JAC Board Class 9th Science Important Questions Chapter 14 Natural Resources
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Most of the water on the earth’s surface is found in
(a) lakes
(b) rivers
(c) oceans and seas
(d) underground
Answer:
(c) oceans and seas
Question 2.
Ozone hole was first observed over
(a) Antarctica
(b) Australia
(c) Arctic ocean
(d) America
Answer:
(a) Antarctica
Question 3.
Nitrogen fixing bacteria cannot fix N2 in the presence of
(a) CO2
(b) N2
(c) O2
(d) light
Answer:
(c) O2
Question 4.
Which of the following compounds is not degraded by any biological process?
(a) CFCs
(b) CH4
(c) Glucose
(d) Nitrites
Answer:
(a) CFCs
Question 5.
Nitrogen – fixing bacteria are found in the roots of
(a) wheat
(b) maize
(c) pulses
(d) sugarcane
Answer:
(c) pulses
Question 6.
Venus and Mars have no life because
(a) they have no atmosphere
(b) their atmosphere has only oxygen
(c) their atmosphere has 95% – 97% carbon dioxide
(d) their atmosphere has 95% – 97% oxygen
Answer:
(c) their atmosphere has 95%-97% carbon dioxide
Question 7.
Which one of the following organisms are very sensitive to the levels of contaminants like sulphur dioxide in air?
(a) Bacteria
(b) Fungi
(c) Algae
(d) Lichens
Answer:
(d) Lichens
![]()
Question 8.
Burning of fossil fuels adds
(a) CO2, SO2, NO2 gases in air
(b) C, SO2, N2 gases in air
(c) O2, SO3, NO3 gases in air
(d) H2O, CO2 NO2, gases in air
Answer:
(a) CO2, SO2, NO2 gases in air
Question 9.
Nitrogen fixation can be done by
(a) Industries
(b) Rhizobium
(c) Lightening
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(d) All of the above
Question 10.
On moon the temperature ranges from – 190°C to 110°C. This is due to
(a) absence of water bodies
(b) presence of water bodies
(c) absence of biogeochemical cycles
(d) absence of atmosphere
Answer:
(d) absence of atmosphere
Question 11.
Depletion of ozone molecules in the stratosphere is due to
(a) chlorine compounds
(b) fluorine compounds
(c) halogen compounds
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) halogen compounds
Question 12.
The life supporting zone of the earth is
(a) lithosphere
(b) hydrosphere
(c) atmosphere
(d) biosphere
Answer:
(d) biosphere
Question 13.
The organism which helps in the formation of soil is
(a) bacterium
(b) moss
(c) lichen
(d) both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(d) both (b) and (c)
Question 14.
The outermost crust of the earth is called
(a) atmosphere
(b) exosphere
(c) lithosphere
(d) hydrosphere
Answer:
(c) lithosphere
Analysing & Evaluating Questions
Question 15.
The atmosphere of the earth is heated by radiations which are mainly
(a) radiated by the sun
(b) re – radiated by land
(c) re – radiated by water
(d) re – radiated by land and water
Answer:
(c) re – radiated by water
Question 16.
The term “water pollution” can be defined in several ways. Which of the following statements does not give the correct definition?
(a) The addition of undersirable substances to water bodies
(b) The removal of desirable substances from water bodies
(c) A change in pressure of the water bodies
(d) A change in temperature of the water bodies
Answer:
(c) A change in pressure of the water bodies
Question 17.
When we breathe in air, nitrogen also goes inside along with oxygen. What is the fate of this nitrogen?
(a) It moves along with oxygen into the cells.
(b) It comes out with the CO2 during exhalation.
(c) It is absorbed only by the nasal cells.
(d) Nitrogen concentration is already more in the cells so it is not at all absorbed.
Answer:
(b) It comes out with the CO2 during exhalation.
Assertion Reason Questions
Directions: In the following questions, the Assertions and the Reasons have been put forward. Read the statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following:
(A) Both the assertion and the reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(B) The assertion and the reason are correct but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(C) The assertion is true but the reason is false.
(D) Both the statements are false.
1. Assertion: Plants cannot utilise
nitrogen directly from the atmosphere. Reason: Plants can only use nitrates and nitrites.
Answer:
(B) The assertion and the reason are correct but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
2. Assertion: Water vapour is not a greenhouse gas.
Reason: Water vapour does not contribute in global warming.
Answer:
(D) Both the statements are false.
3. Assertion: The moon has very cold and very hot temperature variations.
Reason: Moon does not possess the atmosphere.
Answer:
(A) Both the assertion and the reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
4. Assertion: It is easier to fly a kite near a sea shore.
Reason: There is a regular unidirectional wind from sea to land.
Answer:
(A) Both the assertion and the reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
5. Assertion: Legumes revive the soil fertility.
Reason: Microbes in the root nodules of legumes fix atmospheric nitrogen.
Answer:
(A) Both the assertion and the reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is biosphere?
Answer:
The life – supporting zone of earth where atmosphere, hydrosphere and lithosphere interact and make life is known as biosphere.
Question 2.
What are the biotic and abiotic components of biosphere?
Answer:
Abiotic or physical components of biosphere consist of geographical conditions such as the temperature, rainfall, soil, seasons and the climate, while biotic components include animals, plants, fungi and bacteria.
Question 3.
What percentage of oxygen and nitrogen is present in the air?
Answer:
About 21% oxygen and 78% nitrogen is present in the air.
![]()
Question 4.
Name the air pollutants released by the industries.
Answer:
Industrial air pollutants are sulphur dioxide, carbon dioxide, oxides of nitrogen, hydrogen sulphide, fumes of acids, dust, particles of unbumt carbon, lead, asbestos and even cement.
Question 5.
What are the two factors that cause changes in our atmosphere?
Answer:
(a) Heating of air, and
(b) formation of water vapour.
Question 6.
State any two harmful effects of air pollution.
Answer:
Two harmful effects of air pollution are:
(a) Respiratory problems
(b) Global warming
Question 7.
What is soil?
Answer:
Soil is a mixture of small particles of rocks of different sizes, humus and microscopic life.
Question 8.
State the major source of minerals in the soil.
Answer:
The mineral nutrients present in a particular soil depend on the rocks it was formed from. This means that the major source of minerals in a soil is their parent rocks.
Question 9.
What is top soil?
Answer:
The topmost layer of the soil that contains humus and living organisms in addition to the soil particles is called top soil.
Question 10.
Name two chemicals that are depleting ozone layer.
Answer:
Chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) and halogenated ozone depleting substance (ODS).
Question 11.
Name two greenhouse gases.
Answer:
Methane and carbon dioxide.
Question 12.
Define nitrification.
Answer:
The biological conversion of ammonia into nitrites and then oxidation of nitrites to nitrates is called nitrification.
Question 13.
Name a nitrogen fixing bacterium.
Answer:
Rhizobium
Question 14.
Define humus.
Answer:
The fertile dark substance present in the topmost layer of the soil which contains dead remains of plants and animal wastes, like excreta, that adds nutrients to the soil is called humus.
Question 15.
What is denitrification?
Answer:
Conversion of nitrates into free nitrogen is called denitrification.
Question 16.
How does carbon exist in all life forms?
Answer:
Carbon is present in all life forms in the form of proteins, carbohydrates, fats, nucleic acids and vitamins.
Question 17.
Name two biologically important compounds that contain both oxygen and nitrogen.
Answer:
Proteins and nucleic acids (DNA and RNA).
Question 18.
Name the two gases given out by the burning of fossil fuels, which dissolve in rain to form acid rain.
Answer:
Sulphur dioxide (SO2) and oxides of nitrogen.
Analysing & Evaluating Questions
Question 19.
A person is burning a huge amount of waste in an open are(a) Which gas is being utilised for burning process and which gas is released into the atmosphere?
Answer:
The process of burning or combustion utilises oxygen and produces carbon dioxide. Thus, oxygen gas is being utilised in the process, and carbon dioxide is released into the atmosphere.
Question 20.
A huge amount of plant and animal waste is being dumped in a lake. What will be the condition of lake after some time?
Answer:
When organic waste (plant and animal residue) is dumped into a water body, the biological oxygen demand of the water increases. This is because the decomposition of organic matter by microorganisms needs more oxygen in water. As a result, there arises oxygen deficiency in water, which leads to the death of other aquatic organisms.
![]()
Question 21.
Some industries release hot water or very cold water into water sources directly. Why should this be stopped?
Answer:
When excessive hot water or cold water is released into water bodies, it may affect some aquatic organisms. This is because these organisms live in a certain range of temperature and any change in this range (due to the release of excessive hot water or cold water) may cause threat to their survival.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
The atmosphere acts as a blanket. How?
Answer:
The blanket of atmosphere, which is covering the earth, keeps the average temperature of the earth fairly steady during the day and even during the course of the whole year. The atmosphere prevents the sudden increase in temperature during the daylight hours. And during the night, it slows down the escape of heat into outer space.
Question 2.
What are the consequences of global warming?
Answer:
(a) An increase in temperature of earth even by 1°C may lead to the melting of ice on the poles.
(b) The melting of ice will result in rise of sea level.
(c) Due to rise in sea level, many coastal cities will be flooded or submerged.
(d) Increase in temperature of earth results in change in weather and may cause excessive raining or drought or extreme hot or cold weather conditions.
Question 3.
Name the various organisms involved in nitrogen cycle.
Answer:
(a) Nitrogen fixing bacteria, e.g., Rhizobium, Azotobacter.
(b) Bacteria which convert complex nitrogenous organic compounds (proteins) into ammonia, e.g., Clostridium, Proteus.
(c) Nitrifying bacteria which convert ammonia into nitrates, e.g., Nitrosomonas and Nitrobacter.
(d) Denitrifying bacteria, e.g., Pseudomonas.
Question 4.
What does the presence of smog in an area indicate?
Answer:
The presence of smog in an area indicates the high percentage of smoke released in the air by combustion of fossil fuels in industries, thermal power plants or automobiles. It is an indicator of air pollution.
Question 5.
Write three ways to prevent soil pollution.
Answer:
(a) By judicious use of fertilizers and pesticides.
(b) By proper management of disposal of household waste.
(c) By practising intensive cropping and terrace farming.
Question 6.
How is greenhouse effect related to global warming?
Answer:
Higher concentration of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, methane, nitrous oxide, etc., in the atmosphere causes absorption of reflected heat and avoids their escape into the space. This phenomenon is called greenhouse effect. This leads to rise in the temperature of earth’s atmosphere throughout the world causing global warming. This global warming caused by greenhouse gases like CO2, CH4, etc., leads to the melting of glacier and polar ice. This would cause rise in the level of sea and other climate changes. Hence, we can say that global warming is a consequence of greenhouse effect.
Question 7.
What is air pollution? How is it caused? Write its two harmful effects.
Answer:
The contamination of air with unwanted gases, particles like dust, etc, which makes it unfit for inhalation is called air pollution.
- Causes:
- (a) Burning of fossil fuels releases SO2, CO2 and NO2 gases.
- (b) Burning of fuels releases unbumt carbon particles and smoke.
- (c) Smoke from industries and vehicles.
- Harmful effects:
- (a) It causes respiratory problems.
- (b) It causes allergies, asthma, cancer and heart diseases.
Question 8.
What is acid rain? Write its harmful effects.
Answer:
The gases released due to combustion of fossil fuels are SO2, NO2 and CO2. These gases remain suspended in the air. When it rains, the rainwater mixes with these gases to form sulphuric acid, nitrous acid, carbonic acid and comes down on the surface of the earth in the form of acid rain.
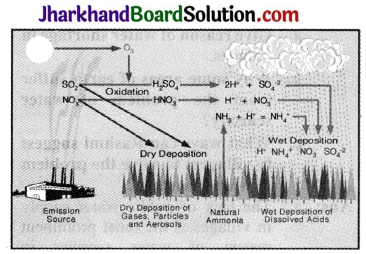
(a) It corrodes statues, monuments of marble, buildings, etc.
(b) It makes the soil acidic.
(c) It damages crops and plantations.
Question 9.
What is water pollution? Give its causes and harmful effects.
Answer:
When water is contaminated with unwanted substances and chemicals which make it unfit for use and cause diseases, it is called water pollution.
- Causes:
- (a) Sewage from towns, cities is dumped in the water.
- (b) Fertilizers, pesticides, insecticides get washed away into the waterbodies from farmlands.
- (c) Effluent from industries.
- Harmful effects:
- (a) Polluted water, when consumed, causes many diseases which are water – borne, like cholera, typhoid, etc.
- (b) Mercury in salts dumped by industries causes a brain disorder called Minamata disease.
- (c) Many life – forms which are susceptible to temperature changes die.
Question 10.
What is the difference between fog and smog? Give two harmful effects of smog.
Answer:
The water vapour present in air when condenses due to very low temperature is called fog. The smoke released in the air, due to burning of fuels, mixes with the fog and forms smog. Harmful effects of smog: It decreases the visibility and causes adverse effect on aeroplane landing, railways and road transport.
Question 11.
State in brief the role of photosynthesis and respiration in carbon-cycle in nature.
Answer:
Photosynthesis is performed by green plants in the presence of sunlight and it converts carbon dioxide into carbohydrates that are utilised by other living organisms through food chain. Oxygen is replenished in nature only through the process of photosynthesis. Oxygen enters the living world through the process of respiration, i.e., it oxidises the food material (glucose molecules) and produces energy and carbon dioxide.
Question 12.
Explain the importance of ozone to mankind.
Answer:
Ozone covers the earth’s atmosphere. It is present in stratosphere. It does not allow the harmful ultraviolet radiations coming from the sun to enter our earth. These ultraviolet radiations cause ionizing effect and can cause cancer and genetic disorder in any life form. The ozone is getting depleted at the South Pole near Antarctica The ozone depletion is due to the halogens like CFCs (Chlorofluorocarbons) released in the air. Chlorine and fluorine react with the ozone and split it, thereby leading to the formation of a big hole called ozone hole.
![]()
Question 13.
How are winds caused and what decides the breeze to be gentle, strong wind or a terrible storm?
Answer:
Movement of air, terrible storm and rains, all these phenomena are the result of changes that take place in our atmosphere due to the heating of air and the formation of water vapour. Water vapour is formed due to the heating of water bodies and the activities of living organisms. The atmosphere can be heated from below by the radiation that is reflected back or re-radiated by the land or water bodies. On being heated, convection currents are set up in the air. This causes wind. The pressure gradient or the pressure difference determines the speed and intensity of wind. Larger the gradient, more is the wind speed.
Question 14.
Why is step farming common in hills?
Answer:
At hills, the rainwater flows with a very high speed which provides very less time to absorb rainwater into the soil. So, the fields contain wide steps which slow down the speed of fast flowing water. Therefore, farming fields get more chances to absorb rainwater, i.e, more water can seep into the soil for better farming. Besides this, step farming also reduces soil erosion.
Question 15.
Write the harmful effects of ozone layer depletion.
Answer:
Harmful effects of ozone layer depletion are as follows:
- Due to depletion of ozone layer, more ultraviolet (UV) radiation will reach the earth. UV radiation causes skin cancer, damage to eyes and immune system.
- UV radiation kills microorganisms, such as bacteria, even useful ones.
- Ozone layer depletion may lead to variation in rainfall, ecological disturbances and dwindling of good food supply.
Analysing & Evaluating Questions
Question 16.
Rashmi visited her village during summer vacations and found that there is severe shortage of water for villagers and animals.
1. Give reason of water shortage in villages.
2. Why some areas of earth suffer from the problem of water scarcity?
3. What ways can Rashmi suggest to villagers to solve the problem of water shortage?
Answer:
- The lack of public water supply in villages is the most prominent reason of water scarcity in villages. Villagers depend on natural sources of water which often dry up due to excessive heat during summer.
- The water scarcity occurs due to uneven distribution of freshwater on the earth.
- Rainwater harvesting is an effective way to solve the problem of water scarcity in villages as well as in cities. The rainwater can be stored in underground tanks, check dams and recharges the groundwater. This groundwater can be drawn for use at the time of shortage of water.
Question 17.
A farmer followed the practice of sowing cereal crops regularly in his field for several seasons. After sometime, he found decline in cereal production.
(a) What may be the reason for less cereal production in farmer’s field?
(b) How the farmer can increase production in his field?
Answer:
(a) Sowing a same crop regularly in the field for several seasons makes the soil deficient of certain essential nutrients.
Thus, the fertility of soil declines after sometime and the crop production becomes less.
(b) The farmer can grow leguminous crops after cereal crop. The nitrogen fixing bacteria that live in root nodules of legume crops help in replenishment of lost nitrogen in the soil by fixing atmospheric nitrogen.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe the carbon – cycle in nature.
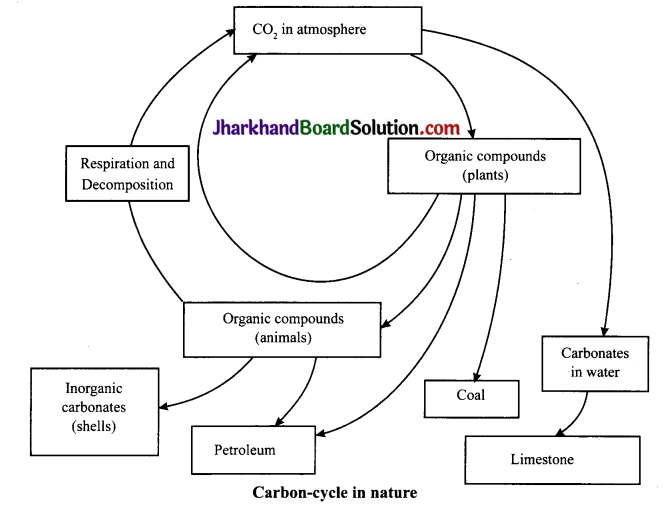
Answer:
All living things are made of carbon. Carbon is also a part of the oceans, air, and even rocks. Because the earth is a dynamic place, carbon does not stay still. Carbon – cycle is the series of processes by which carbon compounds are interconverted in the environment, involving the incorporation of carbon dioxide into living tissues by photosynthesis and its return to the atmosphere through respiration, the decay of dead organisms and the burning of fossil fuels.
If we see from the beginning, CO2 in the atmosphere is taken by the plants which use it to make glucose, water and oxygen. Also, direct CO2 from air forms carbonates in water which later turns into limestone. Then, these plants are eaten us and other animals, i.e., we indirectly use COus and other animals, i.e., we indirectly use CO2 present in the plants. Also, we respire CO2 back in atmosphere.
Then, organic compounds (plants / animals) form coal and petroleum, or we can say fossil fuel. And also, animal body present in the plants. Also, we respire CO2 back in atmosphere. Then, organic compounds (plants / animals) form coal and petroleum, or we can say fossil fuel. And also, animal body forms inorganic carbonates or shells. But nowadays, we bum fossil fuels too much (and also cut the trees) which is harmful. As a result, we are not getting rid of excess CO2 from our atmosphere.
Question 2.
Why is replenishment of forests necessary?
Answer:
Forests need to be replenished because of the following reasons:
- Rainfall: During transpiration, trees give out enormous amount of water vapour. This water vapour helps in the formation of clouds. So, if trees are cut and not replenished, the rainfall in the area will reduce.
- Natural rate of tree growth: Forests cannot be re – grown in a few days or months as trees take many years to grow fully. Thus, it becomes necessary to replenish the forests periodically.
- Soil erosion: If a large number of trees are cut, the soil becomes naked. The topsoil, which is rich in organic matter will be washed away by water or carried away by wind. Trees help in binding the soil.
- Carbon dioxide – oxygen balance: Forests have a very large number of trees which give out 02 and take in C02 by photosynthesis. In this way, they help in maintaining the carbon dioxide-oxygen balance in the atmosphere.
- Timber and fuel: Forests are the best suppliers of timber for furniture and fuel. So, for their constant supply, forests need to be replenished.
Question 3.
Draw a labelled diagram to show nitrogen cyclele in nature.
Answer:
Nitrogen exists as free nitrogen in the atmosphere. In air, N2 is about 78%. This free nitrogen is fixed into compounds of ammonia and nitrates. Most of the organisms cannot utilise molecular nitrogen. Fixation of Nitrogen:
Fixation of free nitrogen into compounds takes place by the following means:
1. Certain blue green algae and bacteria can fix atmospheric nitrogen.
2. Nitrogen – fixing bacteria found in the root nodules of legumes such as grams, beans, pulses, etc., fix atmospheric nitrogen into nitrogen containing compounds.
3. Lightning also helps in the formation of nitrogen containing compounds. Nitrogen containing fertilisers produced artificially in factories are the fixed form of nitrogen. Plants take up compounds containing nitrogen from the soil. From plants nitrogen passes into food web Decay of dead plants and animals and excreta like urine, faeces, cause return of nitrogen compounds to the soil. Denitrifying bacteria and fire cause liberation of free nitrogen in the atmosphere.
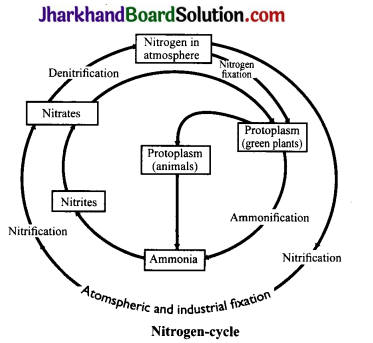
Importance of Nitrogen – cycle: Nitrogen is an important constituent of tissues, proteins, enzymes, nucleic acids and amino acids. Atmosphere contains about 78 per cent nitrogen but plants and animals cannot use nitrogen in this form. Plants take nitrogen in the form of nitrates, the usable form. From plants, nitrogen travels to animals through food. If nitrogen in the form of proteins, amino acids, enzymes, etc., remains locked up in the bodies of organisms, there will be shortage of usable form of nitrogen. Therefore, circulation of nitrogen in nature is very essential.
Question 4.
Explain the oxygen – cycle in nature.
Answer:
Oxygen is an important component of everyday life. We cannot survive without oxygen. It comprises about 21% of atmospheric air. It is a component of several biological molecules such as carbohydrates, proteins, nucleic acids and fats. Like carbon dioxide, oxygen too is cycled through the process of photosynthesis and respiration. Oxygen is also utilised during combustion or burning.
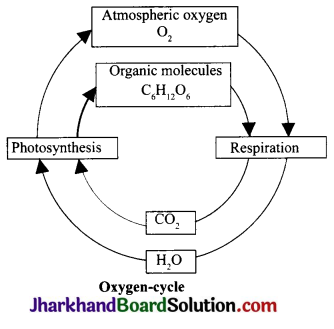
Oxygen – cycle: Oxygen from the atmosphere is used up in three processes, viz., combustion, respiration and in the formation of oxides of nitrogen.
- Animals take in oxygen through the process of respiration. They release CO2 into the atmosphere.
- Carbon dioxide, released by animals, is used by plants in the process of photosynthesis.
- Plants release oxygen into the atmosphere as a by-product of photosynthesis.
- Fuels need oxygen for combustion, so they take oxygen and release CO2 into the atmosphere as a by-product along with other gases.
- CO2 is released into the air in the process of decaying of dead animals and plants.
- This CO2 is taken up by plants for the process of photosynthesis and O2 is released and this process continues.
Question 5.
Describe water – cycle.
Answer:
Water is one of the most important physical components which is essential for survival of life on the earth. The water from the water bodies on evaporation moves up. As the vapours rise up in the atmosphere they become cooler and condense to form clouds which fall down as rain. Rainwater then passes through rivers and gets collected again in the ocean. The circulation of water in this manner is known as water – cycle. The cycle is also performed by living beings like absorption and transpiration of water by plants and drinking by animals. Animals lose water during respiration and perspiration. They lose water through excretion also.
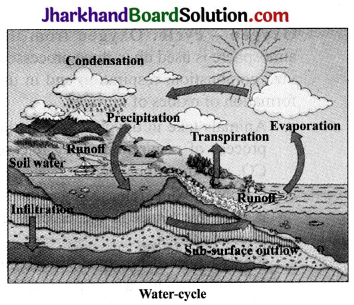
Analysing & Evaluating Questions
Question 6.
There are several sources like respiration by living organisms, combustion, burning of fossil fuels and forest fires which contribute immensely in the carbon dioxide levels of atmosphere. Despite all these activities, the air contains only a mere fraction of carbon dioxide in it. How does it happen?
Answer:
The level of carbon dioxide does not increase in atmosphere because atmospheric carbon dioxide is fixed continuously in different components by the following ways.
- The plants ‘fix’ or capture the carbon dioxide and convert it into glucose through the process known as photosynthesis.
- Animals get their carbon directly by eating plants or indirectly by eating herbivores. Many marine animals use carbonates dissolved in seawater to make their shells.
- The fossil fuels are also the storehouse of carbon. These are the deposits of organic materials formed from decayed plants and animals deep inside the earth. By exposure to heat and pressure in the earth’s crust over hundreds of millions of years, these dead decaying organisms changed into fossil fuels, such as coal and petroleum.
- The water rich in carbon dioxide accumulates at the bottom of water bodies and forms limestone or carbonated rocks. It involves a series of chemical reactions that remove carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and deposits it in the form of rocks.
Activity 1
- Take the following:
- (i) a beaker full of water
- (ii) a beaker full of soil/sand and
- (iii) a closed bottle containing a thermometer.
- Measure the temperature of all these in shade.
- Now, keep them in bright sunlight for three hours and measure the temperature of all three vessels.
Observations:
- The temperature of air is less in shade than the temperature of sand or water.
- The temperature of water does not rise quickly whereas sand gets heated up easily.
- The temperature of air in the closed bottle is more than the temperature of air in open. This is because heat received from the sun has no outlet to reflect back the heat radiation. The glass does not allow to escape reflected heat radiations to go out.
Activity 2
- Place a candle in a beaker or wide mouthed bottle and light it. Light an incense stick and take it to the mouth of the beaker as shown in the figure.
- Now, keep the incense stick near the edge of the mouth, a little above the candle, and in other regions. Record your observations.
Observations:
- When the incense stick is kept near the edge of the mouth, the smoke flows inwards towards the flame. The hot air around the candle rises up and cold air from the surroundings rushes in to fill the space. This air rushing inside the beaker brings smoke towards the flame.
- The smoke rises up along with hot rising air when incense stick is kept a little above the candle.
- In other places, the smoke from the incense stick rises up and then diffuses in the air.
Activity 3
Take two identical trays and fill them with soil. Plant mustard or green gram or paddy in one of the trays and water both the trays regularly for a few days, till the first tray is covered with plant growth. Now, tilt both the trays and fix them in that position. Make sure that both the trays are tilted at the same angle. Pour equal amount of water gently on both trays such that the water flows out of the trays.

1. Study the amount of soil that is carried out of the trays by the water.
2. Now pour equal amounts of water on both the trays from a height. Pour three or four times the amount that you poured earlier.
3. Study the amount of soil that is carried out of the trays now. Record your observations.
Observations:
- The tray without vegetation loses more soil and holds more water than the tray that has plants.
- On pouring water on both the trays from a height, more soil flows along with water in the tray without vegetation.
- Less amount of soil is washed out earlier than that washed out when water was poured from a height.
Value Based Questions
Question 1.
Sudha saw a child sleeping in a car parked, with closed doors and glasses rolled up, in an open area on a sunny day near the market. She immediately raised an alarm and with the help of police she got the window rolled down.
1. Why was it not safe to keep the doors with window glasses rolled up for a child inside the car?
2. Name two gases that can lead to the above effect.
3. What value of Sudha is reflected in the above act?
Answer:
- It was not safe for the child in the car with locked doors and windows rolled up because the sunlight would result in the greenhouse effect in the car. This would increase the temperature in the car and also result in the increase in CO2 level which would lead to suffocation.
- Carbon dioxide gas and methane gas can lead to greenhouse effect.
- Sudha reflects the value of an aware citizen and responsible behaviour.
![]()
Question 2.
After doing a project on “save water”, Sumit realised the problem of shortage of drinking water on the earth. Sumit started checking the misuse of water in his vicinity.
1. What is the percentage of drinking water available on the earth?
2. Give any two practices that one should follow to save water.
3. What value of Sumit is reflected in this act?
Answer:
- 1% of drinking water is available on the earth.
- To save water:
- Do not use shower to take bath every day, instead use a bucket of water.
- Mop the floor instead of washing.
- Sumit showed the value of responsible behaviour and participating citizen.
- A project on “save water”, Sumit realised the problem of shortage of drinking water on the earth.