JAC Board Class 10th Social Science Solutions Geography Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources
JAC Class 10th Geography Minerals and Energy Resources InText Questions and Answers
Page 48
Question 1.
Find out how many minerals are used to make a light bulb. Answer:Minerals used to make a light bulb are:
| Part of Bulb | Material Used | Mineral from which obtained |
| Filament | Tungsten | Scheelite, Wolframite, ferberite or hubnerite (Metallic oxides of Tungsten) |
| Bulb | Glass | Silica (Silicon dioxide) |
| Connecting wires | Copper | Chalcolite (Cuprous sulphide) |
| Metallic part of body | Aluminium | Bauxite (Aluminium oxide) |
![]()
Question 2.
Collect “Nutritional Facts” printed on food labels.
Answer:
Do it yourself activity. Sample answer is given.A sample of nutritional facts printed on a packet of glucose biscuits is given below:
| Energy | 453 cal |
| Fat | 13.0 gm |
| Carbohydrate | 77.5 gm |
| Protein | 6.5 gm |
| Calcium | 15 mg |
| Dietary fibre | 0.6 gm |
Page 50
Question 3.
What is the difference between an open pit mine, a quarry and an underground mine with shafts?
Answer:
Differences between an open pit mine, a quarry and an underground mine with shafts are as follows:
| Open pit mine | Question uarry | Underground mine with shafts |
| Minerals are removed from a pit dug in the ground. | Minerals are removed from a shallow pit dug in the ground. | Minerals are removed through deep shafts dug in the ground. |
| Used where commercially useful minerals are found near the surface. | Generally, used for extracting building materials like dimension stone. | Used where the mineral occurs as veins in hard rock deep below the surface of the Earth. |
| Extracted using Earthmoving machinery. | Extracted using Earthmoving machinery. | Extracted using elevators that can carry minerals, extraction equipment as well as persons into the area where the mineral is available. |
page 51
Question 4.
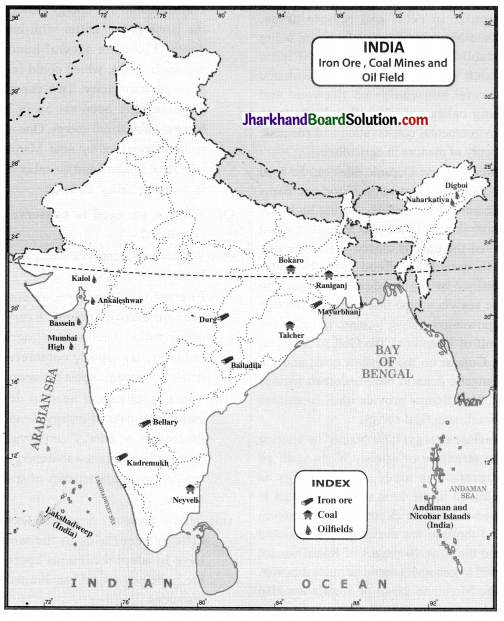
Superimpose the maps showing distribution of iron ore, manganese, coal and iron and steel industry. Do you see any correlation? Why?
Answer:
The iron and steel industries are located in the same regions of India where the iron ore, coal and manganese mines are located. As coal and manganese are required as inputs to the iron and steel industry, their availability in the same region saves the transportation costs and ease of availability. So it is profitable to locate these industries in the regions where these minerals are available.
Page 53
Question 5.
Locate the mines of bauxite on the physical map of India.
Answer:
Do it yourself.
Page 54
Question 6.
Study the maps to explain why Chota Nagpur is a storehouse of minerals.
Answer:
We can understand by studying the maps given in the textbook why the Chota Nagpur plateau is considered as a storehouse of minerals. The reasons are:
- Chota Nagpur is a part of old Gondwana land. Part of it is made of solidified magma. The area is rich in minerals.
- It is such in minerals like iron ore, coal, manganese, bauxite, copper, mica, etc.
- The coal fields in this area supply most of the cooking coal to the industries.
Page 55
Question 7.
Name some river valley projects and write the names of the dams built on these rivers.
Answer:
Name of some river valley projects and dams-built on them:
- Bhakra Nangal Project: Bhakra and Nangal dams on the Satluj river in Punjab.
- Hirakud Project: Hirakud dam on the Mahanadi river in Odisha.
- Nagarjuna Sagar Project: Nagaijuna Sagar dam on the Krishna river in Andhra Pradesh.
- Chambal Project: Jawahar Sagar, Gandhi Sagar and Rana Pratap Sagar dams on the Chambal river in Rajasthan and Madhya Pradesh.
- Tungabhadra Project: Tungabhadradam on the Tungabhadra river in Karnataka.
- Mettur Project: Mettur dam on the Kaveri river in Tamil Nadu.
- Sardar Sarovar Project: Sardar Sarovar dam on the Narmada river in Gujarat and Madhya Pradesh.
- Damodar Valley Project: On the Damodar river in Bihar.
- Farakka Project: On the Ganga river in West Bengal.
- Mahi Project: Mahi dam on the Mahi river in Gujarat.
- Tehri Project: Tehri dam on the Bhagirathi river in Uttarakhand.
Page 60
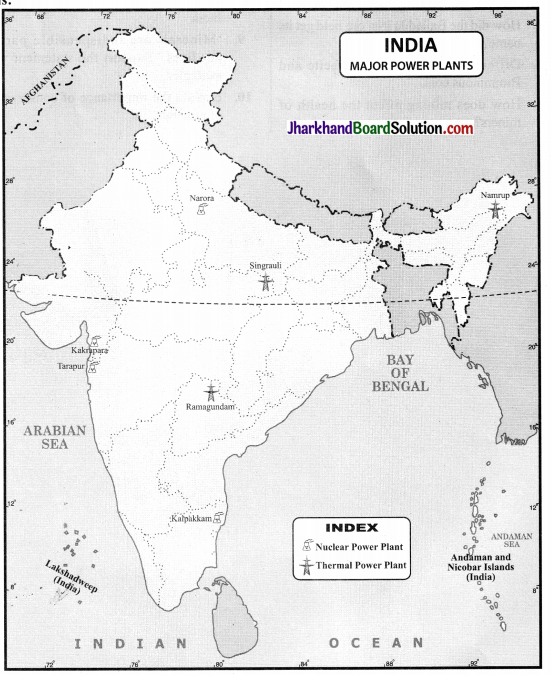
Question 8.
Collect information about thermal/ hydel power plants located in your state. Show them on the map of India.
Answer:
Do it yourself.
![]()
Question 9.
Collect information about newly established solar power plants in India.
Answer:
India is now home to world’s largest solar plant on a ‘single location’. The plant, in Kamuthi, Tamil Nadu, comes with a capacity of 648 MW and covers an area of 10 sq m/km. It also bears the capacity of charging its own solar panels. Furthermore, when in full swing, the plant is capable of producing electricity for 150,000 homes.
The cost of this project was ‘ 46,535,570,550. With this, India’s total installed capacity of solar plants has nudged across the 10 GW mark. Thus, India will be the world’s third-biggest solar market from next year onwards, after China and the US. However, we are still lagging a bit in regard to the expectations that the government has set for the nation.
Question 10.
Locate the 6 nuclear power stations and find out the state in which they are located.
Answer:
- Tarapur Atomic Power Station: it is located in Maharashtra.
- Rajasthan Atomic Power Station: it is located in Rajasthan
- Kakrapar Atomic Power Station: it is located in Gujarat
- Kudankulam Nuclear Power Plant: it is located in Tamil Nadu
- Kaiga Nuclear Power Plant: it is located in Karnataka
- Gorakhpur Atomic Power Station: it is located in Haryana
JAC Class 10th Geography Minerals and Energy Resources Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below.
(i) Which one of the following minerals is formed by decomposition of rocks, leaving a residual mass of weathered material?
(a) Coal
(b) Bauxite
(c) Gold
(d) Zinc
Answer:
(a) Coal
(ii) Koderma, in Jharkhand is the leading producer of which one of the following minerals?
(a) Bauxite
(b) Mica
(c) Iron ore
(d) Copper
Answer:
(b) Mica
(iii) Minerals are deposited and accumulated in the stratas of which of the following rocks?
(a) Sedimentary rocks
(b) Metamorphic rocks
(c) Igneous rocks
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(a) Sedimentary rocks
(iv) Which one of the following minerals is contained in the Monazite sand?
(a) Oil
(b) Ur0anium
(c) Thorium
(d) Coal
Answer:
(c) Thorium
![]()
Question 2.
Answer the following questions in about 30 words.
(a) Distinguish between the following in not more than 30 words.
- Ferrous and non-ferrous minerals
- Conventional and non-conventional sources of energy
(b) What is a mineral?
(c) How are minerals formed in igneous and metamorphic rocks?
(d) Why do we need to conserve mineral resources?
| Ferrous minerals | Non-ferrous minerals |
| (i) Ferrous minerals contain iron ; content. | (i) These minerals do not contain iron content. |
| (i) They provide a strong base in the development of metallurgical industries. | (ii) They play an important role in a number of industries like, engineering and electrical industries. |
| (iii) Iron ore, manganese, cobalt, etc., are the examples of ferrous kminerals. | (iii) Copper, zinc, lead and aluminium are the examples of non-ferrous minerals. |
| Conventional sources of energy | Non-conventional sources of energy |
| (i) Conventional sources of energy have been used since a long time. | (i) The sources of energy which are of recent origin and have not been commonly used. |
| (ii) These are expensive in the long run. | (ii) These are cheaper in the long mn. |
| (iii) These are used extensively. | (iii) These are used locally. |
| (iv) They are non-renewable and exhaustible sources of energy. | (iv) They are renewable sources of energy. |
(b) A mineral is a naturally occurring homogeneous substance with a definable interior structure. Mineral that will be formed from a certain combination of elements depends upon the physical and chemical conditions under which the material forms.
(c) In igneous and metamorphic rocks minerals may occur in the cracks, crevices, faults or joints. The smaller occurrences are called veins and the larger are called lodes. In most cases, they are formed when minerals in liquid/molten and gaseous forms are forced upward through cavities towards the earth’s surface. They cool and solidify as they rise.
(d) We are rapidly consuming mineral resources that require millions of years to be created and concentrated. The geological processes of mineral formation are so slow that the rates of replenishment are infinitely small in comparison to the present rates of consumption. Mineral resources are, therefore, finite and non¬renewable. That is why we need to conserve mineral resources and use them wisely.
![]()
Question 3.
Answer the following questions in about 120 words.
(a) Describe the distribution of coal in India.
(b) Why do you think that solar energy has a bright future in India?
Answer:
(a) In India, coal is the most abundantly available fossil fuel. It provides a substantial part of the nation’s energy needs.
(i) In India, coal occurs in rock series of two main geological ages, viz., Gondwana, a little over 200 million years in age and in tertiary deposits which are only about 55 million years old. The major resources of Gondwana coal, which are metallurgical coal, are located in Damodar valley (West Bengal-Jharkhand). The important coal fields are Jharia, Raniganj and Bokaro. The Godavari, Mahanadi, Son and Wardha valleys also contain coal deposits.
(ii) Tertiary coals occur in the north eastern states of Meghalaya, Assam, Arunachal Pradesh and Nagaland.
(iii) Lignite is a low grade brown coal, which is soft with high moisture content. The principal lignite reserves are in Neyveli in Tamil Nadu and are used for generation of electricity.
Distribution of coal in India:
- Anthracite is found in Jammu and Kashmir.
- Bituminus is found in Jharkhand, Odisha, West Bengal, Chhattisgarh and Madhya Pradesh.
- Lignite is found in Tamil Nadu and Rajasthan.
(b) India has enormous possibilities of tapping solar energy. Photovoltaic technology converts sunlight directly into electricity. Solar energy is fast becoming popular in rural and remote areas. Some big solar power plants are being established in different parts of India which will minimise the dependence of rural households on firewood and dung cakes, which in turn will contribute to environmental conservation and adequate supply of manure in agriculture.
NCERT Activity
Question 1.
Fill the name of the correct mineral in the crossword below:
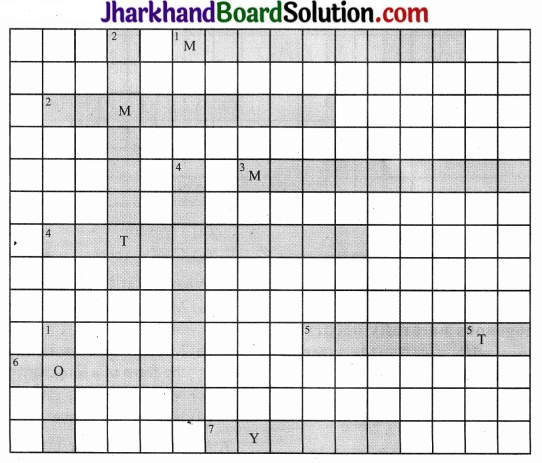

DOWN
- Found in placer deposit (4)
- Iron ore mined in Bailadila (8)
- Indispensable for electrical industry (4)
- Geological Age of coal found in northeast India (8)
- Formed in veins and lodes (3)
ACROSS
- A ferrous mineral (9)
- Raw material for cement industry (9)
- Finest iron ore with magnetic properties (9)
- Highest quality hard coal (10)
- Aluminium is obtained from this ore (7)
- Khetri mines are famous for this mineral (6)
- Formed due to evaporation (6)