JAC Board Class 9th Science Important Questions Chapter 15 Improvement in Food Resources
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium are examples of …………….
(a) micronutrients
(b) macronutrients
(c) fertilizers
(d) both (a) and (c)
Answer:
(b) macronutrients
Question 2.
Cyprinus and Parthenium are types of …………….
(a) diseases
(b) pesticides
(c) weeds
(d) pathogens
Answer:
(c) weeds
Question 3.
Using fertilisers in farming is an example of …………… .
(a) no cost production
(b) low – cost production
(c) high – cost production
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) high – cost production
Question 4.
What is the other name for Apis cerana indica?
(a) Indian cow
(b) Indian buffalo
(c) Indian honeybee
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Indian honeybee
![]()
Question 5.
The management and production of fish is called …………… .
(a) pisciculture
(b) apiculture
(c) sericulture
(d) aquaculture
Answer:
(a) pisciculture
Question 6.
Pasturage is related to …………… .
(a) cattle
(b) fishery
(c) apiculture
(d) sericulture
Answer:
(c) apiculture
Question 7.
What is the process of growing two or more crops in a definite pattern called?
(a) Crop rotation
(b) Intercropping
(c) Mixed cropping
(d) Organic cropping
Answer:
(b) Intercropping
Question 8.
The kharif season extends from …………… .
(a) November to April
(b) June to October
(c) March to November
(d) December to March
Answer:
(b) June to October
Question 9.
For mixed cropping, which of the following combinations of crops is not suitable?
(a) Wheat + maize
(b) Wheat + gram
(c) Wheat + mustard
(d) Groundnut + sunflower
Answer:
(a) Wheat + maize
Question 10.
Catla, Rohu and Mrigals constitute …………… .
(a) marine fishes
(b) brackish water fishes
(c) fresh water fishes
(d) both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(c) fresh water fishes
Analysing & Evaluating Questions
Question 11.
Madhu visited a dairy farm with her friends. There they saw the various kinds of cattle kept in sheds, food given to them and so on. What are the main components of feed provided to the cattle?
(a) Roughage
(b) Concentrates
(c) Water
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 12.
Find out the correct sentences.
(i) Hybridisation means crossing between genetically dissimilar plants.
(ii) Cross between two varieties is called interspecific hybridisation.
(iii) Introducing genes of desired character into a plant gives genetically modified crop.
(iv) Cross between plants of two species is called intervarietal hybridisation.
(a) (i) and (iii)
(b) (ii) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iii)
(d) (iii) and (iv)
Answer:
(a) (i) and (iii)
Question 13.
The characteristic which is not chosen for selective breeding in dairy animals is
(a) lactation period
(b) resistance to diseases
(c) good shelter
(d) nutritional requirement
Answer:
(c) good shelter
Assertion Reason Questions
Directions: In the following questions, the Assertions and the Reasons have been put forward. Read the statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following:
(A) Both the assertion and the reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(B) The assertion and the reason are correct but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(C) The assertion is true but the reason is false.
(D) Both the statements are false.
1. Assertion: Organic matter is important for crop production.
Reason: Organic matter provides major essential nutrients to the plant.
Answer:
(C) The assertion is true but the reason is false.
2. Assertion: Manure is better than fertilisers in maintaining soil fertility.
Reason: Manure improves soil structure and increases the water holding capacity of soil.
Answer:
(A) Both the assertion and the reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
3. Assertion: It is better to grow soyabean with maize in the same field.
Reason: Root nodules of soyabean plants have nitrogen fixing bacteria which enrich the soil with nitrogen.
Answer:
(A) Both the assertion and the reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
4. Assertion: Mixed cropping is a good practice in agriculture.
Reason: By mixed cropping, number of weeds in the field can be reduced.
Answer:
(C) The assertion is true but the reason is false.
5. Assertion: Grains to be stored should have low moisture level.
Reason: Low moisture level in grains inhibits the growth of bacteria and fungi.
Answer:
(A) Both the assertion and the reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
State one demerit with composite fish culture system.
Answer:
Many fishes breed only during monsoon so hormonal stimulation has to be given. Also, good quality fish seeds are not available.
Question 2.
State one importance of photoperiod in agriculture.
Answer:
Photoperiod in agriculture provides adequate light for flowering.
Question 3.
Name two micronutrients and two macronutrients which plants take from the soil.
Answer:
(a) Macronutrients are: calcium (Ca), magnesium (Mg)
(b) Micronutrients are: boron (B), chloride (Cl)
Question 4.
How does catla differ from mrigal?
Answer:
Catla belongs to genus Catla while mrigal belongs to genus Cirrhinus. Catla is a surface feeder and native to the Northern waters of India while mrigal is a bottom – feeder and native to the Ganges and Brahm putra rivers of India.
![]()
Question 5.
Name the two vitamins which are added in the poultry feed.
Answer:
Vitamins A and K.
Question 6.
From where do plants acquire the following nutrients?
(a) Nitrogen
(b) Hydrogen
Answer:
(a) Soil (b) Water
Question 7.
Which nutrients are supplied by cereals and pulses?
Answer:
Carbohydrates and proteins are supplied by cereals and pulses, respectively.
Question 8.
Name any two weeds of crop field.
Answer:
Xanthium (chota dhatura), Parthenium (gajar ghas), Cyperinus rotundus (motha).
Question 9.
Define animal husbandry.
Answer:
Animal husbandry is the practice of management and care of farm animals by humans for profit.
Question 10.
Mention two exam pies of crop combinations that are grown in mixed cropping.
Answer:
Some combinations of mixed cropping are:
(a) Wheat and mustard
(b) Maize and urad (pulse)
(c) Groundnut and sunflower
Question 11.
(a) Name an exotic variety of honeybee grown in India.
(b) What is the rearing of fish on a large scale called?
Answer:
(a) Apis cerana indica
(b) Pisciculture
Question 12.
Name two exotic cattle breeds with long lactation periods?
Answer:
The period of milk production after the birth of a calf is called lactation period. Jersey and Brown Swiss are two exotic cattle breeds having long lactation periods.
Question 13.
Between broiler and layer, which one matures earlier?
Answer:
Broilers have fast growth rate.
Question 14.
State the difference between compost and vermicompost.
Answer:
| Compost | Vermicompost |
| The compost is obtained by decomposition of organic waste like animal excreta, plant waste, etc., naturally due to decomposition by bacteria. | To fasten the process of decomposition redworms are added to the organic matter to obtain compost. |
Question 15.
Name two varieties of food required for milch animals.
Answer:
(a) Food to keep animals healthy,
(b) Food to increase lactation.
Question 16.
Define apiculture.
Answer:
Keeping bee for obtaining honey commercially is called apiculture.
Question 17.
Define hybridisation.
Answer:
Hybridisation refers to crossing between genetically dissimilar plants to obtain better variety of crops.
Analysing & Evaluating Questions
Question 18.
A farmer wants to use a crop variety that can give a good yield. What should he do to select the variety to get the desired result?
Answer:
A good crop yield can be obtained by selecting varieties having useful characteristics such as disease resistance, response to fertilizers and high yields.
Question 19.
A bee – keeper tries to collect a good yield of honey from his apiaries. However, he is unable to collect adequate honey. Suggest him a way to produce more honey.
Answer:
The bee – keeper should maintain his apiaries in between the fields of flowering plants or pasturage. This will allow bees to collect plenty of nectar and pollen from the variety of flowers. Also, the taste of honey depends on the variety of flowers available to the bees.
Question 20.
A dairy farmer wants to maintain a good and clean shelter for his dairy animals. How can he do this so that his animals stay healthy and produce clean milk?
Answer:
The shelter for dairy animals should have following features.
- It should be well – ventilated to allow fresh air to enter.
- It should have leakage – proof roof to protect them from rain, heat and cold.
- The floor of cattle shed should be sloping for easy cleaning and keeping it dry.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Distinguish between a mullet and a prawn.
Answer:
Mullet is a type of fish while prawn is a crustacean. Both live in water and serve as a food supplements worldwide. Prawn belongs to the phylum arthropoda, whereas mullet belongs to the group of pisces. So one can use their characteristic features to distinguish between the two.
Question 2.
What are genetically modified (GM) crops?
Answer:
GM (Genetically Modified) crops are the crops in which a gene from some other organism, like another plant or a microorganism, is inserted to get desired characteristics such as disease resistance, response to fertilisers, product quality and high yields. For example, varieties of cotton, maize, papaya, soyabean, sugar beet, squash, etc., have been modified genetically.
Question 3.
Give the technical terms for milk -producing females and farm labour animals.
Answer:
Milk – producing females are called milch animals (dairy animals), while the ones used for farm labour are called draught animals.
![]()
Question 4.
Mention the preventive and control measures used before the grains are stored.
Answer:
Cleaning of the produce before storage, proper drying of the produce first in sunlight and then in shade, and fumigation using chemicals that can kill pests.
Question 5.
What is the effect of deficiency of nutrients?
Answer:
Deficiency of nutrients affects physiological processes in plants including reproduction, growth, susceptibility to diseases, yield, etc. General health of the plants depends on the nutrients.
Question 6.
In what way does manure help in soil fertility?
Answer:
Manure helps in enriching the soil with mainly organic matter and small quantities of nutrients. The bulk of organic matter in the form of manure helps in increasing water holding capacity in sandy soil. In clayey soil, the large quantities of organic matter help in drainage and avoiding waterlogging.
Question 7.
Give two advantages of using chemical fertilisers over manure.
Answer:
Two advantages of using chemical fertilisers over manure are as follows:
- Chemical fertilisers are ‘nutrient specific’ and can provide specific elements like nitrogen, phosphorus or potassium to the soil in any desired quantity. Manure is, however, not nutrient specific.
- Chemical fertilisers, being soluble in water, are readily absorbed by the crops. This is not so in the case of manures.
Question 8.
What is green revolution?
Answer:
Bumper production of cereals (grains) using high-yielding varieties (HYV), higher dose of fertiliser and better modes of irrigation is known as green revolution.
Question 9.
What are pesticides? Give four methods of pest control.
Answer:
Pesticides are the chemicals used to control weeds, insects, rodents, fungi and diseases of plants. They include weedicides, insecticides and fungicides. Some methods of pest control are:
- Use of resistant varieties
- Optimum time of sowing the seeds
- Follow crop rotation and cropping pattern
- Deep ploughing of the field in summers to destroy undesirable weeds and pathogens.
Question 10.
Define organic farming.
Answer:
It is the farming in which no chemical fertilisers, pesticides or herbicides are used. It uses all organic matter for the growth of plants like manure, neem leaves as pesticides during grain storage, etc.
Question 11:
What desirable traits are focused to develop hybrids by cross-breeding indigenous and exotic breeds of fowl?
Answer:
Desirable traits are focused to develop hybrids by cross-breeding indigenous and exotic breeds of fowl:
- Number and quality of chicks
- Dwarf broiler parent for commercial chick production as they require less space and food.
- Summer adaptation capacity a tolerance to high temperature
- Low maintenance requirements
- Reduction in the size of the layer with ability to utilise more fibrous and cheaper diets which are formulated using agricultural by – products.
Question 12.
What decides the quality and quantity of honey production in an apiary?
Answer:
The quality and quantity of honey production in an apiary:
- For quality of honey: The pasturage, i.e., the kind of flowers available to the bees for nectar and pollen collection will determine the taste of the honey.
- For quantity of honey: Variety of bee used for the collection of honey. For example, A. mellifera is used to increase yield of honey.
Analysing & Evaluating Questions
Question 13.
What would happen if poultry birds are larger in size and have no summer adaptation capacity? In order to get small-sized poultry birds having summer adaptability, what method will be employed?
Answer:
The maintenance of optimum temperature is required for better egg production in poultry farming. The large size of birds with no adaptability to high temperature may cause decline in egg production. To obtain small-size birds with high – temperature adaptability during summer season, cross – breeding of poultry birds for desired characteristics can be done. Small size is also needed for better housing and less feed.
Question 14.
Figure below shows the two crop fields (plots A and B) that have been treated by manures and chemical fertilisers respectively, keeping other environmental factors same. Observe the graph and answer the following questions:
(a) Why does plot B show sudden increase and then gradual decrease in yield?
(b) Why is the highest peak in plot A graph slightly delayed?
(c) What is the reason for the different pattern of the two graphs?
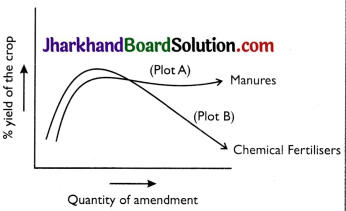
Answer:
(a) The addition of chemical fertilisers initially leads to rise in crop yield because of the release of the NPK (nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium) and some other nutrients in high quantity. The gradual decline in yield, as shown in plot B, is due to the continuous use of these fertilisers, which cause killing of useful microbes in the soil and alter the chemical composition of soil.
(b) Manures supply nutrients to the soil slowly, as these contain organic matter in high amount. Therefore, manures enrich the soil with nutrients slowly and continuously for a long time. This is the reason that the highest peak in plot A is delayed but maintained for longer period.
(c) In case of plot A, it indicates that the use of manure remains beneficial for longer duration in terms of crop yield and remains high even when the quantity of manure is increased. In case of plot B, chemical fertilisers when used for longer period cause various problems. The loss of soil fertility occurs due to killing of useful microbes in the soil that reduces decomposition of organic matter.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Name two fresh initiatives taken to save water and increase the water availability for agriculture.
Answer:
Two new irrigation systems have been developed to save water and increase the availability of water to the crops.
These are:
1. Drip irrigation system: Here, water is supplied to the roots of the plants directly in a drop wise manner. This prevents unnecessaiy wastage of water.

2. Sprinkler system: Here, water is sprinkled over the crops like it happens in rain. So, water is distributed uniformly and absorbed by the soil in a better way.

Question 2.
What are the factors for which variety improvement of crop is done?
Answer:
The factors for which variety improvement of crop is done are as follows:
- Higher yield: To increase productivity of the crop per acre.
- Improved quality: The quality of crop products varies from crop to crop, e.g., protein quality is important in pulses, oil quality in oilseeds, longer shelf life in fruits and vegetables.
- Biotic and abiotic resistance: Biotic factors are the diseases, insects and nematodes while abiotic factors are drought, salinity, water logging, heat, cold and frost which affect the crop productivity. Varieties resistant to these factors can increase the crop production.
- Change in maturity duration: Shorter maturity period of crop reduces the cost of crop production and makes the variety economical. Uniform maturity makes the harvesting process easy and reduces losses during harvesting.
- Wider adaptability: It allows the crops to be grown under different climatic conditions in different areas.
- Desirable agronomic characteristics: It increases productivity, (e) g., tallness and profuse branching are desirable characters for fodder crops; while dwarfness is desired in cereals, so that less nutrients are consumed by these crops.
Question 3.
Define manure. What are its three different types?
Answer:
Manure contains large quantities of organic matter and also supplies small quantities of nutrients to the soil. It is prepared by the decomposition of animal excreta and plant waste. It helps in enriching the soil with nutrients and organic matter and increasing soil fertility. On the basis of the kind of biological waste used to make manure, it can be classified into three types:
- Compost
- Vermicompost
- Green manure
1. Compost: It can be farm waste material such as livestock excreta (cow dung, etc.), vegetable waste, animal refuse, domestic waste, sewage, straw, eradicated weeds, etc. These materials are decomposed in pits and this process of decomposition is called composting.
2. Vermicompost: The compost which is made by the decomposition of plant and animal refuse with the help of redworms is called vermicompost.
3. Green manure: Prior to the sowing of the crop seeds, some plants like sun hemp or guar are grown and then mulched by ploughing them into the soil. These green plants thus turn into green manure which helps in enriching the soil in nitrogen and phosphorus.
![]()
Question 4.
What are fertilisers? Excessive use of fertilisers is not advisable. Explain.
Answer:
Fertilisers are commercially produced plant nutrients. Fertilisers supply nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium to the crops. They are used to ensure good vegetative growth (leaves, branches and flowers), giving rise to healthy plants. Fertilisers are an important factor in the higher yields of high – cost farming.
Excessive use of fertilisers is not advisable as:
- It leads to soil and water pollution.
- It can destroy the fertility of soil.
As the soil is not replenished, microorganisms in the soil are harmed by fertilisers.
Question 5.
How does intercropping differ from mixed cropping?
Or
What are the different cropping systems?
Answer:
It includes different ways of growing crops so as to get the maximum benefit. These different ways include the following:
1. Mixed cropping: Mixed cropping is growing two or more crops simultaneously on the same piece of land, e.g., wheat + gram, or wheat + mustard, or groundnut + sunflower. This reduces disease risk and gives some insurance against failure of one of the crops.
2. Intercropping: It involves growing two or more crops simultaneously on the same field in a definite proportion or pattern. A few rows of one crop alternate with a few rows of the other crop, e.g., soyabean + maize, or finger millet (bajra) + cowpea (lobia). The crops are selected such that their nutrient requirements are different. This ensures maximum utilisation of the nutrients supplied and also prevents pests and diseases from spreading to all the plants belonging to one crop in a field. This way, both the crops can give better yield.
3. Crop rotation: The growing of different crops on a piece of land in a pre-planned succession is known as crop rotation. Depending upon the duration, crop rotation is done for different crop combinations. The availability of moisture and irrigation facilities decide the choice of the crop to be cultivated after one harvest. If crop rotation is done properly, two or three crops can be grown in a year with good harvest.
Question 6.
Explain the various methods of irrigation in India.
Answer:
Proper irrigation is very important for the success of crops. Different kinds of irrigation systems include wells, canals, rivers and tanks.
- Wells: These are of two types, viz., dug wells and tube wells. In a dug well, water is collected from water bearing strata Tube wells can tap water from the deeper strat(a) From these wells, water is lifted by pumps for irrigation.
- Canal system: Water from the main river or reservoir is carried by canal into the field which is divided into branch canals having further distributaries to irrigate the field.
- River lift system: In areas where canal flow is insufficient or irregular due to inadequate reservoir release,
the lift system is more rational. Water is directly drawn from the rivers for supplementing irrigation in areas close to rivers, - Tanks: These are small storage reservoirs which intercept and store the run-off of smaller catchment areas.
Question 7.
Describe the different types of fisheries.
Answer:
The different types of fisheries are marine fisheries, mariculture, inland fisheries, aquaculture and capture fishing.
- Marine fisheries: They are caught using fishing nets. Large schools of fishes are located by satellites. Some are farmed in sea water.
- Mariculture: They are cultured in seawater. This culture of fisheries is called mariculture.
- Inland fisheries: The fisheries in fresh water resources like canals, ponds, reservoirs and rivers are called inland fisheries.
- Aquaculture: Culture of fish done in different water bodies is called aquaculture.
- Capture fishing: It is the method of obtaining fishes from natural resources, both marine and fresh water.
Question 8.
List six facilities that must be provided to cattle to ensure their good health and production of clean milk.
Answer:
Following facilities must be provided to cattle:
- Regular brushing to remove dirt and loosen hair.
- Well – ventilated roofed sheds for shelter that can protect them from rain, heat and cold.
- The floor of the cattle shed needs to be sloping so as to keep them dry and to facilitate cleaning and spraying of disinfectants at regular intervals.
- A balanced diet should be given which contains:
- roughage which provides high amount of fibre, and
- concentrate that provides high levels of proteins and other nutrients.
- Certain food additives containing micronutrients that promote the health and milk output of dairy animals.
- Vaccinations of farm animals, at proper time, against major viral and bacterial diseases.
Analysing & Evaluating Questions
Question 9.
Meena belongs to an agricultural family. She attended a seminar of agricultural practices organised by her school. By listening to the research work of scientists, she learned that spraying pesticides on crops is very harmful for the environment. Next day, she saw the stored tanks of pesticides at her home and told her parents not to use these in excessive quantity.
1. Why are pesticides used in crop fields?
2. What are the various types of pesticides used by the farmers?
3. How can Meena convince her parents to stop using pesticides in large quantities?
4. What alternatives could Meena suggest to her parents instead of using pesticides?
Answer:
- The pesticides are used in fields to protect the plants from disease – causing organisms, i.e., bacteria, fungi, viruses, nematodes and mycoplasmas.
- Depending on the type of organisms, they destroy, pesticides can be of the following types.
- Herbicides (for weeds)
- Insecticides (for insects)
- Fungicides (for fungi)
- Bactericides (for bacteria)
- Meena can tell her parents that regular and excessive use of pesticides contaminates water and soil, causing pollution in the environment. The pesticides affect the quality of food and leave residues on food items which may affect the health of consumers.
- She could suggest the use of biological control methods or use of disease-resistant varieties of crops.
Activity 1
Visit a weed – infested field in the month of July or August and make a list of the weeds and insect pests in the field.
Observations:
- Do it yourself.
- Weeds are unwanted plants in the cultivated field, e.g., Xanthium (chota dhatura), Parthenium (gajar ghas) and Cyperinus rotundus (motha). They compete for food, space and light.
- Some insect pests of crop fields include aphids, blister beetles, common stalk borer, com borer, flour beetle, etc.
Activity 2
Visit a local poultry farm. Observe the types of breeds and note the type of ration, housing and lighting facilities given to them. Identify the layers and broilers.
Observations:
- Do it yourself and note down:
- types of breeds of poultry: Aseel, white Leghorn, Rhode Island Red.
- types of ration, housing and lighting facilities given to them.
- Identify the layers, for example, White leghorn, Rhode Island Red, and broilers, for example, Plymouth Rock or Aseel or any other.
Value Based Questions
Question 1.
A group of eco – club students made a compost pit in the school, they collected all the biodegradable waste from the school canteen and used it to prepare the compost.
1. Name two wastes that can be used for the compost and two wastes obtained from canteen which cannot be used for the compost making?
2. What is the other important component required for making the compost?
3. What values of eco – club students are reflected in this act?
Answer:
The compost:
- Two wastes used for compost are vegetable peels and fruit peels. Two waste materials that cannot be used as compost are polythene bags and plastic items.
- Bacteria and fungi present in soil are the other important component for making compost.
- Eco – club students reflect the value of group work and responsible citizens.
Question 2.
Large number of Bhetki fish died and got crushed in the turbines of hydroelectric power stations while
they migrated from river to sea The environmentalist gave power plant the solution of this problem. Now all Bhetki fish is removed with the help of a special technique and hence do not enter the turbines to crush and die.
1. Suggest two different varieties of fish.
2. What value of environmentalist is reflected in the above case?
Answer:
The turbines to crush and die:
- Two varieties of fish are bony and cartilaginous.
- Environmentalist showed the value of concern and caring individuals.