JAC Board Class 8th Social Science Solutions Civics Chapter 1 The Indian Constitution
JAC Class 8th Civics The Indian Constitution InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Discuss with your teacher what you understand by the term ‘constitutive’. Provide one example of ‘constitutive rules’ from your everyday life.
Answer:
Students need to attempt it on their own (with the help of their teacher).
Hint:
Constitutive means fundamental.
![]()
Question 2.
Why did the people of Nepal want a new Constitution?
Answer:
The people of Nepal wanted a new Constitution because the country got a new democratic government and they were free from monarch rule. Hence, they need to change all its constitutive rules to make a new country for the people of Nepal.
Page 7

Question 3.
In what way is the class monitor misusing his power?
Answer:
The class monitor made false complains about Anil to the teacher. In this way, he was misusing his power. Though Anil did not do anything but the class monitor convinced the teacher that Anil was not obeying him and was talking loudly in the absence of teacher. When the teacher heard this, she was angry • with Anil and didn’t listen to Anil and scolded and punished him.
Question 4.
In which of the following situations is a minister misusing his power:
(a) refuses to sanction a project of his ministry for sound technical reasons;
(b) threatens to send his security staff to rough up his neighbour;
(c) calls up the police station asking them not to register a complaint that is likely to be filed against his relative.
Answer:
A minister misusing his power in thefollowing situations:
(b) threatens to send his security staff to rough up his neighbour;
(c) calls up the police station asking them not to register a complaint that is likely to be filed against his relative.
Page 8

Question 5.
Who is in a minority in the above storyboard? In what way is this minority being dominated by the decision taken by the majority?
Answer:
In the above storyboard, girls are in a minority. The minority are being dominated by the majority as they imposed their wish. Hence, girls have to do what the boys want.
Page 9

Question 6.
Why was Shabnam happy that she had not watched TV? What would you have done in a similar situation?
Answer:
Shabnam was happy that she had not watched TV because instead of watching her favoutite show, she revised her 2 chapters for the test. As a result, she performed well in the rest as most of the questions came from that 2 chapters only.
If I would have been in Shabnam’s place, I would have done the same.
Page 13
Question 7.
Discuss the difference between State and Government with your teacher.
Answer:
| State | Government |
| The state refers to the political institution that represents a sovereign people who occupied a definite area. Such as the different states of India. | It is responsible for administering and enforcing law in the whole country. It can change with elections. |
Question 8.
Which Fundamental Rights will the following situations violate:
(a) If a 13-year-old child is working in a factory manufacturing carpets.
(b) If a politician in one state decides to not allow labourers from other states to work in his state.
(c) If a group of people are not given permission to open a Telugu- medium school in Kerala.
(d) If the government decides not to promote an officer of the armed forces for being a woman.
Answer:
Fundamental Rights that violate the situations:
(a) Right against Exploitation
(b) Right o Freedom
(c) Cultural and Educational Rights
(d) Right to Equality.
Page 15
Question 9.
The Constitution also mentions Fundamental Duties. Find out with the help of your teacher what these include and why it is important for citizens in a democracy to observe these.
Answer:
Students need to do it on their own with the help of teacher.
![]()
Question 10.
Illustrate each of the 11 Fundamental Duties with drawings, pictures, poems or songs and discuss them in the classroom.
Answer:
Students need to do it on their own.
JAC Class 8th Civics The Indian Constitution Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Why does a democratic country need a Constitution?
Answer:
A democratic country needs a Constitution because of the following reasons:
- Constitution lays out certain ideals that form the basis of the kind of country that we as citizens aspire to live in.
- It lays out all important instructions and regulations that govern decision making within different societies of the country.
- Constitution provides as a strength of rules and principles as the basis of the way in which people want their country to be governed.
- It presents rules and regulations to safeguard the interests of minorities and prevent them from being dominated by the majority section.
- It also lays down certain directives based on which people belonging to different religions and communities can co-exist in harmony.
- It provides rules that guard against this misuse of authority by our political leaders.
- It also provides certain fundamental rights to its citizens and protects their freedom.
Question 2.
Look at the wordings of the two documents given below. The first column is from the 1990 Nepal Constitution. The second column is from the more recent Constitution of Nepal.
| 1990 Constitution of Nepal Part 7: Executive | 2015 Constitution of’ Nepal Part 7: Federal Executive |
| Article 35: Executive Power: The executive power of the Kingdom of Nepal shall be vested in His Majesty and the Council of Ministers. | Article 75: Executive Power: The executive power of Nepal shall, pursuant to this Constitution and law, be vested in the Council of Ministers |
What is the difference in who exercises ‘Executive Power’ in the above two Constitutions of Nepal?
Answer:
The difference in exercises ‘Executive Power’ in the above two Constitutions of Nepal are:
| 1990 Constitution of Nepal Part 7: Executive | 2015 Constitution of’ Nepal Part 7: Federal Executive |
| Article 35 of the 1990 Constitution of Nepal states that the whole powers to rule the country is vested in the king of the country and the ministers appointed under him. | Article 75 of the 2015 Constitution of Nepal states that the rules and management of the country will be based on the laws mentioned in the Constitution of the country under the supervision of the council of ministers. |
Question 3.
What would happen if there were no restrictions on the power of elected representatives?
Answer:
If there are no restrictions on the power of the elected representatives then the leaders might misuse their powers and authority. The outcome would have emerged as injustice against the people of the country. Therefore, the Indian constitution has provided certain guidelines to safeguard the country against such misuse of power by our political leaders.
Question 4.
In each of the following situations, identify the minority. Write one reason why you think it is important to respect the views of the minority in each of these situations.
(a) In a school with 30 teachers, 20 of them are male.
(b) In a city, 5 per cent of the population are Buddhists.
(c) In a factory mess for all employees, 80 per cent are vegetarians.
(d) In a class of 50 students, 40 belong to more well-off families.
Answer:
The minorities are:
(a) Female teachers :
The 10 female teachers teaching in the school come under the minority category. It is important to respect the views of the minority so that they do not feel underpowered by the majority. They also contribute to the standard of teacher.
(b) Buddhists:
Buddhist population are in minority and their views should be respected. People should be careful while taking any decision for the interest of the majority as it should not hurt the religious feelings or beliefs of the Buddhist population.
(c) Non-Vegetarians:
20 percent of non-vegetarians are minority. In the factory mess, it is important that the food prepared must be prepared to fulfill the diet requirements of both vegetarians and non-vegetarians.
(d) Not from well-off families – The 10 students come under the minority category who do not belong to well- off families. It is important to respect their views as they are also equal to others and there should be no kind of discrimination based on the financial backgrounds of students in the class.
![]()
Question 5.
The column on the left lists some of the key features of the Indian Constitution. In the other column write two sentences, in your own words, on why you think this feature is important:
| Key Features Significance | |
| Federalism | |
| Separation of Powers | |
| Fundamental Rights | |
| Parliamentary Form of Government | |
| Key Features | Significance |
| Federalism | Both Center and states have their respective powers and cooperate with each other keeping in view the integrity and unity of the nation. |
| Separation of Powers | Separate powers are given to legislatives, executives |
| Fundamental Rights | Rights are given to all citizens without any discrimination for their development on the basis of caste, creed, religion or sex. |
| Parliamentary Form | Parliament has two wings – Lok Sabha and Rajya Sabha. A bill becomes an act after passing from both the wings and consented by the President of India. To be a member of Lok Sabha, every citizen can contest an election and had to win it. |
Question 6.
Write down the names of the Indian States, which share borders with the following neighbouring nations:
(a) Bangladesh
(b) Bhutan
(c) Nepal
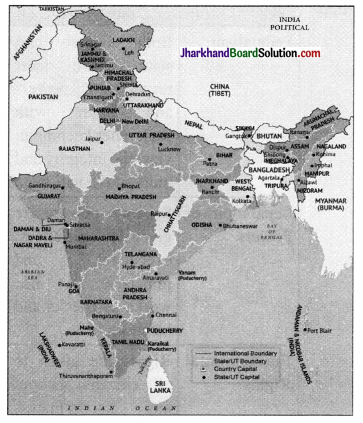
Answer:
Meghalaya, Mizoram, Tripura, West Bengal, Assam, are the Indian states, shared boarders with Bangladesh. Arunachal Pradesh, Sikkim, West Bengal, Assam, share boarder with Bhutan. Uttarakhand, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Sikkim, West Bengal share boarder with Nepal.
JAC Class 8th Civics The Indian Constitution Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Question
Question 1.
On which date the Indian Constitution came into effect?
(a) On 26 November 1949
(b) On 26 January 1950
(c) On 26 September 1949
(d) On 26 March 1950
Answer:
(b) On 26 January 1950
Question 2.
The important fundamental rights to Equality is mentioned in of the constitution?
(a) Article 14-18
(b) Article 29-30
(c) Article 23-24
(d) Article 19-22
Answer:
(a) Article 14-18
Question 3.
Which one of the following is not a key feature of the Indian Constitution?
(a) Separation of Power
(b) Presidential form of Government
(c) Secularism
(d) Federalism
Answer:
(b) Presidential form of Government
![]()
Question 4.
Fundamental rights refer to:
(a) The list of subjects of the state government.
(b) The list of subjects of both the state and central governments.
(c) The list of subjects of the central government.
(d) The basic rights which are granted to citizens for the holistic growth of the individuals.
Answer:
(d) The basic rights which are granted to citizens for the holistic growth of the individuals.
Question 5.
The fundamental right that guarantees the citizens the right to practise and propagate the religion they desire is
(a) Freedom of Belief
(b) Freedom of Faith
(c) Freedom of Religion
(d) Freedom of Caste
Answer:
(c) Freedom of Religion
Question 6.
……….was the President of the Constituent Assembly.
(a) Mahatma Gandhi
(b) Lala Fajpat Rai
(c) Jawaharlal Nehru
(d) Dr. Rajendra Prasad
Answer:
(d) Dr. Rajendra Prasad
Question 7.
Dr B.R. Ambedkar is the……..
(a) Father of the Indian Constitution
(b) Father Of the Nation
(c) Nation’s pride
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Father of the Indian Constitution
Question 8.
Answer:
…….. is the third tier of Government in India.
(a) State Government
(b) Municipal Government
(c) Panchayati Raj
(d) Central Government
Answer:
(c) Panchayati Raj
Question 9.
The monarchy system was in……. till 2006.
(a) Bhutan (b) Sri Lanka
(c) Burma
(d) Nepal
Answer:
(d) Nepal
Question 10.
……. was/were the member/s of the Constituent Assembly.
(a) Sardar Vallabhbhai Patel
(b) Jawaharlal Nehru
(c) AKAyyar
(d) A11 of these
Answer:
(d) Nepal
Very Short Answer Type Question
Question 1.
Name the Father of the Indian Constitution.
Answer:
Dr B.R. Ambedkar is known as the Father of the Indian Constitution.
Question 2.
In Nepal, when did the Interim Constitution come into effect?
Answer:
In Nepal, the Interim Constitution came into effect from January 15, 2007.
Question 3.
What do you mean by monarchy?
Answer:
A form of government in which final authority and power are rested with the King is known as monarchy.
Question 4.
What do you mean by a ‘State’?
Answer:
A political institution that represents a sovereign people who occupy a definite territory is known as a ‘State’.
Question 5.
What is universal adult franchise?
Answer:
Universal Adult Franchise means that the right to vote should be given to all adult citizens without the discrimination of caste, class, colour, religion or gender.
![]()
Question 6.
How does the Indian Constitution protect minority rights?
Answer:
The Constitution usually contains rules and regulations that ensure that minorities are included in everything that is routinely available to the majority.
Question 7.
State any three provisions made in the Constitution to prevent exploitation.
Answer:
Three provisions made in the Constitution to prevent exploitation are as follows:
- prohibits human trafficking,
- forced labour,
- employment of children under 14 years of age.
Question 8.
What do you mean by Right to Constitutional Remedies?
Answer:
Right to Constitutional Remedies means that this allows citizens to move to the court if they believe that any of their Fundamental Rights have been violated by the State.
Question 9.
What do you mean by Right to Freedom of Religion?
Answer:
Right to Freedom of Religion means religious freedom is provided to all citizens. Every person has the right to practice, profess and propagate the religion of their choice.
Question 10.
Write in brief on Cultural and Educational Rights.
Answer:
Cultural and Educational Rights means the Constitution states that all minorities, religious or linguistic can set up their own educational institutions in order to preserve and develop their own culture.
short answer type questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by tyranny of majority?
Answer:
Tyranny of the majority refers to unhealthy situations where a majority continuously enforces decisions that exclude minorities and go against their interests. Every society is prone to this tyranny of the majority. The Constitution usually contains rules that ensure that minorities are not excluded from anything that is routinely available to the majority. Constitution is precisely prevent this tyranny or domination by the majority of a minority.
Question 2.
What are the functions of the three main organs of the government?
Answer:
Three main organs are the legislature, the executive and the judiciary. The functions of these three main organs of government are:
- The basic function of Legislative body is to make laws, introduce new legislation in the Parliament or State Assembly and the members of these bodies are directly elected by the citizens for Lower Houses and indirectly in the case of Upper Houses.
- The Executive body has the duty to execute and implement the laws & legislation laid out the legislative body and the duty lie with Chief Minister of a State and Prime Minister of India, both represent executive organ of State and Union respectively.
- However, since some laws and legislation made needs to be interpreted as well, then in that situation Judiciary has its jurisdiction, highest court in India is Supreme Court, state highest court is High Court and rest are District Courts.
Question 3.
What are the factors the drafting committee had to take into consideration while drafting the constitution?
Answer:
The country was made up of several different communities who spoke different languages, belonged to different religions and had distinct cultures and traditions. Also, when the Constitution was being written, India was going through considerable turmoil. The partition of the country into India and Pakistan was imminent, some of the Princely States remained undecided about their future, and the socio-economic condition of the vast mass of people appeared dismal. All of these issues played on the minds of the members of the Constituent Assembly as they drafted the Constitution.
![]()
Question 4.
What is the importance of constitution?
Answer:
Importance of constitution:
- A Constitution helps serve as a set of rules and principles that all persons in a country can agree upon as the basis of the way in which they want the country to be governed.
- The Constitution often lays down rules that guard against this misuse of authority by our political leaders.
- Constitution ensures that a dominant group does not use its power against other, less powerful people or groups.
- The Constitution helps to protect us against certain decisions that we might take that could have an adverse effect on the larger principles that the country believes in.
Question 5.
How constitution of India is formed?
Answer:
The long experience of authoritarian rule under the colonial state convinced Indians that free India should be a democratic country in which everyone should be treated equally and be allowed to participate in government. To work out the ways in which a democratic government would be set up in India and the rules that would determine its functioning was being planned. This was done not by one person but by a group of around 300 people who became members of the Constituent Assembly in 1946 and who met periodically for the next three years to write India’s Constitution. Between December 1946 and November 1949, the Constituent Assembly drafted a constitution for independent India.
Question 6.
What do you mean by the legislature, the executive and the judiciary?
Answer:
The legislature refers to our elected representatives. The executive is a smaller group of people who are responsible for implementing laws and running the government. The judiciary refers to the system of courts in this country.
Question 7.
What were the important points of the text prepared by Dr. B.R. Ambedkar, who was the Chairman of the constitution drafting committee? The Answer:
important points of the text prepared by Dr. Ambedkar are:
- Constitutional guarantees and protections for individual citizens
- Freedom of religion
- Abolition of untouchability
- Outlawing of all forms of discrimination
- Economic and social rights for women
- Reservations of jobs in the civil services, schools and colleges for members of scheduled castes and scheduled tribes.
Question 8.
What do you think are the negative things of a democratic society?
Answer:
The negative things in a democratic society is that power can be misused. Sometimes the majority can suppress the minority. The citizens need certain rules to save themselves from folly.
Question 9.
Define the term Constitution.
Answer:
In large societies in which different communities of people live together, the rules are formulated through consensus, and in modem countries this consensus is usually available in written form. A written document in which we find such rules is called a Constitution.
Question 10.
What did Dr Ambedkar state about scheduled caste?
Answer:
Dr. Ambedkar stated about scheduled caste that although the laws might exist, scheduled castes still had reason to fear because the administration of these laws were in the hands of ‘caste Hindu officers’. Therefore, he urged scheduled castes to join the government as well as the civil services.
Long Answer Type Question
Question 1.
Describe in detail the various features of Indian constitution.
Answer:
The various features of Indian Constitution are as follows:
Federalism:
Federalism refers to the existence of more than one level of government in the country. In India, we have governments at the state level, at the center and Panchayati Raj is the third tier of government.
Parliamentary Form of Government: The different tiers of government consist of representatives and authorities who are elected by the people. The constitution of Indian guarantees universal adult franchise for all citizens. This means that the people of India have a direct role in electing their leaders or representatives. Apart from this, every citizen of the country, irrespective of his/ her social background, can also contest j- in elections. These representatives are accountable to the people.
Separation of Powers:
According to the Constitution, there are three organs of government. They are the legislature, the executive and the judiciary. In order to prevent the misuse of power by any one branch of government, the Constitution says that each of these organs should exercise different powers.
![]()
Fundamental Rights:
The section on Fundamental Rights has often been referred to as the ‘conscience’ of the Indian Constitution. Fundamental Rights protect citizens against the arbitrary and absolute exercise of power by the State. The Constitution guarantees the rights of individuals against the State as well as against other individuals. The Constitution also guarantees the rights of minorities against the majority.
The Constitution also has a section called Directive Principles of State Policy. This section was designed by the members of the Constituent Assembly to ensure greater social and economic reforms and to serve as a guide to the independent Indian State to institute laws and policies that help reduce the poverty of the masses.
Secularism:
A secular state is one in which the state does not officially promote any one religion as the state religion.
Question 2.
Describe briefly on the struggle for freedom in Nepal.
Answer:
Nepal has witnessed several people’s struggles for freedom and democracy. There was a people’s struggle in 1990 that established democracy which lasted for 12 years until 2002. In October 2002, King Gyanendra, citing the Maoist uprising in the countryside as his reason, began taking over different aspects of the government with the army’s assistance. The King then finally took over as the head of government in February 2005. In November 2005, the Maoists joined other political parties to sign a 12-point agreement. This agreement signalled to the larger public an imminent return to democracy and peace. In 2006, this people’s movement for democracy began gaining immense force. It repeatedly refused the small concessions that the King made and finally in April 2006 the King restored the Third Parliament and asked the political parties to form a government. In 2007, Nepal adopted an Interim Constitution.