Jharkhand Board JAC Class 9 English Solutions Grammar Clauses Exercises Questions and Answers.
JAC Board Class 9 English Grammar Clauses Exercises
Clauses, complex sentences की श्रेणी में आते हैं । अतः सबसे पहले यह जानना आवश्यक है कि एक Simple Sentence क्या होता है तथा एक Complex Sentence. की वाक्य रचना किस प्रकार की होती है, जैसे
- I gave him a book.
- She was playing football.
- They will help us.
उपरोक्त तीनों ही वाक्य Simple Sentences हैं क्योंकि तीनों ही वाक्यों में केवल एक ही finite verb-gave, playing व help दी हुई है ।
![]()
परिभाषा के अनुसार –
A simple sentence is a sentence which has only one finite verb, and may have a subject and a predicate. एक साधारण वांक्य वह वाक्य होता है जिसमें केवल एक ही नियंत्रित क्रिया (finite verb) होती है व एक ही कर्ता व विधेय (predicate) हो सकता है ।
ऊपर दिये गये तीनों वाक्य Clause कहलाते हैं क्योंक एक Simple Sentence में केवल एक ही Clause प्रयुक्त होता है ।
अब पुन: इन वाक्यों को देखिये-
- I told him then.
- He was reading in the room.
इन दोनों ही वाक्यों को जोड़कर एक वाक्य एक प्रकार से बनाया जा सकता है ।
I told him when he was reading in the room.
उक्त वाक्य एक Complex Sentence कहलाता है क्योंकि
A complex sentence is a sentence which consists of two or more clauses.
एक जटिल वाक्य या मिश्रित वाक्य (Complex Sentence) वह होता है जिसमें दो या दो से अधिक उपवाक्य (Clauses) हों और यहाँ पर वाक्य He was reading in the room को then के स्थान पर when लगाकर जोड़ा गया है । चुंकि then एक adverb है, अतः यहाँ पर जोड़ा गया when he was reading in the room एक adverbial clause है। इस प्रकार से एक Complex Sentence में दो या दो से अधिक Subject-Predicate Structures हो सकते हैं । दूसरे शब्दों में,
A complex sentence is one that contains one main clause (Principal Clause) and one or more subordinate clauses.
एक Complex Sentence वह होता है जिसमें एक प्रधान उपवाक्य (Principal clause) तथा एक या अधिक आश्रित उपवाक्य (Subordinate Clauses) होते हैं ।
उक्त वाक्य में ‘I told him’ Principal Clause है तथा when he was reading in the room एक Sub-ordinate Clause है क्योंकि यह Principal Clause के लिये Adverb का काम रहा है । यहाँ पर यह स्पष्ट हो जाता है कि Subordinate Clause को Principal Clause से जोड़ने के लिए एक Conjunction का प्रयोग किया जाता है । यहाँ पंर दोनों वाक्यों को जोड़ने के लिएकwhen का प्रयोग किया गया है जो कि एक conjunction है ।
नोट – एक Principal Clause को Subordinate Clause से जोड़ने के लिए जिन conjunctions का प्रयोग किया जाता है वे Subordinating Conjunctions कहलाते हैं । अब निम्नलिखित उदाहरण को ध्यानपूर्वक देखो-
- I know it.
- The thief has escaped.
हम इन दोनों ही वाक्यों को इस प्रकार से जोड़ सकते हैं कि दूसरा वाक्य पहले वाक्य के object के स्थान पर लग जाये व object का काम करे।
I know that the thief has escaped.
Clause “that the thief has ecaped”, Principal Clause “I know” के लिए direct object का काम कर रहा है और
इस प्रकार से यह एक Subordinate Clause है ।
![]()
एक Complex sentence में Clauses की संख्या का पता लगाना अत्यन्त ही आसान है। एक Complex sentence में जितनी finite verbs होती हैं उसमें उतने ही Clauses होते हैं।
अर्थात् – The number of finite verbs = the number of clauses
जैसे – I am writing a book.
उक्त वाक्य में केवल एक ही finite verb-writing दी हुई है, अतः इसमें केवल एक ही Clause है व यह एक साधारण वाक्य (Simple sentence) है । लेकिन
This is the boy who stole my pen.
इस वाक्य में दो finite verbs-is व stole दी हुई हैं । अतः इस वाक्य में दो
Clauses –
- This is the boy
- who stole my pen हैं ।
who stole my pen एक Subordinate clause है तथा who एक Subordinating conjunction है ।
इसी प्रकार से – If you do not strike while the iron is hot, you cannot mould it. उक्त वाक्य में तीन finite verbs-strike, is व mould हैं । अतः उक्त वाक्य में तीन Clauses हैं ।
(i) If you do not strike
(ii) while the iron is hot
(iii) you cannot mould it तथा if व while दो Subordinating conjunctions हैं ।
तथा if व while दो Subordinating conjunctions हैं ।
![]()
Principal Clause व Subordinate Clause को पहचानना
एक Complex Sentence में Principal Clause व Subordinate Clause को पहचानना अत्यन्त ही आसान है ।
Shortcut – Subordinate Clause के पूर्व किसी न किसी Subordinating Conjunction का प्रयोग अवश्य ही होता है जबकि एक Principal Clause के पूर्व किसी भी Conjunction का प्रयोग नहीं होता है । जैसे – She feels that we should buy a car.
उक्त वाक्य में that का प्रयोग we should buy a car के पूर्व हुआ है, अतः यह एक Subordinate Clause है तथा She feels के पूर्व किसी भी Conjunction का प्रयोग नहीं हुआ है, अतः यह एक Principal Clause है ।
अन्य उदाहरण –
Test Exercise 1
Identify the main clause, the subordinate clause and the conjuction in each of the following sentences :
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों में प्रधान उपवाक्य, सहायक उपवाक्य व संयोजक को पहचानिये-
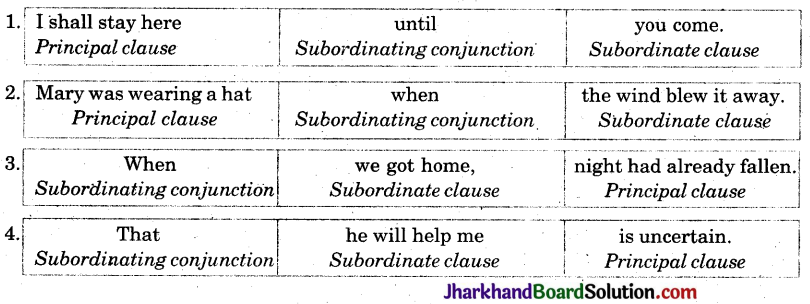
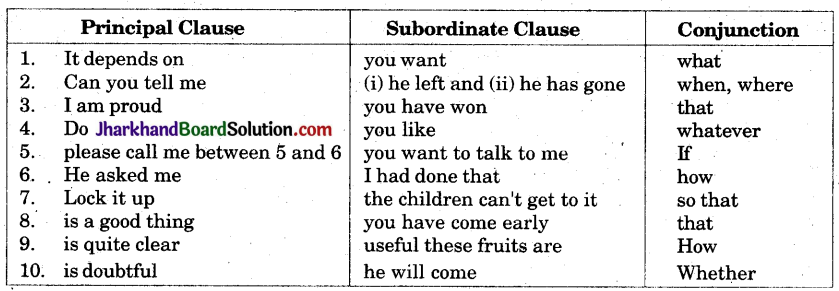
1. It depends on what you want.
2. Can you tell me when he left and where he has gone.
3. I am proud that you have won.
4. Do whatever you like.
5. If you want to talk to me, please call me between 5 and 6.
6. He asked me how I had done that.
7. Lock it up so that the children can’t get to it.
8. That you have come early is a good thing.
9. How useful these fruits are is quite clear.
10. Whether he will come is doubtful.
Answers:
1. Noun Cluses
A noun clause is a subordinate clause that can be used in one of the positions that is usually occupied by a noun/pronoun/noun phrase in a sentence – subject, object or complement.
एक Noun clause वह आश्रित उपवाक्य होता है जो किसी संज्ञा/सर्वनाम/noun phrase द्वारा किसी वाक्य में किये जा रहे कार्य को करे ।
![]()
अर्थात् – Noun Clause वह Clause है जो Noun का काम करे ।
Noun Clause को निम्नलिखित पाँच रूपों में पहचान सकते हैं-
(1) Subject to a Verb ( क्रिया के subject के रूप में ) :
- What he said pleased me.
- Where she is going is not known.
- That he went there is uncertain.
उपर्युक्त वाक्यों में तिरछे छपे शब्द Subordinate Noun Clauses हैं । ये Sentences में subjects का कार्य करते हैं ।
नोट – ऐसा प्रयोग सदैव Principal Clause के पहले होता है और Principal Clause का कर्त्ता ‘it’ छिपा रहता
(2) Object to a Verb ( क्रिया के object के रूप में ) :
- He told me that he was going to Kolkata.
- I do not know where he lives.
उपर्युक्त वाक्यों में तिरछे छपे शब्द अपने-अपने Sentence में Object का कार्य कर रहे हैं । अतः ये Subordinate Noun Clauses हैं ।
नोट – ये प्रायः Principal Clause के बाद आते हैं ।
(3) Object to a Preposition (Preposition के कर्म के रूप में) :
- Listen to what your teacher says.
- It all depends on how she does.
उपर्युक्त वाक्यों में तिरछे अक्षरों में छपे Clauses, Subordinate Noun Clauses हैं । ये Prepositions to, on के बाद प्रयुक्त हुए हैं ।
(4) Complement to a Verb ( क्रिया के पूरक के रूप में) :
- This is what I want to say.
- Life is what we make.
उपर्युक्त वाक्यों में तिरछे अक्षरों में छपे Clauses अपूर्ण क्रिया के पूरक हैं । ये Subordinate Noun Clauses हैं और अपने पूर्व आने वाले Clauses के Verbs के Complements हैं।
(5) Case in Apposition to a Noun or Pronoun (संज्ञा/सर्वनाम के समानाधिकरण के रूप में ) :
- The news that he died is incorrect.
- It is good that he has come back.
जब एक Noun या Pronoun के बाद दूसरा Noun या Pronoun आये और वे दोनों समानार्थक हों अर्थात् एक ही व्यक्ति या वस्तु के लिए प्रयुक्त हों तो दूसरा Noun या Pronoun पहले वाले Noun या Pronoun का Case in Apposition कहलाता है ।
वाक्य 1 में news (Noun) के लिए $h e$ (Pronoun) died; वाक्य 2 में it (Pronoun) के लिए $h e$ (Pronoun) has come back; आये हैं । अतः ये सभी दूसरे शब्द पहले शब्दों के Case in Apposition हैं।
अध्ययन की सुविधा की दृष्टि से हम Noun Clause को दो भागों में बाँट सकते हैं-
- That-Noun Clause – वे clause जो केवल statement को जोड़ने के लिए प्रयुक्त होते हैं ।
- Question Clause – वे clause जो प्रश्नवाचक वाक्य को जोड़ने के लिए प्रयुक्त होते हैं ।
ये केवल statements को ही जोड़ते हैं तथा इनमें Subordinating conjunction के रूप में केवल that का ही प्रयोग किया जाता है । यह निम्नलिखित प्रकार से वाक्य में प्रयुक्त हो सकता है-
![]()
(A) Subject के रूप में : एक That-Noun clause एक वाक्य में subject का कार्य कर सकता है ।
- That he will tell a lie is known to all.
- That she has taken food is uncertain.
(B) Direct Object के रूप में एक That-Noun Clause एक सकर्मक क्रिया के direct-object का काम कर सकता है । जैसे –

उक्त उदाहरण कि that they have won the match एक that-noun clause है जो Principal clause “I know” के लिए Subordinate Clause का काम कर रहा है – कुछ क्रियाएँ ऐसी हैं जिनके साथ That-Noun Clause का प्रयोग oljeci के रूप में किया जा सकता है, जो निम्नलिखित हैं|
(C) Subject Complement के रूप में : Linking verb ‘be’ (is, am, are, was, were) के पश्चात् That-Noun Clause का प्रयोग कर्ता के पूरक के रूप में किया जा सकता है ।

अन्य उदाहरण –
(i) The fact is that I won’t attend the party.
(ii) The problem was that nobody was ready to believe me.
कुछ संज्ञाएँ ऐसी हैं जिनके साथ Subject complement के रूप में That – Noun Clause का प्रयोग किया जा सकता है । इस प्रकार की कुछ Nouns निम्नलिखित हैं –

(D) ‘It’ के साथ : That-Noun Clause का प्रयोग ‘it’ के साथ कर्त्ता के रूप में हो सकता है । जैसे –
- It is strange that there are no lights on.
- It is obvious that she will not help you.
यहाँ ‘it’ को Introductory Subject कहते हैं तथा That-Noun Clause को delayed subject कहते हैं । नोट – appear, happen, occur, seem तथा turn out के साथ भी subject के रूप में it का प्रयोग किया जाता है ।
- It appears that it was you.
- It seemed that some one was calling me.
(E) Adjective complement के रूप में : That-Noun Clause का प्रयोग कभी-कभी एक adjective के complement के रूप में भी हो सकता है। जैसे –
We were glad that everybody helped us.
नीचे कुछ adjectives व past participles (Verb की III form) दिये जा रहे हैं जिनके साथ that-noun clause का प्रयोग होता है-
(F) Noun complement के रूप में : कुछ abstract nouns (भाववाचक संज्ञाओं) के साथ that-noun clause का प्रयोग किया जाता है । जैसे-
- The fear that someone will beat him is baseless.
- The hope that we shall win is not fulfilled.
इस प्रकार की कुछ भाववाचक संज्ञाएँ (abstract nouns) निम्नलिखित हैं –

![]()
A Noun Claused Derived from Questions
प्रश्नवाचक वाक्यों से बनने वाले Noun Clauses को भी दो भागों में बाँटा जा सकता है –
(A) Wh-Clauses
(B) Yes / No Question Clauses
(A) Wh – Clauses
वे Noun Clauses जिनको wh – question word वाले प्रश्नवाचक वाक्यों से जोड़कर बनाया जाता है । जैसे Where are you going ?
यह एक Wh-question word से बनने वाला प्रश्नवाचक वाक्य है । यदि इसका प्रयोग एक subordinate clause के रूप
में किया जाए तो यह इस प्रकार से होगा –
I don’t know where you are going.
यहाँ प्रयुक्त होने वाला wh – question word subordinate तथा Principal Clause के भाव के अनुसार ही प्रयुक्त होता है। इसके लिए किसी नियम विशेष को प्रयुक्त नहीं किया जा सकता है। जैसे –
(i) I never believed (when / where / what) you told her.
Answer:
I never believed what you told her.
मुझे कभी विश्वास नहीं हुआ कि आपने उससे क्या कहा।
(ii) May I know …………….. (where / when / what) I can go home ?
Answer:
May I know when I can go home?
क्या मैं जान सकता हूँ कि मैं घर कब जा सकता हूँ ?
(iii) I don’t know (whom / who / which) she is.
Answer:
I don’t know who she is
उक्त उदाहरणों से स्पष्ट है कि Wh – Question words का अर्थ इस प्रकार से होता है what = कि ……….. क्या when =कि ………. कब who = कि ……….. कौन अर्थात् wh – Question Words का प्रयोग वाक्य के भाव के अनुसार होता है।
(B) Yes/No Question Clauses
(i) Are you coming with me ?
(ii) Can I leave office now?
(iii) Can you remember it?
उपरोक्त तीनों ही वाक्य Yes/No answer type प्रश्नवाचक वाक्य हैं। इनका प्रयोग भी Subordinate clauses के रूप में object की तरह से किया जा सकता है। इस प्रकार के वाक्यों के conjunction के रूप में “if” का प्रयोग किया जाता है। जैसे –
- He asked me if you are coming with me.
- Tell me if I can leave office now.
- I wonder if you can remember it.
Test Exercise 2
Put the most suitable words in the spaces to complete the following sentences choosing from the bracket given against each space:
प्रत्येक रिक्त स्थान के सम्मुख दिये गये कोष्ठक में से सबसे उपयुक्त शब्द चुनकर निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को पूरा करो-
1. She is sure ……………….. (where/that/which) he will make a mistake.
2. Do you want to know ……………….. (how/why/where) the train comes late?
3. Do you know ……………….. (what/if/which) he has passed the exam?
4. ……………….. (That/What/What) he told a lie was his fault.
5. ……………….. (That/What/Where) he will come with us is not sure.
6. Tell me ……………….. (which/where/that) you have seen my purse.
7. Ask her ……………….. (if/where/which) she is ready.
8. I would like to know ……………….. (if/what/where) he was at home yesterday.
9. Ask the bus conductor ……………….. (what/where/if) it is time for the bus to start.
10. I am sure ……………….. (that/where/what) the train is going to depart.
11. No one can doubt ……………….. (that/where/what) he is an intelligent student.
12. I want to know ……………….. (if/what/whose) you met her.
13. I did not hear ……………….. (where/what/that) my father said.
14. Do you know ……………….. (who/when/what) lives in that room ?
15. Can you tell me ……………….. (how/which/whose) you found my purse?
Answers:
1. that
2. why
3. if
4. That
5. That
6. where
7. if
8. if
9. if
10. that
11. that
12. if
13. what
14. who
15. how.
![]()
Test Exercise 3
Put the most suitable words in the spaces to complete the following sentences choosing from the bracket given against each space:
प्रत्येक रिक्त स्थान के सम्मुख दिये गये कोष्ठक में से सबंसे उपयुक्त शब्द चुनकर निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को पूरा करो-
1. ………………… (That/What/Which) you have committed a crime is clear.
2. I wonder ………………… (where/why/whose) house that is. (wonder = जानना चाहता हूँ )
3. My teacher told me ………………… (that/who/whom) the earth moves round the sun.
4. Nobody doubts ………………… (which/whose/that) he is very sincere.
5. Can you tell me ………………… (whom/who/that) wrote the Ram Charit Manas?
6. I will not forget ………………… (that/which/who) you are kind to me.
7. Tell me ………………… (that/if/who) you live in this house.
8. I believe ………………… (that/if/who) you have acted wrongly.
9. I don’t know ………………… (who/that/if) they are.
10. I wonder ………………… (if/what/that) you will manage it.
11. ………………. (That/Which/Who) honesty is the best policy is known to all.
12. I wonder …………. (who/that/which) that woman is.
13. Do you accept …………. (that/which/who) you told a lie?
14. I did not hear …………. (what/that/who) he said.
15. I am sure ………….. (that/what/which) he is going to fall.
Answers:
1. That
2. whose
3. that
4. that
5. who
6. that
7. if
8. that
9. who
10. if
11. That
12. who
13. that
14. what
15. that.
![]()
Test Exercise 4
Put the most suitable words in the spaces to complete the following sentences choosing from the bracket given against each space:
प्रत्येक रिक्त स्थान के सम्मुख दिये गये कोष्ठक में से सबसे उपयुक्त शब्द चुनकर निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को पूरा करो-
1. Tell me …………. (whom/that/if) you saw at the party.
2. Tell me …………. (who/that/if) came to your house.
3. He was certain …………. (who/that/whose) Raman could do it.
4. Do you know …………. (whom/that/if) Helen talked to?
5. Tell me …………. (what/which/when) happened.
6. I don’t know …………. (whose/what/that) book it is.
7. Tell me …………. (what/that/when) he said.
8. Don’t you know …………. (what/when/who) a clause is ?
9. I can’t remember …………. (what/which/whom) kind of car Jim has.
10. Tell me …………. (if/what/which) he has left school.
11. I agree …………. (that/whose/which) everybody will like it.
12. I can’t even remember …………… (how/when/what) old their children are.
13. Could you please tell me ………….(where/what/that) I can catch the bus’?
14. It was sad ………….. (that/if/which) we had to do that.
15. Do you know …………. (who/when/what) broke the window ?
Answers:
1. whom
2. who
3. that
4. whom
5. what
6. whose
7. what
8. what
9. what
10. if
11. that
12. how
13. where
14. that
15. who.
![]()
Test Exercise 5
Put the most suitable words in the spaces to complete the following sentences choosing from the brackets given against each space :
प्रत्येक रिक्त स्थान के सम्मुख दिये गये कोष्ठक में से सबसे उपयुक्त शब्द चुनकर निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को पूरा करो-
1. Will you please tell me ……….(a)……….. (that/when/where) you are returning from office? The fact is ………..(b)………… (that/what/when) I am very busy so I won’t be able to see you. It will be very kind of you ……….(c)………. (that/if/what) you inform me as you reach here. I’ll tell you ………..(d)……….(that/what/which) to buy and what not.
2. Yesterday I went to Jaipur to visit Rajmandir cinema. The fact is (that/which/what) I had never seen that cinema before so I was very curious. But a very bad incident took place with me. I don’t know . ………..(b)………… (how/which/if) it took place. I did not notice ……….(c)………… (that/how/when) a pick-pocket was standing after me. I didn’t know ………. (d) ……….. (which/what/when) to do then.
3. One day when young Edison was at school, the teacher was teaching ……….(a)……….. (when/that/how) birds fly. He got up and asked ……….(b)………. (when/what/why) we couldn’t fly like birds. The teacher replied ……….(c)……….. (that/when/where) men had no wings. The young boy asked ……….(d)……….. (how/when/where) kite can fly though it doesn’t have wings.
4. His shop was still there ……….(a)………. (how/when/where) kite can fly made boots only ……….(b)………. (that/when/where) I was a boy of fourteen. He wonderful. He told me ………..(c)………. (how/when/where) his job had been snatched by the large firms. The fact is ……….(d)………. (that/which/where) it is due to advertisements.
5. A rich man had two sons. They could get ………….(a)…………. (that/what/how) they wanted. They were prodigal. The rich man was not happy at this. The reason is ………..(b)……….. (that/which/how) he did not know how to amend all his sons. On the contrary one day the younger son came to the father and demanded ………..(c)……….. (when/what/that) was in his share. The rich man was annoyed ………..(d)……….. behaved like that. (prodical=अपव्ययी) own son
6. The stipulated period of twelve years of exile was drawing to a close. Yudhishthira noticed with sorrow ………..(a)………….. (that/how/when) all of them had lost their cheerfulness and courage. He asked Nakul ………..(b)…………. (that/if/how) he could see any pool or river nearby. He climbed a tree to look around. He was glad ………..(c)………… (if/what/that) there was water at some distance but he was hopeful ………..(d)……….. (that/what/if) he would be able to reach there. (stipulated= निर्धारित)
7. Last night I had a very horrible dream. I dreamt …………(a)………… (what/that/if) I was followed by a criminal. To make sure ………..(b)…………. (that/where/if) he was following me I entered a street. I started walking fast. I don’t know ………..(c)……….. (how/ what/when) fast I was walking but the man also started walking fast. I couldn’t decide ………..(d)……….. (why/what/which) he was following me.
Answers:
1. (a) when (b) that (c) if (d) what
2. (a) that (b) how (c) that (d) what
3. (a) how (b) why (c) that (d) how
4. (a) when (b) when (c) how (d) that
5. (a) what (b) that (c) what (d) that
6. (a) that (b) if (c) that (d) that
7. (a) that (b) if (c) how (d) why.
![]()
Test Exercise 6
Combine each of the following set of sentence into one complex sentence using Noun Clause :
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों के समूहों को Noun Clause का प्रयोग करते हुए complex sentence में बदलिये-
1. He will make a mistake. She is sure of it.
2. Your opinion is not correct. Mohan is a thief.
3. That was his fault. He told a lie.
4. He will come with us. That is not sure.
5. I don’t know. It will rain.
6. Good students work hard. It is true.
7. The train is going to depart. I am sure of it.
8. No one can doubt this fact. He is an intelligent student.
9. My father said something. I did not hear that.
10. How did you find my purse ? Can you tell me?
Answers:
1. She is sure that he will make a mistake.
2. Your opinion that Mohan is a thief is not correct.
3. That he told a lie was his fault.
4. That he will come with us is not sure.
5. I don’t know if it will rain.
6. It is true that good students work hard.
7. I am sure that the train is going to depart.
8. No one can doubt that he is an intelligent student.
9. I did not hear what my father said.
10. Can you tell me how you found my purse ?
Test Exercise 7
Combine each set of simple sentence into one complex sentence by using a Noun Clause :
Simple Sentence के प्रत्येक युग्म को Noun Clause का प्रयोग करते हुए एक complex sentence के रूप में संयोजित करो –
1. It is clear. You have committed a crime.
2. The earth moves round the sun. My teacher told me.
3. He is very sincere. Nobody doubts it.
4. Who wrote the Ram Charit Manas ? Can you tell me ?
5. You are kind to me. I will not forget it.
6. He is very honest. I do not doubt it.
7. You have acted wrongly. I believe so.
8. The rains would come. That was our hope. Our hope was wrong.
9. Honesty is the best policy. That is known to all.
10. You told a lie. Do you accept it ?
Answers:
1. That you have committed a crime is clear.
2. My teacher told me that the earth moves round the sun.
3. Nobody doubts that he is very sincere.
4. Can you tell me who wrote the Ram Charit Manas?
5. I will not forget that you are kind to me.
6. I do not doubt that he is very honest.
7. I believe that you have acted wrongly.
8. Our hope that the rains would come was wrong.
9. That honesty is the best policy is known to all.
10. Do you accept that you told a lie?
2. Relative Clause
Relative Clause वह clause है जो वाक्य में एक adjective का कार्य करे अर्थात् जो किसी Noun या Pronoun को qualify करे। यह अपनी पूर्ववर्ती-संज्ञा (Antecedent Noun) के बारे. में कुछ बताता है। जैसे –
- This is the camera which I have recently bought.
- You can buy the books that you need.
- The boy whom you helped is very poor.
- The man who stole your purse has been arrested.
उपर्युक्त उदाहरणों में
……………….. which I have recently bought. कैमरे के बारे में बताता है ।
……………….. that you need. पुस्तकों के बारे में बताता है ।
……………….. whom you helped ……………. लड़के के बारे में बताता है ।
तथा ……………..who stole your purse ………….. व्यक्ति के बारे में बताता है ।
Relative clause को जोड़ने में प्रयुक्त होने वाले शब्द Relative Pronouns कहलाते हैं ।
Relative Clauses दो प्रकार के होते हैं –
(1) Defining Clauses : ये किसी व्यक्ति/वस्तु/जानवर के विषय में ‘विशेषण’ के रूप में जानकारी प्रदान करते हैं । Defining Clauses के बिना किसी संज्ञा की पहचान अधूरी रहती है IDefining Clauses में commas (,) का प्रयोग नहीं किया जाता है । ये संज्ञा के विषय में Restrictive Meaning प्रदान करते हैं, जैसे –
My brother who lives in London visited us last week. (Defining Clause)
यहाँ Defining Clause ‘who lives in London’ का प्रयोग हुआ है ।
यहाँ My brother की विशेषता who lives in London से बताई गई है । उक्त वाक्य का आशय यह हुआ कि
‘मेरा (एकंमात्र) भाई जो लन्दन में रहता है पिछले सप्ताह हमारे यहाँ आया ।’ इस प्रकार Defining Clause ने ‘My brother’ के Meaning को Restrict (सीमित) कर दिया ।
(2) Non-defining Clauses : ये अपने पूर्ववर्ती संज्ञा के विषय में सीमित जानकारी प्रदान नहीं करते । ये संज्ञा के विषय में Continuative Meaning प्रदान करते हैं ।
Non-defining clauses में clauses को commas (,) द्वारा बंद किया जाता है, जैसे –
My brother, who lives in London, visited us last week. (Non-defining Clause)
Commas (,) के प्रयोग के कारण यहाँ ‘who lives in London’ Non-defining Clause है ।
इस वाक्य का अर्थ होगा ‘मेरा (एक) भाई जो लन्दन में रहता है वह पिछले सप्ताह हमारे यहाँ आया ।’ अतः Non-defining Clauses के कारण My brother का meaning Restrictive (सीमित) न होकर continuative हो गया । दोनों वाक्यों का
![]()
अन्तर निम्न प्रकार रहा –
(1) Defining Clause वाले वाक्य के अनुसार ‘मेरा केवल एक ही भाई है जो लन्दन में रहता है ।’ (Restrictive Meaning)
(2) Non-defining Clause के अनुसार ‘मेरा एक भाई लन्दन में रहता है तथा मेरे अन्य भाई भी हैं ।'(Continuative Meaning)
Relative Pronouns जो Defining Relative Clauses में प्रयुक्त होते हैं ।
| Subject | Object | Preposition | Possessive | |
| For persons | who that | whom/who that | ’that ……. ……… preposition | whose |
| For things | which that | which that | that …….. ……… preposition | whose/ of which |
Relative Pronouns जो Non-defining Relative Clauses में प्रयुक्त होते हैं –
| for persons | for things | |
| Subject | —, who — , | —, which —, |
| Object | —whom/who —, | —, which —, |
| Preposition | —, preposition + whom —, | —, preposition + which —, |
| — whom — preposition, | — , which — preposition, | |
| Possessive | — whose — | —, of which/whose —, |
Relative Prondins के पयाल जब वाव्य में रिकत ए्यान दिया हो
Shortcuts
1. Who का प्रयोग
1. Who का प्रयोग
यदि रिक्त स्थान से पूर्व कोई (Person) व्यक्ति है तथा रिक्त स्थान के पश्चात् कोई Verb ( क्रिया) है तो उत्तर who ही आयेगा।
Pattern ( सूत्र ) : Person Verb ………………
1. I know Mr Sharma, …………… teaches you English.
Answer. who
2. The boy………….. is standing there is my brother.
Answer. who
2. Whom का प्रयोग
यदि रिक्त स्थान से पूर्व कोई व्यक्ति (Person) तथा रिक्त स्थान के पश्चात् कोई व्यक्ति (Person) + Verb हो तो उत्तर whom ही आयेगा ।

Answers:
1. whom
2. whom
3. whom
3. Whose का प्रयोग – जिसका, जिनका, जिसकी आदि ।
यदि रिक्त स्थान से पूर्व कोई व्यक्ति (Person) तथा रिक्त स्थान के पश्चात् कोई वस्तु (thing) + Verb या thing + Person + Verb या Person + Person + Verb या Person + Verb हो तो whose का प्रयोग किया जा सकता है ।
Pattern : Person …………………… + thing + Verb …………………….
Person …………………… + thing + person + Verb ……………………
Person …………………… + person + person + Verb ……………………
Person …………………… + person + Verb ……………………
किन्तु whom तथा whose का अन्तर समझने में सावधानी अवश्य रखें ।
नोट – वाक्य के अर्थ के अनुसार यहाँ whose का प्रयोग करें, न कि whom का ।
Answer:
1. whose
2. whose
3. whose
4. whose
![]()
4. Which का प्रयोग – जिसका, जिसकी, जिसके
रिक्त स्थान से पूर्व यदि कोई Lifeless thing या Animal (निर्जीव वस्तु या जानवर) हो तथा रिक्त स्थान के पश्चात् Noun या Verb हो तो रिक्त स्थान में which का प्रयोग होता है । जैसे –
1. The dog ………………………. bit you is his.
Answer: which
2. The book ……………………… Mohan gave me is yours.
Answer: which
नोट – यदि रिक्त स्थान से पूर्व वस्तु/जानवर + Preposition हो तो रिक्त स्थान में which का ही प्रयोग होगा। जैसे –
1. The post for ………………. I was selected is temporary.
Answer: which
2. I don’t like the house in ……………….. he lives.
Answer: which
5. What का प्रयोग – जो
(1) वाक्य के प्रारम्भ में रिक्त स्थान होने पर ।
(2) Verb के पश्चात् रिक्त स्थान होने पर ।
(3) Verb + Object के पश्चात् रिक्त स्थान होने पर तथा वाक्य में कोई भी Antecedent नहीं होने पर । जैसे
1. …………. cannot be cured must be endured (वाक्य के प्रारम्भ में रिक्त स्थान)
Answer: What
2. This is ………….. he likes (verb)
Answer: What
3. Do …………. you please. (verb)
Answer: what
4. Give him ………… he demands. (verb +obj.)
Answer: what
5. Please tell me …………. you need (verb + obj.)
Answer: what
6. When का प्रयोग – जब, जिस समय
यदि रिक्त स्थान के ठीक पहले समय दिया हो तो when का ही प्रयोग किया जाता है । जैसे –
1. It was midnight ………………. the thief entered the house.
Answer: when
2. It was Sunday ………………. we went on a picnic.
Answer: when
3. It was 2010 ………. my father purchased this house.
Answer: when
![]()
7. Where का प्रयोग – जहाँ
यदि वाक्य में रिक्त स्थान के पूर्व दिए गए शब्द का सम्बन्ध स्थान से हो या स्थान सूचक हो तो where का प्रयोग किया जाता है । जैसे –
1. This is the temple ………. Gandhiji was shot dead.
Answer: where
2. This is the school ……….. I studied for five years.
Answer: where
3. The house ……………. I am staying is very big.
Answer: where
8. Why का प्रयोग – कि – क्यों
जब रिक्त स्थान के पूर्व reason (कारण) दिया हो । जैसे –
1. This is the reason he didn’t come.
Answer: why
2. This is the reason I called you.
Answer: why
9. That का प्रयोग
That के प्रयोग की पाँच प्रमुख शर्तें – हम who, whom या which के स्थान पर that का प्रयोग कहाँ करें, इसकी प्रमुख शर्तें निम्न प्रकार हैं –
(i) यदि वाक्य में रिक्त स्थान के पहले वाले Noun (Antecedent) से पूर्व superlative degree हो। जैसे
Mohan is the tallest boy ……… reads in our school. (boy से पहले superlative degree)
Answer: that
(ii) यदि वाक्य Interrogative है तो Relative Pronouns – who, whom, which के स्थान पर that का प्रयोग होता है । जैसे –
1. Who is he ………. troubles you ?
Answer: that
2. What is it ……… worries him so much ?
Answer: that
3. Who is the man ………. abuses you ?
Answer: that
4. What is it ………….. you like?
Answer: that
(iii) यदि रिक्त स्थान के पूर्व only, any, same, all, nothing, no one, nobody, anybody, anything, none, little आदि शब्द हों । जैसे –
1. All ……… glitters is not gold.
Answer: that
2. This is the same person ……… you beat.
Answer: that
(iv) यदि किसी वाक्य में रिक्त स्थान के पूर्व व्यक्ति + वस्तु (Person + thing) या व्यक्ति + जानवर
(Person + Animal) आये हों तो that लगेगा । जैसे-
1. The man and the dog .. you see live the next door.
Answer: that
2. The cowherd and his cow we see walking on the ground live in this village.
Answer: that
(v) यदि Preposition का प्रयोग Relative Clause की Verb के पश्चात् हुआ हो तो that का प्रयोग होगा न कि who, whom या whieh का । जैसे –
1. I know the man that you are talking about. (Prep.)
यदि Preposition पहले आता तो वाक्य बनता –
I know the man about whom you are talking. (Prep.)
2. I know the house that he lives in. (Prep.)
3. This is the book that I told you about. (Prep.)
![]()
Test Exercise 1
Fill in the blanks with suitable Relative Pronouns given in the bracket :
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों में रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति कोष्ठक में दिए गए उपयुक्त Relative Pronouns से करो
1. The building ………. (where/that/who) I live in was built in the 1920s.
2. That’s Peter, the boy …………….. (who/which/whom) has just arrived at the airport.
3. Do you remember the name of the man (whom/whose/that) car you crashed into?
4. I mean ………….. (that/which/what) I say.
5. The hotel ………….. (that/which/where) we stayed in was very good for the price.
6. This is the best book …………….. (that/which/whose) I’ve ever loved.
7. Mrs Richa ………….. (that/who/whom) is a taxi driver, lives in a village.
8. Thank you very much for your e-mail ………….. (that/who/when) was very interesting.
9. The man ………….. (whose/which/that) father is a professor forgot his umbrella.
10. The children ……………….. (whom/who/that) shouted in the street are not from our school.
Answers:
1. that
2. who
3. whose
4. what
5. where
6. that
7. who
8. that
9. whose
10. who.
Test Exercise 2
Fill in the blanks with when, where or why :
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों में रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति when, where या why से करो :
1. We visited the school ………….. my father taught.
2. I met her last year ………….. he came to my house.
3. We all looked at the place ………….. the fire had started.
4. I met him in the cafe ……………. he was working as a waiter.
5. Do you remember the time ………….. Vinod fell off his bicycle?
6. Did they tell you the reason ………….. they were late?
7. The cat sat on the wall ……… it had a good view of the birds.
8. I’m talking about the time ………….. they didn’t have cars.
9. Last year I spent my holiday in Spain ………….. I met Shashi.
10. I couldn’t understand the reason ………….. they were so rude.
Answers:
1. where
2. when
3. where
4. where
5. when
6. why
7. where
8. when
9. where
10. why.
Test Exercise 3
Fill in the blanks with suitable Relative Pronouns given in the brackets :
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों में रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति कोष्ठक में दिए गए उपयुक्त Relative Pronouns से करो-
1. Do you remember the day …………… (which/that/when) we bought it ?
2. The only present ……………. (that/whose/when) I didn’t like was the gold ring.
3. We live in a city ……………. (when/which/where) new restaurants open every day.
4. This is the book ……………. (which/that/when) I told you about.
5. I saw the man ……………. (whose/who/whom) car you hit.
6. The tower ………………. (that/whose/where) blew down in the storm was over 10 years old.
7. Jodhpur is the city ……………. (where/that/which) I was born.
8. The photo …………… (that/who/when) you are looking at was taken by my sister.
9. Do you know the woman ……………. (that/which/whose) son won the lottery ?
10. Jyoti Prakash will never forget the day ……………. (when/that/which) he passed his last exam.
11. This is the place ……………. (when/that/where) I hurt myself last week.
Answers:
1. when
2. that
3. where
4. that
5. whose
6. that
7. where
8. that
9. whose
10. when
11. where.
![]()
Test Exercise 4
Fill in the blanks with suitable Relative Pronouns given in brackets:
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों में रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति कोष्ठक में दिए गए उपयुक्त Relative Pronouns से करो-
1. This is the machine
2. Have you read the book ……………. (that/who/when) costs ten lakh rupees.
3. Mary, ……………. (which/that/what) I gave you ?
4. The house ……………. (that/who/whom) had been listening to the conversation, looked angry.
5. Mrs Sinha, ……………. (that/who/whom) she bought three months ago looked lovely.
6. Is this the person ……………. (that/who/whom) had been very ill, died yesterday.
7. I didn’t receive the letters ……………. (who/that/whom) stole your hand bag ?
8. We didn’t like the secretary ……………. (that/when/whose) she sent me.
9. I didn’t find the money ……………… (who/whom/which) the agency sent.
10. Kamal, ……………. (who/whom/that) everybody loves, is absent today.
Answers:
1. that
2. that
3. who
4. that
5. who
6. that
7. that
8. whom
9. that
10. whom.
Test Exercise 5
Put the most suitable words in the spaces to complete the following sentences choosing from brackets given against each space :
प्रत्येक रिक्त स्थान के सम्मुख दिये गये कोष्ठक में से सबसे उपयुक्त शब्द चुनकर निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को पूरा करो-
1. One of the employees, ………. (a)……… (who/that/which) was a postman and also helped at the post office, went to his boss laughing heartily and showed the letter ………. (b) ………. (whom/which/whose) Lencho had written to God. The post master but almost turne. (who/whom/which) was a fat, amiable fellow also broke out laughing, (that/who/whom) he had got.
Answer:
(a) who (b) which (c) who (d) that
2. The following Sunday Lencho, ……….(a)………. (who/when/whom) wrote a letter to God, came a bit earlier than usual to ask if there was a letter for him. It was the postman himself ……….(b)………. (whom/who/which) handed the letter to him while the postmaster, experiencing the contentment of a man ………. (c)……….. (who/which/when) has performed a good deed, looked on from his office. Lencho showed not the slightest surprise to find the money ………..(d)………. (who/that/whose) was in the envelope.
Answer:
(a) who (b) who (c) who (d) that
3. The house ……….(a) ……… (who/whom/that) was the only one in the entire valley sat on the crest of a low hill. From this height one could see the river and the field of ripe corn dotted with the flowers
……….(b)……….. (that/whom/where) always promised a good harvest. The only thing ………. (c) ………. (that/whose/who) the earth needed was a downpour or at least a shower. Throughout the morning Lencho ………. (d) ………. (who/that/which) knew his fields intimately, had done nothing else but see the sky towards the north-east.
Answer:
(a) that (b) that (c) that (d) who
4. The young seagull ………. (a)………. (who/whom/whose) was alone on his ledge had been afraid to fly with his two brothers and his sister. He ran back to the little hole under the ledge ………. (b) ………. (which/that/where) he slept at night. Even each of his brothers and his little sister ………. (c) ………. (who/whose/whom) wings were far shorter than his own ran to the brink and flew away. But he failed to muster up courage to take that plunge ………..(d)…………. (which/who/whom) appeared to him so desperate.
Answer:
(a) who (b) where (c) whose (d) which
![]()
5. There was no answer. The radio ……….(a)………. (that/whose/whom) was in my old Dakota was dead too. I had no radio, no compass, and I could not see the place ……….(b)……….. (which/where/when) I was. I was lost in the storm. Then, in the black clouds quite near to me, I saw another aeroplane ……….(c)………. (which/when/where) had no lights on its wings but I could see it flying next to me through the storm. I could see the face of the pilot ………. (d)………. (who/whom/where) was flying that aeroplane.
Answer:
(a) that (b) where (c) which (d) who
6. My father ………. (a)………. (who/whom/that) was the most adorable father I have ever seen, didn’t marry my mother ……….(b)………. (when/until/while) he was thirty-six and she was twenty-five. My sister ………. (c)………… (whose/who/whom) name is Margot was born in Frankfurt in Germany in 1926. I was born on 12 June 1929. I lived in Frankfurt …………..(d)………. (until/when/while) I was four.
Answer:
(a) who (b) until (c) whose (d) until
7. Dearest Kitty, Our entire class is quaking in its boots. The reason, of course, is the forthcoming meeting in ….. (a)………. (which/whom/who) the teachers decide………..(b)………. (who/whom/when) wifi move up to the next form and ……….(c)………. (who/whom/that) will be kept back. Half the class is making bets. G.N. and I laugh ourselves silly at the two boys behind us, C.N. and Jacques ……….(d)………. (that/which/who) have staked their entire saving on their bet.
Answer:
(a) which (b) who (c) who (d) who
8. With the opening of that sack began a phase of my life ……….(a)………. (that/when/who) has not yet ended, and may, for all I know, not end before I do. It is, in fact, a thraldom to otters, an otter fixation, ……….(b)…………. (that/when/who) I have since found to be shared by most other people, ……….(c)………. (who/whom/which) have ever owned one. The creature ……….(d)…………. (that/who/whom) emerged from this sack on to the spacious tiled floor of the Consulate bedroom resembled most of all a very small, medievally-conceived dragon.
Answer:
(a) that (b) that (c) who (d) that
9. One day ………..(a)………. (when/where/which) I was in the fifth standard at the Rameshwaram Elementary School, a new teacher came to our class. I used to wear a cap ……….(b)………. (who/which/whose) marked me as a muslim, and always sat in the front row ……….(c)……… (who/that/whom) was next to Ramanadha Sastry, ……….(d)……… priest’s son sitting with a muslim boy.
Answer:
(a) when (b) which (c) that (d) who
10. That day had come about through the unimaginable sacrifices of thousands of my people, people ……….(a)………. (when/whose/where) suffering and courage can never be counted or repaid. I felt that day, as I have on so many other days; ……….(b)………. (that/when/ who) I was simply the sum of all those African patriots ……….(c)………. (who/when/ whom) had gone before me. That long and noble line ended and now began again with me. I was pained that I was not able to thank them and that they were not able to see ……….(d)……….. (when/what/where) their sacrifices had wrought.
Answer:
(a) whose (b) that (c) who (d) what.
Test Exercise 6
Join the following sentences using suitable Ralative Pronouns:
Clause: Simple Sentence के प्रत्येक युग्म को Adjective का प्रयोग करते हुए complex sentence के रूप में संयोजित करो –
1. I met Meera. Her friends like dogs. (whose)
2. I met Dolly. Her request was for a sweet song. (whose)
3. I saw Sohan. He was a bus conductor. (who)
4. This is Anil. All like him. (whom)
5. This is Ram. Your father was calling him. (whom)
6. Where is Dr Singh ? You were talking about him. (whom)
7. Mother told stories of Han Ram. He used to cheer his soldiers. (who)
8. Puneet is living with his uncle. His parents are in Mumbai. (whose)
9. Prachi is studying in Pune. She is my niece. (who)
10. The Taj Mahal was built by Shah Jahan. It is very beautiful. (which)
![]()
Test Exercise 6
Join the following sentences using suitable Ralative Pronouns :
उपयुक्त Ralative Pronouns का प्रयोग करते हुए निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को जोड़ो –
1. I met Meera. Her friends like dogs. (whose)
2. I met Dolly. Her request was for a sweet song. (whose)
3. I saw Sohan. He was a bus conductor. (who)
4. This is Anil. All like him. (whom)
5. This is Ram. Your father was calling him. (whom)
6. Where is Dr Singh ? You were talking about him. (whom)
7. Mother told stories of Hari Ram. He used to cheer his soldiers. (who)
8. Puneet is living with his uncle. His parents are in Mumbai. (whose)
9. Prachi is studying in Pune. She is my niece. (who)
10. The Taj Mahal was built by Shah Jahan. It is very beautiful. (which)
Answers:
1. I met Meera whose friends like dogs.
2. I met Dolly whose request was for a sweet song.
3. I saw Sohan who was a bus conductor.
4. This is Anil whom all like.
5. This is Ram whom your father was calling.
6. Where is Dr Singh about whom you were talking ?
7. Mother told stories of Hari Ram who used to cheer his soldiers.
8. Puneet, whose parents are in Mumbai, is living with his uncle.
9. Prachi, who is my niece, is studying in Pune.
10. The Taj Mahal, which is very beautiful, was bulit by Shah Jahan.
Test Exercise 7
Combine each set of simple sentence into one complex sentence by using an Adjective
Clause: Simple Sentence के प्रत्येक युग्म को Adjective का प्रयोग करते हुए complex sentence के रूप में संयोजित करो –
1. My brother will come from Delhi. I do not know the time.
2. The pen is mine. It is on the table.
3. Ramesh is a good boy. He belongs to a good family.
4. I have a dog. It is very faithful.
5. We came upon a certain cottage. Here a shepherd was living with family.
6. The boy is standing there. He is my brother.
7. He did not come to school today. Do you know the reason?
8. Will you give me the watch ? It is on the table.
9. I bought a pen a few days back. I have lost it.
10. The book is in my hand. I like it most.
11. I know a man. He eats paper.
Answers:
1. I do not know the time when my brother will come from Delhi.
2. The pen which is on the table is mine.
3. Ramesh, who belongs to a good family, is a good boy.
Or
Ramesh, who is good boy, belongs to a good family.
4. I have a dog which is very faithful.
5. We came upon a certain cottage where a shepherd was living with his family.
6. The boy who is standing there is my brother.
7. Do you know the reason why he did not come to school today?
8. Will you give me the watch that is on the table?
9. I have lost the pen which I bought a few days back.
10. The book which I like most is in my hand.
11. I know a man who eats paper.
![]()
3. Adverbial Clause of Condition
(शर्त वाले क्रिया-विशेषण उपवाक्य)
शर्तवाचक वाक्य (Conditional Sentence) दो उपवाक्यों (Clauses) से बना होता है-

जैसे – If you call him, he will come. यदि तुम उसे बुलाओगे तो वह आयेगा । उपर्युक्त वाक्य में ‘If you call him’ को If-Clause, Conditional Clause या Subordinate Clause कहते हैं । इसके द्वारा कोई शर्त व्यक्त की जाती है.।
दूसरा वाक्य ‘he will come’ Main Clause या Principal Clause कहलाता है । इसके द्वारा शर्त का परिणाम व्यक्त किया जाता है ।
नोट – यहाँ यह आवश्यक नहीं है कि वाक्य रचना हमेशा Conditional Clause + Principal Clause ही हो। यह Principal Clause + Conditional Clause की भी हो सकती है ।
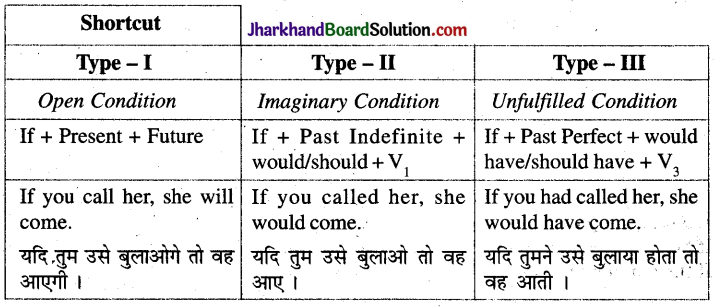
अर्थात् – If you call him, he will come को He will come, if you call him. भी लिख सकते हैं । Conditional Sentences के द्वारा तीन प्रकार की शर्तें व्यक्त की जा सकती हैं –
- Open or Probable Conditions.
- Hypothetical, Unlikely, Improbable
or
Imaginary Conditions. - Impossible or Unfulfilled Conditions.
(A) Open or Probable Conditions
खुली या सम्भाव्य शर्त या Type-I
इस प्रकार के वाक्यों में Conditional Clause द्वारा ऐसी शर्त रखी जाती है कि यदि उसे पूरा कर दिया जाये तो Main Clause में कही गई बात पूरी हो सकती है। अर्थात् इस प्रकार के वाक्यों से केवल सम्भावना प्रकट होती है । इसलिए इसे Open Condition भी कहते हैं । जैसे –
(i) If you work hard, you will pass.
यदि आप कठोर परिश्रम करेंगे तो आप पास होंगे ।
(अर्थात पहली शर्त मानने पर दूसरी बात पूरी हो सकती है ।)
(ii) If I go to Agra, I shall visit the Taj Mahal.
यदि मैं आगरा जाऊँगा तो ताजमहल घूमने जाऊँगा।
(iii) If you run fast, you will catch the train.
यदि आप तेज दौड़ेंगे तो आप गाड़ी पकड़ लेंगे ।
(iv) He will have a sunstroke, if he plays in the sun.
यदि वह धूप में खेलेगा तो उसे लू लग जाएगी ।
(v) We shall get wet, if it rains.
यदि बरसात होगी तो हम भीग जाएँगे ।
उक्त उदाहरणों से यह स्पष्ट है कि इस प्रकार की शर्त व्यक्त करने के लिए If-clause present में तथा
Main Clause → future में होता है ।
वाक्य रचना – If + Present + Future
Main Clause में will के स्थान पर may/can/must आदि का प्रयोग भी हो सकता है । जैसे –
(a) If + present + may/might (possibility व्यक्त करता है |)
If you call him, he may/might come. (सम्भव है वह आये ।)
(b) If + present + may (permission के लिए ।)
If you complete your work, you may go home.
(c) If + present + can (permission तथा ability के लिए |)
If you bet, I can lift this.
(d) If + present + must / should इत्यादि (command, request or advice व्यक्त करने के लिए ।) If you want to lose weight, you must eat less bread.
(e) If + present + present (Natural law, Habitual Reactions, General truth तथा Scientific fact के लिए 1)
If you heat butter, it melts.
यदि आप मक्खन को गर्म करोगे तो यह पिघलेगा । (दूसरा कार्य स्वतः ही होता है ।)
![]()
Test Exercise 1
Fill in the blanks using correct tense and form of the verbs given in brackets :
कोष्ठक में दी गई क्रियाओं के सही tense व form का प्रयोग करते हुए रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति करो –
1. If you ………….. (work) hard, you will get success.
2. If you ………….. (have) headache, you can take rest.
3. If you don’t do your home work, the teacher …………. (punish) you.
4. If she …………. (be) careless, she will hurt her finger.
5. If he …………. (not work) hard, he will not get through.
6. They will get wet, if it …………. (rain).
7. We ………….. (play) chess, if you come to my house tomorrow.
8. The water will suit the patient, if the water …………. (be) fresh.
9. Plants grow quickly, if you …………. (water) them.
10. I cannot understand you, if you ……………. (speak) Chinese.
Answers:
1. work
2. have
3. will punish
4. is
5. does not work
6. rains
7. shall play
8. is
9. water
10. speak.
(B) Hypothetical, Unlikely, Improbable or Imaginary Conditions
असम्भाव्य या काल्पनिक शर्त या Type – II
इस प्रकार के शर्त वाले वाक्यों में If – Clause में ही ऐसी शर्त रख दी जाती है जो वर्तमान में ही पूरी नहीं हो सकती । अत: Main Clause में व्यक्त किये गये परिणाम प्राप्त हो ही नहीं सकते । इस प्रकार के वाक्यों में If – Clause past tense में व main clause – would/should +V की I form में होता है अर्थात्
If + Past + ………….. would / should }+V की I Form
(i) If I knew his address, I would give you.
यदि मुझे उसका पता याद हो तो मैं तुम्हें दूँ।
(अर्थात् न तो वर्तमान में मुझे पता याद है और न ही मैं दूँगा ।)
(ii) If I had money, I would lend you.
यदि मेरे पास धन हो तो मैं तुम्हें उधार दूँ।
(iii) If a ghost appeared here, all would flee away.
यदि यहाँ भूत आ जाये तो सभी भाग जायें ।
ज्ञात तथ्यों के विपरीत परिकल्पना (contrary to known facts) प्रस्तुत करने के लिए –
If + ………….. were ………. +…………….. would/should.
का प्रयोग किया जाता है, जैसे –
(i) If I were a bird, I would fly in the sky.
यदि मैं एक पक्षी होऊँ, तो मैं आसमान में उड़ँ ।
(अर्थात् न तो मैं पक्षी हूँ और न ही आसमान में उडूँगा ।)
(ii) If I were a lion, I would roar.
यदि मैं एक शेर होऊँ तो मैं दहाड़ँ।
(iii) Were I you, I would buy this.
यदि मैं तुम जैसा होऊँ तो मैं यह खरीद लूँ।
(If के स्थान पर were का प्रयोग किया जा सकता है ।)
Test Exercise 2
Fill in the blanks using correct form and tense of the verbs given in brackets :
रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति कोष्ठकों में दी गई क्रियाओं के सही form व tense से करो –
1 I would lend you, if I ………………. (have) money
2. If I were the Prime Minister, I …..(make) you the Home Minister.
3. I ………………. (read) this hook, if I knew Chinese.
4. If I were you, I ………………. (help) her.
5. If he ………………. (work) hard, he would pass.
6. If I knew her mobile number, I ………………. (tell) you.
7. I would not do it, if I ………………. (be) you.
8. If I saw Radha, I ………………. (be) delighted.
9. The bridge ………………. (collapse), if a heavy truck went over it.
10. What would happen, if she………………. (call) me?
11. He ………………. (speak) to you, if he saw you.
12. III had time, I ………………. (come) and (see) you.
13. What …………………you (do), if you met Mr Lohar?
14. If he ………………. (write) to me, I should write to him.
15. If the sun didn’t shine, the fruit ………………. (not ripen).
Answers:
1. had
2. would make
3. would read
4. would help
5. worked
6. would tell
7. were,
8. would be
9. would collapse
10. called
11. would speak
12. would come, see
13. would, do
14. wrote
15. would not ripen.
![]()
(c) Impossible ox Jornfillod Condition
असम्भव या अपूर्ण शर्त या Type – III
इस प्रकार के वाक्यों में If-clause द्वारा जो शर्त व्यक्त की जाती है वह भूतकाल की होती है जिसे वर्तमान में पूरा नहीं किया जा सकता है इसलिए Main Clause में व्यक्त परिणाम भी प्राप्त नहीं होगा । अतः इन्हें Impossible Condition कहते हैं । जैसे –
(i) If I had run fast, I would have caught the train.
यदि मैं तेज दौड़ा होता तो मैंने गाड़ी पकड़ ली होती ।
(अर्थात् न तो मैं तेज दौड़ा और न ही गाड़ी पकड़ी ।)
(ii) If Neeraj had worked hard, he would have succeeded.
यदि नीरज ने कठिन परिश्रम किया होता तो वह सफल हो गया होता ।
(iii) If the gardener had watered the plants, they would not have withered.
यदि माली ने पौधों को पानी दिया होता तो वे नहीं सूखते ।
Note – If के स्थान पर had का प्रयोग करके भी इस प्रकार के conditional sentence को बनाया जा सकता है’। Had पहले लगाने पर यह If का कार्य करेगा । जैसे Had he gone to Agra, he would have seen the Taj Mahal. यदि वह आगरा गया होता तो वह ताजमहल देख पाता ।
वाक्य रचना –
If + Past perfect + ………. would/should + have + V की III form……….
अर्थात् – If – clause Past perfect में होगा व Main Clause में would / should + have +V की III form आएगी
Test Exercise 3
Fill in the blanks using the correct form and tense of the verbs given in brackets :
कोष्ठकों में दी गई क्रियाओं के सही form व tense का प्रयोग करते हुए रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति करो –
1. If she had caught the train, she ……….. (reach) in time.
2. You wouldn’t have been hungry now, if you ………… (take) lunch.
3. If I had known that you were ill, I ……….. (visit) you in the hospital.
4. You would have saved money, if you ……….. (buy) this bike last year.
5. If they had played better, they ……….. (win) the match.
6. If you ……….. (be) at the meeting, I should have seen you.
7. They would have heard better, if you ……….. (speak) louder.
8. It would have been better, if they ……….. (not come).
9. If he hadn’t explained it t me, I ……….. (never understand).
10. She would have done it, if they ………… (know) how to.
Answers:
1. would have reached
2. had taken
3. would have visited
4. had bought
5. would have won
6. had been
7. had spoken
8. had not come
9. would never have understood
10. had known.
![]()
Different Ways of Expressing Conditions
निम्नलिखित में से किसी भी रूप में Condition व्यक्त की जा सकती है-
1. Unless = If ………… not के द्वारा । जैसे-
If you do not work hard, you will not pass.
Unless you work hard, you will not pass.
यदि आप कठोर परिश्रम नहीं करोगे तो आप पास नहीं होंगे ।
यदि रखिये Unless वाले Clause में not नहीं लगाया जाता है परन्तु –
If you work hard, you will pass.
Unless you work hard, you will not pass.
यदि If-clause में not नहीं है तो unless लगाने पर main clause में not लगाया जाता है ।
2. ‘should, were, had’ helping Verbs से जो वाक्य आरम्भ होते हैं, वे condition का अर्थ रखते हैं, जैसे –
(i) Should you be feeling unwell, you may go.
Or If you should be feeling unwell, you may go.
(ii) Were I a king, I would reward you.
Or If I were a king, I would reward you.
(iii) Had I been at fault, I would have confessed it.
Or If I had been at fault, I would have confessed it.
3. Conjunctional Phrase जैसे in case के द्वारा । जैसे-
यह सम्भावना के प्रति सजगता (carefulness) को प्रदर्शित करता है तथा इसमें हमेशा main clause + in case + subordinate clause होता है ।
(i) Take an umbrella in case it rains.
एक छाता ले लो अगर वर्षा हो जाए ।
(ii) Call me in case you need my help.
यदि तुम्हें मेरी मदद की जरूरत पड़े तो मुझे बुलाना ।
4. Participle Phrase “Provided/Provided that, on condition that, so long as” का प्रयोग करके, जब शर्त का भाव strong तरीके से व्यक्त करना हो । जैसे-
(i) You can use my bike so long as you don’t give it to anybody else.
(ii) Provided you allow me, I shall speak to him.
5. Imperative Mood का प्रयोग करके । जैसे-
(i) Work hard and you will pass. Or If you work hard, you will pass.
(ii) Neglect your work and you will fail. Or If you neglect your work, you will fail.
(iii) Bring your book or you will be turned out. Or If you do not bring your book, you will be turned out.
6. Interrogative sentences द्वारा । जैसे-
(i) Will you go there ? Then I will also go with you.
Or
If you go there, I will also go with you.
(ii) Have you paid the cost? Then take away the cycle.
Or
If you have paid the cost, take away the cycle.
(iii) Have you paid your fare? Then come in.
Or
If you have paid your fare, come in.
7. Prepositional Phrase ‘But for’ को अपने Object के साथ प्रयोग करके । जैसे
(i) But for your help, I should have been ruined. = If it had not been your help, I should have been ruined. यदि तुम्हारी मदद नहीं होती तो मैं बर्बाद हो गया होता ।
(ii) But for the car we wouldn’t be in time. = If it weren’t the car, we wouldn’t be in time.
यदि कार नहीं हो तो हम समय पर न पहुँचें।
8. Phrase ‘One more’ का प्रयोग करके । जैसे-
(i) One more such loss and we are ruined.
(ii) One more absence and we shall be turned out of the class.
9. Suppose/Supposing का प्रयोग करके । जैसे-
Suppose/Supposing + past + past (असंभव कल्पना व्यक्त करने के लिए ।)
Suppose/Supposing + present + future (ऐसी कल्पना जो पूरी हो सकती है ।)
![]()
(i) Suppose you get a hundred rupee note, what will you do?
= What will you do if you get a hundred rupee note?
मान लो आपको ₹ 100 का एक नोट मिले तो आप क्या करोगे ?
(ii) Supposing the plane came late, what would happen?
= What would happen if the plane came late ?
मान लो हवाई जहाज देरी से आए तो क्या हो ?
10. Whether ……. or = if ……….. or
(इसका प्रयोग दो विकल्पों में से एक विकल्प का चुनाव करने के लिए किया जाता है ।)
You will have to do it whether you are ready or not.
= You will have to do it if you are ready or not.
आपको यह करना है चाहे आप तैयार हों या ना हों ।
11. If only = wish, hope तथा regret व्यक्त करने के लिए । जैसे
(i) If only + Present / Future = hope (आशा / उम्मीद ) व्यक्त करता है If only he comes in time. = हमें उम्मीद है कि वह समय पर आयेगा ।
(ii) If only + Past / Past Perfect = regret (पश्चाताप) व्यक्त करने के लिए । If only she didn’t come. = हमें पश्चाताप है कि वह नहीं आएगा ।
(iii) If only + would = वर्तमान कार्य के लिए पश्चाताप व्यक्त करने के लिए । वर्तमान कार्य पर पश्चाताप व्यक्त करता है ।
If only it would rain. =\mathrm{We} wish it would rain.
हमारी इच्छा है कि बरसात हो जाए, लेकिन नहीं हो रही है ।
12. Once का प्रयोग करके । जैसे
Once you read this book, you will like it:
= If you read this book once, you will like it.
यदि आप इस पुस्तक को एक बार पढ़ोगे तो इसे पसंद करोगे।
13. even if = भले ही
You must do it even if you are not ready.
भले ही आप तैयार न हो आपको यह करना ही है ।
14. Otherwise = if this doesn’t happen / didn’t happen/hadn’t happened = अन्यथा You must do it; otherwise I will punish you. = यदि तुम यह नहीं करोगे तो मैं तुम्हें सजा दूँगा ।
15. Let का प्रयोग करके –
Let it be a cone. मान लो कि यह एक शंकु है ।
इसके द्वारा कल्पना या आदेश/निर्देश को व्यक्त किया जाता है ।
एक ही वाक्य को विभिन्न Conditional Sentences में इस प्रकार से परिवर्तित किया जा सकता है। जैसे-
- If you permit me, I shall go there.
- Unless you permit me, I shall not go there.
- Supposing you permit me, I shall go there.
- Provided you permit me, I shall go there.
- I shall go there, in case you permit me.
- Permit me and I shall go there.
Test Exercise 4
Write the short form of the verbs given in brackets so as to complete the following
Conditional Sentences : कोष्ठकों में दी गई क्रियाओं का सही प्रयोग करते हुए निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को Conditional Sentences के रूप में पूरा कीजिए –
1. If he ……………… to me, I shall give him a book. (come)
2. If you had enough money, you a ……………… moped. (buy)
3. If you had not gone by taxi, you ……………… the train. (miss)
4. If you practiced hard, you……………… the race. (win)
5. The milk will turn sour if you ……………… it at times. (not boil)
6. If you heat ice, it ……………… into water. (turn)
7. If you want to get success, you ……………… very hard. (work)
8. If she had come to me, ………………. her a nice gift. (give)
9. If you insulted me, I ………………you. (beat)
10. If you had said me, I ………………. meal for you. (cook)
Answers:
1. comes
2. would buy
3. would have missed
4. would win
5. do not boil
6. turns
7. must work
8. would have given
9. would beat
10. would have cooked.
![]()
Test Exercise 5
Write the correct form of the verbs given in brackets so as to complete the following
Conditional Sentences : कोष्ठकों में दी गई क्रियाओं का सही प्रयोग करते हुए निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को Conditional Sentences के रूप में पूरा कीजिए –
1. If you ……….. him, he might come. (call)
2. He ……….. the tree if you had given him an axe. (cut)
3. Mamta ………… good marks if you guided her. (get)
4. You would not have got wet if you ……….. an umbrella with you. (have)
5. The stranger could have been saved if someone ……….. treatment in time. (give)
6. If I ……….. wings, I would fly in the sky. (have)
7. If he had started earlier from his house he ……….. the train. (get)
8. If you paid the bill in time ……….. a rebate on it. (get)
9. If you take a shortcut, you ……………. much time. (spare)
10. If he had not left schooling, he ………..a great scholar. (become)
Answers:
1. call
2. would have cut
3. would get
4. had had
5. had given
6. had
7. would have got
8. would get
9. can spare
10. would have become.
Test Exercise 6
Fill in the blanks with correct form of the verbs given in brackets :
कोष्ठकों में दी गई क्रियाओं के सही रूप से रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति कीजिए –
1. If you ………….. (find) a skeleton in the cellar, dont mention it to anyone.
2. If you pass your examination, we ………….. (have) a celebration.
3. What ………….. (happen) if I press this button?
4. I should have voted for her if I ………….. (have) a vote then.
5. If you go to Paris, where you ………….. (stay).
6. if someone offered to buy you one of those rings, which you ………….. (choose).
7. The flight may be cancelled if the fog ………….. (get) thicker.
.8,. Ifthernilkman ………….. (come), tell him to leave two litre.
9. Someone ………….. (sit) on your glasses if you leave them there.
10. You would play better bridge if you ………….. (not talk) so much. (bridge = ताश का खेल)
Answers:
1. find
2. will have
3. will happen
4. had had
5. will stay
6. would choose
7. gets
8. comes
9. will sit
10. did not talk.
![]()
Test Exercise 7
Complete the conditional sentences. Decide whether to use Type I, II or III.
शर्त वाले वाक्यों को पूर्ण करो । यह निश्चय करो कि क्या Type I, II या III का प्रयोग करना है –
1. If I had time, I ……………. (go) shopping with you.
2. If you ……………. (speak) English, you will get along with them perfectly.
3. If they had gone for a walk, they ……………. (turn) the light off.
4. If she ……………. (come) to see us, we will go to the zoo.
5. I would have told you, if I ……………. (see) him.
6. Would you mind, if I …………….(invite) me……………….. (open) the window ?
8. My friend …………….(invite) me, I wouldn’t have said no.
9. If I ……………. (meet) me at the station, if he gets the afternoon off.
10. If they ……………. (not do) it, nobody would do it.
11. If we ……………. (have) time at the weekend, they will come to see us.
12. If I ……………. (know) about your problem, we would have helped you …………….. (be) you, I would not buy that dress.
Answers:
1. would go
2. speak
3. would have turned
4. comes
5. had seen
6. opened
7. had invited
8. will meet
9. did not do
10. have
11. had known
12. were.
Test Exercise 8
Put the most suitable words in the spaces to complete the following sentences choosing from the brackets given against each space :
प्रत्येक रिक्त स्थान के सम्भुख दिये गये कोष्ठक में से सबसे उपयुक्त शब्द चुनकर निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को पूरा करो-
1. If you let me known about the situation, I. ………(a)……….. (will help/help/would help) you in the matter. If I ……… (b)……….. (am/were/was) you I would tell everything in detail. If you …………(c)……….. (met/had met/meet) me earlier, you would have known what type of a person I am. Provided you ………………(d)……………. (told/tell/had told) me, I shall not tell it to anyone else.
Answer:
(a) will help (b) were (c) had met (d) tell
2. Yesterday I met one of my old friends. I think that he had not recognized me. If he ……..(a)……….. (had recognized/recognized/recognizes) me, he would have talked to me. If he had seen me waving my hand towards him, he …………..(b)……….. (will reply/ will have replied/would have replied) in the same way. Now I think that if I …………..(c)………… (phone/will phone/phoned) him about the matter, he will recognize me easily. I feel that I had made a mistake. If I …………..(d)………….. (talked/had talked/ will talk) to him, he would have recognized me.
Answer:
(a) had recognized (b) would have replied (c) phone (d) had talked
3. Today I would have missed the train if I ……….(a)……….. (had not hired/did not hire/do not hire) a taxi for station. When I reached station, the train had already arrived. I knew that I had to catch the train even if I…………(b)………. (did not buy/had not bought/do not buy) a ticket. If I ……….. (c)………… (went/go/had gone) to the booking window, I would not be able to catch the train so I did not buy ticket. If the train had not been on the platform, I ……….. (d)………… (would have bought/would buy/will buy) ticket.
Answer:
(a) had not hired (b) did not buy (c) had gone (d) would have bought
4. If you want to get a reservation on a train, you ………..(a)……….. (have/will have/would have) to go to reservation counter and apply for the same. If you ………..(b)………… (don’t have/didn’t have/hadn’t had) the reservation form, you can get it on the counter. Once you ……….(c)………. (fill/filled/fills) the form you will have to present it to the clerk at the booking window. If the seat (d). ……….(d)………. (is/was/will be) available, you will get reservation easily.
Answer:
(a) will have (b) don’t have (c) fill (d) is
![]()
5. If you ………..(a)……….. (want/wanted/had wanted) to buy this car, you should get it booked in advance. If you ………..(b)………. (want/had wanted/wanted) to get its delivery right now, you will have to pay extra. But I want to tell you that if I ………(c)……….. (were/was/am) you, I would get it booked in advance. There is no need to spend extra money. If you ……….(d)……….. (had told/told/tell) me earlier, I would have booked it for you.
Answer:
(a) want (b) want (c) were (d) had told
6. If you ………….(a)…………. (want/wanted/had wanted) to get up early, you should buy an alarm clock. It will help you in getting up early. If you ………….(b)…………. (didn’t know/ don’t know/hadn’t know) from where to buy, I will tell you everything. I will help you. If you don’t have money, I ………….(c)…………. (will lend/would lend/will have lent) you. If you had informed your parents in time, they ……………(d)…………. (will have sent/would send/would have sent) you money for an alarm clock.
Answer:
(a) want (b) don’t know (c) will lend (d) would have sent
7. Get up early and you …………..(a)…………. (will getlgetJwould get) enough time for morning exercise. If you do morning exercise you ………….(b)….. (will be/would be/are) fit and healthy. Unless you ………….(c)…………. (get up/don’t get up/didn’t get up) early, you will not be able to take exercise. If I myself had followed this advice, I ………….(d)…………. (would have been/will have been/will be) fit and healthy.
Answer:
(a) will get (b) will be (c) get up (d) would have been
8. What will you do if you ………….(a)……….. (lost/lose/will lose) your purse? If I …………..(b)……….. (have lost/had lost/will have lost) my purse, I would have borrowed money from my friends. But I don’t know what you ………….(c)………… (will do/will have done/would do). Please tell me. If you …………..(d)………….(don’t have/didn’t have/hadn’t have) money, you will not be able to reach home.
Answer:
(a) lose (b) had lost (c) will do (d) don’t have
9. The Sharmas are working very hard this year. If they …….(a)………. (work/worked! will work) really hard, they will all get to go on vacation. Sushil is a real estate agent. If he ……(b) ………. (sells/sold/had sold) 20 more houses than last year, he will have enough money to take the family to Goa. Sushila is an interior designer, if she finds 25 new clients, the family ……… (c) ……… (will be/would be/will have been) able to stay in a 5 star resort. Grandma Sonali walks to the convenience store every day and buys a lottery ticket. If she ……….(d)……… (wins/won/had won) the jackpot, 8he will be able to retire in the Taj Hotel! (jackpot = किसी खेल की इनाम की राशि) )
Answer:
(a) work (b) sells (c) will be (d) wins
10. Peter doesn’t have much self-confidence. He always doubts himself, “If I.. …(a) ……… (were/are/have been) smarter, I would get good grades.” “If I were taller, I ……… (b)……… (can be/could be/could have been) on the basketball team.” “If I ………….(c)……… (were/are/had been) stronger, I could be on the wrestling team.” “If I were better looking, I ………(d)……… (would have/will have/have) a girlfriend.” “If I were funnier, .I’d have more friends.”
Answer:
(a) were (b) could be (c) were (d) would have.
4. Adverbial Clause Of time
ये Complex Sentences होते हैं । इनमें भी एक Principal Clause व एक या अधिक Subordinate Clauses होते हैं। जैसे –
- I met Kavita after she had taken food.
- I have not seen him since he left Mathura.
- While I was watching T V, my brother was studying.
उक्त तीनों ही वाक्यों में after she had taken food, since he left Mathura व While I was watching TV, Subordinate Clauses हैं जो समय को व्यक्त कर रहे हैं ।
वे Subordinate Clause जो समय को व्यक्त करते हैं Time Clause कहलाते हैं ।
Position of Time Clauses :
- After the Main Clause – सामान्यतया Time Clause को Main Clause के ठीक बाद में रखा जाता है। जैसे – She phoned me when I was not at home.
- Before the Main Clause – Time Clause को Main Clause के पूर्व भी रखा जा सकता है । जैसे After I had taken food, I went home.
- In the middle of the Main Clause – Time Clause को कभी-कभी Main Clause के बीच में भी रखा जा सकता है । जैसे –
His father, when he was at Kota, was a manager in a Carrier Point.
Chief Conjunctions
Conjunctions जिनका प्रयोग time clauses के साथ होता है वे सामान्यतया निम्नलिखित हैंwhen, as soon as, as long as, until (till) before, after, by the time, while, as, since, no sooner …………… than, scarcely (hardly) ……………. when, आदि ।
विशेष – Time Clause कभी भी Future Tense में नहीं होता है । जब एक Future Tense के वाक्य को Time Clause के रूप में प्रयुक्त किया जाता है तो उसे Present में बदल दिया जाता है। जैसे –
(i) He will come. वह आयेगा ।
We will take food. हम खाना खायेंगे ।
When he comes, we will take food.
जब वह आयेगा, हम खाना खायेंगे ।
![]()
(ii) I will be at school. I will learn English.
When I am at school, I will learn English.
जब मैं स्कूल में होऊँगा तो मैं अँग्रेजी सीखूँगा ।
महत्त्वपूर्ण Sabordinate Conjunetions के प्रयोग
(A) When
(1) जब किसी लम्बी चलती घटना के बीच में कोई. छोटी घटना घटित हो –
- They were watching TV when they heard the door bell. जब उन्होंने दरवाजे की घण्टी सुनी वे टी.वी. देख रहे थे।
- She was cooking food when the milkman called. जब दूध वाले ने आवाज लगाई वह खाना पका रही थी।
- I was reading a novel when someone called me. जब किसी ने मुझे पुकारा मैं उपन्यास पढ़ रहा था।
(2) जब एक घटना के बाद दूसरी हो –
- When the lights went out, I lit some candles. जब लाइट चली गई तो मैंने कुछ मोमबत्तियाँ जलाईं।
- When the rain stops, we will go out. जब बरसात रुकेगी तो हम बाहर जायेंगे।
(3) भूतकाल को समयावधि या जीवन की अवधध की बात करने के लिए –
- When I was a baby, I was called Guddu. जब मैं बच्चा था तब मुझे गुड्डू पुकारा जाता था।
- When we lived in Kota, we had three servants. जब हम कोटा में रहते थे तब हमारे तीन नौकर थे।
(4) हर समय
- When my mother comes in my room, I am studying. जब जब भी मेरी माँ मेरे कमरे में आती है मैं पढ़ता रहता हूँ।
- He was standing every time when his wife came in. जब जब भी उसकी पत्नी अन्दर आती थी, वह हर बार खड़ा होता था।
(B) As
(1) जब दो घटनाएँ एक साथ हों या एक घटना के पूरी होते-होते ही दूसरी घटना भी घटित हो जाए (‘ठीक उसी समय’ के अर्थ में)
(i) As you turn, you will see me.
जैसे ही तुम घूमोगे तो तुम मुझे देख लोगे ।
(ii) As I entered the room, the phone started ringing.
जैसे ही मैं कमरे में घुसा फोन बजने लगा ।
(2) जब आप कोई एक कार्य कर रहे होते हैं तभी दूसरा कार्य हो जाए ।
(i) My mother slipped as she was going downstairs.
सीढ़ियों से नीचे उतरते समय मेरी माँ फिसल गई ।
(ii) He was seen as he was climbing over the wall.
दीवार फाँदते समय उसे देखा गया ।
(3) As + a situation = because.
(i) As he was not there, he didn’t know anything.
चूँकि वह वहाँ पर नहीं था इसलिए उसे कुछ भी पता नहीं है।
(C) While
इसका प्रयोग जब, जिस समय के अर्थ में होता है –
(i) I met a lot of people while I was on a holiday.
जिस समय मैं छुट्टी पर था उस समय मैं कई लोगों से मिला ।
(ii) What did you say about me while I was out?
जिस समय मैं बाहर था उस समय आपने मेरे बारे में क्या कहा ?
(D) As soon as = ज्यों ही
जब एक कार्य के पूरा होते ही दूसरा हो –
(i) He saw me. He called me.
As soon as he saw me, he called me.
ज्यों ही उसने मुझे देखा, उसने मुझे पुकारा ।
(ii) Come back as soon as you can.
ज्यों ही तुम आ सको वापस आओ ।
![]()
(E) No sooner……………..than.
No sooner के साथ verb उसी प्रकार से प्रयुक्त होती है जिस प्रकार से एक प्रश्नवाचक वाक्य में होती है अर्थात् उसमें helping verb को subject के पूर्व रखा जाता है।
Pattern – No sooner + H.V. + subject + M.V. + …… + than + subject + verb
(i) He saw me. He called me.
No sooner did he see me than he called me.
(ii) He had taken food. He began to feel drowsy.
No sooner had he taken food than he began to feel drowsy.
(F) Hardly / scarcely ………. when.
इसका प्रयोग भी उसी प्रकार से होता है जैसे
No sooner ……………. than का होता है ।
Pattern –
Hardly/Scarcely + H. V. + Subject + M. V …. + when + Subject + Verb …
Hardly/Scarcely had he taken food when he began to feel drowsy.
Hardly के साथ when का प्रयोग किया जाता है।
(G) Before = पहले
जब दो कार्यों में एक कार्य के समाप्त होने से पहले दूसरा समाप्त हो जाए ।
Pattern – Past Perfect + before + Past Indefinite.
Or
Before + Past Indefinite + Past Perfect
अर्थात् Subordinate Clause Past Indefinite में होगा ।
(i) The patient had died before the doctor came.
या
Before the doctor came, the patient had died.
डॉक्टर के आने के पहले मरीज मर चुका था ।
(ii) The film had started before we reached the theatre.
हमारे थियेटर पहुँचने से पहले फिल्म शुरू हो चुकी थी।
(H) After = पश्चात्
जब दो कार्यों में एक कार्य के समाप्त होने के पश्चात् दूसरा कार्य समाप्त हो ।
Pattern – After + Past Perfect + Past Indefinite.
Or
Past Indefinite + after + Past Perfect.
अर्थात् after के साथ वाला clause (Subordinate Clause) Past Perfect में होगा ।
(i) The patient died after the doctor had come.
डॉक्टर के आ जाने के पश्चात् मरीज मरा ।
(ii) After we had reached the station, the train departed.
हमारे स्टेशन पहुँचने के पश्चात् गाड़ी रवाना हुईं।
(I) Since (तब) से, (उस समय) से
इसका प्रयोग Perfect Tenses के साथ होता है । जैसे –
(i) I haven’t seen her since I left school.
जब से मैंने स्कूल छोड़ा तब से मैंने उसे नहीं देखा है।
(ii) He has been studying since they came here.
जब से वे यहाँ आए तब से वह पढ़ रहा है।
![]()
(J) till/until = जब तक कि नहीं
(i) Wait here till (until) the light changes to green. जब तक लाइट हरी नहीं हो जाए तब तक यहीं इंतजार करो।
(ii) Don’t move until I say. तब तक मैं नहीं कहूँ हिलना मत।
until और till में कोई अन्तर नहीं है और वे एक दूसरे का स्थान ले सकते हैं। जैसे
Do not go till I get ready.
Or
Do not go until I get ready.
(K) Some More Examples of Time Clauses
(i) I’ll have completed it by the time you get back.
(ii) Now you tell it, I suppose I must have seen you somewhere before.
(iii) She has not phoned me since she went to Kota.
(iv) No sooner had he arrived than he demanded a meal.
(v) Scarcely had he left the house before we missed the train.
Test Exercise 1
Put the most suitable words in the space to complete the following sentences choosing from the bracket given against each space :
प्रत्येक रिक्त स्थान के सम्मुख दिये गये कोष्ठक में से सबसे उपयुक्त शब्द चुनकर निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को पूरा करो-
1. I will cook food ……………. (as soon as/till/before) I come home.
2. I want to finish my work …………….. (till/after/before) we go out.
3. She is going to look after the cat ……………. (as/before/while) I am away on holiday.
4. I’ll e-mail you ……………. (as soon as/while/till) I arrive.
5. We’ll find a hotel ……………. (when/till/no sooner) we arrive in Mathura.
6. Don’t cross the road ……………. (as/when/until) you see the red signal.
7. I’ll give you a ring ……………. (when/before/until) we get back from our vacation.
8. Dad donates his suits to charity ……………. (after/before/while) he has worn them a year.
9. Anne ate an apple …………….. (as/when/before) she studied her vocabulary.
10. ……………. (While/Till/After) they feed the birds, older people love to sit in the park.
Answers:
1. as soon as
2. before
3. while
4. as soon as
5. when
6. until
7. when
8. after
9. as
10. While.
Test Exercise 2
Put the most suitable words in the space to complete the following sentences choosing from the bracket given against each space:
प्रत्येक रिक्त स्थान के सम्मुख दिये गये कोष्ठक में से सबसे उपयुक्त शब्द चुनकर निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को पूरा करो-
1. ………. (We&/Since) I was much younger, I enjoyed camping out.
2. ………. (After/As long as/Before) the man had stopped his car to help, Ramesh recognized him.
3. You seem happy ……….. (till/when/after) you help others.
4. …………….. (‘When/As/Since) the cat is away, the mice will play.
5. I will wash up ……….. (before/when/while) he goes to bed.
6. ………. (No sooner/When/Hardly) it gets cold, I’ll light the fire.
7. …………… (When/Till/Than) the queen arrives, the audience will stand up.
8. I will pay you ………. (when/before/since) I get my cheque.
9. He will have to behave better ………. (when/as/before) he goes to school.
10. ………. (When/As long as/Till) he returns, I’ll give him the keys.
Answers:
1. When
2. After
3. when
4. When
5. before
6. When
7. When
8. when
9. when
10. When
![]()
Test Exercise 3
Put the most suitable words in the space to complete the following sentences choosing from the bracket given against each space :
प्रत्येक रिक्त स्थान के सम्मुख दिये गये कोष्ठक में से सबसे उपयुक्त शब्द चुनकर निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को पूरा करो-
1. Heat the water ………. (until/as/before) it begins to vapour.
2. I won’t wait ………. (till/as/since) he comes back.
3. We will turn on TV ………. (till/as soon as/for) the light comes.
4. She will send me the mobile ………. (as soon as/before/till) she receives my payment.
5. I’ll wait there ………. (as/as long as/after) you like.
6. ……….. (As soon as/No sooner/Hardly) the children saw the river, they wanted to bathe.
7. …….. (As/When/While) we visit the zoo, we’ll go to Jai Garh Fort.
8. What will you do ………. (when/since/as soon as) you finish painting the bridge?
9. ………. (While/When/Since) you have served the meal, you can go home.
10. Anil will go to America ………. (no sooner/hardly/as soon as) he receives his visa.
Answers:
1. until
2. till
3. as soon as
4. as soon as
5. as slong as
6. As soon as
7. When
8. when
9. When
10. as soon as.
Test Exercise 4
Put the most suitable words in the space to complete the following sentences choosing from the bracket given against each space:
प्रत्येक रिक्त स्थान के सम्मुख दिये गये कोष्ठक में से सबसे उपयुक्त शब्द चुनकर निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को पूरा करो-
1. Don’t give the milk to the baby …………….. (until/when/as) it cools.
2. I don’t want anyone to know the secret, but I will tell you ………………. (until/when/before) we are alone.
3. All the flates in Jamuna Dham ar€ exactly the same so …………….. (when/while/after) you see one, you have seen them all.
4. ……… (As soon as/Since/No sooner) the train stopped, I jumped out.
5. I will do your home work ……………… (hardly/as soon as/before) I do my own.
6. Don’t forget to look both sides …………….. (after/before/hardly) you cross the road.
7. Give this letter to your teacher …………….. (as soon as/since/after) he comes.
8. You will have to wait for me …………….. (till/as/when) I finish my lunch.
9. This car won’t be mine …………….. (until/while/after) I make payment.
10. Don’t forget to sweep the floor …………….. (before/after/as) you start your prayer.
Answers:
1. until
2. when
3. when
4. As soon as
5. as soon as
6. before
7. as soon as
8. till
9. until
10. before.
![]()
Test Exercise 5
Fill in the blanks with the suitable conjunction given in the bracket:
कोष्ठक में दिए गए उपयुक्त Conjunction से रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति करो-
1. There was a time ………….. [while/as/when] all stories were printed on paper.
2. They turned the pages ………….. [who/whose/which] were yellow and crinkly.
3. She had been doing worse and worse ………….. [when/while/until] her mother had shaken her head sorrowfully.
4. The Margie hated most was the slot ………….. [when/while/where] she had to put homework on test papers.
5. I don’t know ………….. [what/who/whom] kind of school they had all that time ago.
6. ………….. [If/When/While] you don’t like it, you don’t have to read the book.
7. Margie was thinking about ……………….. [how/till/until] the kid must have loved it in the old days.
8. It was discovered. It ……………….. [hat/who/whom] her hearing was severly impaired.
9. There were advised ……………….. [that/what/which] she should be fitted hearing aids.
10. If you work hard and know ……………….. [where/when/while] you are going, you will get there.
11. I could hear ……………….. [till/as/while] I was eleven.
12. That doesn’t explain ……………….. [how/what/when] she managed to learn French.
13. ……….. [When/While/As] she plays the xylophone, she can sense the sound passing up the stick into her fingertips.
14. They see that there is nowhere ……………….. [while/that/when] they cannot go.
15. She has given inspiration to those ……………….. [who/whom/which] are handicapped.
Answers:
1. when
2. which
3. until
4. where
5. what
6. If
7. how
8. that
9. that
10. where
11. till
12. how
13. when
14. that
15. who
Test Exercise 6
Fill in the blanks withthe suitable conjunctions given in the bracket:
कोष्ठक में दिए गए उपयुक्त Conjunction से रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति करो-
1. A barber from a family of professional musicians ………………. [who/whom/which] had excess to the royal palace, decided to improve the tonal quality of the pungi.
2. In the evening ………………. [when/while/that] he came home she stood near the staircase.
3. She sat on a stool ………………. [until/while/when] he woke and stretched.
4. ……………….. [While/When/As] Alice was putting her to bed she grew suddenly afraid.
5. …………………….. [When/While/I’ill] he finally did learn to speak, he uttered everything twice.
6. Einstein did not know ……………….[what/that/which] to do with other children.
7. He went to high school in Munich ………………. [where/whom/who] Einsteins family had moved.
8. Einstein got his wish to continue his education in German-speaking Switzerland, in a city …………… [which/where/while] was more liberal than Munich.
9. He also felt a special interest in a fellow student Mueva Marie, ………………….. [whom/who?/which] he found to be a ‘clever creature’.
10. Letters survive in [which/whom/where]they put their affection into words.
11. ………………. [While/When/As soon as] he was supposed to be assessing other people’s inventions, Einstein was actually developing his ideas in secret.
12. ……… [While/When/As] Einstein was solving the most difficult problems in physics, his private life was unravelling.
13. She thought Mileva, ……………………. [who/that/whom] was three year older than her son, was too old to him.
14. In 1915, he. d published his General Theory of Relativity ……………… [which/what/whose] provide a new interpretation of gravity.
15. An eclipse the sun in 1919 brought proof ……………… [that/when/who] it was accurate.
Answers:
1. who
2. when
3. until
4. while
5. when
6. what
7. where
8. which
9. whom
10. which
11. while
12. while
13. who
14. which
15. that.
![]()
Test Exercise 7
Fill in the blanks with the suitable conjunctions given in the bracket:
कोष्ठक में दिए गए उपयुक्त Conjunction से रिक्त स्थानों की पूर्ति करो-
1. I …………. [When/While/No sooner] the Nazis came to power in Germany in 1933, Einstein emigrated to the united states.
2. The topic came up ……….. [when/while/which] we were discussing snakes.
3. ………….. could say [that/what/when] the rates and I shared the room.
4. I also possessed one the solitary black coat ………. [which/whom/whose] I was then wearing.
5. One feels tempted to look into a mirror …………..[when/while/whom] it is near one.
6. I would get married to a woman doctor. …………………. [who/whom/when] had plenty of money.
7. ………. [If/As/When] I made some silly mistake and needed to run away she should not be able to run after me and catch me.
8. I ran and ran ………….. [till/when/while] I reached a friends house.
9. It was the snake ………….. [which/when/whom] was taken with its own beauty.
10. We lived in our ancestral house ………….. [which/when/where] was built in the middle of the nineteenth century.
11. The Second World War was broke out in 1939 ………….. [when/where/how] I was eight years old.
12. …….. [While/When/As] I was leaving his house, Sivasubramania Iyer invited me to join him for dinner again the next weekend.
13. I lived with a man once ………….. [whom/who/that] used to make me mad that way.
14. The girl was given the name ‘Santosh’ ………….. [which/which/whom] means contentment.
15. The right moment came ………….. [when/where/which] she turned sixteen.
Answers:
1. when
2. when
3. that
4. which
5. when
6. who
7. If
8. till
9. which
10. which
11. when
12. when
13. who
14. which
15. when.