JAC Board Class 9th Social Science Solutions Geography Chapter 3 Drainage
JAC Class 9th Geography Drainage InText Questions and Answers
Find Out (Page No. 17)
Question 1.
Which river has the largest basin in India?
Answer:
Ganga river.
Find Out (Page No. 22)
Question 1.
The name of the biggest waterfall in India.
Answer:
Jog Falls (Karnataka) – 253 m (830 ft.)
Activity (Page No. 23)
Question 1.
Make a list of natural and artificial lakes with the help of the atlas.
Answer:
Natural Lakes: Nainital, Sambhar, Loktak, Pulicat, Bhimtal, Wular, Dal, Chilika, Kolleru and Barapani.
Artificial Lakes: Hirakud, Jaisamand lake, Nagaijuna Sagar, Gandhi Sagar, Gobind Sagar, Govind Ballabh Pant Sagar, Rana Pratap Sagar, Nizam Sagar.
JAC Class 9th Geography Drainage Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below:
1. In which of the following states is the Wular lake located?
(a) Rajasthan
(b) Uttar Pradesh
(c) Punjab
(d) Jammu and Kashmir.
Answer:
(d) Jammu and Kashmir.
2. The river Narmada has its source at:
(a) Satpura
(b) Brahmagiri
(c) Amarkantak
(d) Slopes of the Western Ghats.
Answer:
(c) Amarkantak
3. Which one of the following lakes is a saltwater lake?
(a) Sambhar
(b) Dal
(c) Wular
(d) Gobind Sagar.
Answer:
(a) Sambhar
4. Which one of the following is the longest river of the Peninsular India ?
(a) Narmada
(b) Krishna
(c) Godavari
(d) Mahanadi.
Answer:
(c) Godavari
5. Which one amongst the following rivers flows through a rift valley?
(a) Mahanadi
(b) Tungabhadra
(c) Krishna
(d) Tapi
Answer:
(d) Tapi
![]()
Question 2.
Answer the following questions briefly:
1. What is meant by a water divide? Give an example.
Answer:
Any elevated area, such as a mountain or an upland, which separates two drainage basins, is known as a water divide. Example Ambala. It is located between the Indus and the Ganga river.
2. Which is the largest river basin in India?
Answer:
The Ganga river basin.
3. Where do the rivers Indus and Ganga have their origin?
Answer:
The river Indus originates in Tibet near the Mansarovar Lake and the Ganga originates at the Gangotri glacier. Both of them have their origin in the Himalayas.
4. Name two headstreams of the Ganga. Where do they meet to form the Ganga?
Answer:
The two headstreams of the Ganga are Bhagirathi and Alaknanda.They meet at
Devaprayag in Uttarakhand to form the Ganga.
5. Why does the Brahmaputra in its Tibetan part have less silt, despite a longer course?
Answer:
In Tibet, the river Brahmaputra carries smallest volume of water (due to less rain¬fall) and less silt as it is a cold and dry area. But when this river enters India, it passes through a region of high rainfall and thus, carries a large volume of water and considerable amount of silt.
6. Which two Peninsular rivers flow through troughs?
Answer:
The Narmada and the Tapi flow through troughs.
7. State some economic benefits of rivers and lakes.
Answer:
Some economic benefits of rivers and lakes are:
- They can be used for developing hydel power.
- They can be used for irrigation.
- They help to develop tourism and provide recreation.
Question 3.
Below are given names of a few lakes of India. Group them under two categories Natural lakes and lakes created by human beings: Wular, Dal, Nainital, Bhimtal, Gobind Sagar, Loktak, Barapani, Chilika, Sambhar, Rana Pratap Sagar, Nizam Sagar, Pulicat, Nagarjuna Sagar, Hirakud.
Answer:
Natural lakes: Wular, Dal, Nainital, Bhimtal, Loktak, Barapani, Chilika, Sambhar, Pulicat.
Man – made lakes: Gobind Sagar, Rana Pratap Sagar, Nizam Sagar, Nagarjuna Sagar, Hirakud.
![]()
Question 4.
Discuss the significant difference between the Himalayan and the Peninsular rivers.
Answer:
Difference between the Himalayan and the Peninsular rivers:
| Basic | The Himalayan Rivers | The Peninsular Rivers |
| 1. Source | These rivers originate from the lofty Himalayan ranges and are thus named as the Himalayan rivers. | These rivers originate in the Penin-sular plateau and are thus named as Peninsular rivers. |
| 2. Basins | These rivers have large basins and catchment areas. | These rivers have small basins and catchment areas. |
| 3. Valleys | The Himalayan rivers form deep I-shaped valleys called the gorges. | The Peninsular rivers flow in comparatively shallow valleys. |
| 4. Water flow | The Himalayan rivers are peren¬nial in nature, i.e. the water flows throughout the year in these rivers. | Most of the Peninsular rivers receive water only from rainfall and water flows in these rivers in rainy season only, so these rivers are seasonal or non-perennial. |
| 5. Stage | They are still in a youthful stage. | These are mature rivers. |
| 6. Meander | The Himalayan rivers form meanders and often shift their courses. | The rivers of the Peninsular plateau follow more or less straight course and do not form meanders. |
| 7. Deltas and Estuaries | The Himalayan rivers form big del-tas at their mouths, for example the Ganga Brahmaputra delta is the largest delta in the world. | The Peninsular rivers form comparatively small deltas. Narmada and Tapti form estuaries. |
Question 5.
Compare the east-flowing and the west-flowing rivers of the Peninsular plateau.
Answer:
Comparison between the East-Flowing and the West-flowing Peninsular rivers:
| The East-Flowing Rivers | The Wast-Flowing Rivers |
| 1. These rivers drain into the Bay of Bengal. | 1. These rivers drain into the Arabian Sea. |
| 2. These rivers form deltas. | 2. These rivers form estuaries. |
| 3. These rivers have large tributaries. | 3. These rivers have small-sized tributaries. |
| 4. These rivers flow through shallow valleys. | 4. These rivers flow through rift valleys. |
| 5. Important east-flowing rivers are Mahanadi, Godavari, Krishna and Kaveri. | 5. Important west-flowing rivers are Narmada and Tapi. |
![]()
Question 6.
Why are rivers important for the country’s economy?
Answer:
The importance of rivers for the country’s economy can be summarised as follows:
1. They provide water which is necessary for the survival of man.
2. They provide water for irrigation.
3. They make the soil fertile which can be used for cultivation.
4. They are also able to provide food as fish is available in plenty.
5. They serve as the arteries of commerce.
6. They are used as a means of transportation.
7. They are also used for the generation of electricity.
Question 7.
(i) On an outline map of India mark and label the following rivers: Indus, Ganga, Satluj, Damodar, Krishna, Narmada, Tapi, Mahanadi and Brahmaputra.
Answer:
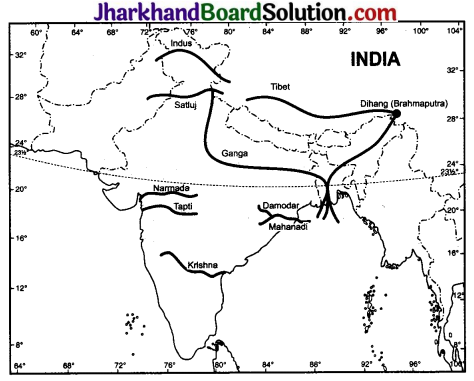
![]()
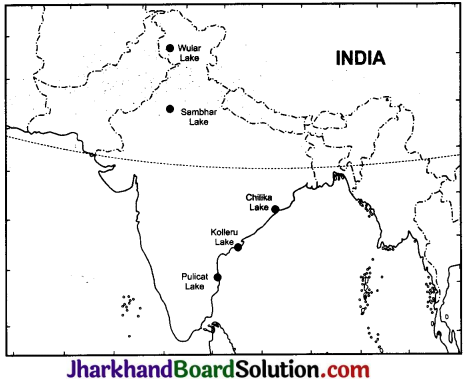
Question 8.
(ii) On an outline map of India mark and label the following lakes: Chilika, Sambhar, Wular, Pulicat, Kolleru.
Answer:
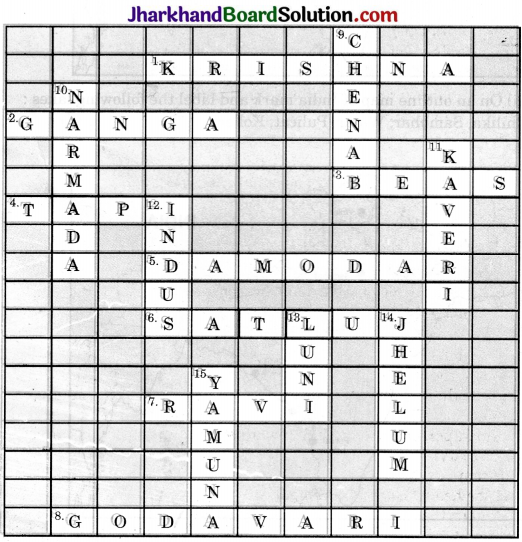
Solve this crossword puzzle with the help of given clues:
Across
1. Nagarjuna Sagar is a river valley project. Name the river.
2. The longest river of India.
3. The river which originates from a place known as Beas Kund.
4. The river which rises in the Betul district of MP and flows westwards.
5. The river which was known as the “sorrow” of West Bengal.
6. The river on which the reservoir for Indira Gandhi Canal has been built.
7. The river whose source lies near Rohtang Pass.
8. The longest river of Peninsular India.
Down
9. A tributary of Indus originating from Himachal Pradesh.
10. The river flowing through fault, drains into the Arabian Sea.
11. A river of South India, which receives rainwater both in summer and winter.
12. A river which flows through Ladakh, Gilgit and Pakistan.
13. An important river of the Indian desert.
14. The river which joins Chenab in Pakistan.
15. A river which rises at Yamunotri Glacier.
Answer: