JAC Board Class 9th Science Important Questions Chapter 7 Diversity in Living Organisms
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Whittaker classified all organisms into
(a) five kingdoms
(b) four kingdoms
(c) three kingdoms
(d) two kingdoms
Answer:
(a) five kingdoms
Question 2.
A housefly belongs to which phylum?
(a) Nematoda
(b) Annelida
(c) Porifera
(d) Arthropoda
Answer:
(d) Arthropoda
Question 3.
The five kingdom classification is based on the complexity of
(a) mode of nutrition
(b) body organisation
(c) cell structure
(d) all of these
Answer:
(d) Arthropoda
Question 4.
Which one of the following belongs to coelenterata?
(a) Sycon
(b) Hydra
(c) Spongilla
(d) Planaria
Answer:
(b) Hydra
Question 5.
In which of the following are the reproductive organs hidden?
(a) Cryptogamae
(b) Phanerogamae
(c) Gymnosperms
(d) Angiosperms
Answer:
(a) Cryptogamae
Question 6.
Which phylum of animals is also called flatworms?
(a) Porifera
(b) Coelenterata
(c) Platyhelminthes
(d) Nematoda
Answer:
(c) Platyhelminthes
Question 7.
The excretory system in annelids consists of tubes called
(a) flame cells
(b) metanephridia
(c) nephridia
(d) protonephridia
Answer:
(c) nephridia
Question 8.
What is the phylum of octopus?
(a) Arthropoda
(b) Mollusca
(c) Annelida
(d) Cnidaria
Answer:
(b) Mollusca
![]()
Question 9.
What is the mode of nutrition in bacteria?
(a) Autotrophic
(b) Heterotrophic
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
Question 10.
In which organism do flame cells form the excretory system?
(a) Flatworm
(b) Earthworm
(c) Insect
(d) Crab
Answer:
(a) Flatworm
Question 11.
Which sub – group in plant kingdom produces flowers?
(a) Angiosperm
(b) Fungus
(c) Moss
(d) Fern
Answer:
(a) Angiosperm
Question 12.
The mode of nutrition in fungi is
(a) only saprotrophic
(b) saprotrophic or parasitic
(c) only parasitic
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(b) saprotrophic or parasitic
Question 13.
Which among the following is exclusively marine?
(a) Arthropoda
(b) Mollusca
(c) Echinodermata
(d) Coelenterata
Answer:
(c) Echinodermata
Analysing & Evaluating Questions
Question 14.
Meena and Hari observed an animal in their garden. Hari called it an insect, while Meena said it was an earthworm. Which of the following characteristics confirms that it was an insect?
(a) Bilaterally symmetrical body
(b) Body with jointed legs
(c) Cylindrical body
(d) Body with little segmentation
Answer:
(b) Body with jointed legs
Question 15.
After studying the characteristics of Agaric us, Madan noted them as follows:
I. It is fleshy.
II. It has an umbrella-like cap called pileus.
III. Spores are produced by the stipe.
IV. Its body is made of filaments.
Which observation is not correct?
(a) I
(b) II
(c) III
(d) IV
Answer:
(c) III
Question 16.
Preeti studied the following
features in a preserved specimen – bilateral symmetry, true segmentation, clitellum and mouth. It is a/an
(a) tapeworm
(b) cockroach
(c) earthworm
(d) roundworm
Answer:
(c) earthworm
Assertion Reason Questions
Directions: In the following questions, the Assertions and the Reasons have been put forward Read the statements carefully and choose the correct alternative from the following:
(A) Both the assertion and the reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
(B) The assertion and the reason are correct but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
(C) The assertion is true but the reason is false.
(D) Both the statements are false.
1. Assertion: Bacteria and blue – green algae belong to the same phylum, i.e. Monera.
Reason: Both the bacteria and blue – green algae are unicellular prokaryotic organisms.
Answer:
(A) Both the assertion and the reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
2. Assertion: Most of the amphibians lay their eggs in water.
Reason: Young ones of amphibians have gills at the initial stages of there lives.
Answer:
(A) Both the assertion and the reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
3. Assertion: Snake and turtle belong to the same group.
Reason: Both the snake and the turtle are cold – blooded and have four – chambered heart.
Answer:
(C) The assertion is true but the reason is false.
4. Assertion: Dolphins do not belong to pisces.
Reason: Dolphins respire through lungs and possess four – chambered heart.
Answer:
(A) Both the assertion and the reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation of the assertion.
5. Assertion: Roundworms lack a digestive tract.
Reason: Roundworms are endoparsites.
Answer:
(B) The assertion and the reason are correct but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is evolution?
Answer:
Evolution is the gradual unfolding of organisms, from the pre – existing ones, through changes since the beginning of life.
Question 2.
Name the scientist who described the idea of organic evolution and the book in which he explained it.
Answer:
Charles Darwin first described the idea of evolution in his book ‘The Origin of Species’.
![]()
Question 3.
What is lichen?
Answer:
Lichens are a complex life form that is a symbiotic partnership of two separate organisms, i.e., a fungus and an alga The alga can be either a green alga or a blue-green alga (also known as cyanobacteria).
Question 4.
What is a symbiotic relationship or symbiosis?
Answer:
It is a relationship between two organisms in which both of them are benefited, e.g., in the symbiotic association of lichens, fungi get food from blue – green algae and in return, blue-green algae get shelter.
Question 5.
Who proposed the two kingdom classification?
Answer:
Carolus Linnaeus.
Question 6.
What is biodiversity?
Answer:
Different forms of living organisms found in a particular region is known as biodiversity of that region.
Question 7.
Define species.
Answer:
A species includes all organisms that are similar enough to interbreed and perpetuate naturally.
Question 8.
Define mycoplasma.
Answer:
Mycoplasma are the smallest and the simplest organisms. They are prokaryotes having a nucleoi(d) Their body can change shape easily. They are heterotrophs.
Question 9.
Define ‘taxonomy’.
Answer:
The branch of science that classifies living organisms among different categories or groups is called taxonomy. Taxonomy is the science of identifying and naming species and organising them into systems of classification.
Question 10.
Define Taxon.
Answer:
A taxon is a unit of classification of organisms which can be recognised to a definite category at any level of classification, for e.g., fishes, birds, insects, etc.
Question 11.
In how many kingdoms does Carolus Linnaeus divided living beings?
Answer:
Two kingdoms, viz., Plantae (plants) and Animalia (animals).
Question 12.
Name the division of plant kingdom which is also called the amphibians of plant kingdom.
Answer:
Bryophyta, e.g., Lunaria (moss).
Question 13.
What is meant by bilateral symmetry?
Answer:
When the left and right halves of the body have the same design, it is called bilateral symmetry.
Question 14.
What is thallus?
Answer:
Thallophytes have a simple plant body. The plant body is not differentiated into root, stem and leaves and is called thallus.
Question 15.
What is moss?
Answer:
Moss is a radially symmetrical leafy bryophyte having multicellular rhizoids, Funaria, Bryum, Sphagnum.
Question 16.
Why are bryophytes called the amphibians of the plant kingdom?
Answer:
Bryophytes are known as amphibians of the plant kingdom because these plants can live in soil but are dependent on water for sexual reproduction. Usually, they are found in humid and damp areas.
Analysing & Evaluating Questions
Question 17.
The external features of some living organisms are given below as I, II, III and IV. Read these and write the name of their respective animal phylum or class.
I. Streamlined body, covered with scales and divided externally into head, trunk and tail.
II. Skin is dry, covered with epidermal scales and bear two pairs of limbs each with five toes ending in horny claws.
III. Body is externally segmented and covered with a thick exoskeleton made up of chitin. The segments are grouped to form head, thorax and abdomen.
IV. Body is flattened, leaf-like or ribbon – like and bilaterally symmetrical.
Answer:
I – Phylum chordata (superclass pisces)
II – Phylum chordata (class reptilia)
III – Phylum arthropoda
IV – Phylum platyhelminthes
Question 18.
An animal is described as worm-like with unsegmented body and shows some features of invertebrates and some of chordates. Identify the described animal.
Answer:
The animal is Balanoglossus.
Question 19.
Atrip to Himalayan foothills was organised by the school of Raman and Riya During the trip, they noticed tall trees having needle – like leaves and cones. Name the trees Raman and Riya saw there.
Answer:
They saw Pinus trees.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are the steps in classification of organisms?
Answer:
Organisms are classified into large groups first on the basis of independent characteristics. The characteristic in the next level would be dependent on the previous one and would decide the variety of organisms in the next level. Thus, one can build up a whole hierarchy of mutually related characteristics to be used for classification.
Question 2.
Write the hierarchy of classification proposed by Linnaeus.
Answer:
The hierarchical categories are as follows:
- Kingdom: Plant kingdom and Animal kingdom.
- Phylum (for animals)Division (for plants): A group of closely related classes having certain common characteristics.
- Class: A group of closely related orders having certain common characteristics.
- Order: A group of closely related families having certain common characteristics.
- Family: A group of closely related genera having certain common characteristics.
- Genus: A group of closely related species having certain common characteristics.
- Species: A group of organisms which are similar enough to breed and perpetuate.
Question 3.
What are the characteristics of kingdom Monera?
Answer:
- These organisms do not have clearly defined nucleus, i.e., nucleus is not enclosed in a nuclear membrane.
- Cell organelles are not covered with membranes.
- The organisms do not show multicellular body design, i.e., they are unicellular.
- Some organisms have cell wall, others do not have cell wall.
- The mode of nutrition may be autotrophic or heterotrophic.
Question 4.
Why are blue green algae included under Monera and not under Plantae?
Answer:
Monera is a kingdom of prokaryotes while organisms of kingdom Plantae shows a definite nucleus, membrane- bound organelles and multicellular body design. Blue green algae are prokaryotes having nucleoid with naked DNA. The cell organelles are also not enclosed within a membrane. As they also do not possess multicellular body design, these characteristics bring them closer to Monera and exclude them from the kingdom Plantae.
Question 5.
Give four main features of organisms placed under Protista.
Answer:
The four main features of organisms placed under Protista are as follows:
- This kingdom includes unicellular algae, diatoms and protozoans.
- The organisms in this kingdom are unicellular, eukaryotic organisms (as well – defined nucleus and other membrane-bound cell organelles are present).
- Mode of nutrition is either autotrophic (like in algae and diatoms) or heterotrophic (like in protozoans).
- Some Protists bear hair – like cilia or whip – like flagella for movement. In some protists, like Amoeba, movement takes place by pseudopodia (false feet).
![]()
Question 6.
What are the characteristics of fungi? Give examples.
Answer:
Characteristics of fungi are as follows:
- They are heterotrophic.
- The organisms are saprophytic, i.e., they use decaying organic material as food or may be parasitic.
- They have membrane bound nucleus.
- They have cell walls made of chitin.
- Some of them have the capacity to become multicellular organisms at certain stages in their lives.
- Some of the fungal species have symbiotic relationship where they are mutually dependent on the blue – green algae. These are called lichens.
- Examples: Rhizopus, Yeast, Agaricus (mushrooms), Penicillium.
Question 7.
On what basis are plants divided into two sub-kingdoms?
Answer:
Based on whether the reproductive organs are conspicuous (clearly visible) or not, plants are divided into two subkingdoms:
- Cryptogamae: Non – flowering or seedless plants which include thallophytes, bryophytes and pteridophytes.
- Phanerogamae: Flowering plants which include gymnosperms and angiosperms.
Question 8.
How are angiosperms further divided?
Answer:
Angiosperms are divided into two groups on the basis of the number of cotyledons present in the seeds.
- Monocotyledonous (Monocots): These are the plants with seeds having a single cotyledon, e.g., maize, wheat, rice, etc.
- Dicotyledonous (Dicots): These are the plants with seeds having two cotyledons, e.g., pea, gram, bean, etc.
Question 9.
List the similarities between plants and animals.
Answer:
In spite of certain external differences, plants and animals show a number of very obvious similarities which are as follows:
- Plants and animals are made up of microscopic units called cell.
- Both contain living substance called protoplasm.
- Certain life processes, i.e., respiration, digestion, reproduction, assimilation, etc., take place in both the groups in an identical manner.
- Both show response to external stimuli.
- Both of them show growth.
- Both reproduce and pass on their hereditary characters to their offsprings by the same mechanism.
- Both are multicellular and eukaryotic organisms having division of labour in their cells.
Question 10.
Differentiate between algae and fungi.
Answer:
| Algae | Fungi |
| (a) Contain chlorophyll (green in colour). | (a) Do not contain chlorophyll (nongreen). |
| (b) Autotrophic nutrition. | (b) Heterotrophic nutrition. |
| (c) Food is stored in the form of starch. | (c) Food is stored in the form of glycogen. |
| (d) The cell wall is made up of cellulose. | (d) The cell wall is made up of chitin. |
| (e) Example: Spirogyra. | (e) Example: Rhizopus (bread mould) |
Question 11.
What are the conventions followed for writing the scientific names?
Answer:
The conventions followed while writing the scientific names are as follows:
- The name of the genus begins with a capital letter.
- The name of the species begins with a small letter.
- When printed, the scientific name is given in italics.
- If it is handwritten, the genus name and the species name have to be underlined separately.
Question 12.
Identify the different parts A, B, C and D of fern plant shown in the figure given below.
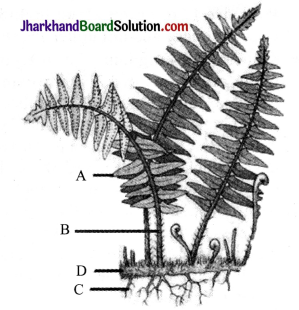
Answer:
(A) Leaflet
(B) Stipe
(C) Adventitious roots
(D) Rhizome
Question 13.
Define bryophytes. Give some examples.
Answer:
- Bryophytes:
- These are also called the amphibians of the plant kingdom.
- Plant body may be thalloid or leafy.
- True roots are absent, instead rhizoids develop.
- No specialised conducting tissue. These grow on damp walls and on the bark of tree.
- These include two groups:
- Liverworts
- Mosses
- Examples: Marchantia, Riccia, Sphagnum, etc.
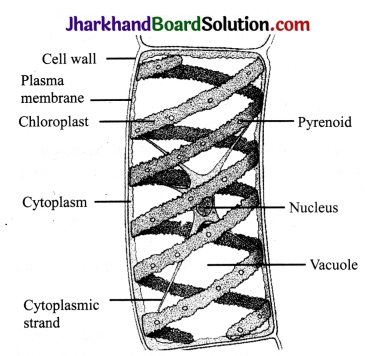
Question 14.
Draw a labelled diagram of Spirogyra cell.
Answer:
Question 15.
Define pteridophytes.
Answer:
Pteridophytes are vascular cryptogams and are the first vascular land plants. The main plant body is the saprophyte, which is differentiated into true roots, stems and leaves. Their xylem lacks companion cells. They have specialised tissue for the conduction of water and other substances from one part of the plant body to another. Examples: Mars ilea, ferns and horse tail.
Question 16.
Define coelom.
Answer:
Coelom is a cavity which lies in between the body wall and gut (alimentary canal) and is lined by mesodermal cells. It allows greater body flexibility. In it, the organs of the body can accommodate in a better way.
Question 17.
Differentiate between diploblastic and triploblastic animals.
Answer:
| Diploblastic | Triploblastic |
| The animals whose bodies are developed from two layers of gastrula, i.e., ectoderm and endoderm, are called diploblastic For example, coelenterates (Hydra). | The animals whose bodies develop from three layers of gastrula, i.e., ectoderm, mesoderm and endoderm, are called triploblastic, e.g., tapeworm. |
Question 18.
State the features of chordates.
Answer:
The main features of chordates are as follows:
- They have bilaterally symmetrical body.
- They have notochord and internal skeleton.
- They have dorsal nerve cord.
- They are triploblastic.
- They are coelomate.
- Respiration is mainly through lungs in land vertebrates and by gills in aquatic animals.
Question 19.
Discuss the characteristics of sponges.
Answer:
Phylum (Porifera) – Sponges:
- Animals have pores (called ostia) all over the body.
- Body is not well differentiated.
- Non – motile animals, remain attached to solid support.
- Body is covered with hard skeleton.
- Reproduction is both asexual (by budding and gemmule formation) and sexual (through fertilisation).
- Examples: Sycon, Spongilla and Euplectella.
Question 20.
Give specific features of coelenterata.
Answer:
Phylum (Cnidaria) – Coelenterata
- All coelenterates are found in water.
- Body is radially symmetrical.
- These are the first of multicellular animals which possess tissue level of organisation with a distinct division of labour.
- The body has a single, sac – like central cavity, called coelenteron or the gastrovascular cavity, with only one opening.
- Some coelenterates live in colonies (Obelia) while others live solitary (Hydra).
- Examples: Hydra, Aurelia, sea anemone and jelly fish.
![]()
Question 21.
Give the general characteristics of Platyhelminthes.
Answer:
- Their body is dorsoventrally flattened and leaf-like or ribbon like.
- Body symmetry is bilateral, i.e., left and right halves have the same design.
- They are mostly hermaphrodite.
- Body cavity or true coelom is absent.
- There are three layers of cells from which differentiated tissues can be forme(d) So, animals are triploblastic.
- They are either free living or parasitic.
- Examples: Planaria, Fasciola hepatica (liver fluke) and Taenia solium (tape worm) are parasitic.
Question 22.
Give the characteristics of Arthropoda with two examples.
Answer:
- This is the largest group of animals.
- They possess jointed legs/ appendages.
- They have bilaterally symmetrical and segmented body.
- Body cavity is filled with blood.
- There is an open circulatory system, i.e., the blood does not flow in definite blood vessels.
- Examples: Apis (honey bee), Musca (housefly), Anopheles (mosquito), Palaemon (prawn), crabs, etc
Question 23.
Give the characteristics of Echinoder – mata.
- They are free living, marine animals.
- They are triploblastic and have a coelomic cavity.
- They have peculiar water-driven tube system used for moving around.
- They have a hard calcium carbonate structure that is used as skeleton.
- Sexes are separate.
- Examples: Asterias (starfish),
Question 24.
Echinus (sea urchin), Antedon (feather star), etc Give the characteristics of Nematoda.
- Most of the Nematodes have small cylindrical or round body.
- Body cavity is not a true coelom. A pseudocoelom is present.
- Body is bilaterally symmetrical and triploblastic.
- Sexes are separate.
- Examples: Ascaris (round worm), Ancylostoma (hook worm) and Wuchereria (filarial worm).
Question 25.
Give the characteristics of phylum Annelida.
- They have elongated and segmented body.
- Body bears lateral appendages for locomotion in the form of chitinous setae or parapodia.
- The body is bilaterally symmetrical and triploblastic.
- Reproduction by sexual means. Sexes may be either separate or united.
- They have true coelom (body cavity).
- Examples: Pheretima (earthworm), Hirudinaria (blood sucking leech) and Nereis.
Question 26.
List the main features of phylum Mollusca.
Answer:
- They have unsegmented or soft body with little segmentation.
- The body is divided into three regions—head, dorsal visceral mass and ventral foot.
- Body is bilaterally symmetrical.
- The coelomic cavity is reduced.
- They have open circulatory system and kidney-like organs for excretion.
- Some molluscs have hard calcareous shell, an outer covering of the body.
- Respiration is by gills called ctenidia.
- Examples: Pila (snail), Unio (fresh water mussel) and Octopus.
Analysing & Evaluating Questions
Question 27.
You are given leech, Nereis, Scolopendra, prawn and scorpion and all have segmented body organisation. Will you classify them in one group? If no, give the important characteristics based on which you will separate these organisms into different groups.
Answer:
Leech, Nereis, Scolopendra, prawn and scorpion belong to different groups.
- Leech and Nereis belong to phylum Annelida They have metameric segmentation, closed circulatory system and unjointed appendages.
- Scolopendra, prawn and scorpion belong to phylum Arthropoda They have open circulatory system and jointed appendages.
Question 28.
Sakshi’s younger brother frequently suffered from stomach ache and vomiting. Her mother took him to a clinic for treatment. Doctor advised for a stool test before prescribing some medicines. The report diagnosed that the stool is infected with common roundworms. Answer the following questions asked by Sakshi to the doctor:
(a) What are common roundworms?
(b) Are there any other worms that live as parasites in our body and cause diseases?
(c) How do roundworms enter our body? What can be done to prevent such infections?
Answer:
- Common roundworms are parasites that live inside the human digestive tract and feed on the food present inside the tract. During feeding, they damage the stomach and the intestines. The scientific name of roundworms is Ascaris.
- Some other common parasitic worms that cause different diseases in our body are Wuchereria (filarial worm), Enterobius (pinworm) and Ancylostoma (hookworm).
- Roundworms enter our body through contaminated food and water. Hence, one should always maintain hygienic food habits to avoid these parasites.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe the three basic features for grouping all organisms into five major kingdoms.
Answer:
Basic criteria such as nature of cell, cellularity and mode of nutrition were used by Whittaker to classify the living organisms into five kingdoms,
(a) Nature of cell relates to the pres – ence or absence of membrane bound organelles in it. On the basis of this category, we can clas¬sify the living organisms in two broad categories prokaryotes and eukaryotes.
- Prokaryotes, such as all bacteria, have poorly developed nuclear material called nucleoid and no membrane – bound organelles.
- Eukaryotes such as protozoans, fungi, plants and animals have well developed genetic material called nucleus and all membrane – bound organelles.
(b) Cellularity refers to the number of cells present in an organism. Unicellular organisms, such as bacteria, and protozoans, are made up of single cell while multicellular organisms such as many fungi, plants and animals are made up of many cells.
(c) Mode of nutrition categorises all living organisms into autotrophs and heterotrophs. Euglena is a dual organism because of its mode of nutrition. It can act as both an autotroph (makes its own food) as it contains chlorophyll and heterotroph (feeds on other substances). Also, in presence of excess organic matter or darkness, it can act as a saprophytic organism. So, as it shows features of both plants and animals, it is a dual organism.
Question 2.
Give the outline classification of animal kingdom upto the level of phyla
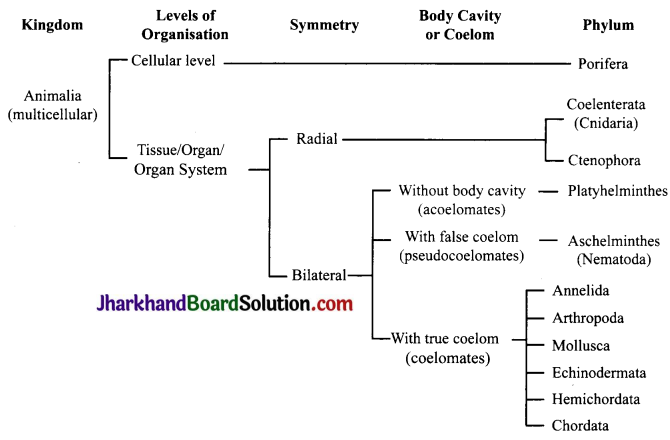
Question 3.
What are the differences between plants and animals?
Answer:
| Animals | Animals |
| (a) Most of the plants around us are stationary and do not move from one place to another. | (A) Most of the animals around us are mobile, i.e., they can move from one place to another. |
| (b) Plants can synthesise their own food in the presence of sunlight from water and carbon dioxide. In their green parts like leaves,chlorophyll pigment is found which helps in food making by the process of photosynthesis. | (b) Animals cannot synthesise their food because they lack chlorophyll. So, they directly or indirectly depend on plants. |
| (c) Most of the plants continue growing throughout their life. The growth may be in length (height) or producing lateral branches. | (c) Animals stop growing, especially in length, (height) after attaining a certain maturity. |
| (d) Plant cells have cell walls as outermost covering. | (d) Animal cells do not have cell walls. |
Question 4.
Differentiate between bryophytes and pteridophytes.
Answer:
| Bryophytes | Pteridophytes |
| (a) Plant body is either leafy or thalloid. | (a) Plant body is differentiated into roots, stem and leaves. |
| (b) The cells in plant body are haploid. | (b) The cells in plant body are diploid. |
| (c) Vascular tissue like xylem and phloem is absent. | (c) Vascular tissue like xylem and phloem is present. |
| (d) In life cycle, the gametophyte is dominant. | (d) In life cycle, the sporophytes are dominant. |
| (e) Sporophytic phase completely depends upon gametophytes. | (e) Sporophytic phase is independent and autotrophic. |
| (f) The spores are produced in the capsule part of the sporophytes. | (f) The spores are produced in sporangia bom on the leaves called sporophylls. |
| (g) Example: Moss. | (g) Example: Fem. |
Question 5.
Give the classification of plant kingdom.
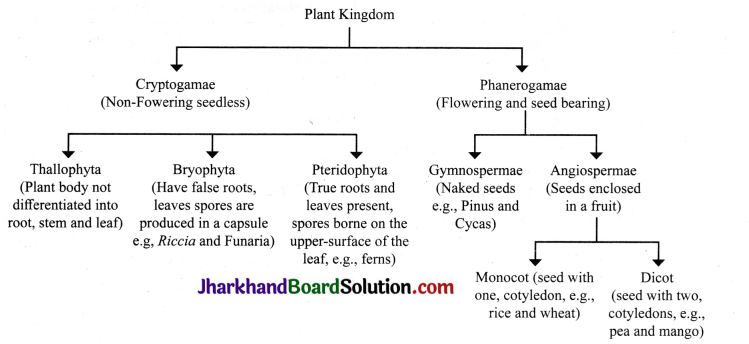
Question 6.
Write the characteristics of flat worms, round worms and segmented worms. Write their phylum also.
Answer:
| Flat worms | Round worms | Segmented worms |
| 1. Phylum – Platyhelminthes. | 1. Phylum – Nematoda | 1. Phylum – Annelida. |
| 2. Dorsoventrally flat, i.e., flat body. | 2. Body is cylindrical. | 2. Body is segmented from head to tail. |
| 3. No true body cavity (acoelomates). | 3. Pseudocoelom (false body cavity). | 3. True body cavity (eucoelomates). |
| 4. Mostly hermaphrodite, i.e., male and female sex organs present in the same individual. | 4. Sexes are separate. | 4. May be unisexual or bisexual. |
Analysing & Evaluating Questions
Question 7.
Observe the plant given below and answer the questions that follow.
1. Identify the plant and name the phylum it belongs to.
2. What is its habitat?
3. List any two of its special features.
4. How does transport of substances take place in this plant?
Answer:
- It is a Cycas plant. It belongs to the phylum gymmosperms.
- It is found mainly in colder regions of the earth.

- Plant body is sporophyte. Ovules are not enclosed in ovary, thus produce naked seeds.
- Vascular tissues are present for the conduction of substances.
Activity 1
Find out the scientific names of the following animals and plants:
(a) Frog
(b) Peacock
(c) Human
(d) Neem
(e) Maize
(f) Honeybee
Observations
It is difficult to remember names of a species in different languages. There was a need for some system to create uniform naming convention.
| Animal/Plant | Scientific Name |
| 1. Frog | 1. Rana tigrina |
| 2. Peacock | 2. Pavo cristatus |
| 3. Human | 3. Homo sapiens |
| 4. Honeybee | 4. Apis indica |
| 5. Neem | 5. Azadirachta indica |
| 6. Maize | 6. Zea mays |
Activity 2
- Soak seeds of green gram, wheat, maize, pea and tamarin(d) Once they become tender, try to split the seeds. Observe if the seeds break into two nearly equal halves.
- Now, observe the roots, leaves and flowers of these plants and record your observations.
Observations - All seeds do not break into two nearly equal halves.
- Out of the given seeds, gram, pea and tamarind are dicots while wheat and maize are monocots.
- Dicot plants have tap-roots and monocots have fibrous root system.
- Dicot plant leaves have reticulate venation, whereas monocot leaves have parallel venation.
- In monocot flowers, petals are three or in multiples of three (trimerous). In dicot flowers, petals are five or in multiples of five (pentamerous).
Value Based Questions
Question 1.
Many medicinal plants are getting extinct every year. A group of students who had gone for educational trip clicked photographs of endangered plants. These photographs were used by the school laboratory to study these plants.
1. Name two endangered plants.
2. Name any one medicinal plant and write its medicinal use.
3. What value of students is reflected in the above act?
Answer:
- Two endangered plants are: Lotus comiculatus and Acacia planifrons.
- Aloe – vera Juice of Aloe vera is used in case of indigestion, treating skin infections, etc.
- Students are caring citizens, showing responsible behavior.
Question 2.
Due to global warming, coral is getting diminished in all the oceans/water bodies. People in the Lakshadweep island protect their corals by not allowing people/tourists to take few pieces away.
1. Name the phylum of coral.
2. What is coral made up of?
3. What values of people in Lakshadweep island are reflected?
Answer:
- Phylum of coral is coelenterata.
- Coral is made up of calcium carbonate.
- People in Lakshadweep island reflect the values of being responsible citizens, respecting environment and nature.