Students must go through these JAC Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metal to get a clear insight into all the important concepts.
JAC Board Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 3 Metals and Non-metal
→ Metals : Metals possesses lustre in their pure state. Metals are hard. It possesses property of malleability and ductility. Metals are good conductors of heat and electricity and their melting points are high. Metals are sonorous.
→ Non-metals: Non-metals are either solids or gases (Exception: Bromine, it is a liquid). They are neither malleable, nor ductile. They are non-conductors of heat and electricity (Exception: Graphite, it is conductor). Their melting points and boiling points are low (Exception : Diamond, it has the highest melting point).
→ Metals combine with oxygen to form metal oxides.
![]()
→ Oxides of alkali metals are soluble in water.
→ Metals form basic (For example, Na2O, MgO) and amphoteric oxides (For example, ZnO, Al2O3), while non-metals form acidic and neutral oxides (For example, H2O, CO, Cl2O7).
→ Metals react with acid and water forming hydrogen gas. Non-metals do not release hydrogen gas by reaction with acid and water.
→ When metals reacts with nitric acid, hydrogen gas is not evolved, because nitric acid is a strong oxidising agent.
→ Reactivity series of metals is an arrangement of metals in the descending order of their reactivity. In reactivity series, more reactive metals (elements) are placed at top while less reactive metals (elements) are placed at bottom.
→ A more reactive metal displaces a less reactive metal from its salt solution or from its molten state.
→ Metallurgy The various processes involved in the extraction of metals from their ores in different steps and finally refining the metals.
→ Ionic compounds: The compounds formed by the transfer of electrons from a metal species to a non-metal species forming ions are known as ionic compounds.
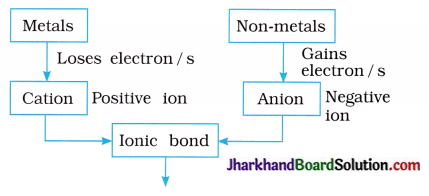
→ Properties of ionic compounds : Ionic compounds are brittle. They have high melting point and boiling point. They are soluble in water but insoluble in petrol and kerosene (non-polar solvents). These compounds do not conduct electricity in solid state but they conduct electricity in an aqueous solution or in their molten state.
![]()
→ Roasting: The process of strongly heating the sulphide ores in excess of air and converting them into oxides is called roasting.
→ Calcination: The process of strongly heating the carbonate (or hydroxide) ores in a limited supply of air and converting them into metal oxides is called calcination.
→ Alloys: The homogenous mixture of two or more metals or metal and non-metal is called an alloy. For example, brass, bronze, stainless steel, etc.