Jharkhand Board JAC Class 10 Science Solutions Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
JAC Board Class 10 Science Solutions Chapter 1 Chemical Reactions and Equations
Jharkhand Board Class 10 Science Chemical Reactions and Equations Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Which of the statements about the reaction below are incorrect?
2PbO(s) + C(s) → 2Pb(s) + CO2(g)
(a) Lead is getting reduced.
(b) Carbon dioxide is getting oxidised.
(c) Carbon is getting oxidised.
(d) Lead oxide is getting reduced.
(i) (a) and (b)
(ii) (a) and (c)
(iii) (a), (b) and (c) (iv) all
Answer:
(i) (a) and (b) s
Question 2.
Fe2O3 + 2Al → Al2O3 + 2Fe
The above reaction is an example of a…
(a) combination reaction.
(b) double displacement reaction.
(c) decomposition reaction.
(d) displacement reaction.
Answer:
(d) displacement reaction.
Question 3.
What happens when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to iron fillings?
(a) Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are s produced.
(b) Chlorine gas and iron hydroxide are produced.
(c) No reaction takes place.
(d) Iron salt and water are produced,
Answer:
Hydrogen gas and iron chloride are produced.
Question 4.
What is a balanced chemical equation? Why should chemical equations be balanced?
Answer:
A chemical reaction in which atoms of $ different elements of reactant and product side are equal then the chemical equation S is called balanced chemical equation.
Now, according to the law of conservation of mass, matter can neither be created, nor be destroyed. Hence in a chemical reaction, mass of reactants S should be equal to the mass of products.
Number of atoms of each element should be equal on both side of the reaction for keeping mass constant.
Hence, it is essential to balance the chemical equation.
![]()
Question 5.
Translate the following statements into chemical equations and then balance them:
(a) Hydrogen gas combine with nitrogen to form ammonia.
(b) Hydrogen sulphide gas burns in air to give water and sulphur dioxide.
(c) Barium chloride reacts with aluminium sulphate to give aluminium chloride and a precipitate of barium sulphate.
(d) Potassiam metal reacts with water to give potassium hydroxide and hydrogen gas.
Answer:

Question 6.
Balance the following chemical equations:
(a) HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 → Ca(NO3)2 + H2O
(b) NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + H2O
(c) NaCl + AgNO3 → AgCl + NaNO3
(d) BaCl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + HCl
Answer:
(a) 2HNO3 + Ca(OH)2 → Ca(NO3)2 + 2H2O
(b) 2NaOH + H2SO4 → Na2SO4 + 2H2O
(c) NaCl + AgNO3 → AgCl + NaNO3
(d) BaCl2 + H2SO4 → BaSO4 + 2HCl
Question 7.
Write the balanced chemical equations for the following reactions :
(a) Calcium hydroxide + Carbon dioxide → Calcium carbonate + Water
(b) Zinc + Silver nitrate → Zinc nitrate + Silver
(c) Aluminium + Copper chloride → Aluminium chloride + Copper
(d) Barium chloride + Potassium sulphate → Barium sulphate + Potassium chloride
Answer:
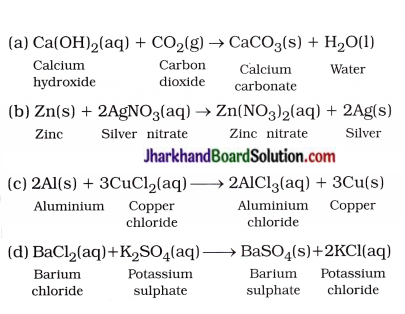
Question 8.
Write the balanced chemical equation for the following and identify the type of reaction in each case :
(a) Potassium bromide (aq) + Barium iodide(aq) → Potassium iodide(aq) + Barium bromide (s)
(b) Zinc carbonate(s) → Zinc oxide (s) + Carbon dioxide (g)
(c) Hydrogen (g) + Chlorine (g) → Hydrogen chloride (g)
(d) Magnesium (s) + Hydrochloric acid(aq) → Magnesium chloride(aq) + Hydrogen(g)
Answer:
(a) 2KBr(aq) + Bal2(aq) → 2KI(aq) + BaBr2(s)
The given reaction is a double displacement reaction.

Given reaction is a thermal decomposition reaction.
(c) H2(g) + Cl2(g) → 2HCl(g)
Given reaction is a combination reaction.
(d) Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g)
Given reaction is a displacement reaction.
Question 9.
What does one mean by exothermic and endothermic reactions? Give examples.
Answer:
Exothermic reaction : A chemical reaction in which heat energy is evolved during the formation of product is called an exothermic reaction.
For example, Combustion of natural gas (methane) is an exothermic reaction.
CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) + heat
Endothermic reaction : A chemical reaction in which heat is absorbed during the formation of products is called an endothermic reaction.
For example, Decomposition of silver chloride in presence of sunlight is called an endothermic reaction.
![]()
Question 10.
Why is respiration considered an exothermic reaction? Explain.
Answer:
We need energy for staying alive. We get S this energy from the diet (food), we eat. Food is broken down into simple substances during digestion.
For example, Rice, potatoes and bread consists of carbohydrates. These carbohydrates are broken down to form glucose. This glucose combines with oxygen in the cells of our body and provides energy. This reaction (process) is called respiration. Thus, energy is released during respiration process, it is called an exothermic reaction.
C6H12O6(aq) + 6O2(aq) → 6CO2(aq) + 6H2O(1) + Energy
Question 11.
Why are decomposition reactions called the opposite of combination reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Answer:
In decomposition reaction, a single molecule of reactant by absorbing heat is broken down into two or more products (atoms), while in combination reaction, opposite phenomenon to decomposition reaction is observed. In combination reaction, two or more substances (elements or compounds) combine to form a single product with heat change.
Decomposition reactions :
AB + Energy → A + B
![]()
Combination reactions :
A + B > AB + Energy
C(s) + O2(g) → CO2(g) + Energy
Question 12.
Write one equation each for decomposition reactions where energy is supplied in the form of heat, light or electricity.
Answer:
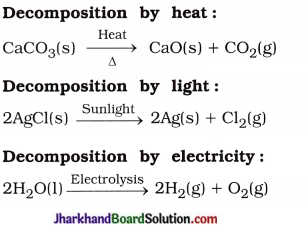
Question 13.
What is the difference between displacement and double displacement reactions? Write equations for these reactions.
Answer:
In displacement reaction, more reactive element displaces less reactive element from its solution. For example, In case of Zn and Ag, Zn being more reactive than Ag, it displaces Ag from its solution of AgNO3.
(i) Zn(s) + 2AgNO3(aq) → Zn(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag(s)
Similarly, Fe being more reactive displaces Cu from CuSO4 solution.
(ii) Fe(s) + CuSO4(aq) → FeSO4(aq) + Cu(s)
In double displacement reaction, two / compounds exchange their ions to form s two new compounds.
For example,
- Na2SO4(aq) + BaCl2(aq) → BaSO4(s) + 2NaCl(aq)
- 2KBr(aq) + BaI2(aq) → 2KI(aq) + BaBr2(s)
![]()
Question 14.
In the refining of silver, the recovery of silver from silver nitrate solution involved displacement by copper metal. Write down the reaction involved.
Answer:
Cu(s) + 2AgNO3(aq) → Cu(NO3)2(aq) + 2Ag(s)
Question 15.
What do you mean by a precipitation reaction? Explain by giving examples.
Answer:
Chemical reaction, in which reactants react to form insoluble precipitate is called precipitation reaction.
For example,
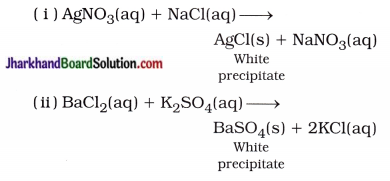
Question 16.
Explain the following in terms of gain or loss of oxygen with two examples each:
(a) Oxidation (b) Reduction
Answer:
(a) Oxidation: It is a reaction in which atom or molecule gains oxygen or loses hydrogen.
For example,
C + O2 → CO2
2Cu + O2 → 2CuO
In above reactions, ‘C’ and ‘Cu’ undergo Oxidation.
(b) Reduction : It is a reaction in which atom or molecule loses oxygen or gains hydrogen.
For example,
CuO + H2 → Cu + H20
CO2 + H2 → CO + H2O
In above reactions, ‘CuO’ and ‘CO2’ undergo reduction.
Question 17.
A shiny brown coloured element ‘X’ on heating in air becomes black in colour. Name the element ‘X’ and the black coloured compound formed.
Answer:
Here, element ‘X’ is copper (Cu). When it is heated in air, it forms black coloured copper oxide (CuO).
For example,
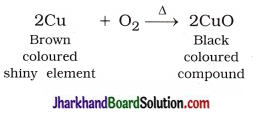
In this reaction, Cu is oxidised to CuO.
Question 18.
Why do we apply paint on iron articles?
Answer:
Iron objects undergo rusting due to metal corrosion; hence, surface of iron is coated with paint to prevent it from rusting. As a result, iron does not come in contact with air. Thus, iron objects remain safe for longer period and rusting does not occur.
Question 19.
Oil and fat containing food items are flushed with nitrogen. Why?
Answer:
Food items containing oil and fat reacts with oxygen and become rancid. Such food items have bad smell and are harmful to health. Hence, to prevent the spoilage of food items, they are flushed with unreactive gas like nitrogen, which acts as an antioxidant.
Question 20.
Explain the following terms with one example each:
(a) Corrosion
(b) Rancidity
Answer:
(a) Corrosion:
Metal gets corroded in the presence of acid and moisture. This process is called corrosion. Rusting of iron, tarnishing of silver, green coating of salt on the utensils of copper are the examples of corrosion.
- Due to corrosion, iron gets covered with a red brown substance (powder) which is called rusting of iron (or corrosion).
- Corrosion causes damage to the articles (objects) made from iron such as car-bodies, bridges, iron railings, ships, etc. There is a huge expenditure to control corrosion.
- Rusting can be prevented by painting the surface of iron or coating the surface of iron with more reactive metal (Zn).
- Prevention of corrosion by coating iron surface with zinc is called galvanisation.
(b) Rancidity:
When food containing oil and fat is kept in an open air, it undergo oxidation and become rancid; due to which their smell and taste changes. This process is called rancidity.
Usually, to avoid rancidity in food containing oil and fat, substances are added which prevent oxidation. Such substances are known as antioxidant substances. Food kept in air-tight containers helps to slow down its oxidation and rancidity is retarded.
Manufacturers of potato chips flush bags of chips with gas such as inactive nitrogen gas as antioxidant to prevent the oxidation of potato chips.
Jharkhand Board Class 10 Science Chemical Reactions and Equations InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Why should a magnesium ribbon be cleaned before burning in air?
Answer:
Magnesium ribbon is more reactive and when it is exposed to air, a layer of MgO is formed on its surface.
2Mg(s) + O2(g) → 2MgO(s)
This layer of MgO is removed by rubbing with sand paper before burning in air. Therefore, magnesium ribbon easily reacts with oxygen. Thus, magnesium ribbon is cleaned before burning in air.
Question 2.
Write the balanced equation for the following chemical reactions :
(1) Hydrogen + Chlorine → Hydrogen chloride
(2) Barium chloride + Aluminium sulphate Barium sulphate + Aluminium chloride
(3) Sodium + Water → Sodium hydroxide + Hydrogen
Answer:
(1) H2(g) + Cl2(g) 2HCl(g)
(2) 3BaCl2(aq) + Al2(SO4)3(aq) → 3BaSO4(s) + 2AlCl3(aq)
(3) 2Na(s) + 2H2O(l) → 2NaOH(aq) + H2(g)
Question 3.
Write a balanced chemical equation with physical state symbols for the following reactions :
(1) Solutions of barium chloride and sodium sulphate in water react to give insoluble barium sulphate and the solution of sodium chloride.
(2) Sodium hydroxide solution (in water) reacts with hydrochloric acid solution (in water) to produce sodium chloride solution and water.
Answer:
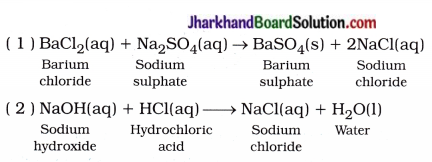
Question 4.
A solution of a substance ‘X’ is used for whitewashing.
(1) Name the substance ‘X’ and write its s formula.
(2) Write the reaction of the substance ‘X’ named in (1) above with water.
Answer:
(1) Substance X is calcium oxide. Its formula is CaO.
(2) Calcium oxide reacts vigorously with water and forms slaked lime (Ca(OH)2) and liberates large amount of heat. It is an exothermic reaction.
CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq) + Heat
Question 5.
Why is the amount of gas collected s in one of the test tubes in activity 1.7 double of the amount collected in the other? Name these gases.
Answer:
Hydrogen and oxygen are obtained separately during the electrolysis of water. Water is made-up of two parts of hydrogen and one part of oxygen. Hence, two parts of hydrogen gas in one test tube and one part of oxygen l gas in another test tube are obtained during the electrolysis of water. Hence, hydrogen and oxygen gases are obtained in the ratio of 2 : 1 by volume.
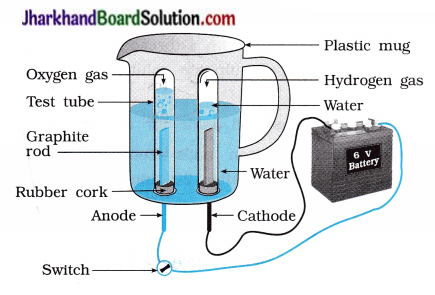
Question 6.
Why does the colour of copper sulphate solution change, when an iron nail ( is dipped in it?
Answer:
When an iron nail is dipped in copper s sulphate solution, iron being more reactive than l copper, it displaces copper from the solution, s As a result, iron sulphate is formed, which is green in colour. Thus, colour of copper sulphate s solution changes.

Question 7.
Give an example of double displacement reaction other than the one ? given in activity 1.10.
Answer:
When sodium carbonate reacts with calcium chloride, it forms a precipitate of calcium S carbonate and sodium chloride. In this reaction, ( exchange of carbonate and chloride ions form two 5 new compounds.
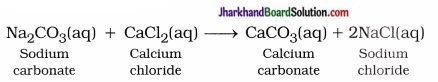
This is double displacement reaction.
Question 8.
Identify the substances that are oxidised and the substances that are reduced in the following reactions:
(1) 4Na(s) + O2(g) → 2Na2O(s)
(2) CuO(s) + H2(g) → Cu(s) + H2O(1)
Answer:
(1) 4Na(s) + O2(g) → 2Na2O(s)
In this reaction, sodium (Na) metal is oxidised to Na20 and O2 is reduced.
(2) CuO(s) + H2(g) → Cu(s) + H2O(1)
In this reaction, CuO is reduced to Cu, while H2 is oxidised to H2O.
Activity 1.1 [T. B. Pg. 1]
Aim : To study the burning of magnesium ribbon in air.
Caution: It is necessary that this activity should be performed in the presence of a teacher. For safety purpose, teacher and student should wear goggles.
Activity:
- Take approximately 3-4 cm long magnesium ribbon and make it clean by rubbing it with sand paper.
- Hold it with a pair of tongs and heat on the flame of burner or spirit lamp and the ash being formed collects in the watch-glass as shown in the figure 1.1.
- Collected ash in the watch-glass is of magnesium oxide.
- Burn the magnesium ribbon. Keeping it away as far as possible from your eyes.
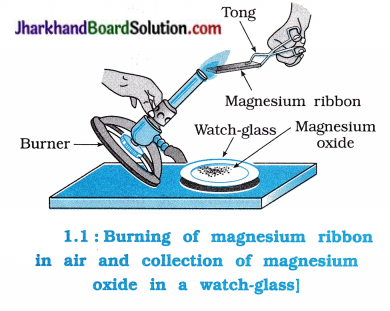
Questions:
Question 1.
Why is magnesium ribbon selected?
Answer:
Magnesium ribbon is highly reactive and burns easily in air.
Question 2.
What is the colour of magnesium ribbon initially?
Answer:
Magnesium ribbon, initially, rubbed with sand paper appears silvery white.
Question 3.
Which type of flame is formed during the burning of magnesium ribbon?
Answer:
Magnesium ribbon burns with dazzling white flame in the flame of burner.
![]()
Question 4.
What is the composition of ash collected in watch-glass?
Answer:
White ash collected in watch-glass is of magnesium oxide (MgO).
Note: Due to O2 and N2 present in air, MgO is formed as a major product, moreover traces of Mg3N2 is also obtained.
Question 5.
Write the chemical reaction of forming the magnesium oxide.
Answer:
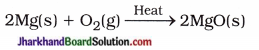
Activity 1.2 [T.B.Pg.2]
Aim : To study the reaction between lead nitrate and potassium iodide.
Activity:
- Take lead nitrate solution in a test tube.
- Add the solution of potassium iodide in it.
Questions :
Question 1.
What is the colour of lead nitrate solution?
Answer:
Lead nitrate solution is colourless.
Question 2.
What is the colour of an aqueous solution of potassium iodide?
Answer:
The solution of potassium iodide is colourless.
Question 3.
Write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction that takes place between lead nitrate and potassium iodide.
Answer:
Pb(NO3)2(aq) + 2KI(aq) → PbI3(s) + 2KNO3
Question 4.
What is the colour of PbI2?
Answer:
PbI2 is yellow.
Question 5.
Identify the type of the above reaction.
Answer:
This reaction is a double displacement reaction.
Activity 1.3 [T. B. Pg. 2]
Aim : To study the reaction between zinc metal and dilute sulphuric acid.
Caution: Use the acid with care.
Activity:
- Take a conical flask.
- Add a piece of zinc granules in it.
- Then add dilute hydrochloric acid or dilute sulphuric acid.
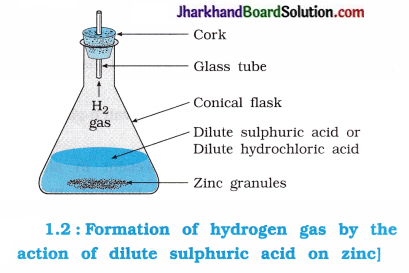
Questions :
Question 1.
What appears around the zinc granules?
Answer:
The granules of zinc react with dilute hydrochloric acid evolving hydrogen gas. Hence, bubbles of hydrogen gas appear around granules of zinc.
Question 2.
What happens to the conical flask?
Answer:
Conical flask becomes hot which can be felt on touching to it.
Question 3.
State the reaction occurring between the pieces of zinc and dilute HC1.
Answer:
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
Question 4.
Which type of reaction takes place between the pieces of zinc and dilute HCl?
Answer:
Reaction taking place between zinc granules and dilute HCl is an exothermic reaction.
Activity 1.4 [T. B. Pg. 6]
Aim: To study the reaction between calcium oxide and water.
Activity:
- Take some quick lime (Calcium oxide – CaO) in a beaker. Add water to it slowly.
- Touch the beaker as shown in the figure 1.3.
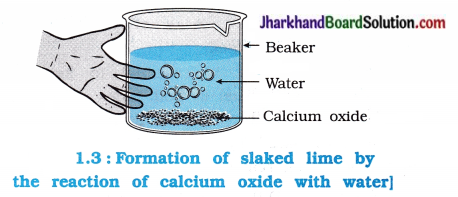
Questions:
Question 1.
What is formed by reaction of quick lime with water? Write reaction.
Answer:
The reaction between quick lime and water forms Ca(OH)2.
CaO(s) + H2O(l) → Ca(OH)2(aq)
Question 2.
What is called the reaction occurring between quick lime and water?
Answer:
Reaction occurring between slaked lime and water is called slaking of lime.
Question 3.
What do you feel by touching the beaker outside?
Answer:
By touching the beaker, it is observed that the beaker becomes warm since, heat is evolved during reaction.
Question 4.
What is slaked lime?
Answer:
Calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) is known as slaked lime.
Activity 1.5 [T. B. Pg. 8]
Aim: To study the decomposition of ferrous sulphate on heating
Activity:
- Take approximately 2 g of ferrous sulphate crystals in a dry boiling tube.
- Heat the boiling tube over the flame of a burner.
- Observe the colour of the ferrous sulphate crystals carefully during the heating.
- Observe the colour of the crystals after heating it.
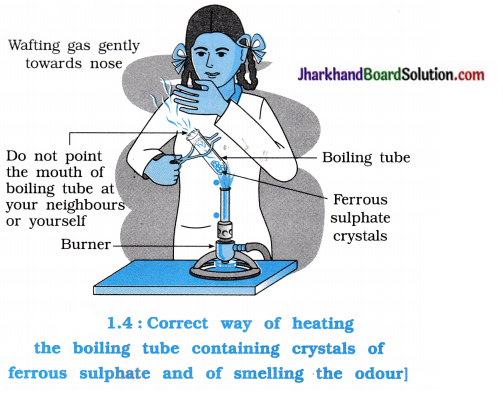
Questions :
Question 1.
What is the colour of crystals of ferrous sulphate?
Answer:
The crystals of ferrous sulphate are greenish (or faint or light green).
Question 2.
Which colour is observed on heating the crystals of ferrous sulphate?
Answer:
On heating the ferrous sulphate, it is decomposed into Fe2O3 and green colour changes to (reddish) brown.
Question 3.
On heating ferrous sulphate in boiling tube, a gas evolved which has a characteristic smell. What is its reason?
Answer:
On heating ferrous sulphate, a gas having specific smell is evolved due to combustion of sulphur. The combustion of sulphur forms SO2(g) and SO3(g) which possesses strong irritating smell.
Activity 1.6 [T. B. Pg. 8]
Aim : To study the decomposition of lead nitrate.
Activity:
- Take about 2 g of lead nitrate powder in a boiling tube.
- Hold the boiling tube with a pair of tongs and heat it over the flame of a burner.
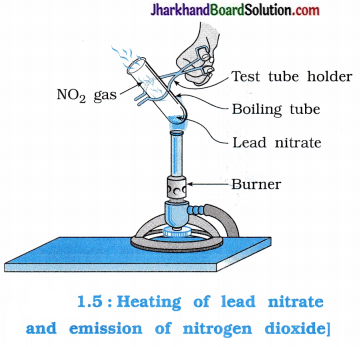
Questions :
Question 1.
Which gas is evolved from boiling tube on heating lead nitrate?
Answer:
Nitrogen dioxide (NO2) is evolved from the boiling tube on heating lead nitrate. It is brown coloured gas.
Question 2.
Write the equation of reaction of heating lead nitrate.
Answer:

Activity 1.7 [T. B. Pg. 9]
Aim : To study electrolysis of water.
Activity:
- Take a plastic mug. Drill two holes at the base of the mug. Fix two rubber corks in it; as shown in the figure 1.6.
- Arrange the: test tubes in inverted position such that carbon electrodes remains in it as shown in the figure.
- Add water in a mug such that electrodes are immersed.
- Add a few drops of dilute sulphuric acid to water.
- Connect electrodes to a 6 volt battery.
- Now, switch on the current and leave the apparatus undisturbed for some time.
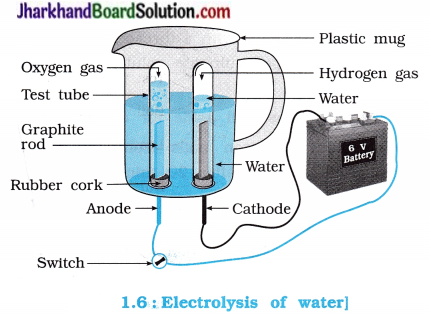
Questions :
Question 1.
What is an electrode?
Answer:
Platinum or carbon rod which remains dipped in the solution of electrolyte and on the surface of which chemical reactions occur is known as an electrode.
Question 2.
Which gas is evolved at anode during electrolysis of water?
Answer:
Oxygen gas is evolved at anode during electrolysis of water.
Question 3.
Which gas is evolved at cathode during electrolysis of water?
Answer:
Hydrogen gas is evolved at cathode during elecrolysis of water.
![]()
Question 4.
Are the volumes of the gases collected during electrolysis are same?
Answer:
No
Question 5.
State the chemical equation of reaction of electrolysis of water.
Answer:
![]()
Question 6.
What happens when O2(g) and H2[g) evolved are brought close to the burning candle?
Answer:
O2(g) does not burn, while H2(g) burns with popping sound.
Activity 1.8 [T. B. Pg. 9]
Aim : To study photochemical decomposition of silver chloride.
Activity:
- Take about 2 g of silver chloride in a china dish.
- Put this china dish in sunlight for some-time.
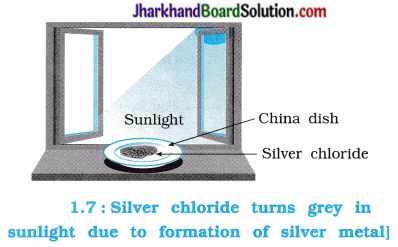
Questions :
Question 1.
What was the colour of silver chloride before exposure to sunlight?
Answer:
Silver chloride was white in colour before its exposure to sunlight.
Question 2.
What is the change in colour of silver chloride during its exposure to sunlight for sometime?
Answer:
When silver chloride is exposed to sunlight for sometime, its white colour changes to grey.
Question 3.
State tire chemical equation of decomposition reaction of silver chloride and silver bromide in presence of sunlight.
Answer:
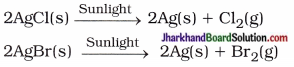
Question 4.
Does the decomposition of silver bromide occur in sunlight?
Answer:
Yes
Question 5.
State the uses of AgCl and AgBr.
Answer:
AgCl and AgBr are used in black and white photography in films.
Activity 1.9 [T. B. Pg. 10]
Aim : To study the displacement reaction taking place between iron nail and solution of copper sulphate.
Activity:
- Take three iron nails and clean their surface by rubbing them with a sand paper.
- Take two test tubes labelled as (A) and (B). Take about 10 mL solution of copper sulphate in each test tube.
- Tie two iron nails with a thread and immerse them in copper sulphate solution for about 20 minutes.
Keep one iron nail aside for comparison. - Take out the iron nails from the copper sulphate solution after 20 minutes.
- Compare the colour of both iron nails with the nail kept aside.
- Compare the intensity of the colour of copper sulphate solutions of both the test tubes, (A) and (B).
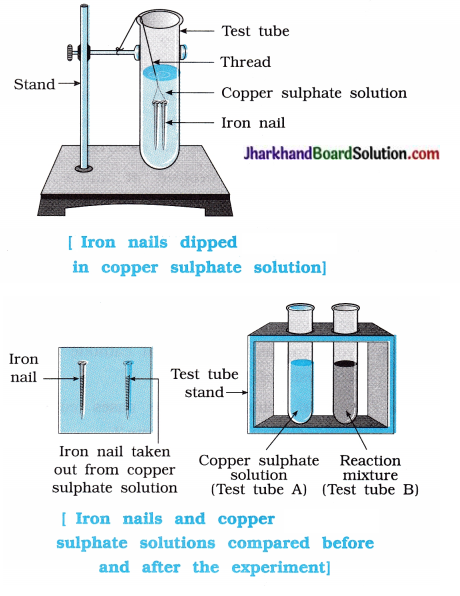
Questions:
Question 1.
What would be the colour of iron nail placed in the solution of CuSO4 ?
Answer:
Iron nail become brownish in colour.
Question 2.
What would be the change in colour of solution of copper sulphate ?
Answer:
Blue colour of copper sulphate solution fades (or becomes light blue).
Question 3.
Which reaction takes place when iron nail is dipped in the solution of copper sulphate ?
Answer:

Question 4.
What type of chemical reaction occur, when iron nail is dipped in copper sulphate solution?
Answer:
Reaction of iron nail with the solution of copper sulphate is a displacement reaction.
Activity 1.10 [T. B. Pg. 11]
Aim: To study double displacement reaction between barium chloride and sodium sulphate.
Activity:
- Take about 3 mb of sodium sulphate solution in a test tube.
- In another test tube, take about 3 mL of barium chloride solution.
- Mix the two solutions as shown in the figure.
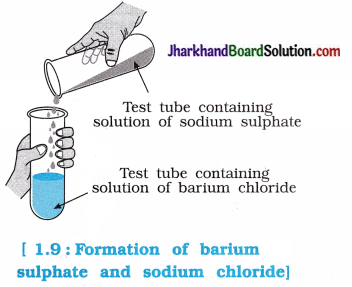
Questions:
Question 1.
What is the colour of sodium sulphate and barium chloride solutions?
Answer:
Sodium sulphate and barium chloride are colourless solutions.
Question 2.
Which precipitate is obtained by mixing the solution of sodium sulphate and barium chloride ? Mention its colour.
Answer:
When solutions of sodium sulphate and barium chloride are mixed, a precipitate of barium sulphate (BaSO4) is formed, which is white in colour.
Question 3.
Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction between barium chloride and sodium sulphate.
Answer:
BaCl2(aq) + Na2SO4(aq) → BaSO4(s) + 2NaCl(aq)
Question 4.
What type of chemical reaction takes place between barium chloride and sodium sulphate?
Answer:
A chemical reaction taking place between barium chloride and sodium sulphate is a double displacement reaction.
Activity 1.11 [T. B. Pg. 12]
Aim: To study oxidation of copper to copper oxide.
Activity:
- Take 1 g of copper powder in a china dish and heat it as shown in the figure 1.10.
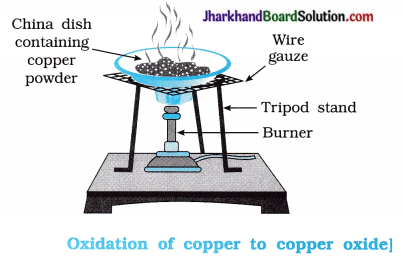
Questions:
Question 1.
What happens on heating the copper powder?
Answer:
Copper powder, on heating forms copper (II) oxide on its surface.
Question 2.
State the colour of copper oxide.
Answer:
The colour of copper oxide is black.
Question 3.
What type of reaction is represented by the reaction of formation of copper oxide from copper?
Answer:
The reaction of formation of copper oxide from copper is an oxidation reaction.
Question 4.
Which product is obtained by passing hydrogen gas over hot copper oxide?
Answer:
Copper is obtained by passing hydrogen gas over hot copper oxide.
![]()
Question 5.
Name the reaction of forming copper from copper oxide.
Answer:
The reaction to form copper from copper oxide is a reduction reaction.