JAC Board Class 10th Social Science Important Questions Civics Chapter 1 Power Sharing
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
What is the linguistic composition of Belgium?
(a) 59% speak French, 40% speak Dutch, 1% speaks German
(b) 59% speak French, 40% speak German, 1% speaks Dutch
(c) 59% speak Dutch, 40% speak French, 1% speaks German
(d) 59% speak German, 40% speak Dutch, 1% speaks French
Answer:
(c) 59% speaks Dutch, 40% speaks French, 1% speaks German
Question 2.
What are the Tamil natives of Sri Lanka called?
(a) Indian Tamils
(b) Buddhist Sinhala
(c) Muslim Tamils
(d) Sri Lankan Tamils
Answer:
(d) Sri Lankan Tamils
![]()
Question 3.
What are the forefathers who came from India to Sri Lanka as plantation workers during colonial period, called?
(a) Indian Tamils
(b) Sinhala
(c) Sri Lankan Tamils
(d) Hindu Tamils
Answer:
(a) Indian Tamils
Question 4.
When did Sri Lanka emerge as an independent country?
(a) 1984
(b) 1948
(c) 1849
(d) 1894
Answer:
(b) 1948
Question 5.
Why did the democratically elected government in Sri Lanka adopt a series of majoritarian measures?
(a) To establish Tamil supremacy
(b) To foster Buddhism
(c) To establish Sinhala supremacy
(d) To establish Tamil Elam
Answer:
(c) To establish Sinhala supremacy
![]()
Question 6.
When was the Act passed to recognise Sinhala as the only official language, thus disregarding Tamil?
(a) 1596
(b) 1695
(c) 1965′
(d) 1956
Answer:
(d) 1956
Question 7.
Which religion did the new constitution stipulate that the state of Sri Lanka shall protect and foster?
(a) Buddhism
(b) Islam
(c) Hinduism
(d) Christianity
Answer:
(a) Buddhism
Question 8.
What led to Civil War in Sri Lanka?
(a) Power sharing .
(b) Principle of majoritarianism
(c) Community government
(d) Modem democracies
Answer:
(b) Principle of majoritarianism
Question 9.
Constitution of which country prescribes that the number of Dutch and French-speaking ministers shall be equal in the central government?
(a) England
(b) Sri Lanka
(c) India
(d) Belgium
Answer:
(d) Belgium
![]()
Question 10.
In which country are the state governments not subordinate to the Central government?
(a) Belgium
(b) Sri Lanka
(c) Both Sri Lanka and Belgium
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Belgium
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is the meaning of the term ‘ethnic’?
Answer:
The term ‘ethnic’ is a social division based on shared culture. People belonging to the same ethnic group believe in their common descent because of similarities of physical type or of culture or both. They need not always have the same religion or nationality.
Question 2.
Name the countries Brussels shares its border with.
Answer:
Brussels shares its border with France, the Netherlands, Germany and Luxembourg.
Question 3.
What was the special problem faced by Brussels?
Answer:
Brussels presented a special problem. The Dutch-speaking people constituted a majority in the country, but a minority in the capital.
Question 4.
What is majoritarianism?
Answer:
Majoritarianism is a belief that the majority community should be able to rule a country in whichever way it wants, by disregarding the wishes and needs of the minority.
Question 5.
What did the Sri Lankan government adopt to establish Sinhala supremacy?
Answer:
The democratically elected government of Sri Lanka adopted a series of majoritarian measures to establish Sinhala supremacy.
Question 6.
In which part of Sri Lanka did the political organisations demand an independent Tamil Eelam (state) be formed?
Answer:
By 1980s several political organisations were formed demanding an independent Tamil Eelam (state) in northern and eastern parts of Sri Lanka.
Question 7.
What is ‘community government’?
Answer:
The third kind of government in Belgium is the ‘community government’, elected by people belonging to one language community Dutch, French and German-speaking no matter where they live. This government has the power regarding cultural, educational and language-related issues.
![]()
Question 8.
What is the meaning of power sharing?
Answer:
Sharing of power by various groups in the society and levels of the government for the smooth functioning of the nation is known as power sharing.
Question 9.
Which community enjoys majority in Sri Lanka?
Answer:
The Sinhala community enjoys a big majority in Sri Lanka.
Question 10.
Differentiate between ‘Sri Lankan Tamils’‘and ‘Indian Tamils’.
Answer:
Tamil natives of the country of Sri Lanka are called ‘Sri Lankan Tamils’. The rest, whose forefathers came from India as plantation workers during colonial period, are called ‘Indian Tamils’.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe the ethnic composition of Belgium.
Answer:
Ethnic Composition of Belgium
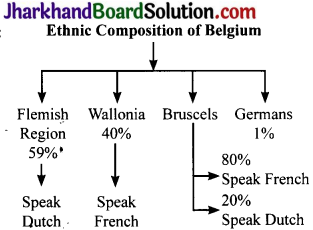
The ethnic composition of Belgium is very complex. Of the country’s total population, 59 per cent lives in the Flemish region and speaks Dutch language. Another 40 per cent people living in the Wallonia region and speak Belgians speak German. In the capital city Brussels, 80 per cent speak French while 20 per cent are Dutch-speaking.
Question 2.
What led to tensions between the French and Dutch in Belgium?
Answer:
The minority French-speaking community was relatively rich and powerful. This was resented by the Dutch-speaking community who got the benefit of economic development and education much later. This led to tensions between the Dutch-speaking and French-speaking communities during the 1950s and 1960s. The tension between the two communities was more acute in Brussels. Brussels faced a special problem. The Dutch-speaking people constituted a majority in the country, but a minority in the capital.
Question 3.
Describe the ethnic composition of Sri Lanka.
Answer:
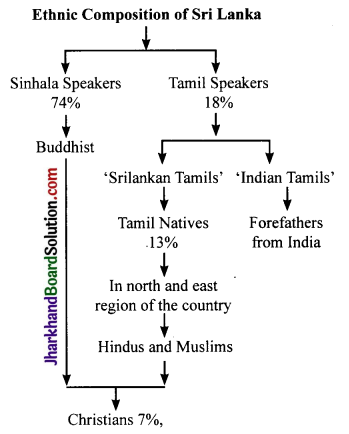
Sri Lanka has a diverse population. The major social groups are the Sinhala
speakers (74 per cent) and the Tamil speakers (18 per cent). Among Tamils there are two sub-groups. Tamil natives of the country are called ‘Sri Lankan. Tamils’ (13 per cent). The rest, whose forefathers came from India as plantation workers during colonial period, are called ‘Indian Tamils’. Sri Lankan Tamils are concentrated in the north and east of the country. Most of the Sinhala-speaking people are Buddhists, while most of the Tamils are Hindus or Muslims. There are about 7 per cent Christians, who are both Tamil and Sinhala.
Question 4.
How was majoritarianism established in Sri Lanka?
Answer:
When Sri Lanka emerged as an independent country in 1948, the leaders of the Sinhala community sought to secure dominance over government by virtue of their community. The democratically elected government adopted a series of. majoritarian measures to establish Sinhala supremacy. In 1956, an Act was passed to recognise Sinhala as the only official language, thus, disregarding Tamil. The governments followed preferential policies that favoured Sinhala applicants for university positions and government jobs. A new constitution stipulated that the state shall protect and foster Buddhism.
![]()
Question 5.
What are the different ways in which minority communities get a fair share in poweb?
Answer:
- Power can be shared among different social groups such as religious and linguistic groups.
- The ‘community government’ in Belgium is elected by the people belonging to one language community, no matter where they live. The government has the power regarding cultural, educational and language-related issues.
- In some countries there are constitutional and legal arrangements to support the weaker sections and women to get representation in the legislatures and administration.
- This allows the diverse social groups to participate in the functioning of the government, who would otherwise feel alienated from the government.
Question 6.
How did the Tamil community of Sri Lanka react to the majoritarianism in Sri Lanka?
Answer:
- The Sri Lankan Tamils launched parties and struggles for the recognition of Tamil as an official language, for regional autonomy and equality of opportunity in securing education and jobs.
- But their demand for more autonomy to provinces populated by the Tamils was repeatedly denied.
- By the 1980s several political organisations were formed demanding an independent Tamil Eelam (state) in northern and eastern parts of Sri Lanka.
- The distrust between the two communities turned into widespread conflict. It soon turned into a civil war.
Question 7.
How is the Belgian government similar to that of Indian government?
Answer:
- Both India and Belgium follow federal form of power. Power is shared among governments at different levels.
- While in Belgium, different levels of government is known as Federal form of government. In India it is known as Central or Union government.
- Power is also shared among different social groups, such as religious and linguistic groups. There is ‘community government’ in Belgium and ‘reserved constituencies’ in assemblies and the parliament in India.
Question 8.
Power sharing arrangements can also be seen in the way political parties, pressure groups and movements control or influence those in power. Justify.
Answer:
- In contemporary democracies, citizens have the freedom to choose among various contenders. This occurs in the form of competition among different political parties.
- Power is shared among different political parties to represent different ideologies and social groups. Sometimes this sharing can be direct when parties form an alliance to contest elections or form a coalition government.
- Interest groups, such as those of industrialists, farmers, traders and businessmen also have a share in governmental power, either through participation in governmental committees or bringing influence on the decision-making process.
Question 9.
Why is power sharing necessary in a country like India?
Answer:
- India is a country of diverse culture, tradition, language, tribes and socially and economically weaker people.
- With diverse composition of population, it becomes necessary to support and encourage each group to participate in the functioning of the government.
- Only if everyone is kept together, a country can run peacefully. It teaches us tolerance and we learn from each other und accept each other. It widens our views and approach to running the nation.
- The various groups are represented in the legislatures and administration. The constitution clearly lays down the laws for their representation. Therefore, power sharing is necessary in a country like India.
![]()
Question 10.
How many times did the Belgian leaders amend their constitution between 1970 and 1993, and why?
Answer:
The Belgian leaders recognised the existence of regional differences and cultural diversities. Between 1970 and 1993, they amended their constitution four times as to work out an arrangement that would enable everyone to live together in the same country.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Discuss the Belgian model of accommodating and recognising the existence of regional differences and cultural diversities.
Answer:
The Belgian leaders took a few steps to accommodate and recognise the existence of regional differences and cultural diversities. These were:
- Constitution mentions that the number of Dutch and French-speaking ministers shall be equal in the central government. Some special laws require the support of majority of members from each linguistic group. Thus, no single community can make decisions unilaterally.
- Many powers of the central government have been given to state governments of the two regions of the country. The state governments are not subordinate to the Central Government.
- Brussels has a separate government in which both the communities have equal representation. The French-speaking people accepted equal representation in Brussels because the Dutch-speaking community has accepted equal representation in the Central Government.
- The third kind of government is the ‘community government’, elected by the people belonging to one language community Dutch, French and German-speaking, no matter where they live. This government has the power regarding cultural, educational and language-related issues.
Question 2.
Discuss in detail why power sharing is desirable.
Answer:
There are two different reasons why power sharing is desirable.
(i) Prudential Reasons:
Power sharing reduces the possibility of conflict between social groups. As social conflict often leads to violence and political instability, power sharing is a good way to ensure the stability of political order. Although, imposing the will of the majority community over the others may look like an attractive option in the short run, in the long run it undermines and damages the unity of the nation.
(ii) Moral Reasons:
The second deeper reason is that power sharing is the spirit of democracy. Democracy involves the participation of people in the functioning of the coyntry. People have the right to be informed and consulted on how they are to be governed. A legitimate government is one where citizens, through participation, acquire a stake in the system.
Question 3.
Discuss the system of checks and balances.
Answer:
- Power is shared among different organs of the government, such as the legislature, executive and judiciary.
- This horizontal distribution of power allows different organs of the government placed at the same level to exercise different powers.
- This ensures that none of the organs exercise unlimited power. Each organ checks the others.
- Even though ministers and government officials exercise power, they are responsible to the Parliament or State Assemblies.
- Similarly, the judges are appointed by the executives but they can check the functioning of executives or laws made by the legislatures. This results in a balance of power among various institutions.
- This arrangement is called a system of checks and balances.
![]()
Question 4.
Explain how power can be shared among governments at different levels.
Answer:
- Power can be shared among governments at different levels a general government for the entire country and governments at the provincial or regional level.
- In some countries, general government for the entire country is called the federal government.
- In India, it is the Central or Union Government. The governments at provincial level are called by different names in different countries.
- In India, it is known as State Government. The constitution clearly lays down the powers of different levels of government.
- The same principle can be extended to levels of government lower than the State government, such as the municipality and panchayat.
- The division of power involving higher and lower levels of government is called vertical division of power.
Activity Based Questions
Read the clues and search for the answers from the word search box:
- A social division based on shared culture
- A belief that majority community should be able to rule a country in whichever way it wants, by disregarding the wishes and needs of the minority
- The only official language in Sri Lanka, as passed by Act in 1956
- A violent conflict between opposing groups within a country that becomes so intense that it appears like a war
- These reasons stress that power sharing will bring out better outcomes
- These reasons emphasise the very act of power sharing as valuable
- Anew constitution in Sri Lanka stipulated that the state shall protect and foster this religion
Answer:
1. Ethnic
2. Majoritarianism
3. Sinhala
4. Civil war
5. Prudential
6. Moral
7. Buddhism