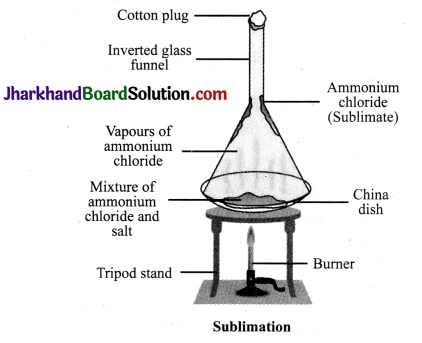
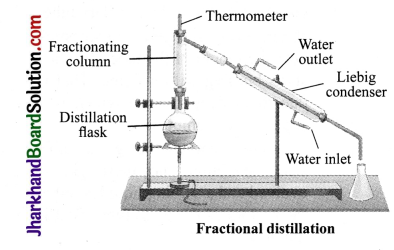
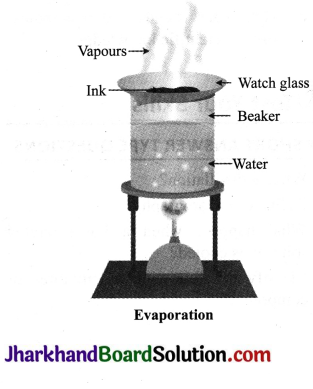
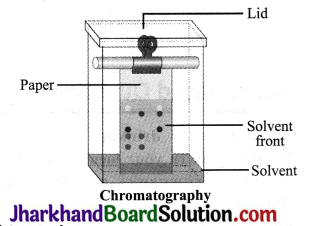
JAC Board Class 9th Science Important Questions Chapter 5 The Fundamental Unit of Life
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Who coined the term protoplasm for the fluid substance of the cell?
(a) Hugo von Mohl
(b) Robert Brown
(c) W. Flemming
(d) Robert Hooke
Answer:
(a) Hugo von Mohl
Question 2.
Which of the following scientists coined the term ‘cell’?
(a) Leeuwenhoek
(b) J.E. Purkinje
(c) Robert Hooke
(d) Robert Brown
Answer:
(c) Robert Hooke
Question 3.
The powerhouse of a cell is
(a) Chloroplast
(b) Golgi apparatus
(c) Mitochondria
(d) Vacuole
Answer:
(c) Mitochondria
Question 4.
Proteins are formed in
(a) Golgi bodies
(b) nucleus
(c) plastids
(d) ribosomes
Answer:
(d) ribosomes
Question 5.
The solution in which a cell will gain water by osmosis is termed as
(a) isotonic solution
(b) hypertonic solution
(c) hypotonic solution
(d) both (a) and (b)
Answer:
(c) hypotonic solution
![]()
Question 6.
The inner membrane of mitochondria is folded because
(a) it has no space inside
(b) it helps in the transportation of materials
(c) it increases the surface area
(d) it stores more food
Answer:
(c) it increases the surface area
Question 7.
The opening and closing of stomata is due to
(a) sunlight
(b) osmosis
(c)plasmolysis
(d) endocytosis
Answer:
(b) osmosis
Question 8.
Which of the following molecules is known as the energy currency of the cell?
(a) DNA
(b) RNA
(c) ATP
(d) Amino acid
Answer:
(c) ATP
Question 9.
The largest cell in the human body is
(a) nerve cell
(b) muscle cell
(c) liver cell
(d) kidney cell
Answer:
(a) nerve cell
Question 10.
The network of endoplasmic reticulum is present in the
(a) nucleus
(b) nucleolus
(c) cytoplasm
(d) chromosomes
Answer:
(c) cytoplasm
Question 11.
Mitochondria are found
(a) in all types of living cells
(b) only in animal cells
(c) only in plant cells
(d) in eukaryotic cells only
Answer:
(d) in eukaryotic cells only
Question 12.
Which organelle is considered as suicide bag of the cell?
(a) Centrosomes
(b) Mesosomes
(c) Lysosomes
(d) Chromosomes
Answer:
(b) Mesosomes
Question 13.
Centriole performs the function of
(a) formation of spindle fibres
(b) nucleolus formation
(c) cell wall formation
(d) cell division initiation
Answer:
(c) cell wall formation
Analysing & Evaluating Questions
Question 14.
A student observed a slide containing onion peel cells under a microscope in low and high magnification. In low magnification, he would have observed
(a) fewer cells in a brighter field of view
(b) more cells in a brighter field of view
(c) more cells in a darker field of view
(d) fewer cells in a darker field of view
Answer:
(a) fewer cells in a brighter field of view
![]()
Question 15.
A person with swollen gums rinses his mouth with lukewarm salt water and the swelling of his gums decreases. This is because
(a) the swollen gums absorb the salt water solution
(b) the salt water solution lowers the temperature of the water in the gums
(c) the salt in the solution moves against the concentration gradient
(d) the water in the gums moves out due to the high concentration of salt in the solution
Answer:
(b) the salt water solution lowers the temperature of the water in the gums
Question 16.
In a biology laboratory, Arjun observed two unknown cells namely Cell A and Cell B, by using a microscope. He identified Cell A as a plant cell and Cell B as an animal cell. His teacher told him that he identified the cells correctly. What did Arjun most likely observe to correctly identify the cells?
(a) Cell B had a cell membrane and Cell A did not.
(b) Cell A had a cell wall and Cell B did not.
(c) Cell B had a chloroplast and Cell A did not.
(d) Cell A had a nucleus and Cell B did not.
Answer:
(b) Cell A had a cell wall and Cell B did not.
Assertion Reason Questions
Directions: In the following questions, the Assertions and the Reasons have been put forward Read the statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following:
(A) Both the assertion and the reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(B) The assertion and the reason are correct but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(C) The assertion is true but the reason is false.
(D) Both the statements are false.
1. Assertion: Cell membrane is semi – permeable but cell wall is non – permeable.
Reason: Cell membrane is made up of lipids whereas cell wall is made up of proteins.
Answer:
(D) Both the statements are false.
2. Assertion: Plant cells are more rigid than animal cells.
Reason: Plant cells have cell wall made up of cellulose.
Answer:
(A) Both the assertion and the reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
3. Assertion: Mitochondria are semi – autonomous organelles.
Reason: Mitochondria lack their own DNA, RNA and ribosomes.
Answer:
(C) The assertion is true but the reason is false.
4. Assertion: Chromosomes are visible at the time of cell division only.
Reason: Chromosomes in a cell are more condensed at the time of cell division.
Answer:
(A) Both the assertion and the reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
5. Assertion: About 50 – 80 % of a plant cell is coupled by the vacuole.
Reason: Vacuole of a plant cell stores many essential materials.
Answer:
(B) The assertion and the reason are correct but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are plastids?
Answer:
Plastids are double membrane – bound organelles found inside plants and some algae, which are primarily responsible for activities related to making and storing food Many plastids are photosynthetic, but some are not.
Question 2.
Name the smallest cell and the longest cell in the human body.
Answer:
The smallest cell is the sperm cell in male. The longest cell is the nerve cell.
Question 3.
What did Robert Hooke observe in the cork of a plant?
Answer:
Robert Hooke observed that cork consists of box – like compartments which form a honeycomb structure.
Question 4.
What is diffusion?
Answer:
The movement of molecules from higher concentration to lower concentration across a semi-permeable membrane is called diffusion.
Question 5.
What is the full form of DNA?
Answer:
The full form of DNA is Deoxyribonucleic acid It is a complex molecule found in all living cells that determines all the characteristics of a living thing.
Question 6.
Name the cell organelle that helps in packaging of substances.
Answer:
Golgi apparatus.
![]()
Question 7.
What are cisternae?
membrane – bound vesicles arranged in stacks called cistemae.
Question 8.
Which organelle makes the digestive enzymes of lysosomes?
Answer:
Rough endoplasmic reticulum makes the digestive enzymes of lysosomes.
Question 9.
What is the function of cell wall and plasma membrane?
Answer:
Cell wall gives rigidity, shape and protection to the plant cell. Cell membrane allows only selected materials to move in and out of the cell.
Question 10.
What is endocytosis? Give one example.
Answer:
The process in which a cell, due to flexible cell membrane, engulfs food and other materials from its external environment is known as endocytosis. Amoeba acquires its food through this process.
Question 11.
What is chromatin material?
Answer:
Inside the nucleus, a tangled mass of threadlike structure is present which is called chromatin material. Chromatin material is the combination of DNA and proteins.
Question 12.
What are genes?
Answer:
Genes are segments of DNA present linearly on chromosomes. (They are the functional units of chromosomes.)
Question 13.
Who discovered the first living cell? Give an example of a unicellular organism.
Answer:
Anton von Leeuwenhoek discovered the cells in living organisms. An example of unicellular organism is Amoeba.
Question 14.
Define chromosomes.
Answer:
Chromosomes are rod – shaped structures found in the nucleus of a cell. They contain information for inheritance of features from parents to the next generation in the form of DNA molecules.
Question 15.
What is the function of centrosome?
Answer:
Centrosome helps in cell division in animal cells. The polar caps perform the same function in a plant cell.
Question 16.
What is the function of mitochondria?
Answer:
In mitochondria, digested food is broken down to release energy. This released energy is stored in the form of ATR
Question 17.
Define plasmolysis.
Answer:
When a living plant cell loses water through osmosis, there is shrinkage or contraction of the protoplasm away from the cell wall. This phenomenon is called plasmolysis.
Analysing & Evaluating Questions
Question 18.
Aperson takes concentrated solution of salt and after sometime, he starts vomiting. What is the phenomenon responsible for such situation.
Answer:
The concentrated salt solution is hy – pertonic When consumed, it causes exosmosis of the cells of various digestive organs of the body. This causes uncomfortable stretching of cells resulting into reverse peristaltic movements, ultimately leading to vomiting.
Question 19.
If cells of onion peel and RBC are separately kept in hypotonic solution, what will you observe in each case?
Answer:
When kept in hypotonic solution, the RBCs will swell up and then burst due to endosmosis. In case of onion peel kept in hypotonic solution, a rigid cell wall counteracts the pressure when the cells become turgid The endosmosis stops and onion peel cells do not burst.
![]()
Question 20.
Bacteria do not have chloroplast but some bacteria are photoautotrophic in nature and perform photosynthesis. Which part of bacterial cell performs this?
Answer:
In some photoautotrophic (photosyn – thetic) bacteria, photosynthetic pigments are present inside some vesicles which may be attached to the plasma membrane.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
State two conditions required for osmosis.
Answer:
- The difference in the concentration of water, i. e., one should have higher concentration than the other,
- Semi – permeable membrane is also required through which water will flow.
Question 2.
Differentiate between smooth endoplasmic reticulum and rough endoplasmic reticulum.
Answer:
- Smooth endoplasmic reticulum: It looks smooth. SER helps in the manufacture of fat molecules or lipids.
- Rough endoplasmic reticulum: It looks rough. Ribosomes are attached to RER which synthesises proteins.
Question 3.
What is the function of nucleus in a cell?
Answer:
Nucleus controls the hereditary characteristics of an organism. It is responsible for protein synthesis, cell division, growth and differentiation. It stores hereditary material in the form of deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) strands. It also stores proteins and ribonucleic acid (RNA) in the nucleolus. Nucleolus produces ribosomes and is known as protein factory of the cell. It also regulates the integrity of genes and gene expression.
Question 4.
What is the function of plastids?
Answer:
Plastids are present only in plant cells. There are two types of plastids: chromoplast (coloured plastids) and leucoplasts (colourless).
- By trapping solar energy, green plastids manufacture food through photosynthesis.
- Chromoplast provides colour to various flowering parts.
- Leucoplasts help in storage of proteins, starch and fats.
Question 5.
What are ribosomes? Where are they located in the cell? What is their function?
Answer:
Ribosomes are spherical organelles present in the cells which are either freely distributed in the cytoplasm or may be attached to the endoplasmic reticulum. It consists of ribosomal RNA (Ribonucleic acid) and proteins. It helps in the synthesis of proteins.
Question 6.
Define membrane biogenesis.
Answer:
The endoplasmic reticulum helps in the manufacture of proteins and fat molecules or lipids which are important for the cell function. These proteins and lipids help in the building up of the cell membrane. This process is known as membrane biogenesis.
Question 7.
Draw various cells of human body.
Answer:
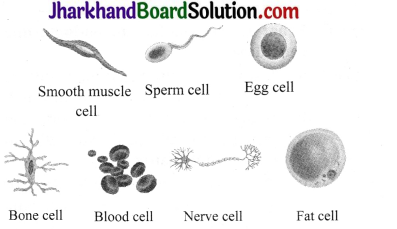
Question 8.
What is the significance of cell wall in a plant cell?
Answer:
The cell wall performs following functions in the plant cells:
(a) It gives a definite shape to the cell.
(b) It provides rigidity and strength to the cell.
(c) It protects the plasma membrane and inner cell organelles by bounding the cell from outside.
(d) It allows cells of plants, fungi and bacteria to withstand very dilute external media without bursting.
(e) It helps in transport of the materials in and out of the cell.
(f) It maintains the shape of the cell when cytoplasm shrinks away from cell wall during plasmolysis.
(g) It prevents desiccation of cells.
Question 9.
Distinguish between plasma membrane and cell wall.
Answer:
| Plasma membrane | Cell wall |
| (a) It consists of proteins and lipids. It is living. | (a) It is made up of a complex carbohydrate called cellulose. It is dead or non-living. |
| (b) It is found in both plants and animal cells. | (b) It is found in plant cells only. |
| (c) It is semi permeable. | (c) It is freely permeable. |
| (d) It is soft and elastic. | (d) It is hard and rigid. |
Question 10.
What is the function of endoplasmic reticulum?
Answer:
(a) ER helps in transporting materials from one part of the cell to the other.
(b) It acts as skeletal framework and provides mechanical strength to cytoplasmic matrix.
(c) It provides larger surface area for synthesis of various metabolic activities.
(d) It contains various enzymes which act as catalyst in synthesis of lipids and proteins.
(e) SER is also involved in the process of detoxification of drugs and poisons.
Question 11.
What is lacking in a virus which makes it dependent on a living cell to multiply?
Answer:
Viruses lack selectively permeable plasma membrane and cell organelles. Thus they lack a basic structural organisation to perform various life processes effectively in their own way. After entering a living cell, a virus utilises its own genetic material and machinery of host cell to multiply.
![]()
Question 12.
Write three main points of cell theory as expressed by Scleiden, Schwann and Virchow.
Answer:
Cell Theory: Schleiden and Schwann proposed that:
- All plants and animals are composed of cells.
- The cell is the basic unit of life. Later on Virchow added that
- All cells arise from pre-existing cells.
Question 13.
What are the functions of Golgi apparatus?
Answer:
Functions of Golgi apparatus are as follows:
- Golgi apparatus is the secretory organelle of the cell. It packages and dispatches the material synthesised in the cell to intracellular (plasma membrane and lysosomes) and extracellular targets.
- Golgi complex is also involved in the formation of lysosomes.
- Golgi apparatus is also involved in the synthesis of many substances such as polysaccharides, glycoproteins, etc.
Question 14.
Differentiate between unicellular and multicellular organisms. How is multi-cellularity advantageous over unicellularity?
Answer:
Differences between unicellular and multicellular organisms are as follows:
| Unicellular organisms | Multicellular organisms |
| (a) Their body consists of single cell. | (a) Their body consists of more than one cell. |
| (b) All functions associated with life take place in a single cell. | (b) Different parts of body perform different functions. |
| (c) Example: Amoeba and Chlamydomonas. | (c) Banyan tree and horse. Multicellularity provides division of labour. This helps the organisms to perform various life processes in a better way. |
Analysing & Evaluating Questions
Question 15.
We eat food composed of all the nutrients like carbohydrates, proteins, fats, vitamins, minerals, and water. After digestion, these are absorbed in the form of glucose, amino acids, fatty acids, glycerol, etc What mechanisms are involved in absorption of digested food and water?
Answer:
The absorption of these digested nutrients and water follows the following mechanisms:
(a) Carbohydrates (glucose), proteins (amino acids) and some ions (minerals) – by active transport.
(b) Fats (fatty acids) and glycerol – by passive transport (diffusion).
(c) Water – by osmosis.
Question 16.
Karan observed onion peel cells in biology laboratory. He could view the cell wall, cytoplasm, and nucleus clearly. Suddenly his friend spilled a few drops of salty water on the slide containing the onion peel. After some time, Karan observed the slide again and found some changes in the onion cells.
1 .What changes would have been observed by karan?
2. Name the process that brought changes in the onion cells.
Answer:
- Karan observed the process of exosmosis in onion peel cells. Salty water, being a hypertonic solution, causes water to flow out from the cell due to exosmosis. As a result, cytoplasm along with plasma membrane shrinks and separates from the cell wall,
- Plasmolysis.
Long Answer Type Questions
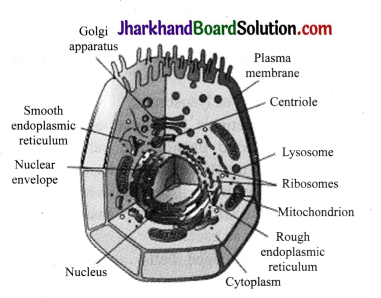
Question 1.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of animal cell.
Answer:
Question 2.
Draw a neat labelled diagram of plant cell and label its parts.
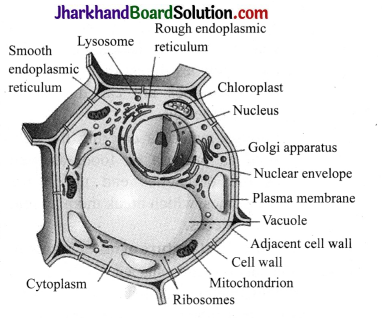
Question 3.
What will happen if an animal or a plant cell is put into a solution of sugar and water?
Answer:
Osmosis is the net movement of water from an area of higher water potential to an area of lower water potential across a semi – permeable membrane.If a living cell is placed in a solution with a lower water potential (such as concentrated solution of sugar or salt) than the water potential of the cell, water will move out of the cell due to exosmosis. When this occurs, the cytoplasm of the cell shrinks in volume due to water loss. This process is known as plasmolysis.
Question 4.
Describe the role played by the lysosomes.
Answer:
Functions of lysosomes:
- Sometimes lysosomal enzymes are released outside the cell to break down extracellular material.
- Lysosomes also destroy any foreign material which enters inside the cell such as bacteria.
- In damaged cells, ageing cells or dead cells, lysosomes get ruptured and enzymes are release(d) These enzymes digest their own cell.
- Lysosomes contain about 40 ydrolytic enzymes. When the cell gets damaged, lysosomes burst and their enzymes digest their own cell. So, lysosomes are called ‘suicide bags’ of the cell.
- Foreign materials entering the cell, such as bacteria or food, as well as old organelles end up in the lysosomes, which break them up into small pieces.
Question 5.
Describe the structure of mitochondria
Answer:
Mitochondria are shaped perfectly to maximise their productivity. They are made up of two membranes. The outer membrane covers the organelle and contains it like a skin. The inner membrane folds over many times and creates layered structures called cristae. The gel like material in the mitochondria is called matrix. The folding of the inner membrane increases the surface area inside the organelle. Since many of the chemical reactions happen on the inner membrane, the increased surface area creates more space for reactions to occur.
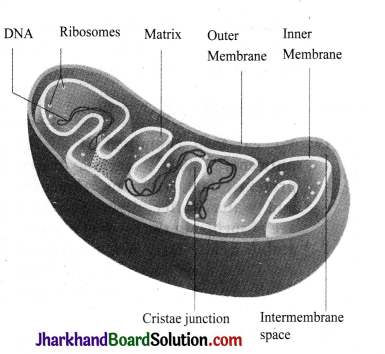
Mitochondria are special because they have their own ribosomes and DNA floating in the matrix. There are also structures called granules which may control the concentration of ions.
Question 6.
Write a note on the structure of a cell.
Answer:
1. Cell is the fundamental unit of all living organisms. It is enclosed by an outer ‘plasma membrane’ (PM) which is selectively permeable. Plant cells have an additional covering called ‘cell wall’, outside to the plasma membrane.
2. Inside the plasma membrane, there is a translucent viscous substance called cytoplasm in which the organelles are embedded The control centre of the cell is the nucleus; it contains all the information necessary for the cell to function and to reproduce. Surrounding the nucleus is the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) in which ribosomes may be embedded Ribosomes are granular structures which are the site of protein synthesis.
3. The powerhouse of the cell is the mitochondria which help in releasing energy by the oxidation of food in cell. There is a membranous secretory organelle in the cell called Golgi body.
4. In plant cells, an additional structure located near the nucleus, called the chloroplast, is also present. They are the site of photosynthesis.
5. Cells also contain lysosomes which are also called suicide bags. They digest and remove the unwanted debris of the cell. Centrioles located near the nucleus help in cell division. Cytoplasm also contains vacuoles filled with cell sap. In plant cells, vacuole is large and centrally placed.
Analysing & Evaluating Questions
The diagram given below shows a beaker containing 30% salt solution and a suspended cell containing 10% salt solution
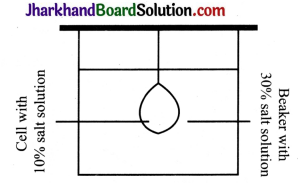
1. What will happen to the cell in this set – up after 20 minutes?
2. Which part of the cell limits the entry or exit of materials into or from the cell and why?
3. Explain the process that occurred in this set – up.
Answer:
- Since the solution outside the cell has more salt concentration (30%) than that present inside the cell, the water will move out from the cell and the cell will shrink.
- Cell membrane limits the entry or exit of materials into or out of the cell due to its selective permeability.
- Exosmosis occurred in this set – up. It is the process in which water moves out of the cells through the cell membrane, if surrounded by the hypertonic solution.
Activity – 1
- Let us take a small piece of onion peel with the help of a pair of forceps.
- Keep it immediately in a watch glass containing water.
- Take a glass slide, put a drop of water on it at the centre, and transfer a small piece of onion peel on the slide from the watch glass.
- Make sure that the peel is perfectly flat on the slide.
- Now put a drop of iodine solution on this piece followed by a cover slip.
- Take care to avoid the entry of air bubbles while putting the cover slip with the help of a mounting needle.
- Now focus the slide under compound microscope and observe.
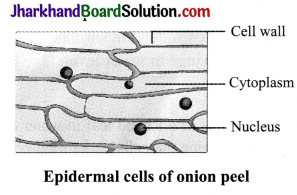
Observations
- Small compartment – like structures are observed.
- Each cell shows a cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus and cytoplasm.
Activity-2
- Remove the shell of an egg by dissolving it in dilute hydrochloric acid The shell is
mostly calcium carbonate. A thin outer skin now encloses the egg. Put the egg in pure water and observe after five minutes. - Record your observations.
- Place a similar de – shelled egg in a concentrated salt solution and observe after five minutes.
Observations
- The egg swells when kept in pure water because water enters it by osmosis.
- Water passes out of the egg cells into the salt solution because the salt solution is more concentrated Water flows from the region of higher water concentration to the region of lower water concentration.
Activity 3
- Take dried raisins or apricots in normal water and leave them overnight.
- Then place them into a concentrated solution of sugar or salt.
- Record your observations. Observations
- Each raisin/apricot gains water and swells when placed in pure water.
- But, when placed in the concentrated solution, it loses water and shrinks.
- There is no change in water level.
Activity 4
- Mount the peel of a Rhoeo leaf in water on a slide and examine the cells under high power of the microscope. Note the small green granules, called chloroplasts. They contain a green substance called chlorophyll. Put a strong solution of sugar or salt on the mounted leaf on the slide. Wait for a minute and observe under a microscope.
- Now place some Rhoeo leaves in boiling water for a few minutes. This kills the cells. Then mount one leaf peel on a slide and observe it under a microscope. Put a strong solution of sugar or salt on the mounted leaf on the slide. Wait for a minute and observe it again.
Observations
- In this experiment, water from the cells moves out by osmosis thereby shrinking the cells. This process is called plasmolysis.
- On boiling the leaves, the cells are dead and the osmosis does not take place in these leaves.
Activity 5
- Take a glass slide with a drop of water on it. Using an ice cream spoon, gently scrap the inside surface of the cheek.
- With the help of a needle transfer this material on a clean glass slide and spread it evenly. To colour the material, put a drop of methylene blue solution on it. Put a cover slip on it.
- Observe the slide under the microscope.
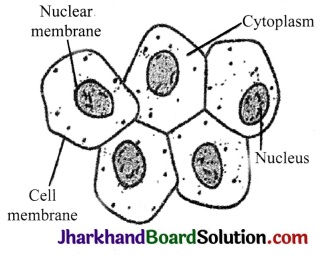
Observations
- The cells are seen on the slide with no cell wall but prominent nucleus.
- The cells are slightly round/oval in shape. They are cheek cells.
Value Based Questions
Question 1.
A teacher fixed one stained temporary mount of leaf peel cells under one microscope and another slide of cheek cells in the other microscope. He focused both slides under respective microscopes. Then the teacher asked the students to observe the slides under the microscopes and located the following in peel cells and cheek cells:
(a) A densely stained body, called nucleus in both the slides.
(b) A lightly stained substance, called cytoplasm surrounding the nucleus. After observation, the teacher asked the following questions:
1. What do you infer from this activity?
2. What is the key message conveyed about plants and animals?
Answer:
- Plants are also formed of cells like us or other animals.
- Plants are also living things. We should not harm them unnecessarily, rather we should protect them.
Question 2.
Our body is formed of millions of cells. Now, you can imagine how minute the cells are(a) We cannot see unicellular bacteria or our cheek cells without the help of a microscope but we can see a type of cell with naked eye. These are shelled eggs, for example, egg of a hen. Eggs of a bird after hatching give rise to young ones (chick).
With this information, answer the following questions:
(a) Egg of which bird is the largest?
(b) Why is it advised to eat one egg daily?
(c) Why should we not eat more eggs daily for a long period?
(d) What is your duty after getting this information?
Answer:
(a) Ostrich (Struthio cameras). Its egg size is about 15 cm x 13 cm, weighing about 3 pounds.
(b) An egg provides sufficient proteins, fats, vitamin A and vitamin D.
(c) Eggs contain lots of cholesterol that may cause heart diseases. We should not eat many eggs in a day for a long period.
(d) Our duty is that we should make our friends, relatives and community aware about useful and harmful effects of eating eggs.