JAC Board Class 7th Social Science Solutions History Chapter 1 Tracing Changes Through a Thousand Years
JAC Class 7th History Tracing Changes Through a Thousand Years InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
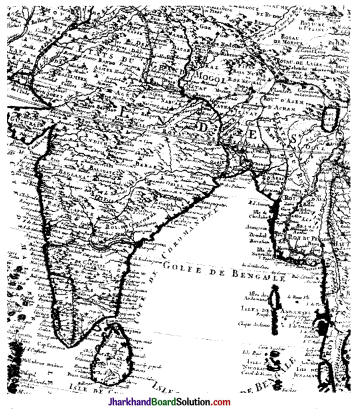
Look at the areas in the interior of the subcontinent on Map 2. Are they as detailed as those on the coast? Follow the course of the River Ganga and see how it is shown. Why do you think there is a difference in the level of detail and accuracy between the coastal and inland areas in this map?
Answer:
No, the areas are not as detailed as those oh the coast. The European merchants and sailors who used this map, did not go to the inland places of the subcontinent much as they interacted with the coastal areas. Hence, the level of detail and accuracy of coastal areas is better than the inland areas, in the map.
Page 3
Question 2.
Can you think of any other words whose meanings change in different contexts?
Answer:
Yes, word-Ruler (King) Ruler (Law makers)
Page 4
Question 3.
When was paper more expensive and easily available in the thirteenth or the fourteenth century?
Answer:
The paper was expensive in 13th century and in 14th century it was easily available.
![]()
Question 4.
Of the technological, economic, social and cultural changes described in this section, which do you think were most significant in the town or village in which you live?
Answer:
Secondary occupations are done in town and in villages they do primary occupations such as agriculture.
Question 5.
Why do you think rulers made such claims?
Answer:
They were real rulers of the country. They were supreme. No other ruler could fight them. They showed others that they are the most powerful rulers. That is why, they made such claims.
Question 6.
Make a list of the languages mentioned by Amir Khusrau. Prepare another list of names of languages spoken today in the regions he mentioned. Underline names that are similar and circle those that are different.
Answer:
Languages mentioned by Amir Khusrau are Lahori, Sindhi, Kashmiri, Dvarsamudri, Gujari, Gauri, Hindawi. List of names of languages spoken today in the regions are Kashmiri, Awadhi, Pahari, Himachali, Punjabi, Gujarati, Sindhi, Marathi, Hindi, Urdu, Bengali, Oriya, Assamese, English, Tamil, Telegu, Gurkhati, Lepena. Similar are Awadhi, Kashmiri, Sindhi Different are Remaining all.
Question 7.
Did you notice that the names by which languages are known have changed over time?
Answer:
Yes, most of them have changed over time.
Answer:
No, the areas are not as detailed as those oh the coast. The European merchants and sailors who used this map, did not go to the inland places of the subcontinent much as they interacted with the coastal areas. Hence, the level of detail and accuracy of coastal areas is better than the inland areas, in the map.
![]()
Question 8.
Find out whether and for how long your state was part of these pan- regional empires.
Ans:
Delhi for about thousand years (700 to 1750), if you reside in Delhi.
Question 9.
Do you remember what Amir Khusrau had to say regarding Sanskrit, Knowledge and Brahmanas?
Ans:
According to Amir Khusrau, Sanskrit was an old language, does not belong to any religion and Brahmanas were great scholars of Sanskrit.
Page 14
Question 10.
Imagine you are a historian. Choose one of the themes mentioned in this chapter, such as economic, social or political history, and discuss why you think it would be interesting to find out the history of that theme.
Answer:
I would choose social and political history. It would be interesting to find out the history of social and political changes because:
- This period saw emergence of new foods beverages.
- New technologies appeared.
- It was period of mobility when people travelled long distances.
- Extension of agriculture brought social changes.
- Important changes occurred in religion.
- Politically different groups become important.
JAC Class 7th History Tracing Changes Through a Thousand Years Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Who was considered a “foreigner” in the past?
Answer:
The word “foreigner” was used in medieval period for any stranger or unknown person who was not a part of the certain society or culture in a said village. A forest dweller might be considered as a foreigner by city dweller. In Hindi a foreigner is termed as pardesi.
Question 2.
State whether true or false:
(a) We do not find inscriptions for the period after 700.
(b) The Marathas asserted their political importance during this period.
(c) Forest-dwellers were sometimes pushed out of their lands with the spread of agricultural settlements.
(d) Sultan Ghiyasuddin Balban controlled Assam, Manipur and Kashmir.
Ans:
(a) False
(b) False
(c) True
(d) False
Question 3.
Fill in the blanks:
(a) Archives are places where………are kept.
(b) …….. was a fourteenth century chronicler.
(c) …….’……..’…….’……….. and …… were some of the new crops introduced into the subcontinent during this period.
Answer:
(a) manuscripts
(b) Ziyauddin Barani
(c) Com, chillies, potatoes, tea, coffee.
Question 4.
List some of the technological changes associated with this period.
Answer:
Some important technological changes associated with this period were:
- The use of spinning wheel in weaving
- The use of Persian wheel in irrigation
- The use of firearms in combat.
Question 5.
What were some of the major religious developments during this period?
Answer:
Some of the major religious developments during this period were as follows:
- Hinduism saw many changes including worship of deities.
- Kings built new temples.
- Brahmanas emerged as a strong group in society. They were the priests in temples.
- The idea of Bhakti emerged.
- The new teaching of Question uran was brought by merchants and migrants. It is the holy book of Muslims.
- They had two sub sects – Shia and Sunni.
- A class of patrons emerged as they were the rulers who provided protection and shelter to ulemas.
(Let’s Understand)
Question 6.
In what ways has the meaning of the term ‘Hindustan’ changed over the centuries?
Answer:
The meaning of the term ‘Hindustan’ changed over the centuries in the • following way:
- ‘Hindustan’ was first used by Minhaj-i-Siraj in 13th century. It included the areas of Punjab, Haryana and the land between Ganga and Yamuna rivers. He used it in a political sense that were a segment of the dominions of the Delhi Sultanate.
- In the sixteenth century, Babur used the term ‘Hindustan’ to describe the geography, fauna and culture of the subcontinent.
- Amir Khusrau, a fourteenth century poet also used the term ‘Hind’ to describe the geographical and cultural entity.
- The term did not carry the political and national meanings as the term ‘India’ is used today.
Question 7.
How were the affairs of jatis regulated?
Answer:
The affairs of Jatis were regulated in the following manner:
- Jatis formulated their own rules and regulations to manage the members.
- These regulations were enforced by the Jati Panchayat.
- They were also required to follow the rule of the villages. Many villages were governed by a Chieftain.
- Jatis were divided on the basis of economic and social position.
Question 8.
What does the term pan-regional empire mean?
Answer:
The term pan-regional empire means an empire spanning over various regions. Some of the dynasties are Mughals, Cholas, Khaljis and the Tughluqs.
(Let’s Discuss)
Question 9.
What are the difficulties historians face in using manuscripts?
Answer:
Historians faced many difficulties in using manuscripts:
- In early days, it was handwritten. Palm leaves were used to write as paper.
- Historians translated the facts as per the manuscripts which they got.
- Different historians presented it in their own manner as the handwriting was not always clear. They introduced some changes as well. Later it was quite difficult to accept which one was the original manuscript.
Question 10.
How do historians divide the past into periods? Do they face any problems in doing so?
Answer:
Historians divide past into periods on the basis of continuity. This continuity is further based on coins, inscriptions, architecture and textual records. Historians divided the past into periods by considering economic, social, cultural and religious changes. British historians divided the Indian history into three periods Hindu, Muslim and British. They only considered the fact that no significant changes occurred other than the religion of the rulers. They ignored the rich diversity of the subcontinent. Historians of the modem days divide history into ancient, medieval and modem history.
Significant changes occurred in the past thousand years. Historians vary to classify the periods as few takes periodization and some consider the socio economic factors of the past to characterize. We see that 16th century was not same as 18th century. Hence, describing the entire period as one historical unit is quite difficult.
(Let’s Do)
Question 11.
Compare either Map 1 or Map 2 with the present day map of the subcontinent, listing as many similarities and differences as you can find.
Answer:

- The Arab geographer, Al-Idrisi made Map 1 in 1154 CE.
- It shows the Indian subcontinent from this larger world map.
- It shows, South India at that place where North India is at present and Sri Lanka is the island at the top.
- Places names are in Arabic. As Kanauj in Uttar Pradesh has been mentioned as Question anauj.
- Present day maps of the subcontinent is more clear as it shows clear directions.
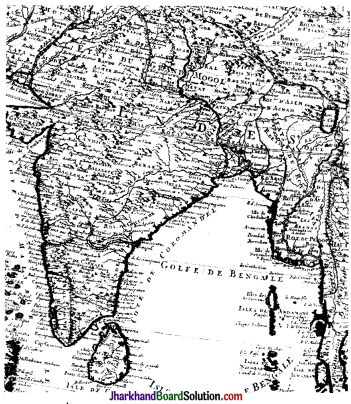
- The French cartographer in 1720 made Map 2. Map 1 is quite different from Map 2. Map 2 was made nearly 600 years later.
- Information provided about the subcontinent changed a lot. Coastal areas are more comprehensive and detailed.
- Cartography technique was different. Hence, this Map 2 appears to be more known and familiar to us.
Question 12.
Find out where records are kept in your village or city. Who writes these • records? Is there an archive? Who manages it? What kind of documents are stored there? Who are the people who use it?
Answer:
In our village, records are kept in the Panchayat office. In cities, records are kept in the municipal offices or municipal corporation. In villages, records are written by Gram Sevak who is a government employee. In cities these records are written and maintained by clerks. In villages, there are no archive and Sarpanch manages it. In cities, there are archives. The kind of documents stored there are government records such as details about land of the village, data of birth and deaths, public properties, rare manuscripts and books. Government officials, Researchers and Scholars use them.
JAC Class 7th History Tracing Changes Through a Thousand Years Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Al-Idrisi drawn the map in
(a) 12th century
(b) 14th century
(c) 1th century
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) 12th century
Question 2.
Cartographer is a person who draws
(a) paintings
(b) maps
(c) pictures
(d) All of these
Answer:
(b) maps
![]()
Question 3.
In Al-Idrisi’s map, places are named in –
(a) Arabic
(b) Persian
(c) Sanskrit
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Arabic
Question 4. In 1720s, maps were made by
(a) German cartographers
(b) Arabic cartographers
(c) French cartographers
(d) English cartographers
Answer:
(b) Arabic cartographers
Question 5.
In 13th century, the term Hindustan was used by the chronicler
(a) Ziyauddin Barani
(b) Al-Idrisi
(c) Babur
(d) Minhaj-i-Siraj
Answer:
(d) Minhaj-i-Siraj
Question 6.
Amir Khusrau was a poet in
(a) Fourteenth century
(b) Sixteenth century
(c) Eleventh century
(d) Thirteenth century
Answer:
(a) Fourteenth century
Question 7.
The term ‘foreigner’ in Hindi means
(a) Ajnabi
(b) Pardesi
(c) Kshatriyas
(d) All of these
Answer:
(b) Pardesi
![]()
Question 8.
Historians used the sources to study this period
(a) Architecture
(b) coins
(c) inscriptions
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 9.
Paper become cheaper and readily available in
(a) Twelfth century
(b) Thirteenth century
(c) Fourteenth century
(d) Eighth century
Answer:
(c) Fourteenth century
Question 10.
Ziyauddin Barani was a 14th century
(a) poet
(b) chronicler
(c) cartographer
(d) painter
Answer:
(b) chronicler
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is the work of cartographer?
Answer:
A cartographer is a person who draws niaps.
Question 2.
What do you mean by archives?
Answer:
Archives are places where manuscripts were collected.
Question 3.
How the locations are shown in Al- Idrisi’s map?
Answer:
In his map, south India is shown at the present north India and at the top is the Sri Lankan island.
Question 4.
What is the study of coins called?
Answer:
The study of coins is called numismatics.
Question 5.
What do you mean by patron?
Answer:
Patron is an influential wealthy individual who supports another person who can be an artist, craftsperson, a learned man or a noble.
![]()
Question 6.
Which term did Minhaj-i-Siraj used and when?
Answer:
The term was ‘Hindustan’ in the 13th century.
Question 7.
Shia and Sunni are sects of which religion?
Answer:
Islam.
Question 8.
What do you mean by pan-regional empire?
Answer:
Pan-regional empire means empire spanning in diverse regions.
Question 9.
What was the name given by Greeks to Indian subcontinent?
Answer:
Indus.
Question 10.
What are the sources used by the historians to study a particular period of history?
Answer:
The sources are coins, textual records, inscriptions and architectures to study a particular period.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Define the following terms Manuscript, Medieval Period, Numismatics, Epigraphy, Archive.
Answer:
Manuscript – The script written by author /writer in his own handwriting. Medieval Period – The period between 700 CE to 1750 CE in Indian history is called medieval period. Numismatics – It is the study of coins. Epigraphy- It is the study of inscriptions. Archive – A place where all manuscripts and documents are stored.
Question 2.
What do the term scribes mean? How did the scribes worked with manuscripts?
Answer:
Scribes were those person who copy down the manuscripts. By hand, manuscripts were copied.
Question 3.
How are navigations and travelogues are important written source?
Answer:
During medieval period, many merchants and sailors visited India. Their writing about the places and the people they met gives us lots of information. They give details about economic, social and cultural things about that place.
Question 4.
How the value of paper was different in thirteenth and fourteenth century?
Answer:
The value of paper was very different in thirteenth and fourteenth century. In 13th century, a learned person wanted to copy a book but he didn’t have much paper, so he washed a portion of the manuscript which he didn’t required and dried the paper and used it. But in 14th century, if any person bought some food in the market and the shopkeeper would wrap it for you in the paper if you are fortunate enough.
![]()
Question 5.
Medieval period helped in the development of Indian history. How?
Answer:
Medieval period has been very helpful in the development of Indian history because of the following reasons:
- Many modem languages developed during this period which we speak nowadays.
- Some of the food items and clothes we wear became very popular during this period.
- Our current religious faiths such as Sikhism, Islam can be traced.
Question 6.
There was a dramatic increase in the variety of textual records during this period. Why?
Answer:
There was a dramatic increase in the variety of textual records during this period because paper was readily available and also very cheap. People started writing holy texts, chronicles of mlers, letters and teachings of saints, judicial records, register of accounts and taxes on papers which can be kept properly.
Question 7.
Describe chronicles.
Answer:
A record of the rule of the kings and life at the court is called a chronicle. Most kings had court chroniclers who wrote in detail about what happened during their reign. Some important chronicles of the medieval period are: Rajatarangini by Kalhana, which is a history of the king of Kashmir.Tarikh-i-Firoz Shahi by Ziyauddin Barani, which describes the history of the Sultans of Delhi till the reign of Firoz Shah Tughluq
Question 8.
Many changes took place during 700 CE and 1750 CE. List some of them.
Answer:
Many changes took place during 700 CE and 1750 CE. Many technologies came into existence like the Persian wheel in irrigation, the spinning wheel in weaving and firearms in combat. New food and beverages also arrived in the subcontinent like potatoes,chillies, com, tea, and coffee.
Question 9.
What do you mean by JatiPanchayafl Who was the chief of the village?
Answer:
The assembly of elders which controlled the conduct of the members of their jati was called the Jati Panchayat. Villages were controlled by chieftains. Even the smaller jati panchayats were obligated to follow the village administration.
![]()
Question 10.
Which group of people become important during medieval period and why?
Answer:
The group of people who becameimportant in this period were the Rajputs, a name derived from ‘Rajputra’ which means the son of a ruler. They included not just rulers but also soldiers and commanders who served in the armies of different rulers in the subcontinent. They claimed to be a kshatriya in caste status.
Question 11.
Why Brahmanas earned a respect in the society?
Answer:
Brahmanas earned respect in the society because they had the knowledge of Sanskrit which no one in general had. Their position was very dominant and consolidated by the support of their patrons – new rulers searching for power and dignity.
Question 12.
Muslim religion has two sects. What are they? How do they differ from each other?
Answer:
The two sects are Shia and Sunni. Shia muslims are those who believe that the Prophet Muhammad’s son-in-law Ali, was the legitimate leader of the Muslim community. Whereas, Sunni muslims are those who accepted the authority of the early leaders (Khalifas) of the community and the succeeding Khalifas.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain medieval period of Indian history. It is termed as one of continuity and change. Why?
Answer:
History is divided into ancient, medieval and modem periods to make it easy to understand. The word medieval comes from.Latin word which means middle age. It saw many changes with the arrival of migrated people to the land. The society and economy of the subcontinent was transformed and reached a high level of richness and prosperity which attracted many merchants and traders.
In early medieval period, the Cholas and Rajput kings dominated the socio economic and political history of the country. In the later medieval period, the Turks and the regional kingdoms which emerged after the end of the Delhi Sultanate and the Mughals largely dominated the subcontinent.
Question 2.
What was the change in the religion during this period? Explain the major developments.
Answer:
During these thousand years, i.e., 700 CE to 1750 CE there has been major changes in religion. It was very prominent in Hinduism. The worship of new deities, the construction of temples by the kings and royals and the growing importance of Brahmanas, priests as a major group in society emerged as the changes. Also the idea of bhakti emerged.
Merchants, traders and migrants brought the teachings of 0uran, the holy book of Muslims. Patron class emerged during this period. They were the rulers who provided shelter and protection to the ulamas, the learned theologists and jurists. During this period, muslims were divided into two sects or groups Shia and Sunni. Shia Muslims believed in Prophet Muhammad’s authority while the Sunnis accepted the authority of the early leaders Khalifas.
![]()
Question 3.
Discuss how coins, inscriptions and architectures are useful sources of information on medieval period.
Answer:
Coins, inscriptions, architectures are very useful sources of information on medieval period. Coins help us to know better the economic conditions of a kingdom. They were generally issued by the emperor of the empire. It helps us to know the provincial extent and duration of reign of the ruler. It helps historians to clarify their doubts about any particular event or dates which are mentioned in the book. Inscriptions are one of the major sources of information about Indian history.
Written records are engraved on stones, pillars, monuments, wall of temples and copper plates. They provide us information about the rulers, their kingdoms and some major events, geographical areas of the kingdom, etc. Inscriptions on copper plates were found around south Indian temples of medieval period. Monuments provide us the information about when they have been constructed and who built it. We get information on socio-economic, political conditions from the religious place of that time. Temples, tombs, mosque, stupas, palaces, forts, help us. Forts in Delhi, Jaipur, Hyderabad give an understanding of the architectural styles of that period.