peel or skin projects out from the cut.
- Remove this peel and put it in a petri dish filled with water.
- Add a few drops of safranin.
- Wait for a couple of minutes and then transfer it onto a slide. Gently place a cover slip over it.
- Observe under microscope.
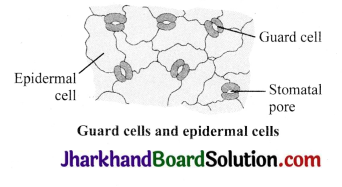
Observations
The epidermis is the outermost covering, usually made of a single layer of cells. The epidermis of leaf bears small pores called stomata.
Value Based Questions
Question 1.
A group of students completed the project of finding the botanical name of all the trees present in the school campus. They prepared metal plates with name carved on it, to fix it on the plant trunks. Shreya was concerned that if the metal plate is fixed into tree many cells of the tree may get damaged. But the group members explained her that the outer layer of trunk does not have living cells and there won’t be any damage to the tree.
1. What types of cells are present on the outer layer of the bark/tree trunk?
2. How does the cork act as a protective tissue?
3. What value of the group is seen in the above case?
Answer:
- On the outer layer of tree/trunk a thick layer of dead cells is present which acts as a protective tissue.
- In cork, all cells are dead without intercellular spaces and the walls of the cells have deposition of suberin.
- The students in a group show team effort, learning and co – operation.
Question 2.
A paralytic patient was unable to walk. The family members of the patient took the utmost care of the patient.
(a) Name two tissues responsible for the movement of a body.
(b) Name the tissues present in brain and spine.
(c) What value of the family members is seen in the above case?
Answer:
(a) The two tissues responsible for movement of the body are muscular tissue and nervous tissue.
(b) The tissues present in brain and spines are nervous tissues.
(c) The family member showed the value of caring, responsibility, dutiful and kindness.