JAC Board Class 9th Social Science Important Questions History Chapter 3 Nazism and the Rise of Hitler
I. Objective Type Questions
1. Germany, Italy and Japan were jointly known as:
(a) Axis powers
(b) Allied powers
(c) Centralist powers
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(a) Axis powers
2. After the Second World War, International Military Tribunal at Nuremberg was established to prosecute war criminals for :
(a) Crimes against humanity
(b) War crimes
(c) Crimes against peace
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(d) All of these.
3. Nazi propaganda skillfully projected Hitler as a:
(a) Saviour
(b) Messiah
(c) Both (a) and (b)
(d) None of these.
Answer:
(c) Both (a) and (b)
4. When did Hitler become the Chancellor of Germany?
(a) in 1933
(b) in 1930
(c) in 1937
(d) in 1948.
Answer:
(a) in 1933
5. Nazis wanted only a society of pure and healthy:
(a) citizens
(b) Jews
(c) Nordic German Aryans
(d) All of these.
Answer:
(c) Nordic German Aryans
6. “In my state, the mother is the most important citizen”. When did Hitler declare it?
(a) In 1933
(b) In 1920
(c) In 1948
(d) In 1942.
Answer:
(a) In 1933
II. Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What was the work entrusted to the International War Tribunal set up in Nuremberg after the war?
Answer:
International War tribunal was set up to prosecute Nazi war criminals for crimes against peace and humanity.
Question 2.
Which were the Allied Powers in the Second World War?
Answer:
United Kingdom, United States of Soviet Russia, France and USA were the Allied Powers in the Second World War.
![]()
Question 3.
Name the countries constituting the Axis Power.
Answer:
Germany, Italy and Japan were the countries constituting the Axis Powers.
Question 4.
What was the German Parliament called?
Answer:
The German Parliament was called Reichstag.
Question 5.
Who were called “November Criminals”?
Answer:
Socialists, Catholics and Democrats, the supporters of the Weimar Republic were called “November Criminals”.
Question 6.
How were the deputies of the Reichstag appointed?
Answer:
The deputies of the Reichstag were elected on the basis of universal adult franchise.
Question 7.
When and between whom was the Treaty of Versailles signed?
Answer:
The Treaty of Versailles was signed on June 28, 1919 between Germany and Britain, France and USA.
Question 8.
What is hyperinflation?
Answer:
Hyperinflation is a situation in which prices is rise very high.
Question 9.
When did the Wall Street Exchange crash?
Answer:
In 1929, the Wall Street Exchange crashed.
Question 10.
In which country was Hitler born?
Answer:
Hitler was born in Austria.
Question 11.
Which party was named as Nazi Party?
Answer:
National Socialist German Workers’ Party was named as the Nazi Party.
![]()
Question 12.
What was the symbol of Nazi party?
Answer:
The red banner with Swastika was the symbol of Nazi party.
Question 13.
When was Hitler offered Chancellorship of Germany and by whom?
Answer:
On 30th January 1933, president Hindburg offered the Chancellorship of Germany, the highest position in the cabinet of ministers, to Hitler.
Question 14.
What was Enabling Act?
Answer:
Enabling Act established dictatorship in Germany.
Question 15.
Which was the most feared security force of Nazi Germany?
Answer:
The Gestapo (secret state police) was the most feared security force of Nazi Germany.
Question 16.
Who was Hjalmar Schacht?
Answer:
Hjalmar Schacht was a great economist who was given the responsibility of economic recovery by Hitler.
Question 17.
Which move of Hitler is said to be a historic blunder?
Answer:
Hitler attacking the Soviet Union in June 1941 is said to be a historic blunder.
Answer:
Question 18.
What was Article 48 of Weimar Constitution?
Answer:
Article 48 of the Weimar Constitution gave the President the powers to impose emergency, suspend civil rights and rule by decree in Germany.
Question 19.
What was the theme of the movie ‘The Eternal Jew’?
Answer:
The theme of the movie ‘The Eternal Jew’ was to create hatred for Jews.
Question 20.
Name the Nazi youth organisation that consisted of all German boys of 14 to 18 years.
Answer:
Jungvolk was the organisation that consisted of all German boys of 14 to 18 years.
Question 21.
Who wrote the ‘Third Reich of Dreams’?
Charlotte Beradt wrote the ‘Third Reich of Dreams’.
![]()
Question 22.
What was the name given to a gas chamber by Nazis?
Answer:
The name given to a gas chamber by Nazis was Disinfection Area.
Question 23.
What was ‘Holocaust’?
Answer:
The ‘Holocaust’ was a Nazi killing operation which was carried out to kill the Jews.
Question 24.
Who wrote the book ‘Mein Kampf?
Answer:
Adolf Hitler wrote the book ‘Mein Kampf.
Question 25.
Which community Hitler hated the most?
The Jews.
III. Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
State the verdict of the Nuremberg Tribunal. Why the Allies did not want to impose harsh punishment on defeated Germany?
Answer:
Germany had waged a genocidal war. It resulted in the mass murder of selected groups of innocent civilians of Europe. After the Second World War, the Nuremberg Tribunal against Germany verdicted only eleven leading Nazis to death while many other were imprisoned for life.
The retribution did come but the punishment of the Nazis was far short compared to the brutality and extent of their crimes they had committed against humanity. The Allies did not want to be as harsh on defeated Germany as they had been after the First World War because they realised that the rise of Adolf Hitler was the result of the humiliation Germany faced after the First World War.
Question 2.
Write a note on the Weimar Republic.
Or
Politically, the Weimer was fragile republic. Explain the statement.
Answer:
The Weimar “epublic is the name given by historians to the parliamentary republic established in 1919 in Germany to replace the imperial form of government. In 1919, a national ass mbly was convened in the city of Weimar, where a new constitution for the Germa Reichstag was written.
This liberal democracy eventually lapsed in the early 1930?., leading to the ascent of the NSDAP and Adolf Hitler in 1933. In its 14 years, the Weimar Republic faced numerous problems, including hyper-inflation, political extremists and their paramilitaries and hostility from the victors of the First World War.
Question 3.
Write the main provisions of the Peace Treaty of Versailles.
Answer:
The main provisions of the Peace Treaty of Versailles were as follows:
1. Germany lost its overseas colonies, one-tenth of its population, 13 per cent of its territories, 75 per cent of its iron deposits and 26 per cent of its coal to France, Poland, Denmark and Lithuania. The Allied Powers demilitarised Germany to weaken its power.
2. The War Guilt Clause held Germany responsible for the war and damages, the Allied countries suffered. Germany was forced to pay war compensation amounting to 6 billion dollars.
3. The Allied armies also occupied the resource rich Rhineland for much of the 1920s. Many Germans held the new Weimar Republic responsible for not only the defeat in the war, but also for the disgrace at Versailles.
![]()
Question 4.
Who were called as the November criminals ? Why were they targeted ? Explain.
Answer:
The First World War had a significant impact on Europe, both psychologically and financially. Europe from a continent of creditors turned into one of debtors. Unfortunately, infant Weimar Republic was being made to pay all the remaining debts.
The Republic also carried burden of war guilt and national humiliation. Those who supported the Weimar Republic mainly socialists, Catholics and democrats, came to be know as ‘November Criminals’. They were targeted because they became easy targets of attack in the conservative nationalist circles.
Question 5.
Explain the impact of the First World War on European society and polity.
Answer:
The First World War left a deep impact on European society and polity which were the following:
- In the society, soldiers were ranked higher than civilians.
- Trench life of the soldiers was glorified by the media.
- Politicians and publicists laid great stress on the need for men to be aggressive, strong and masculine.
- Aggressive war propaganda and national honour occupied centre stage in the public sphere.
- People’s support grew for the recently-established conservative dictatorships.
- Democracy as a young and fragile idea could not survive the instabilities of Europe between the two world wars.
Question 6.
Describe the effect on Germany because of her refusal to pay war compensation in 1923.
Answer:
Following were the effects of refusal to pay war compensation in 1923 on Germany :
- France occupied its leading industrial area, Ruhr, which was rich in coal.
- Germany retaliated with passive resistance and printed paper currency recklessly. With too much printed money in circulation, the value of the German mark fell drastically, causing the prices of goods to soar high.
- Eventually, the Americans helped Germany to recover from the crisis by reworking the terms of reparation to ease the financial burden on Germans.
Question 7.
What was the impact of the Great Depression on the United States of America?
Answer:
The Great Depression started when the Wall Street Exchange of USA crashed in 1929. As a result, values of shares dropped significantly and the national income of the USA fell by half. Hundreds of American banks, factories, mining companies and business firms went bankrupt. There was large-scale unemployment, poverty and starvation in the country. The effects of this recession in the US economy were felt worldwide.
![]()
Question 8.
When was the Enabling Act passed in Germany? How did this act establish dictatorship of Hitler in Germany? Describe.
Answer:
On 3rd March 1933, the famous Enabling Act was passed in Germany. This the Act established dictatorship in Germany. It gave Adolf Hitler all powers to sideline parliament and rule by decree. All political parties and trade unions were banned in Germany, except the Nazi Party and its affiliates.
The new state machinery under Hitler established complete control over the economy, media, army and judiciary. Exclusive surveillance and security forces like the protection squads, the security service Gestapo and criminal police were created to control and mould society in the way that the Nazis wanted.
Question 10.
Describe the Adolf Hitler’s foreign policy. What did Schacht advise to Hitler?
Answer:
Adolf Hitler’s Foreign Policy: The following were the key elements of Adolf Hitler’s foreign policy :
- He pulled Germany out of the League of Nations in 1933.
- Germany reoccupied the Rhindand in 1936.
- He integrated Austria and Germany in 1938 under the slogan ‘one people, one empire and one leader.’
- He then captured German-speaking Sudetenland from Czechoslovakia and later the entire country. However, Schacht advised Hitler not to invest hugely in rearmament because the German state was still surviving on deficit financing.
Question 11.
What was the impact of Adolf Hitler’s attack on Soviet Union? Explain.
Answer:
By the end of 1940, Adolf Hitler was at the height of power. He moved ahead to achieve his long term aim of conquering eastern Europe. He wanted to ensure food supplies and living space for Germans. His attack on Soviet Union in June 1941, proved to be a historic blunder.
In this, he exposed the German Western Front to British aerial bombing and the Eastern front to the powerful Soviet armies. The Soviet Red Army defeated Germany at Stalingrad badly. After this, they established Soviet hegemony over the entire Eastern Europe for half a century.
![]()
Question 12.
“Nazism was an anti-democratic movement”. How?
Answer:
Nazism was an anti-democratic and imperialistic movement.
- It was a movement which arose because of peculiar conditions in Germany.
- Nazism is a sworn enemy of liberalism, democracy and civil liberties.
- According to Nazism, the leader is always right, individual is nothing, the state is everything. This phenomenon of Nazism is totally opposite to democratic concept. Thus, it was an anti-democratic movement.
Question 13.
How were the Jews the worst sufferers in the Nazi Germany?
Answer:
The Jews were the worst sufferers in the Nazi Germany because:
- The Nazi hatred for Jews was rooted in the traditional Christian hostility towards them. They had been stereotyped as killers of Christ and usurers.
- In Nazi Germany, they lived in separately marked areas called ghettos. They were often persecuted through periodically organised violence and expulsion from the land.
- From 1933 to 1938, the Nazis terrorised, pauperised and segregated the Jews, compelling them to leave Germany.
- Hitler believed that ‘the Jewish problem’ could be solved only through total elimination. As a result, they were killed on a mass scale in gas chambers.
Question 14.
‘Nazi rule was barbarous’. Explain any three points to prove this statement.
Answer:
The following three points prove that Nazi rule was barbarous :
- In Nazi Germany, only Nordic German Aryans were considered ‘desirable’, and Jews, Gypsies, Blacks, Russians and Polish people were brutally killed in gas chambers.
- The Jews and communists were tortured in concentration camps. Even ‘undesirable children’ were segregated and taken to the gas chambers.
- Special surveillance and security forces were created to control and carry out atrocities against the selected group of innocent people. Extra-constitutional powers were given to these forces which made the Nazi state as the most dreaded criminal state.
Question 15.
Describe the new education policy introduced by Adolf Hitler in Germany.
Answer:
The following were the main points of the new education policy introduced by Adolf Hitler in Germany:
- School text books were rewritten.
- Jewish teachers were dismissed from the schools.
- Racial science was introduced to justify Nazi ideas of race.
- Children were segregated. Germans and Jew could not sit together or play together.
- Undesirable children, like the Jews, physically handicapped and Gypsies were thrown out of schools.
- Stereotypes about Jews were popularised even through math classes.
- Children were taught to be loyal and submissive, hate Jews and worship Hitler.
- Sports like boxing, which could make children iron-hearted, strong and masculine, were introduced in schools.
![]()
Question 16.
Evaluate the use of media by the Nazis to popularise their ideology in Germany.
Answer:
The following points state the use of media by the Nazis in Germany:
- Nazi ideas were spread through visual images, films, radio, posters, catchy slogans and leaflets.
- It posters, enemies of Germany were stereotyped, mocked and abused.
- Propaganda films were produced to create hatred for Jews.
- Orthodox Jews were stereotyped and marked, being shown with flowing beards and wearing kaftans. They were referred to as vermins, rats and pests.
Question 17.
HowHow did the common people react to Nazism?
The common people reacted to Nazism in the following ways:
- Many people saw the world through Nazi eyes.
- They spoke their mind in Nazi language.
- They felt hatred and anger when they saw someone looked like a Jew.
- They marked the houses of Jews and reported about their suspicious neighbours to government.
- Common men really believed that Nazism would bring happiness and prosperity for them.
- A large majority of Germans were passive onlookers, as they were scared to act or protest against Nazism.
- However, many Germans organised active resistance to Nazism, braving police repression and death.
IV. Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain the impact of the Great Economic Depression on Germany.
Answer:
The German economy was the worst hit by the economic crisis caused by the Great Economic Depression (1929-1932) in the USA. German investments and industrial recovery was largely dependent on loans from the USA. When the USA stock market crashed in 1929, the USA withdraw financial support from Germany. The following points state the impact of Great Economic Depression on Germany :
- By 1932, industrial production was reduced to 40 percent of the 1929 level.
- The number of unemployed rose to 6 million. People with signboards ‘willing to do any work’, unemployed youths playing cards or simply sitting on the streets were common sights. Unemployed youths were sometimes involved in criminal activities and total despair became commonplace.
- The economic crisis created deep anxieties and fears in people. As businesses got ruined, small businessmen, self employed and retailors were filled with the fear of being reduced to the ranks of workers or unemployed. Big businessmen were also in crisis.
- The large mass of peasantry was affected by a sharp fall in agricultural prices.
- The middle classes like salaried employees and pensioners found their savings diminish due to the currency losing its value.
- Women unable to feed their children properly were filled with a sense of despair.
Question 2.
What steps were taken by Hitler to militarise Germany?
Answer:
The steps taken by Hitler to militarise Germany were as follows :
- Special surveillance and security forces were created to control and order society in ways that the Nazis wanted.
- Apart from the already existing regular police in green uniform and the SA or the Storm Troopers, these included the Gestapo (secret state police), the SS (the protection squads), criminal police and the Security Service (SD).
- It was the extra-constitutional powers of these newly-organised forces that gave the Nazi-state its reputation as the most dreaded criminal state.
- People could now be detained in Gestapo torture chambers, rounded up and sent to concentration camps, deported at will or arrested without any legal procedure.
- The police forces acquired powers to rule with impunity.
Question 3.
Describe Hitler’s policy of Nazification.
Answer:
- Gleichschaltung subjected all major German institutions universities, schools, professions, youth organisations to Nazi control. Only the armed forces, the catholic church and some dissenting Lutheran congregations resisted takeover.
- Trade unions were abolished.
- In 1934, the German Parliament (Reichstag) voted its powers to Hitler through the Enabling Law. Popular support for Nazism was mobilized by the dramatisation of the leader cult and through mass political spectacles, of which the annual highlight was the party Rally at Nuremberg.
- A strong appeal to Germanic traditions and false culture was also a major element in Hitler’s Nazification programme.
Question 4.
Who was Adolf Hitler? Trace his rise to power and downfall in Germany.
Answer:
- Hitler was born in Austria in 1889 and he spent his youth in poverty.
- During the First World War, he enrolled himself in the German army, acted as a messanger at the front, became a corporal and earned medals for bravery.
- In 1919, he joined a small group called the German Workers’ Party and subsequently took control of this party, renaming it as the National Socialist German Workers’ Party. This party later came to be known as the Nazi Party.
- In 1923, Hitler was arrested and tried for treason.
- By 1932, the Nazi Party had become the largest party in Germany with 37 per cent votes.
- In 1933, Hitler became the Chancellor of Germany. Having acquired power, Hitler set out to dismantle the structure of democratic rule.
- Hitler went on to rebuild Germany along his personal preferences and the desires of the Nazi Party.
- He believed in racial superiority of Nordic German Aryans. He had full faith in the policy of external expansion.
- Hitler dragged the whole of the world into war once again which came to be known as the Second World War.
- At the height of the war, when defeat was knocking at his doors, Hitler committed suicide.
![]()
Question 5.
Explain the Nuremberg Laws of citizenship.
Answer:
The Nuremberg Laws of citizenship of September 1935 declared the following:
- Only persons of German or related blood would henceforth be German citizens, enjoying the protections of German empire.
- Marriages between Jews and Germans were forbidden.
- Extramarital relations between Jews and Germans were declared a crime.
- Jews were forbidden to hoist the German national flag. Other legal measures included :
(a) Boycott of Jewish businesses.
(b) Expulsion from government services.
(c) Forced selling and confiscation of their properties.
(d) Jewish properties were vandalised and looted, houses attacked, synagogues burnt and men arrested and massacred in November 1938, remembered as the night of broken glass.
Question 6.
Explain the crimes against humanity carried out by the Nazis of Germany.
Answer:
Followings were the crimes against humanity carried out by Nazis of Germany:
- They suspended civic rights like freedom of speech, press and assembly.
- Concentration camps were established to torture the communists.
- Hitler banned all political parties and trade unions except the Nazi Party and 4ts affiliates.
- Special surveillance and security forces were created to control and order society in ways that the Nazis wanted. People could now be detained in Gestapo- .torture” camps.
- The Jews, Gypsies and Blacks were classified as ‘undersirables’ and they were widely persecuted.
- Germany occupied Czechoslovakia and Poland. Captured civilians were forced to serve as slave labour.
- Jewish teachers and ‘politically unreliable’ teachers were dismissed from the schools. Jews, physically handicapped and Gypsies were considered as ‘undesirable children’ and were thrown out of schools.
- Aryan women who deviated from the prescribed code of conduct were publicly condemned and punished.
Question 7.
Describe Hitler’s Policy towards youth.
Answer:
Hitler’s Policy Towards Youth: Hitler’s policy towards youth can be summarised as below:
1. Total Control over Schools:
Hitler was fanatically interested in the youth of the country. He felt that a strong Nazi society could be established only by teaching children the Nazi ideology. This required a control over the child, both inside and outside the school.
2. Purification of Schools:
All schools were cleansed and purified. This meant that teachers who were Jews or seen as ‘politically unreliable’ were dismissed. Children were first segregated : Germans and Jews could not sit together or play together. Subsequently, ‘undesirable children’ were thrown out of schools, and finally, in the 1940s, they were taken to the gas chambers.
3. New Education Policy:
To popularise his ideology, Hitler announced a New Education Policy. Under this, school textbooks were rewritten. Racial science was introduced to justify Nazi ideas of race. Stereotypes about Jews were popularised even through math classes. Children were taught to be loyal and submissive, hate Jews, and worship Hitler.
4. Division of the Life:
Life of the youth was divided into different stages. At each stage, he had to pass through various training and teaching programmes.
5. Formation of Hitler Youth:
The Youth League of the Nazis was founded in 1922. Four years later, it was renamed ‘Hitler Youth’. To unify the youth movement under Nazi control, all other youth organisations were systematically dissolved and finally banned.
![]()
Question 8.
Explain the Nazi’s Art of Propaganda.
Answer:
The Nazi’s Art of Propaganda: The Nazis used language and media with great care. Their art of propaganda can be explained as follows:
1. Various Codes:
Nazis used code language. The terms they coined to describe their various parctices are not deceptive but chilling also. Nazis never used the words, ‘kill’ or ‘murder’ in their official communication. Mass killings were termed special treatment, final solution (for the Jews), euthanasia (for the disabled), selection and disinfection. ‘Evacuation’ meant deporting people to gas chambers. They were labelled ‘disinfection-areas’, and looked like bathrooms equipped with fake showerheads.
2. Use of Mass Media:
Media was carefully used to win support for the regime and popularise its worldview. The Nazi ideas were spread through visual images, radio, posters, catchy slogans and leaflets. In posters, groups identified as the enemies of Germans were stereotyped, mocked, abused and described as evil. Socialists and liberals were presented as weak and degenerate. They were attacked as malicious foreign agents.
3. Films:
Propaganda films were made to create hatred for Jews. The most infamous film was “The Eternal Jew”.
Question 9.
What is Holocaust? How was it practised in Germany?
Answer:
The atrocities and sufferings that the Jews had endured during the Nazi killing
operations is known as the Holocaust. Holocaust was practised in Germany by the Nazis using the following methods:
- Physically eliminating all those who were seen as undesirable (Jews, Gypsies, Blacks and other ‘racially impure’ people) by killing them in gas chambers by the use of poisonous gas.
- Making people from Poland and Russia work as slave labour and imprisoning them in concentration camps.
- Jews were segregated (including Jewish children in school) and pauperised, many of them were forced to leave the country.
- Jews were victimized through the media by circulating films, pictures, leaflets and slogans. They were stereotyped, mocked, abused and described as evil.
- Jews were referred to as vermins, rats and pests. Their movements were compared to those of rodents.
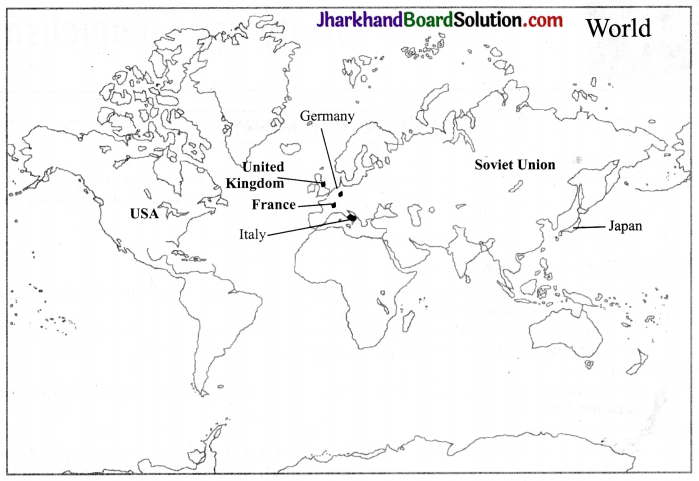
MAP WORK
Question 1.
In an outline map of world, locate/label/identify the following:
Major countries of Second World War Axis Powers: Germany, Italy, Japan
Allied Powers: United Kingdom, France, Soviet Union, USA (show with bold colour)
Answer: