JAC Board Class 10th English Grammar Tenses
JAC Class 10th English Grammar Tenses Textbook Questions and Answers
An event or action may have happened in the past or may happen in the present or the future. To show the time of happening of the events we use tenses.
Tenses are the various forms of the verbs which indicate the time of an action or a condition. Given below are its types.
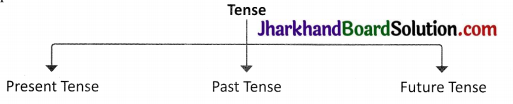
1. Present Tense: The form of the verb that refers to present time is said to be in the Present Tense.
Examples:
Dhruv does his homework daily.
The police inspector catches the thieves.
2. Past Tense: The form of the verb that refers to past time is said to be in the Past Tense.
Examples:
Dhruv did his homework daily.
The police inspector caught the thieves.
3. Future Tense: The form of the verb that refers to future time is said to be in the Future Tense.
Examples:
Dhruv will do his homework daily.
The police inspector will catch the thieves.

Various Forms Of Tenses
Each of the above tenses has four forms as stated below:

1. Present Indefinite Tense:
Use(s) of Present Simple Tense
The Present Simple Tense:
expresses an event or action taking place in the present moment.
Examples:
The police stand guard outside the MP’s residence.
The news anchor on TV speaks eloquently.
denotes the habitual action.
Examples:
Ishaan eats breakfast after exercise.
My mother tends to our garden daily in the evening.
expresses universal truth.
Examples:
The Sun is the ultimate source of energy.
The Earth revolves around the sun.
expresses scientific facts.
Examples:
Sound travels slower than light.
Helium is lighter than hydrogen.

Sentence Construction:
1. Affirmative Sentences: With I, we, you, they and plural nouns, we use first form of the verb. With he, she, it or singular nouns, we use first form of the verb + s or es.
Structure: Subject + V1 (s/es) + other words.
Examples:
Mr. Khurana plays golf in the evening.
They participate in all athletic events.
2. Negative Sentences: I, we, you, they and plural nouns are followed by do not. He, she, it and singular nouns are followed by does not.
Structure: Subject + do/does + not + V1 + other words.
Examples:
I do not do work on Sundays.
My granny does not believe in ghosts.
3. Interrogative Sentences: We place Do or Does before the subject and the first form of the verb after the subject.
Structure: Do/Does + subject + V1 + other words?
Examples:
Do we eat wheat flour or millet flour?
Does the chairman allow the employees to give their feedback?
4. Interrogative-Negative Sentences: To make interrogative-negative sentences, helping verb do/does is placed before the subject and not after that.
Structure: Do/Does + subject + not + V1 + other words?
Examples:
Do you not go to park for morning walk?
Does the lion not eat deer?

2. Present Continuous Tense:
Use(s) of Present Continuous Tense-
The Present Continuous Tense:
denotes an action/event/activity going on at the time of speaking.
Examples:
Kabir’s mother is calling him to complete his homework.
The servant is bringing tea for the guests.
denotes an action which is likely to happen in the near future.
Example:
The economic condition of the nation is going to improve in the current financial year.
Sentence Construction:
1. Affirmative Sentences: We use is with he, she, it and singular noun’, am with / and are with we, you, they and a plural noun.
Structure: Subject + is/am/are + V1 + ing + other words.
Examples:
She is thinking to switch her job.
They are sitting on a dhama against the new tax regime.
I am driving my car.
2. Negative Sentences: To make negative sentences, not is placed between the helping verb and the principal verb.
Structure: Subject + is/am/are + not + V1 + ing + other words.
Examples:
The government is not taking strict action against the criminals.
The new generation computers are not working properly due to a fault in their CPUs. ”
I am not going outside in the rain.
3. Interrogative Sentences: The helping verb is placed before the subject.
Structure: Ts/Am/Are + subject + V1 + ing + other words?
Examples:
Is the new fan making noise?
Am I doing my work properly?
Are we going out for dinner?
4. Interrogative-Negative Sentences: To make interrogative-negative sentences, helping verb is/ am/are come before the subject and not after that.
Structure: Is/Am/Are + subject + not + V1 + ing + other words?
Examples:
Is he not coming to the workshop?
Am I not drawing the sketch neatly?
Are they not frightening the juniors?
3. Present Perfect Tense:
Use(s) of Present Perfect Tense-
The Present Perfect Tense:
expresses an action that has been completed.
Example:
The President of India has addressed the nation.
denotes a past time the result of which is continuing in the present.
Example:
We have lived in Dehradun for ten years.
Sentence Construction
1. Affirmative Sentences: Helping verbs has, have are used as per the number and person of the subject. Has is used with he, she, it and singular nouns and have with I, we, you, they and plural nouns.
Structure: Subject + has/have + V3 + other words.
Examples:
The USA and North Korea have ended their old enmity.
The delivery boy has delivered the pizza.
2. Negative Sentences: To make negative sentences, not is placed between the helping verb and the main verb.
Structure: Subject + has/have + not + V3 + other words.
Examples:
I have not watched any of the new movies.
The maid has not washed the clothes.
3. Interrogative Sentences: The helping verb (has/have) comes before the subject.
Structure: Has/have + subject + V3 + other words?
Examples:
Has Rohit ever been to the Science Museum?
Have you cleared the first-term exams?
4. Interrogative-Negative Sentences: To make interrogative-negative sentences, helping verb has/have comes before the subject and not after that.
Structure: Has/Have + subject + not + V3 + other words?
Examples:
Has she not prepared for the examination?
Have they not completed their work?
Note: Adverbs like yet, so far, ever since, already, just, just now, presently, once, twice, etc., are often used in sentences of present perfect tense.
Example: The fire fighters have already doused the fire.

4. Present Perfect Continuous Tense:
Use(s) of Present Perfect Continuous Tense-
The Present Perfect Continuous Tense is used to express an action/event/activity that started in the past and continues in the present (with a time of reference).
Example: Nikita has been painting a picture for two hours.
Sentence Construction:
1. Affirmative Sentences: Has/Have is accompanied by been before the first form of the verb + ing.
Structure: Subject + has/have + been + V1 + ing + other words + for/since + time phrase.
Examples:
This statue has been standing tall here since the 1950s.
They have been managing the crowd for the past three hours.
2. Negative Sentences: Here, not comes between has/have and been.
Structure: Subject + has/have + not + been + V1 + ing + other words + for/since + time phrase.
Examples:
He has not been studying continuously for seven hours.
I have not been doing my work since morning.
3. Interrogative Sentences: Helping verb has/have comes in the starting of the sentence before the subject and been follows the subject.
Structure: Has/Have + subject + been + V1 + ing + other words + for/since + time phrase?
Examples:
Has the boy been understanding anything for the past half an hour?
Have the devotees been visiting this shrine since 1900s?
4. Interrogative-Negative Sentences: To make interrogative-negative sentences, helping verb has/have comes before the subject and not after that.
Structure: Has/Have + subject + not + been + V1 + ing + other words + for/since + time phrase?
Examples:
Has he not been doing his homework properly for one month?
Have the soldiers been guarding the frontier since the independence?
Use of Since and For
Prepositions since and for are used mainly in perfect continuous tenses.
Since is used with the point of time at which an action started.
Examples:
Everyone has been benefiting from the government’s insurance scheme since its inception.
This shop has been serving its customers since 1970.
For is used with the period of time during which the action continued.
Examples:
The athletes from Australia have been winning the World Championship for nine years.
Rita has been running in the park for one hour.

B. Past Tense
1. Past Indefinite/Simple Tense:
Use(s) of Past Indefinite Tense-
The Past Indefinite Tense:
expresses an action that took place in the past.
Example: Alexander Graham Bell invented the phone in 1876.
denotes a habitual action in the past.
Example: I went to tuition classes till 10th standard.
Sentence Construction:
1. Affirmative Sentences: In affirmative sentences, second form of the verb is used.
Structure: Subject + V2 + other words.
Example: The bird flew right into the glass window.
2. Negative Sentences: In negative sentences, after the subject, did not and the first form of the verb is used.
Structure: Subject + did + not + V1 + other words.
Example: She did not lose her temper after the poor performance.
3. Interrogative Sentences: Helping verb did is placed before the subject and the first form of the verb is used after the subject.
Structure: Did + subject + V1 + other words?
Example: Did Renu bake a chocolate cake for the guests?
4. Interrogative-Negative Sentences: To make interrogative-negative sentences, helping verb did is placed before the subject and not comes after the subject.
Structure: Did + subject + not + V1 + other words?
Example: Did the game not resume after the rain?

2. Past Continuous Tense:
Use(s) of Past Continuous Tense-
The Past Continuous Tense is used to denote an activity that was in progress in the past. f-
Example: Sonia was singing a song on the stage.
It is also used with the simple past tense to denote that one activity was in progress while another took place.
Example: They were sleeping when the door bell rang. .
Sentence Construction:
1. Affirmative Sentences: Helping verbs was, were are used according to the subject, with first form of the Verb + ing.
Structure: Subject + was/were + V1 + ing + other words.
Examples:
Manish was running in the marathon.
The leaves were falling from the tree.
2. Negative Sentences: In negative sentences, not is placed between the helping verb and the present participle (First form + ing) of the main verb.
Structure: Subject + was/were + not + V1 + ing + other words.
Examples:
The teacher was not teaching the students.
We were not going across the canal.
3. Interrogative Sentences: The helping verb was/were is put before the subject.
Structure: Was/were + subject + V1 + ing + other words?
Examples:
Was the commander allowing the soldiers to sleep for seven hours?
Were the sages preaching the people about happiness?
4. Interrogative-Negative Sentences: In it, helping verb was/were is put before the subject and not is placed after the subject.
Structure: Was/were + subject + not + V1 + ing + other words?
Examples:
Was he not researching about his new assignment?
Were the students not studying quietly?

3. Past Perfect Tense:
Use(s) of Past Perfect Tense-
The Past Perfect Tense expresses an action that has already been completed in the past before the beginning of an another action.
Example: Everyone had solved the sum before the teacher dictated the complete statement.
Sentence Construction
1. Affirmative Sentences: The helping verb had and the third form of the verb are used with all the subjects.
Structure: Subject + had + V3 + other words.
Example: Prem had written all four paragraphs before he went to play outside.
2. Negative Sentences: To make negative sentences, we use not after had.
Structure: Subject + had + not + V3 + other words.
Example: The train had not left when I reached the platform.
3. Interrogative Sentences: To make interrogative sentences, had is put before the subject.
Structure: Had + subject + V1 + other words?
Example: Had you booked a hotel room before you started packing for the trip?
4. Interrogative-Negative Sentences: These are formed using had before the subject and not after the subject.
Structure: Had + subject + not + V3 + other words?
Example:
Had Arun not bought any medicine before the doctor prescribed him one?
4. Past Perfect Continuous Tense:
Use(s) of Past Perfect Continuous Tense-
The Past Perfect Continuous Tense expresses an action in the past, which was going on with respect to a given reference of time in the past.
Example: They had,been studying for the examination since evening, when the exam got cancelled.
It is also used to denote an action that began before the time of speaking in the past.
Example: The teacher had been teaching the children of classes 5-10 for thirteen years.
It is also used to denote a repeated action in the past.
Example: The board members had been trying to meet the CEO of the company for the past two weeks.
Sentence Construction:
1. Affirmative Sentences: We use had been and present participle with all the subjects.
Structure: Subject + had + been + V1 + ing + for/since + other words.
Example: Brinda had been watching movies since morning.
2. Negative Sentences: In negative sentences, not is used between had and been.
Structure: Subject + had + not + been + V1 + ing + for/since + other words.
Example: They had not been running their business for fifty years.
3. Interrogative Sentences: In these, had precedes the subject and been follows it.
Structure: Had + subject + been + V1 + ing + for/since + other words?
Example: Had I been using my smart phone since 2015?
4. Interrogative-Negative Sentences: These sentences are formed using had before the subject and not after the subject.
Structure: Had + subject + not + been + V1 + ing + for/since + other words?
Example: Had the new actress not been starring in the TV serials for two years?

3. Future Tense
1. Simple Future Tense:
Use(s) of Simple Future Tense-
The Simple Future Tense expresses an action that takes place at some time in future.
Example: The flight to New York will arrive at 7:40 am.
This tense is also used to denote the opinion of the speaker.
Example: I believe that Ramesh will definitely impress the investors.
In future tense. we use shall and will to denote future time.
Will is used w itli the lirst person, i.e.. 1 and Wo to denote determination and willingness.
Example: My friends will delimteK support me.
Shall is used with the HIM person to denote an offer.
Example: Shall we proceed to the foodcountei?
Sentence Construction:
1. Affirmative Sentences: We use shall with / and we only; and will with rest of the pronouns and all nouns.
Structure: Subject + shall/will + V1 + other words.
Examples:
The renowned author, Mr Rakul will launch his new novel next week.
I shall remain inside the room.
2. Negative Sentences: We add not after will and shall.
Structure: Subject + shall/will + not + V1 + other words.
Examples:
The security guards will not allow anyone to enter into the premises.
We shall not interfere in your work.
3. Interrogative Sentences: We use shall or will before the subject and first form of the verb after the subject.
Structure: Shall/Will + subject + V1 + other words?
Examples: Will the traffic police announce the traffic advisory for smooth flow of vehicles at Diwali?
4. Interrogative-Negative Sentences: In it, we use shall or will before the subject and not after the subject.
Structure: Shall/Will + subject + not + V1 + other words?
Examples:
Will he not shift to Australia for work?
Shall we not allow children to go outside at night?
2. Future Continuous Tense:
Use(s) of Future Continuous Tense-
The Future Continuous Tense denotes an action going on at some time in future.
Example: The babysitter will be taking care of the child on Sunday.
Sentence Construction:
1. Affirmative Sentences: We use shall be/will be according to the subject, followed by first form of the verb + ing.
Structure: Subject + shall/will + be + V1 + ing + other words.
Examples:
I shall be doing my project on my own.
They will be attending the grand celebration party of new year.
2. Negative Sentences: We use not between shall/will and be.
Structure: Subject + shall/will + not + be + V1 + ing + other words.
Examples:
We shall not be writing any letter now.
The crowd will not be protesting against the police.
3. Interrogative Sentences: We use shall or will before the subject and be after the subject.
Structure: Shall/Will + subject + be + V1 + ing + other words?
Examples:
Will Naresh be performing on stage?
Shall I be cutting the pizza into four pieces?
4. Interrogative-Negative Sentences: We use shall and will before the subject and not after the subject.
Structure: Shall/Will + subject + not + be + V1 + ing + other words?
Examples:
Will the company not be disbursing the bonus to the employees?
Shall I not be bringing my pet dog along with me?
3. Future Perfect Tense:
Use(s) of Future Perfect Tense-
The Future Perfect Tense denotes an action that will be completed in future with reference to a given time.
Example: Sahil will have got a government job by next year.
Sentence Construction:
1. Affirmative Sentences: We use shall have/will have according to the subject and add third form of the verb.
Structure: Subject + shall/will + have + V3 + other words.
Examples:
Sagar will have travelled 2000 kms on his bike by next week.
I shall have eaten my food before 8 pm.
2. Negative Sentences: We use not between shall/will and have.
Structure: Subject + shall/will + not + have + V3 + other words.
Examples:
Kiara will not have purchased a new purse by next two years.
We shall not have reached Mumbai before sunset.
3. Interrogative Sentences: We use shall or will before the subject and have after it.
Structure: Shall/Will + subject + have + V3 + other words?
Examples:
Will Malhotras have moved out of this town by next month?
Shall we have donated 50,000 rupees before the new year starts?
4. Interrogative-Negative Sentences: We use shall/will before the subject and not have after it.
Structure: Shall/Will + subject + not + have + V3 + other words?
Examples:
Will the children not have practised enough by the time their exams start?
Shall I not have come to you before this month ends?

4. Future Perfect Continuous Tense:
Use(s) of Future Perfect Continuous Tense-
The Future Perfect Continuous Tense expresses an action continuing beyond some given time in future.
Example:
The direct flight to California will have been completing one year of its successful operation by next week.
Sentence Construction
1. Affirmative Sentences: In affirmative sentences, we use shall have been/will have been followed by the first form of the verb + ing.
Structure: Subject + shall/will + have + been + V1 + ing + other words.
Examples:
The salesman will have been selling all the policies by next week.
I shall have been waiting for twenty minutes, at 6 pm.
2. Negative Sentences: In negative sentences, not is used between shall/will and have been.
Structure: Subject + shall/will + not + have + been + V1 + ing + other words.
Examples:
They will not have been doing their new assignment by next Wednesday.
I shall not have been leaving for Amsterdam next Tuesday.
3. Interrogative Sentences: Shall/Will comes before the subject and have been after it.
Structure: Shall/Will + subject + have + been + V1 + ing + other words?
Examples:
Will Dev have been completing his homework by evening?
Shall we have been watching movie in the theatre in evening?
4. Interrogative-Negative Sentences: We use shall/will before the subject and not have been after it.
Structure: Shall/Will + subject + not + have + been + V1 + ing + other words?
Examples:
Will Vaani not have been going to Mumbai by next Saturday?
Shall we not have been decorating our house by morning?

Exercise (Solved)
(A) PRESENT TENSE
Answer any ten of the questions given below by choosing the most appropriate option. [10 x 1 = 10]
1. My mother usually …………. at five o’clock early in the morning.
(a) gets up
(b) getting up
(c) got up
(d) get up
Answer:
(a) gets up
2. Rohan …………. his grandparents since Monday.
(a) has not been visiting
(b) did not visit
(c) is visiting
(d) had been visiting
Answer:
(a) has not been visiting
3. His friend who …………. from Tamil Nadu visited me yesterday.
(a) hailing
(b) hails
(c) hailed
(d) hail
Answer:
(b) hails
4. He …………. for Vice President in this election.
(a) is not run
(b) is not runs
(c) is not running
(d) is not ran
Answer:
(c) is not running
5. Choose the sentence that is in the form of present perfect continuous tense.
(a) Which TV channel do you usually watch?
(b) Which TV channel are you usually watching?
(c) Which TV channel have you usually watched?
(d) Which TV channel have you been usually watching?
Answer:
(d) Which TV channel have you been usually watching?

6. Choose the sentence that is in the form of present perfect tense.
(a) She has reached the railway station by 9 pm.
(b) She have reached the railway station by 9 pm.
(c) She reaches the railway station by 9 pm.
(d) She has been reaching the railway station by 9 pm.
Answer:
(a) She has reached the railway station by 9 pm.
7. She …………. to Mumbai yesterday.
(a) is gone
(b) has gone
(c) have gone
(d) was gone
Answer:
(b) has gone
8. She …………. in the kitchen for more than an hour.
(a) is not
(b) has not been
(c) have not been
(d) none of the above
Answer:
(b) has not been
9. She …………. living in this house for the last ten years.
(a) is
(b) are
(c) has been
(d) have been
Answer:
(c) has been
10. Rajesh …………. to Karnataka.
(a) belong
(b) belongs
(c) belonged
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) belongs
11. Akash …………. not completed his homework vet.
(a) is
(b) has
(c) was
(d) have
Answer:
(b) has

12. Raju …………. gone to Patna last night.
(a) is
(b) am
(c) are
(d) has
Answer:
(d) has
(B) PAST TENSE
Answer any ten of the questions given below by choosing the most appropriate option. [10 x 1 = 10]
1. Which of the following sentences is not written in the simple past tense?
(a) Hemant did not appear in the examination.
(b) Where did Aruna keep the papers?
(c) Did you visit the trade fair last month?
(d) She had already met her manager.
Answer:
(d) She had already met her manager.
2. The teacher …………… an exciting question in the classroom yesterday.
(a) has asked
(b) has been asking
(c) asked
(d) was asked
Answer:
(c) asked
3. You both were not studying when I …………… for my exam.
(a) preparing
(b) prepared
(c) had prepared
(d) waspreparing
Answer:
(d) waspreparing
4. They were playing basketball yesterday. Change the sentence into simple past tense.
(a) They had been playing basketball yesterday.
(b) They played basketball yesterday.
(c) They had played basketball yesterday.
(d) They were playing basketball yesterday.
Answer:
(a) They had been playing basketball yesterday.
5. Manoj …………… the gift yesterday, because his mother asked him to do so.
(a) would open
(b) have opened
(c) had been opened
(d) opened
Answer:
(d) opened
6. He …………… the door because he …………… for someone.
(a) doesn’t close / was waiting
(b) will not close / waiting
(c) didn’t close / was waiting
(d) close / was waiting
Answer:
(c) didn’t close / was waiting

7. Which of the following sentences is written in past perfect tense?
(a) They were going to school.
(b) The train had left the station before I reached.
(c) They had been working on the project since five weeks.
(d) The boys were playing games when it started raining.
Answer:
(b) The train had left the station before I reached.
8. What …………… you …………… last week?
(a) were/do
(b) did/does
(c) wasn’t/did
(d) did/do
Answer:
(d) did/do
9. She …………… all evening on Monday.
(a) knitting
(b) am knitting
(c) was knitting
(d) has knitted
Answer:
(c) was knitting
10. Raiesh told me that he …………… won a prize.
(a) has
(b) have
(c) had
(d) is
Answer:
(c) had
11. Rakesh …………… keeping well since a vear.
(a) has not been
(b) have not been
(c) had not been
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) had not been
12. Riva …………… a new mobile last month.
(a) purchases
(b) purchased
(c) is purchase
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) purchased

(C) FUTURE TENSE
Answer any ten of the questions given below by choosing the most appropriate option. [10 x 1 = 10]
1. They will be sleeping till late at night on Sunday. Write the sentence in negative interrogative for future continuous tense.
(a) Will they be sleeping till late at night on Sunday?
(b) They will not be sleeping till late at night on Sunday.
(c) They had been sleeping till late at night on Sunday.
(d) Will they not be sleeping till late at night on Sunday?
Answer:
(d) Will they not be sleeping till late at night on Sunday?
2. At three o’clock tomorrow, she …………… at the gym.
(a) will be
(b) is
(c) are
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) will be
3. Mohini …………… to the class next week.
(a) wasn’t coming
(b) will not coming
(c) had not been coming
(d) will not be coming.
Answer:
(d) will not be coming.
4. Which of the following sentences is in future continuous tense?
(a) My mother did a lot for me when she was alive.
(b) She has just started her class.
(c) We have been joined the meeting before we came here.
(d) My parents will be happy tomorrow during my dance performance.
Answer:
(d) My parents will be happy tomorrow during my dance performance.

5. Carol thinks the Congress …………… the election this time.
(a) will win
(b) will be winning
(c) will have won
(d) will have been winning
Answer:
(a) will win
6. You ………….. very differently about this when you are older.
(a) will think
(b) will be thinking
(c) will have been thinking
(d) will have thought
Answer:
(b) will be thinking
7. When …………. all the social studies assignments?
(a) will you have completed
(b) will you not be completing
(c) will you had not been completing
(d) None of the above.
Answer:
(a) will you have completed
8. We …………… to the airport to see off our cousin Madhuri.
(a) shall have gone
(b) shall be going
(c) shall go
(d) shall have been going
Answer:
(c) shall go
9. Will …………… your project by this time next week?
(a) you have finished
(b) you have been finishing
(c) you be finishing
(d) you finish
Answer:
(a) you have finished
10. The vehicles …………… not ply on the road due to lockdown.
(a) is
(b) will
(e) shall
(d) are
Answer:
(b) will

11. New guidelines …………… available for the public soon.
(a) will be
(b) shall be
(c) shall
(d) will
Answer:
(a) will be
12. Will she …………… writing a novel?
(a) has been
(b) have been
(e) has
(d) had
Answer:
(b) have been
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()


 +
+