Jharkhand Board JAC Class 9 Maths Solutions Chapter 14 Statistics Ex 14.3 Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
JAC Board Class 9th Maths Solutions Chapter 14 Statistics Ex 14.3
Page-258
Question 1.
A survey conducted by an organisation for the cause of illness and death among the women between the ages 15 – 44 (in years) worldwide, found the following figures (in %):
| S.No | Causes | Female fatality rate (%) |
| 1. | Reproductive health conditions | 31.8 |
| 2. | Neuropsychiatric conditions | 25.4 |
| 3. | Injuries | 12.4 |
| 4. | Cardiovascular conditions | 4.3 |
| 5. | Respiratory conditions | 4.1 |
| 6. | Other causes | 22.0 |
(i) Represent the information given above graphically.
(ii) Which condition is the major cause of women’s ill health and death worldwide?
(iii) Try to find out, with the help of your teacher, any two factors which play a major role in the cause in (ii) above being the major cause.
Answer:
(i) The data is represented below graphically.
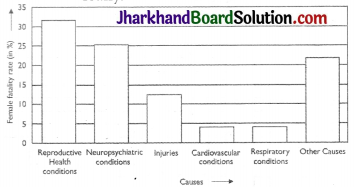
(ii) From the above graphical data, we observe that reproductive health conditions is the major cause of womens ill health and death worldwide.
(iii) Two factors responsible for cause in (ii)
- Lack of proper care and under-standing.
- Lack of medical facilities.
![]()
Question 2.
The following data on the number of girls (to the nearest ten) per thousand boys in different sections of Indian society is given below.
| Section | Number of girls per thousand boys |
| Scheduled Caste (SC) | 940 |
| Scheduled Tribe (ST) | 970 |
| Non SC/ST | 920 |
| Backward districts | 950 |
| Non backward districts | 920 |
| Rural | 930 |
| Urban | 910 |
(i) Represent the information above by a bar graph.
(ii) In the classroom discuss what conclusions can be arrived at from the graph.
Answer:
(i)
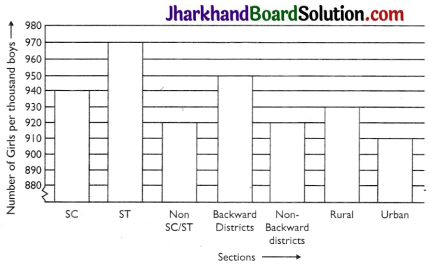
(ii) It can be observed from the above graph that the maximum number of girls per thousand boys is in ST. Also, the backward districts and rural areas have more number of girls per thousand boys than non¬backward districts and urban areas.
Page-259
Question 3.
Given below are the seats won by different political parties in the polling outcome of a state assembly elections:
| Political party | A | B | C | D | E | F |
| Seats won | 75 | 55 | 37 | 29 | 10 | 37 |
(i) Draw a bar graph to represent the polling results.
(ii) Which political party won the maximum number of seats?
Answer:
(i)
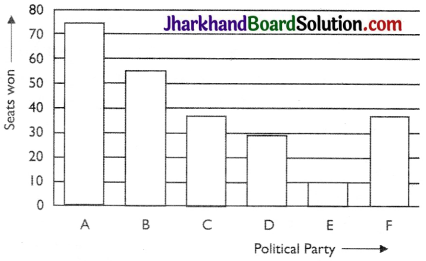
(ii)The party named A has won the maximum number of seats.
Question 4.
The length of 40 leaves of a plant are measured correct to one millimetre, and the obtained data is represented in the following table :
| Length (in mm) | Number of leaves |
| 118 – 126 | 3 |
| 127 – 135 | 5 |
| 136 – 144 | 9 |
| 145 – 153 | 12 |
| 154 – 162 | 5 |
| 163 – 171 | 4 |
| 172 – 180 | 2 |
(i) Draw a histogram to represent the given data. [Hint: First make the class intervals continuous]
(ii) Is there any other suitable graphical representation for the same data?
(iii) Is it correct to conclude that the maximum number of leaves are 153 mm long? Why?
Answer:
(i) The data is represented in a discontinuous class interval. So, first we will make it continuous.
The difference is 1, so we subtract \(\frac{1}{2}\) = 0.5 from lower limit and add 0.5 to the upper limit.
| Length (in mm) | Number of leaves |
| 117.5 – 126.5 | 3 |
| 126.5 – 135.5 | 5 |
| 135.5 – 144.5 | 9 |
| 144.5 – 153.5 | 12 |
| 153.5 – 162.5 | 5 |
| 162.5 – 171.5 | 4 |
| 171.5 – 180.5 | 2 |
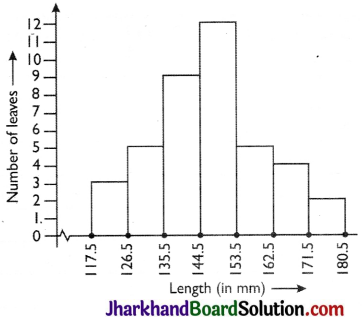
(ii) Yes, the data can also be represented by frequency polygon.
(iii) No, it is incorrect to conclude that the maximum number of leaves are 153 mm long because maximum number of leaves are lying between the length of 144.5-153.5.
![]()
Question 5.
The following table gives the life times of 400 neon lamps:
| Number of lamps | Lifetime (in hours) |
| 300 – 400 | 14 |
| 400 – 500 | 56 |
| 500 – 600 | 60 |
| 600 – 700 | 86 |
| 700 – 800 | 74 |
| 800 – 900 | 62 |
| 900 – 1000 | 48 |
(i) Represent the given information with the help of a histogram.
(ii) How many lamps have a life time of more than 700 hours?
Answer:
(i)
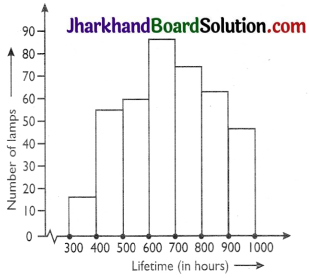
(ii) 74 + 62 + 48 = 184 lamp’s have a life time of more than 700 hours.
Page-260
Question 6.
The following table gives the distribution of students of two sections according to the marks obtained by them:
| Section A | Section B | ||
| Marks | Frequency | Marks | Frequency |
| 0-10 | 3 | 0-10 | 5 |
| 10-20 | 9 | 10-20 | 19 |
| 20-30 | 17 | 20-30 | 15 |
| 30-40 | 12 | 30-40 | 10 |
| 40-50 | 9 | 40-50 | 1 |
Represent the marks of the students of both the sections on the same graph by
two frequency polygons. From the two polygons compare the performance of the two sections.
Answer:
The class mark can be found by (Lower limit + Upper limit)/2.
For section A
| Section A | |
| Marks | Frequency |
| 0-10 | 3 |
| 10-20 | 9 |
| 20-30 | 17 |
| 30-40 | 12 |
| 40-50 | 9 |
For section B
| Section B | |
| Marks | Frequency |
| 0-10 | 5 |
| 10-20 | 19 |
| 20-30 | 15 |
| 30-40 | 10 |
| 40-50 | 1 |
Now, we draw frequency polygons for the given data.
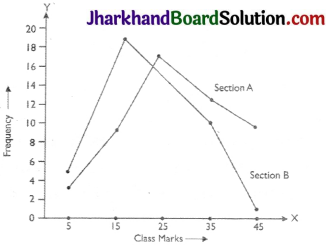
In the two polygons, we observed that most of the students of section A got higher marks. So the result of section A is better.
![]()
Question 7.
The runs scored by two teams A and B on the first 60 balls in a cricket match are given below:
| Number of balls | Team A | Team B |
| 1 – 6 | 2 | 5 |
| 7 – 12 | 1 | 6 |
| 13 – 18 | 8 | 2 |
| 19 – 24 | 9 | 10 |
| 25 – 30 | 4 | 5 |
| 31 – 36 | 5 | 6 |
| 37 – 42 | 6 | 3 |
| 43 – 48 | 10 | 4 |
| 49 – 54 | 6 | 8 |
| 55 – 60 | 2 | 10 |
Represent the data of both the teams on the same graph by frequency polygons.
[Hint: First make the class intervals continuous.]
Answer:
The data given in the form of discontinu¬ous class intervals. So, first we will make them continuous. The difference is 1, so
we subtract \(\frac{1}{2}\) = 0.5 from lower limit and add 0.5 to the upper limit.
| Number of balls | Class Marks | Team A | Team B |
| 0.5 – 6.5 | 3.5 | 2 | 5 |
| 6.5 – 12.5 | 9.5 | 1 | 6 |
| 12.5 – 18.5 | 15.5 | 8 | 2 |
| 18.5 – 24.5 | 21.5 | 9 | 10 |
| 24.5 – 30.5 | 27.5 | 4 | 5 |
| 30.5 – 36.5 | 33.5 | 5 | 6 |
| 36.5 – 42.5 | 39.5 | 6 | 3 |
| 42.5 – 48.5 | 45.5 | 10 | 4 |
| 48.5 – 54.5 | 51.5 | 6 | 8 |
| 54.5 – 60.5 | 57.5 | 2 | 10 |
Now, we draw frequency polygons for the given data.
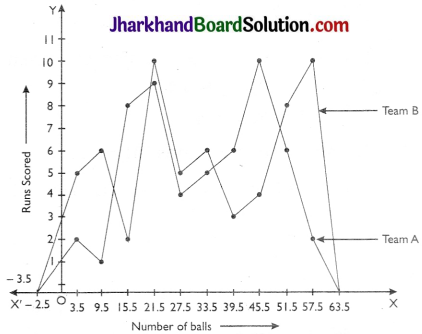
Page-261
Question 8.
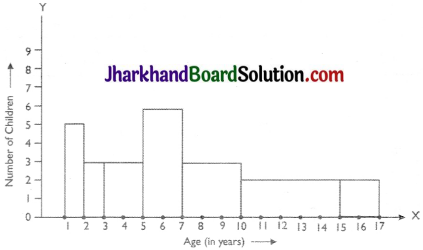
A random survey of the number of children of various age groups playing in a park was found as follows:
| Age (in years) | Number of children |
| 1 – 2 | 5 |
| 2 – 3 | 3 |
| 3 – 5 | 6 |
| 5 – 7 | 12 |
| 7 – 10 | 9 |
| 10 – 15 | 10 |
| 15 – 17 | 4 |
Draw a histogram to represent the data above.
Answer:
The class intervals in the data is having varying width. We know that the area of rectangle is proportional to the frequencies in the histogram. The class interval with minimum class size 1 is selected and the length of the rectangle is proportionate to it.
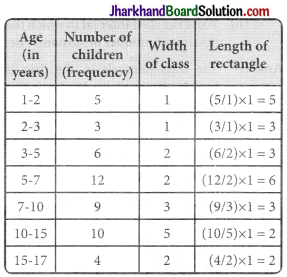
Taking the age of children on x-axis and no. of children on v-axis, the histogram can be drawn as follows.
![]()
Question 9.
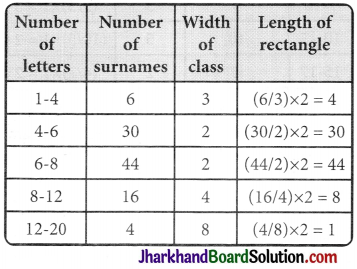
100 surnames were randomly picked up from a local telephone directory and a frequency distribution of the number of letters in the English alphabet in the surnames was found as follows:
| Number of letters | Number of surnames |
| 1 – 4 | 6 |
| 4 – 6 | 30 |
| 6 – 8 | 44 |
| 8 – 12 | 16 |
| 12 – 20 | 4 |
(i) Draw a histogram to depict the gi ven information.
(ii) Write the class interval in which the maximum number of surnames lie.
Answer:
(i) The class intervals in the data is having varying width. We know that the area of rectangle is proportional to the frequencies in the histogram. The class interval with minimum class size 2 is selected and the length of the rectangle is proportionate to it.
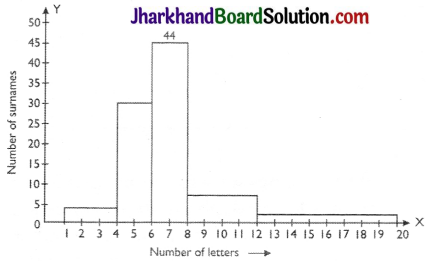
(ii) The class interval in which the maximum number of surnames lie is 6-8.