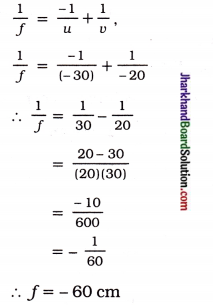Jharkhand Board JAC Class 10 Sanskrit Solutions Shemushi Chapter 7 सौहार्द प्रकृतेः शोभा Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
JAC Board Class 10th Sanskrit Solutions Shemushi Chapter 7 सौहार्द प्रकृतेः शोभा
JAC Class 10th Sanskrit सौहार्द प्रकृतेः शोभा Textbook Questions and Answers
प्रश्न 1.
एकपदेन उत्तरं लिखत (एक शब्द में उत्तर लिखिए)
(क) वनराजः कै दुरवस्थां प्राप्तः?
(वनराज किनके द्वारा दुरवस्था को प्राप्त हुआ?)
(ख) कः वातावरणं कर्कश ध्वनिना आकुली करोति?
(वातावरण को कर्कश ध्वनि से कौन व्याकुल करता है?)
(ग) काकचेष्टः विद्यार्थी कीदृशः छात्रः मन्यते?
(काकचेष्टा विद्यार्थी कैसा छात्र माना जाता है?)
(घ) कः आत्मानं बलशाली, विशालकायः पराक्रमी च कथयति?
(अपने आपको कौन बलशाली, विशालकाय और पराक्रमी कहता है?)
(ङ) वकः कीदृशान् मीनान् क्रूरतया भक्षयति?
(बगुला किस प्रकार की मछलियों को क्रूरता से खा जाता है?)
उत्तराणि :
(क) वानरैः
(ख) काकः
(ग) आदर्श छात्रः
(घ) गजः
(ङ)वराकान्
प्रश्न 2.
अधोलिखित प्रश्नानाम् उत्तराणि पूर्णवाक्येन लिखत। –
(निम्न प्रश्नों के उत्तर पूर्ण वाक्य में लिखिए)
(क) निःसंशय कः क्रूतान्त मन्यते?
(निःसंदेह यमराज कौन कहलाता है?)
उत्तरम् :
यः नृपः वित्रस्तान् पीड्यमानान् जन्तूनं परैः न रक्षति सः निःसंशयः पार्थिव रूपेण कृतान्त (जो राजा डरे तथा पीड़ित जन्तुओं की रक्षा नहीं करता, वह नि:संदेह राजा के रूप में यमराज है।

(ख) वकः वन्यः जन्तूनां रक्षोपायाम् कथं चिन्तयितुं कथयति?
(बगुला वन्य जीवों के रक्षा के उपाय कैसे सोचने के लिए कहता है?)
उत्तरम् :
अहं तु शीतले जलं बहुकालपर्यन्तम् अविचलः ध्यानमग्न स्थितप्रज्ञ इव स्थित्वा सर्वेषां रक्षायाः उपायान् चिन्तमिष्यामि।
(मैं तो शीतल जल में बहुत देर तक अचल ध्यानमग्न हुआ स्थितप्रज्ञ की तरह बैठकर सभी की रक्षा के उपाय सोचूँगा।)
(ग) अन्ते प्रकृति माता प्रविश्य सर्वप्रथमं किं वदति?
(अन्त में प्रकृति माता प्रवेश करके सबसे पहले क्या कहती है?)
उत्तरम् :
भोः भोः प्राणिनः यूयं सर्वे एव मे सन्ततिः। कथं मिथः एव कलहं कुर्वन्ति । वस्तुतः सर्वे वन्यजीविनः अन्योन्याश्रिताः।
(अरे-अरे प्राणियो! तुम सब ही मेरी सन्तान हो। क्यों आपस में ही कलह करते हो। वास्तव में सभी वन्य जीव एक दूसरे पर आश्रित हैं।)
(घ) यदि राजा सम्यक् न भवति तदा प्रजा कथं विप्लवेत्?
(यदि राजा अच्छा न हो तो प्रजा कैसे डूब जाती है?)
उत्तरम् :
यदि राजा सम्यक् न भवति तदा प्रजा-जलधौ अकर्णधारा नौरिव विप्लवेत्।
(यदि राजा सही नहीं होता है तब प्रजा सागर में बिना नाविक की नौका की तरह डूब जाती है।)
(ङ) मयूरः कथं नृत्य मुद्रायां स्थितः भवति?
(मोर कैसे नृत्य मुद्रा में खड़ा होता है?)
उत्तरम् :
मयूरः पिच्छान् उद्घाट्य नृत्य मुद्रायां स्थितः भवति।
(मोर पंखों को उघाड़कर नृत्य की मुद्रा में खड़ा हो जाता है।)
(च) ‘अन्ते सर्वे मिलित्वा’ कस्य राज्याभिषेकस्य तत्पराः भवन्ति?
(अन्त में सभी मिलकर किसका राज्याभिषेक करने के लिए तत्पर होते हैं?)
उत्तरम :
अन्ते सर्वे मिलित्वा उलूकस्य राज्याभिषेकाय तत्पराः भवन्ति।
(अन्त में सभी मिलकर उल्लू का राज्याभिषेक करने के लिए तैयार हो जाते हैं।)

(छ) अस्मिन्नाटके कति पात्राणि सन्ति?
(इस नाटक में कितने पात्र हैं?)
उत्तरम् :
अस्मिन्नाटके द्वादश पात्राणि सन्ति।
(इस नाटक में बारह पात्र हैं।)
प्रश्न 3.
रेखाङ्कित पदमाधृत्य प्रश्न निर्माणं कुरुत –
(रेखांकित पद को आधार बनाकर प्रश्न निर्माण करो)
(क) सिंहः वानराभ्यां स्वरक्षायाम् असमर्थः एव आसीत्।
(ख) गजः पशून् तुदन्तं शुण्डेन पोथयित्वा मारयति।
(ग) वानरः आत्मानं वनराजपदाय योग्यः मन्यते।
(घ) मयूरस्य नृत्यं प्रकृतेः आराधना।
(ङ) सर्वे प्रकृति मातरम् प्रणमन्ति।
उत्तरम् :
(क) सिंह वानराभ्यां कस्याम् असमर्थः एवासीत् ?
(ख) गजः पशून् तुदन्तं केन पोथयित्वा मारयति?
(ग) वानरः आत्मानं कस्मै योग्यः मन्यते?
(घ) मयूरस्य नृत्यम् कस्याः आराधना?
(ङ) सर्वे काम् प्रणमन्ति?
प्रश्न 4.
शुद्ध कथनानां समक्षम् (आम्) अशुद्ध कथनानां च समक्षं (न) इति लिखत –
(शुद्ध कथनों के सामने (आम्) अशुद्ध कथनों के सामने (न) लिखिए)
(ख) का का इति वकस्य ध्वनिः भवति।
(क) सिंहः आत्मानं तुदन्तं वानरं मारयति।
(ग) काकपिकयोः वर्णः कृष्णः भवति।
(घ) गजः लघुकाय निर्बलश्च भवति ।
(ङ) मयूरः वक्रस्य कारणात् पक्षिकुलम् अवमानितं मन्यते।
(च) अन्योन्य सहयोगेन प्राणिनां लाभ: जायते।
उत्तरम् :
(ख) का का इति वकस्य ध्वनिः भवति। – (न)
(क) सिंहः आत्मानं तुदन्तं वानरं मारयति। – (न)
(ग) काकपिकयोः वर्णः कृष्णः भवति। – (आम्)
(घ) गजः लघुकाय निर्बलश्च भवति । – (नं)
(ङ) मयूरः वक्रस्य कारणात् पक्षिकुलम् अवमानितं मन्यते। – (आम्)
(च) अन्योन्य सहयोगेन प्राणिनां लाभ: जायते। – (आम्)

प्रश्न 5.
मञ्जूषातः समुचितं पदं चित्वा रिक्तस्थानानि पूरयत – (मञ्जूषा से उचित पद चुनकर रिक्तस्थान की पूर्ति कीजिए)
[स्थितप्रज्ञ, यथासमयम्, मेध्यामेध्य भक्षकः, अहिभुक्, आत्म श्लाघाहीनः, पिकः]
(क) काकः …………. भवति।
(ख) ………….. परभृत् अपि कथ्यते।
(ग) वकः अविचलं …………. इव तिष्ठति।
(घ) मयूरः …………. इति नाम्नाऽपि ज्ञायते।
(ङ) उलूकः …………. पदनिर्लिप्त चासीत्।
(च) सर्वेषामेव महत्वं विद्यते …………. ।
उत्तरम् :
(क) मेध्यामेध्य भक्षकः
(ख) पिकः
(ग) स्थितप्रज्ञः
(घ) अहिभुक्
(ङ) आत्मश्लाघाहीनः
(च) यथासमयम्
प्रश्न 6.
वाच्य परिवर्तनं कृत्वा लिखत (वाच्य परिवर्तन करके लिखिए)
उदाहरणम् : क्रुद्धः सिंहः इतस्ततः धावति गर्जति च।
क्रुद्धेन सिंहेन इतस्ततः धाव्यते गय॑ते च।
(क) त्वया सत्यं कथितम्।
(ख) सिंहः सर्वजन्तून् पृच्छति।
(ग) काकः पिकस्य सन्तति पालयति।।
(घ) मयूरः विधात्रा एव पक्षिराजः वनराजः वा कृतः।
(ङ) सर्वेः खगैः कोऽसि खगः एव वनराजः कर्तुमिष्यते स्म।
(च) सर्व मिलित्वा प्रकृति सौन्दर्याय प्रयत्न कुर्वन्तु।
उत्तरम् :
(क) त्व सत्यं अकथयः।
(ख) सिंहेन सर्वजन्तवः पृच्छ्यन्ते।
(ग) काकेन पिकस्य सन्ततिः पाल्यते।
(घ) मयूरं विधाता एव पक्षिराज वनराजं वा कृतवान्।
(ङ) सर्वे खगाः कमपि खगं एव वनराजं कर्तुम् इच्छन्ति स्म।
(च) सर्वैः मिलित्वा प्रकृति सौन्दर्याय प्रयत्नः कर्त्तव्य।

प्रश्न 7.
समास विग्रहं समस्तपदं वा लिखत (समासविग्रह या समास पद लिखिए)
(क) तुच्छ जीवैः…………।
(ख) वृक्षोपरि…………।
(ग) पक्षिणां सम्राट…………।
(घ) स्थिता प्रज्ञा यस्य सः………… ।
(ङ) अपूर्वम्…………।
(च) व्याघ्रचित्रको
उत्तरम् :
(क) तुच्छ: च असौ जीव तैः च
(ख) वृक्षस्य उपरि
(ग) पक्षिसम्राट
(घ) स्थित प्रज्ञः
(ङ) न पूर्वम्
(च) व्याघ्रः च चित्रकः च
JAC Class 10th Sanskrit सौहार्द प्रकृतेः शोभा Important Questions and Answers
शब्दार्थ चयनम् –
अधोलिखित वाक्येषु रेखांकित पदानां प्रसङ्गानुकूलम् उचितार्थ चित्वा लिखत –
प्रश्न 1.
वनस्य दृश्यं समीपे एवैका नदी वहति।
(अ) पार्वे
(ब) दूरे
(स) विश्राम्यते
(द) तदैव
उत्तरम् :
(अ) पार्वे
प्रश्न 2.
एवमेव वानराः वारं वारं सिंहं तुदन्ति।
(अ) बाढम्
(ब) अवसादयन्ति
(स) असमर्थः
(द) नेवास्ति
उत्तरम् :
(ब) अवसादयन्ति

प्रश्न 3.
निद्राभङ्गदुःखेन वनराजः सन्नपि तुच्छजीवैः।
(अ) तुच्छजीवैः
(ब) दुरवस्थया
(स) भवन्नपि
(द) किमर्थम्
उत्तरम् :
(स) भवन्नपि
प्रश्न 4.
वस्तुतः वनराजः भवितुं तु अहमेव योग्यः।
(अ) भवितुं तु
(ब) कृष्णवर्णः
(स) काकचेष्टः
(द) यथार्थतः
उत्तरम् :
(द) यथार्थतः
प्रश्न 5.
अलम् अलम् अतिविकत्थनेन।
(अ) प्रचुरम्
(ब) पिकः
(स) समीपतः
(द) श्रृण्वन्नेवादम्
उत्तरम् :
(अ) प्रचुरम्
प्रश्न 6.
भोः गजः मामप्येवमेवातुदन् एते वानराः।
(अ) लोमश
(ब) करिः
(स) सिंहः
(द) शृगालः
उत्तरम् :
(ब) करिः

प्रश्न 7.
अविचलः ध्यानमग्नः स्थितप्रज्ञ इव स्थित्वा।
(अ) विहाय
(ब) स्थित
(स) उपविष्य
(द) रक्षायाः
उत्तरम् :
(स) उपविष्य
प्रश्न 8.
अकर्णधारा जलधौ विप्लवेतेह नौरिव।
(अ) आत्मश्लाघायाः
(ब) ध्यानावस्थाम्
(स) अधिगृह्य
(द) सागरे
उत्तरम् :
(द) सागरे
प्रश्न 9.
अरे वानर! तूष्णीं भव।
(अ) मौनं
(ब) राज्याभिषेकाय
(स) वन्यजीवा
(द) सज्जाः भवन्तु
उत्तरम् :
(अ) मौनं

प्रश्न 10.
यतः मम नृत्यं तु प्रकृतेः आराधना।
(अ) मत्सदृशः
(ब) उपासना
(स) आक्रमणं कर्तारं
(घ) वनराजपदाय
उत्तरम् :
(ब) उपासना
संस्कृतमाध्यमेन प्रश्नोत्तराणि –
एकपदेन उत्तरत (एक शब्द में उत्तर दीजिए)
प्रश्न 1.
मयूरस्य किं प्रमुखं वैशिष्ट्यमस्ति?
(मयूर की प्रमुख विशेषता क्या है ?)
उत्तरम् :
नृत्यम् (नृत्ये)।
प्रश्न 2.
सर्वदा सम्यग्युक्तम् इति कस्मै कथितम्?
(सर्वथा सम्यग्युक्तम् यह किसके लिए कहा गया है?)
उत्तरम् :
सिंहाय (सिंह के लिए)।

प्रश्न 3.
सर्वे पक्षिणः एतयोः पदयोः विशेष्य पदं किम् ?
(सर्वे पक्षिणः इनमें विशेषण पद क्या है?)
उत्तरम् :
सर्वे (सभी)।
प्रश्न 4.
सदयम् पदस्य विलोमपदं लिखत।
(सदयम् पद का विलोमपद लिखिए।)
उत्तरम् :
क्रूरम् (निर्दयम्)।
प्रश्न 5.
प्राणिनां परस्पर विवादेन किम् जायते?
(प्राणियों के परस्पर विवाद करने से क्या होता है?
उत्तरम् :
हानिः (नुकसान)।
प्रश्न 6.
वने का वहति?
(वन में क्या बहती है?)
उत्तरम् :
नदी।
प्रश्न 7.
सिंहस्य कर्णं कः कर्षति?
(सिंह का कान कौन खींचता है।)
उत्तरम् :
वानरः।
प्रश्न 8.
वानराः बार-बार कम् तुदन्ति?
(वानर बार-बार किसे परेशान करते हैं?
उत्तरम् :
सिंहम्। (शेर को)।

प्रश्न 9.
धावन्तं सिंहं दृष्ट्वा वानराः किं कुर्वन्ति?
(दौड़ते हुए सिंह को देखकर वानर क्या करते हैं।)
उत्तरम् :
हसन्ति (हँसते हैं)।
प्रश्न 10.
सिंह केन श्रान्त ?
(सिंह किससे थक गया।)
उत्तरम् :
दुरवस्थया (दुर्दशा से)।
प्रश्न 11.
कीदृशां नृपः कृतान्तः इति कथ्यते?
(कैसा राजा यमराज कहलाता है?)
उत्तरम् :
यः त्रस्तान् पीडितान् च न रक्षति सः नृपः कृतान्तः कथ्यते।
(जो डरे और पीड़ितों की रक्षा नहीं करता, वह राजा यमराज है।)
प्रश्न 12.
‘सत्यं कथितं त्वया’ इति कस्य वाक्यम्।
(‘सत्यं कथितं त्वया’ पद किसका वचन है।)
उत्तरम् :
काकस्य (कौवा का)।

प्रश्न 13.
काके पिकं च किं साम्यम्?
(कौवा और कोयल में क्य समानता है?)
उत्तरम् :
कृष्णत्वम् (कालापन)।
प्रश्न 14.
अतिविकत्थनं कः करोति?
(अधिक आत्मश्लाघा कौन करता है?)
उत्तरम् :
काक :(कौवा)।
प्रश्न 15.
गजस्य पुच्छं कः आकृषय?
(हाथी की पूँछ कौन खींचता है?)
उत्तरम् :
वानरः (बन्दर)।
प्रश्न 16.
गजः कीदृशः अस्ति? (हाथी कैसा है?)
उत्तरम् :
गजः विशालकायः पराक्रमी भयकरश्च अस्ति।
(हाथी विशाल शरीर वाला, पराक्रमी और भय पैदा करने वाला है।)
प्रश्न 17.
वकः बहुकाल पर्यन्तं कुत्र वसति?
(बगुला बहुत समय तक कहाँ रहता है?)
उत्तरम् :
शीतलजले (ठंडे पानी में)।

प्रश्न 18.
स्थितप्रज्ञः इव कः ध्यानमग्नः तिष्ठति?
(स्थित प्रज्ञ की तरह कौन ध्यानमग्न होकर बैठता है?)
उत्तरम् : वकः (बगुला)।
प्रश्न 19.
कीदृशः नेता भवेत्? (कैसा नेता होना चाहिए?)
उत्तरम् :
सम्यक् (उत्तम)।
प्रश्न 20.
कीदृशी नौ जलधौ विप्लवेत?
(कैसी नौका सागर में डूब जाती है?)
उत्तरम् :
अकर्णधारा (बिना नाविक की)।
प्रश्न 21.
‘अरे वानर तूष्णी भव’ इति कः कथयति? (यह कौन कहता है?)
उत्तरम् :
मयूरः (मोर)।
प्रश्न 22.
मयूरस्य स्थाने सव्यङ्ग्यम् किम् पदं प्रयुक्तम्?
(मोर के स्थान पर व्यङ्ग्यसहित किस पद का प्रयोग किया है?
उत्तरम् :
अहिभुक् (सर्पभोजी)।
प्रश्न 23.
मयूरस्य नृत्यं कस्याः आराधना?
(मोर का नृत्य किसकी कृपा से है?)
उत्तरम् :
प्रकृतेः (प्रकृति की)।

प्रश्न 24.
व्याघ्रचित्रको कस्मात् आगतौ?
(बाघ और चीता किसलिए आये थे?)
उत्तरम् :
जलं पातुम् (जल पीने)
प्रश्न 25.
व्याघ्र चित्रको क इव भक्षको।
(बाघ और चीता किसके समान भक्षक हैं?)
उत्तरम् :
सिंह सदृशौ (सिंह के समान)।
प्रश्न 26.
सर्वसम्मत्या कः राजा भवेत?
(सर्व सम्मति से कौन राजा होना चाहिए?)
उत्तरम् :
कोऽपि खगः (कोई पक्षी)।
प्रश्न 27.
पूर्ण दिनं निद्रायमाणः कः तिष्ठति?
(पूरे दिन कौन सोता रहता है?)
उत्तरम् :
उलूकः (उल्लू)।
प्रश्न 28.
खगपशून कलहमानान् अवलोक्य कः प्रविशति?
(पशु-पक्षियों को कलह करते हुओं को देखकर कौन प्रवेश करती है?)
उत्तरम् :
प्रकृतिमाता।

प्रश्न 29.
वन्य प्राणिनः कस्य सन्ततिः ?
(वन्य प्राणी किस की सन्तति हैं ?)
उत्तरम् :
प्रकृतिमातुः (प्रकृति माता की)।
प्रश्न 30.
वन्य जीवानां किम् आश्रयः
(वन्य जीवों का आश्रय क्या है?)
उत्तरम् :
अन्योन्याश्रयः
(एक दूसरे का आश्रय है)।
प्रश्न 31.
अस्माकं सर्वेषां जननी का?
(हम सब की जननी कौन है?)
उत्तरम् :
प्रकृति (निसर्ग)।
प्रश्न 32.
राज्ञः सुखं कस्मिन्?
(राजा का सुख किसमें है?)
उत्तरम् :
प्रजासुखे (प्रजा के सुख में)।
प्रश्न 33.
अगाध जल सञ्चारी अपि को न गवं याति?
(गहरे पानी में विचरण करती हुई कौन नहीं गर्व करती है?)
उत्तरम् :
रोहितः (लोहित मछली)।
पूर्णवाक्येन उत्तरत (पूरे वाक्य में उत्तर दीजिए)
प्रश्न 34.
प्राणिनां लाभः कदा भवति?
(प्राणियों का लाभ कब होता है?)
उत्तरम् :
अन्योन्य सहयोगेन प्राणिनां लाभ: जायते।
(अन्योन्य सहयोग से प्राणियों को लाभ होता है।)

प्रश्न 35.
सुप्ते सिहे वानरः किमकरोत् ?
(सिंह के सो जाने पर वानर ने क्या किया।)
उत्तरम :
सुप्ते सिंहे वानरः तस्य पुच्छ धुनोति स्म।
(सिंह के सो जाने पर वानर ने उसकी पूँछ हिलाई।)
प्रश्न 36.
खगाः सिंहस्य दशां दृष्ट्वा किं कुर्वन्ति?
(पक्षी सिंह की दशा को देखकर क्या करते हैं?)
उत्तरम् :
खगाः सिंहस्य एवं दशां दृष्ट्वा हर्षमिश्रितं कलरवं कुर्वन्ति।
(पक्षी सिंह की ऐसी दशा देखकर हर्षमिश्रित कलरव करते हैं।)
प्रश्न 37.
‘पिकः’ परभृत् कस्मात् कथ्यते?
(पिक परभृत् क्यों कहलाती है?)
उत्तरम् :
परैः काकैः ध्रियते अतः परभृत् कथ्यते।
(दूसरों अर्थात् कौवों के द्वारा पाली जाती है अतः परभृत् कहलाती है।)
प्रश्न 38.
वकः आगत्य किं कथयति?
(बगुला आकर क्या कहता है?)
उत्तरम् :
मां विहाय कथमन्यः कोऽपि राजा भवितुमर्हति?
(मुझे छोड़कर कौन दूसरा राजा हो सकता है?)

प्रश्न 39.
वकः स्थितप्रज्ञ व्याजेन किं करोति? (बगुला स्थितप्रज्ञ के बहाने क्या करता है?)
उत्तरम् :
वकः ध्यानमग्न स्थितप्रज्ञ इति व्याजेन बराकान् मीनान् छलेन अधिगृह्य क्रूरतया भक्षयति।
(बगुला ध्यानमग्न स्थितप्रज्ञ के बहाने बेचारी मछलियों को धोखे से पकड़कर क्रूरता के साथ खा जाता है।)
प्रश्न 40.
मयूरः वन्य पशून् कस्यहेतोः सज्जयितुं कथयति?
(मोर वन्य जीवों से किसके लिए तैयार होने के लिए कहता है?)
उत्तरम् :
वने निवसन्तं माम् वनराजरूपेण द्रष्टुं सज्जाः भवन्तु।
(वन में रहने वाले मुझे वनराज के रूप में देखने के लिए तैयार हो जाइये।)
प्रश्न 41.
मयूरस्य का गर्वोक्ति आसीत्? (मोर की क्या गर्वोक्ति थी?)
उत्तरम् :
न कोऽपि त्रैलोक्ये मत्सदृशः सुन्दरः।
(तीनों लोकों में मेरा जैसा कोई सुन्दर नहीं।)
प्रश्न 42.
सर्वे पक्षिणः कं राज्यासने स्थापयितुमिच्छन्ति।
(सभी लोग किसको राजा के आसन पर बैठाना चाहते हैं।)
उत्तरम् :
सर्वे खगाः कमपि खगमेव राज्यासने स्थापयितुमिच्छन्ति।
(सभी पक्षी किसी पक्षी को ही राज्यासन पर स्थापित करना चाहते हैं।)
प्रश्न 43.
उलूकः रक्षणे कस्मात् अयोग्य आसीत्?
(उल्लू रक्षण में किसलिए अयोग्य था?)
उत्तरम् :
पूर्ण दिने यावत् निद्रायमाणः कथं अस्मान् रक्षिष्यति इति विचार्य काकेन अयोग्यः घोषितः।
(पूरे दिन सोता रहता है, हमारी रक्षा कैसे करेगा, ऐसा विचार कर कौवे ने अयोग्य घोषित कर दिया।)

प्रश्न 44.
प्रीते किं लक्षणम्? (प्रीति का क्या लक्षण है?)
उत्तरम् :
ददाति आददाति गुह्यमाख्याति, पृच्छति भुङ्कते भोजयते च इति षड्विध प्रीते: लक्षणम्।
(देता है, लेता है, गुप्त बात को बताता है, पूछता है, खाता है, खिलाता है, यह छः प्रकार के प्रीति के लक्षण हैं।)
प्रश्न 45.
जीवनं कथं यापयेत? (जीवनयापन कैसे करना चाहिए?)
उत्तरम् :
सर्वे मिलित्वा एव मोदयेयुः जीवनं च रसमयं कुर्युः।
(सभी को मिलकर प्रसन्न रहना चाहिए. तथा जीवन को मधुर बनाना चाहिए।)
प्रश्न 46.
सिंहः किं करोति स्म? (सिंह क्या कर रहा था?
उत्तरम् :
सिंह सुखेन विश्राम्यते स्म। (सिंह आराम से विश्राम कर रहा था।)
प्रश्न 47.
क्रुद्धः सिंहः किं करोति? (नाराज शेर क्या करता है?)
उत्तरम् :
क्रुद्धः सिंहः इतस्ततः धावति गर्जति परं किमपि कर्तुमसमर्थः एव तिष्ठति।
(नाराज सिंह इधर-उधर दौड़ता है, दहाड़ता है लेकिन कुछ भी करने में असमर्थ खड़ा रहता है।)
प्रश्न 48.
क्रोधेन गर्जन सिंहः जन्तून दृष्ट्वा किमवदत्।
(क्रोध से दहाड़ते हुए सिंह ने जन्तुओं को देखकर क्या कहा?)
प्रश्न 49.
काकस्य सत्यप्रियता केन उदाहरणेन व्यज्यते?
(काक की सत्यप्रियता किस वाक्य से व्यक्त की जाती है?)
उत्तरम् :
अनृतं वदसि चेत काकः दशेत् (झूठ बोले कौवा काटे)।

प्रश्न 50.
काक-पिकयोः भेदः कदा ज्ञायेत?
(कौवा और कोयल का भेद कब ज्ञात होता है?)
उत्तरम् :
वसन्त काले प्राप्ते काक-पिकयोः भेदः ज्ञायते।
(बसन्त काल के आने पर कौवा और कोयल का भेद ज्ञात होता है।)
प्रश्न 51.
वानरे वृक्षमारूढे गजः किं करोति?
(वानर के पेड़ पर चढ़ जाने पर हाथी क्या करता है?)
उत्तरम् :
गजः तम् वृक्षम् एव स्वशुण्डेनालोडयति।
(हाथी उस वृक्ष को अपनी सँड़ से ही हिला देता है।)
प्रश्न 52.
वकः कैः सह मिलित्वा रक्षोपायान् करिष्यति?
(बगुला किनके साथ मिलकर रक्षा के उपाय करेगा?)
उत्तरम् :
जन्तुभिः सह मिलित्वा रक्षोपायान् कारयिष्यति।
(जन्तुओं के साथ मिलकर रक्षा के उपाय करायेगा।)
प्रश्न 53.
मयूरः कुतः साट्टहासपूर्वकमवदत्?
(मोर कहाँ से अट्टहासपूर्वक बोला?)
उत्तरम् :
मयूरः वृक्षस्य उपरितः साट्टहासपूर्वकमवदत्।
(मोर वृक्ष के ऊपर से हास्यपूर्वक बोला।)

प्रश्न 54.
वानरः किं कर्तुं कथयति? (वानर क्या करने के लिए कहता है?)
उत्तरम् :
शीघ्रमेव मम राज्याभिषेकाय तत्परा भवन्तु सर्वे वन्यजीवा।
(शीघ्र ही मेरे राज्याभिषेक के लिए सभी वन्यजीव तैयार हो जाएँ।)
प्रश्न 55.
मयूरः कथं केन वा पक्षिराजः नियुक्तः?
(मोर कैसे और किसके द्वारा पक्षिराज नियुक्त किया गया?
उत्तरम् :
विधात्रा शिरसि राज मुकुटमिव शिखां स्थापयता एव अहम् पक्षिराजः कृतः।
(विधाता द्वारा शिर पर राजमुकुट की तरह चोटी स्थापित करके मुझे पक्षिराज बनाया गया।)
प्रश्न 56.
वन्यजीवाः कं रक्षकपद योग्यं न मन्यन्ते।
(वन्य जीव किसे रक्षक के पद के योग्य नहीं समझते हैं।)
उत्तरम् :
वन्यजीवाः कमपि भक्षकं रक्षकपद योग्यं न मन्यन्ते।
(वन के जीव किसी भक्षक को रक्षक पद के योग्य नहीं समझते।)
प्रश्न 57.
किं वैशिष्ठ्यमवलोक्य खगाः उलूकं वनराज पदाय अचिन्वन्?
(किस विशेषता को देखकर पक्षियों ने उल्लू को वनराज पद के लिए चुना है?)
उत्तरम् :
आत्मश्लाघाहीनत्वं पदनिर्लिप्त चावलोक्य उलूकम् वनराजपदाय अचिन्वन्।
(आत्मप्रशंसा से हीन, पद निर्लिप्त उल्लू को देखकर उसे वनराज पद के लिए चुना।)

प्रश्न 58.
काकेन उलूकस्य अवगुणाः कथं वर्णिताः ?
(कौवे ने उल्लू के अवगुणों का कैसे वर्णन किया है?)
उत्तरम् :
उलूकः स्वभावेन रौद्रः, अत्युग्रः क्रूरः, अप्रियवादी च भवति दिवान्ध पूर्णं दिनं यावत् स्वपिति।
(उल्लू स्वभाव से क्रोधी, अति उग्र, क्रूर और अप्रिय भाजी होता है। दिवान्ध वह पूरे दिन सोता रहता है।)
प्रश्न 59.
अस्माकं सर्वेषां कस्मै महत्वं यथाकालम्?
(हम सबका किसके लिए महत्व है?)
उत्तरम् :
अस्माकं सर्वेषां यथासमयं प्रकृत्यै महत्वं विद्यते।
(हम सबका प्रकृति के लिए महत्व है।)
प्रश्न 60.
शफरी कथम् आत्मनः गर्वं दर्शयति?
(शफरी कैसे अपने गर्व को प्रदर्शित करती है?)
उत्तरम् :
अङ्गुष्ठ मात्र जले अपि विचरन्ती शफरी फुफ़रायते।
(अँगूठे के बराबर जल में विचरण करती हुई शफरी फरफराती है।)
अन्वय-लेखनम् –
अधोलिखितश्लोकस्यान्वयमाश्रित्य रिक्तस्थानानि मञ्जूषातः समुचितपदानि चित्वा पूरयत।
(नीचे लिखे श्लोक के अन्वय के आधार पर रिक्तस्थानों की पूर्ति मंजूषा से उचित पद चुनकर कीजिए ।)
1. यो न रक्षति ………………………. न संशयः॥
मञ्जूषा – वित्रस्तान्, रक्षति, कृतान्त, पार्थिवरूपेण।
यः सदा (i)…….. परैः पीड्यमानान् (ii)……. जन्तून् न (iii)…….., सः (iv)……., न संशयः।
उत्तरम् :
(i) पार्थिवरूपेण, (ii) वित्रस्तान्, (iii) रक्षति, (iv) कृतान्तः।

2. यदि न स्यान्नरपतिः ………………………………….. विप्लवेतेह नौरिव।।
मञ्जूषा – जलधौ, नरपतिः, नेता, अकर्णधारा।
यदि (i)…….. सम्यक् (ii)…….. न स्यात्, ततः इह प्रजा (iii)…….. नौः इव (iv)…….. विप्लवेत्।
उत्तरम् :
(i) नरपतिः, (ii) नेता, (iii) अकर्णधारा, (iv) जलधौ।
3. स्वभावरौद्रमत्युग्रं ………………………….. सिद्धिर्भविष्यति।।
मञ्जूषा – सिद्धिः, नृपतिं, अप्रियवादिनम्, अत्युग्रम।
स्वभावरौद्रम् (i)……..क्रूरम् (ii)……..(च) उलूकं (iii)…….. कृत्वा नु का (iv)…….. भविष्यति।
उत्तरम् :
(i) अत्युग्रम् (ii) अप्रियवादिनम् (iii) नृपतिं (iv) सिद्धिः ।।
4. ददाति प्रतिगृह्णाति ……….. …………………… प्रीतिलक्षणम्।।
मञ्जूषा – योजयते, षड्विधम्, आख्याति, प्रतिगृह्णाति।
ददाति (i)…….. गुह्यम् (ii)…….., पृच्छति, भक्ते (iii)…….. च, प्रीतिलक्षणं (iv)……. एव (भवति)।
उत्तरम् :
(i) प्रतिगृह्णाति (ii) आख्याति (iii) योजयते (iv) षड्विधम्।
5. अगाधजलसञ्चारी …………… …………………. फुफुरायते।।
मञ्जूषा – याति, मात्रेण, फुफुरायते, रोहितः।
अगाधजलसञ्चारी (i)……. गर्वं न (ii)…….. । अङ्गुष्ठोदक (iii)……. शफरी (iv)……..।
उत्तरम् :
(i) रोहितः (ii) याति, (iii) मात्रेण (iv) फुफुरायते।

6. प्राणिनां जायते …………………………… प्रजायते।।
मञ्जूषा – लाभः, विवादतः, हानिः, सहयोगेन।
परस्पर (i)…….. प्राणिनां (ii)…….. जायते। अन्योन्य (iii)…….. तेषां (iv)……..प्रजायते। उत्तरम् : (i) विवादतः (ii) हानिः (ii) सहयोगेन (iv) लाभः।
प्रश्ननिर्माणम् –
अधोलिखित वाक्येषु स्थूलपदमाधृत्य प्रश्ननिर्माणं कुरुत –
1. समीपे एव एका नदी बहति। (पास ही एक नदी बहती है।)
2. वानरः आगत्य तस्य पुच्छ धुनाति। (वानर आकर उसकी पूँछ खींचता है।)
3. वानरस्तु कूर्दित्वा वृक्षमारूढः। (वानर कूदकर वृक्ष पर चढ़ गया।)
4. क्रुद्ध सिंहः इतस्ततः धावति। (कुद्ध सिंह इधर-उधर दौड़ता है।)
5. वानराः हसन्ति वृक्षोपरि। (वानर वृक्ष के ऊपर हँसते हैं।)
6. श्रान्तः सर्वजन्तून् दृष्ट्वा पृच्छति। (थके हुए सभी जन्तुओं को देखकर पूछता है।)
7. राजा तु रक्षकः भवति। (राजा तो रक्षक होता है।)
8. अनृतं वदसि चेत् काकः दशेत्। (झूठ बोले कौवा खाये)
9. अस्माकं एक्यं विश्व प्रथितम्। (हमारी एकता विश्व प्रसिद्ध है।)
10. सर्वं सम्भाषणं शृण्वन्नेवाहम् अत्रागच्छम्। (सारी बात सुनकर ही मैं यहाँ आ गया हूँ।)
उत्तराणि :
1. समीपे एव का बहति?
2. वानरः आगत्य तस्य किम् धुनाति?
3. वानरस्तु कूर्दित्वा कम् आरूढ़ ?
4. क्रुद्धः सिंहः कुत्र धावति?
5. वानरः वृक्षोपरि किं कुर्वन्ति?
6. श्रान्तः कान् दृष्ट्वा पृच्छति?
7. राजा तु कीदृशः भवति?
8. अनृत वदसि चेत् कः दशेत् ?
9. अस्माकं किम् विश्व प्रथितम् ?
10. सर्व किं कुर्वन्नेव अहम् अत्र आगच्छम्।
भावार्थ-लेखनम् –
अधोलिखित पद्यांश संस्कृते भावार्थ लिखत –
(i) यो न रक्षति …………………………… कृतान्तो न संशयः।।
भावार्थ – अन्यः वानरः कथयति-अपि नाकर्णिता भवता पञ्चतन्त्रस्य सूक्तिः? ‘यो भयभीतान् भयानि वा पीड्यानान् सर्वदा शत्रुभिः प्राणिनः न त्रायते सः राज्ञः रूपेण यमराज एव इति नात्र शङ्का।
(ii) काकः कृष्णः ……………………………. पिकः पिकः।।
भावार्थ – वायसः श्याम, कोकिलोऽपि श्यामः भवति, वायस कोकिलयोः किमन्तरम् परञ्च मधुमासे तु वायसः वायस रूपेण ज्ञायते यावत कोकिलः कोकिलः इव ज्ञायते।

(iii) यदि न ……………………………… नौरिव।।
भावार्थ – यत् यदि श्रेष्ठः नृपः नायकः च न भवति तदा प्रजाः प्रकृत्यः वाः सागरे नाविक विहीन तरणी व निमज्जति।
(iv) स्वभावरौद्रमत्युग्रं ……………………… सिद्धिर्भवष्यिति।।
भावार्थ – यथार्थतः तु प्रकृत्या कोपान्वितं महत्प्रचण्ड जिम कटुवक्तार उलूकं नृपतिं विधाय किं साध्यं सिद्धं भविष्यति।
(v) ‘ददाति …………………………………. प्रीतिलक्षणम्।।
भावार्थ – प्रकृति माता कथयति-सर्वदा स्मरणं कुरुत-यच्छति, आददाति, गुप्तं, कथयति, प्रश्नयति, खादति, खादयति इति प्रीत्या षड्विध लक्षणम्।
(vi) प्रजासुखे ……………………… प्रियं हितम्।।
भावार्थ – यदि प्रजा प्रकृति वा सुखी भवति तदैव नृपस्य प्रसन्नता भवति प्रजाजनानां लाभस्य कार्ये एव शासकस्य लाभ: यः नृपः स्वार्थ प्रियः भवति नैतत् शासकस्य हितम्। प्रजाजनानां हितं करणमेव सर्वप्रियं हितं भवति।
(vii) अगाध जल सञ्चारी ……………….. फुफुरायते।।
भावार्थ – अति गहने जले विचरन्ती विशालो मृगमीनः नाभिमानं करोति परन्तु वृद्धाङ्गुली मात्र जलेऽपि शफरीति लघु मत्स्यः गर्वेण उद्विग्नो भवति।।
(viii) प्राणिनां जायते ……………………… प्रजायते।।
भावार्थ – मिथः कलहात् जीवानं क्षयमेव भवति परञ्च परस्पर सहयोगे अमीषां लाभः एव भवति।
सौहार्द प्रकृतेः शोभा Summary and Translation in Hindi
पाठ-परिचय – यह पाठ परस्पर स्नेह एवं मैत्री भाव से पूर्ण व्यवहार हो, इसका बोध कराता है। अब हम देख रहे हैं कि समाज में लोग आत्माभिमानी हो गये, वे आपस में तिरस्कार करते हैं। स्वार्थपूर्ति में लगे हुए वे दूसरों के कल्याण के विषय में कुछ भी नहीं सोचते हैं। उनके जीवन का उद्देश्य अब यह हो गया है- नीच, उच्च और अति नीच उपायों से फल ही सिद्ध होना चाहिए।
अतः समाज में आपस में स्नेह की वृद्धि के लिए इस पाठ में पशु-पक्षियों के माध्यम से समाज में व्यवहार किया हुआ, आत्मसम्मान दिखाते हुये प्रकृति माता के माध्यम से अन्त में निष्कर्ष स्थापित किया कि समय पर सभी का महत्व होता है, सभी एक-दूसरे पर आश्रित हैं अतः हमें अपने कल्याण के लिए आपस में प्रेम और मैत्रीपूर्ण व्यवहार से रहना चाहिए।

मूलपाठः,शब्दार्थाः, सप्रसंग हिन्दी-अनुवादः
1. वनस्य दृश्यं समीपे एवैका नदी वहति। एकः सिंहः विश्राम्यते तदैव एकः वानरः आगत्य तस्य पुच्छं धुनाति। क्रुद्धः सिंहः तं प्रहर्तुमिच्छति परं वानरस्तु कूर्दित्वा वृक्षमारूढः। तदैव अन्यस्मात् वृक्षात् अपरः वानरः सिंहस्य कर्णमाकृष्य पुनः वृक्षोपरि आरोहति।
शब्दार्थाः – वनस्य = अरण्यस्य (जंगल का)। दृश्य = दर्शनीयं चित्रणम् (दृश्य), समीपे = पार्वे (पास में), एवैका = एव एका (ही एक), नदी = सरित् (नदी), वहति = प्रवहति (बह रही है)। एकः सिंह = एक: केसरी (एक शेर), सुखेन = सुखपूर्वकं, विश्राम्यते = विश्रामं करोति। (विश्राम करता है)। तदैव = तत्कालमेव (तभी), एकः वानरः = मर्कटः (एक बन्दर), आगत्य = आगम्य, प्राप्य (आकर) तस्य = अमुष्य (उसकी)। पुच्छ = लांगूलं (पूंछ), धुनोति = गृहीत्वा आन्दोलयति, चालयति (हिलाता है), क्रुद्धः = कुपितः (नाराज)। सिंह = हरिः, केसरी (शेर) तम् = अमुम् (उस पर) प्रहर्तुमिच्छति = आघातं कर्तुम् ईहते = (चोट करना चाहता है)। परं = परञ्च (लेकिन) वानरस्तु = कपिः तु (बन्दर तो) कुर्दित्वा = उत्प्लुत्य (उछलकर), वृक्षमारूढ़ = तरोः उपरि आरुरोह (वृक्ष के ऊपर चढ़ गया) तदैव = तत्कालमेव (उसी समय तभी), अन्यस्मात् = अपस्मात्), वृक्षात् = तरोः (वृक्ष से), अपरः अन्यः (दूसरा), वानरः कपिः (बन्दर), सिंहस्यकेसरिणः (शेर से), कर्णम्-श्रोत्रम् (कान को), आकृष्य-कर्षयित्वा (खींचकर), पुनः = भूयः (फिर), वृक्षोपरि-तरोः उपरि (पेड़ पर), आरोहति आरूढ़ भवति।
सन्दर्भ-प्रसङ्गश्च – यह गद्यांश हमारी पाठ्यपुस्तक शेमुषी के ‘सौहार्द प्रकृतेः शोभा’ पाठ से लिया गया है। इस गद्यांश में वन्य पशुओं की परस्पर मैत्रीपूर्ण क्रीडा का वर्णन किया गया है।
हिन्दी अनुवादः – जंगल का दृश्य है। पास में ही एक नदी बह रही है। एक शेर आराम से विश्राम कर रहा है। तभी एक वानर आकर उसकी पूँछ हिलाता (मरोड़ता) है। नाराज हुआ शेर उस पर प्रहार करना चाहता है परन्तु बन्दर तो उछलकर पेड़ पर चढ़ जाता है। तभी दूसरे पेड़ से दूसरा बन्दर सिंह के कान को खींचकर वृक्ष पर चढ़ जाता है।
2. एवमेव वानराः वारं वारं सिंहं तुदन्ति। क्रुद्धः सिंहः इतस्ततः धावति, गर्जति परं किमपि कर्तुमसमर्थः एव तिष्ठति। वानराः हसन्ति वृक्षोपरि च विविधाः पक्षिणः अपि सिंहस्य एतादृशी दशां दृष्ट्वा हर्षमिश्रितं कलरवं कुर्वन्ति।
शब्दार्था: – एवमेव = अनेन प्रकारेण एव (इस प्रक्रम से ही), वानराः = मर्कट (बन्दर), बारंबारम् = मुहुर्मुहुः (बार-बार), सिंहम् = केसरिणं (शेर को), तुदन्ति = अवसादयन्ति (तंग करते हैं), क्रुद्धः सिंहः = प्रकुपितः केसरी (नाराज शेर), इतस्ततः = अत्र-तत्र (इधर-उधर), धावति = पलायते (दौड़ गये), गर्जति = नदति (दहाड़ता है), परं = परन्तु (लेकिन), किमपि = किञ्चिदपि (कुछ भी) कर्तुम् = विधातुम् (करने में), असमर्थ: अक्षमः (असमर्थ), एवास्ति = एव वर्तते (ही है), वानरा: = कपयः (बन्दर), हसन्ति = हासं/उपहासं वा कुर्वन्ति (हँसी उड़ाते हैं) वृक्षोपरि = तरोः उपरि (पेड़ पर), च = तथा (और), विविधा = अनेक प्रकार का (विभिन्न प्रकार के), पक्षिण: = खगाः (पक्षी), अपि सिंहस्य = अपि केसरिणः (शेर के भी), एतादृशी = ईदृशी (इस प्रकार की), दशाम् = स्थितिम् (हालत को), दृष्ट्वा = अवलोक्य (देखकर) हर्षमिश्रितं = आह्लादयुतं (खुशी से युक्त) कलरवम् = कूजनम् (कलरव), कुर्वन्ति = विदधति (करते हैं)।
सन्दर्भ-प्रसङ्गश्च – यह गद्यांश हमारी पाठ्यपुस्तक ‘शेमुषी’ के ‘सौहार्दै प्रकृतेः शोभा’ पाठ से लिया गया है। इस गद्यांश में सिंह के साथ बन्दरों की क्रीड़ा का वर्णन है।
हिन्दी अनुवादः – इस प्रकार बन्दर बार-बार सिंह को परेशान करते हैं। नाराज हुआ सिंह इधर-उधर दौड़ता है, दहाड़ता है। परन्तु कुछ भी करने में असमर्थ है। वानर हँसते हैं और वृक्ष के ऊपर विविध प्रकार के पक्षी भी सिंह की ऐसी स्थिति देखकर प्रसन्नता से मिला कलरव करते हैं।

3. निद्राभङ्गदुःखेन वनराजः सन्नपि तुच्छजीवैः आत्मनः एतादृश्या दुरवस्थया श्रान्तः सर्वजन्तून् दृष्ट्वा पृच्छति –
सिंहः – (क्रोधेन गर्जन) भोः ! अहं वनराजः किं भयं न जायते? किमर्थं मामेवं तुदन्ति सर्वे मिलित्वा?
एकः वानरः – यतः त्वं वनराजः भवितुं तु सर्वथाऽयोग्यः। राजा तु रक्षकः भवति परं भवान् तु भक्षकः। अपि च स्वरक्षायामपि समर्थः नासि तर्हि कथमस्मान् रक्षिष्यसि?
अन्यः वानरः – किं न श्रुता त्वया पञ्चतन्त्रोक्तिः
यो न रक्षति वित्रस्तान् पीड्यमानान्परैः सदा।
जन्तून् पार्थिवरूपेण स कृतान्तो न संशयः।।
शब्दार्थाः – निद्रा = सुप्ति (नींद), भङ = विच्छेद (टूटा), दुःखेन = क्लेशेन, कष्टेन (दुःख से), वनराज: = मृगराजः (सिंह), सन्नपि = भवन्नपि (होते हुए भी), तुच्छजीवैः = लघु प्राणिभिः (छोटे जीवों द्वारा), आत्मनः = स्वकीय (अपना), एतादृश्या = ईदृश्या (इस प्रकार की), दुरवस्थया = दुर्दशया (बुरी स्थिति से), श्रान्तः = श्रमार्तः, क्लांत: (थका हुआ), सर्वजन्तून सर्वान् प्राणिनः (सभी प्राणियों को), दृष्ट्वा अवलोक्य, वीक्ष्य (देखकर), पृच्छति = पृच्छां करोति, प्रश्नयति (पूछता है) क्रोधेन कोपेन (नाराजी से) गर्जन्नादयन् (दहाड़ते हुए), भोः = ओ (अरे) अहं वनराज: अहं मृगराजः (मैं वन का राजा), किं भयं न जायते = अपि भीतिः न भवति (क्या डर नहीं होता) किमर्थम् कस्मात् (क्यों) मामेवमा एव (मुझको ही), सर्वे = मिलित्वा तुदन्ति = सर्वे सम्भूय अवसादयन्ति (सब मिलकर कष्ट दे रहे हो), यतः यस्मात (क्योंकि), त्वम् भवान् (आप),
वनराज = मृगराजः (वन का राजा), भवितु तु = आप्तुम् (होने के), सर्वथाऽयोग्यः = पूर्णतः अक्षमः (पूरी तरह असमर्थ हो), राजा = शासकः, नृपः (राजा), रक्षकःत्राता (रक्षा करने वाला) भवति (होता है), परम्परञ्च (लेकिन), भवान् = तु-त्वं तु (तुम तो) भक्षक: = भोक्ता (खाने वाले), अपि च किं च (और क्या), स्वरक्षायामपिआत्मानं त्रातुमपि (रक्षा करने में), समर्थः = सक्षमः (समर्थ), तदा तर्हि (तो) कथम् केन प्रकारेण (किस प्रकार), रक्षिष्यति = त्रास्यते (रक्षा करेंगे), किं न श्रुता त्वया = अपि भवता न श्रुतं (क्या आपने सुना नहीं), पञ्चतन्त्रोक्तिः पञ्चतन्त्र कथा = ग्रन्थस्य सूक्तय (पञ्चतंत्र की यह युक्ति), श्रुत = आकर्णिता (सुनी), यः न रक्षति वित्रस्तान = यः भयार्तान् न त्रायते (जो भयभीत लोगों की रक्षा नहीं करता), पीड्यमानान्परैः = अन्यैः तुदन्तः (दूसरों से पीड़ित लोगों को), जन्तून = प्राणिना (जीवों को), पार्थिव रूपेण = राज्ञः रूपेण (राजा के रूप में), सः = असौ (यह), न संशयः नि:संदेहः (निःसन्देह), कृतान्तः = यमराजः (यमराज है)।
सन्दर्भ-प्रसङ्गश्च – यह गद्यांश हमारी पाठ्यपुस्तक ‘शेमुषी’ के ‘सौहार्द प्रकृतेः शोभा’ पाठ से लिया गया है। इस गद्यांश में बन्दर सिंह की उपेक्षा करते हुए स्वयं को वनराज के पद के योग्य प्रतिपादित करते हैं।
हिन्दी अनुवादः – नींद टूटने के दुःख से वन का राजा होते हुए भी तुच्छ जीवों द्वारा स्वयं को दुर्दशा से थका हुआ, सभी जन्तुओं को देखकर पूछता है।
सिंह – (क्रोध से दहाड़ता हुआ) अरे! मैं वन का राजा हूँ, तुम्हें डर नहीं लगता। तुम किसलिए मुझे इस प्रकार सब मिलकर परेशान कर रहे हो?
एक वानर – क्योंकि तुम वनराज होने के पूर्णतः अयोग्य हो। राजा तो रक्षक होता है परन्तु आप तो भक्षक हैं और तो और अपनी रक्षा करने में भी समर्थ नहीं हो तो हमारी रक्षा कैसे करेंगे?
अन्य वानर – क्या तुमने पंचतंत्र का कथन नहीं सुना-जो विशेष रूप से डरे हुओं और पीड़ित होते हुए दूसरे प्राणियों की रक्षा नहीं करता, वह निःसंदेह राजा के रूप में यमराज है।

4. काकः – आम् सत्यं कथितं त्वया-वस्तुतः वनराजः भवितुं तु अहमेव योग्यः।
पिकः – (उपहसन्) कथं त्वं योग्यः वनराजः भवितुं, यत्र तत्र का का-इति कर्कशध्वनिना वातावरणमाकुलीकरोषि। न रूपम्, न ध्वनिरस्ति कृष्णवर्णम् मेध्यामध्यभक्षकं त्वां कथं वनराजं मन्यामहे वयम्?
काकः – अरे!अरे! किंजल्पसि? यदि अहंकृष्णवर्णः तर्हि त्वं किंगौरागः? अपि च विस्मर्यते किं यत् मम सत्यप्रियता तु जनानां कृते
उदाहरणस्वरूपा – ‘अनृतं वदसि चेत् काकः दशेत्-इति प्रकारेण। अस्माकं परिश्रमः ऐक्यं च विश्वप्रथितम्। अपि च काकचेष्टः विद्यार्थी एव आदर्शच्छात्रः मन्यते।
शब्दार्था: – आम् = ओम् (हाँ), सत्यम् = ऋतम् (सच), त्वया = भवता (आपने), कथितम् = उक्तम् (कह दिया), वस्तुतः = यथार्थतः (वास्तव में), वनराजः = मृगराजः (सिंह), भवितुं तु = (होने) योग्यः = सक्षमः (योग्य) अहमेव = (मैं ही हूँ) उपहसन् = उपहासं आक्षेपं वा कुर्वन् (उपहास करते हुए), कथम् कस्मात् (कैसे) त्वम् भवान् (आप), योग्य = क्षमः (योग्य), वनराजः भवितुम् मृगराजः इति विधातुम् (राजा के लिए), यत्र-तत्र = यस्मिन् तस्मिन् स्थाने (जहाँ-तहाँ) का का = काँव-काँव (काँव-काँव) कर्कष ध्वनिना = प्रचण्ड कटु स्वरेण (तेज और कटु स्वर से) वातावरणम् पर्यावरणम् (वातावरण को) आकुली करोति = अशान्तं, उद्विग्नं वा करोति (बेचैन करते हो) न रूपम्न = आकार सौन्दर्यम् (न रूप-सौन्दर्य) न ध्वनिः अस्ति = न स्वरम् अस्ति (स्वर भी नहीं है) कृष्णवर्ण: = श्याम, असित रङ्गः (काला रंग) मेध्यामेध्य-भक्षक: विशुद्धम् अशुद्धम् च भोजिन्। (शुद्ध-अशुद्ध का भक्षक) त्वाम् भवन्तम् (आपको), कथं कस्मात् (कैसे) वनराजम् मृगराजम् (वन का राजा), मन्यामहे = मनिष्यामहे (मानेंगे), अरे = अरे रे रे (अरे) किं जल्पसि = किं प्रलपसि (क्या कहता है), यदि= चेत् (यदि) अहं कृष्णवर्ण: अहं श्यामरङ्ग (मैं काला हूँ) तर्हि तदा भवान् (तो आप) किम् गौरा = श्वेताङ्ग (क्या गोरे हो), अपि च विस्मयते किं त्वं = विस्मरति, न स्मरति (क्या तुम्हें याद नहीं है) किम् (क्या) यत् (कि) मम सत्यप्रियता मे सत्यानुग्रह (मेरी सत्यप्रियता) जनानां = कृते जनेभ्यः (लोगों के लिए)। उदाहरणस्वरूपा = निदर्शन योग्य क्षमा (उदाहरण देने योग्य है) अनृतम् = असत्यम् (झूठ) वदसि = ब्रूषे (बोले) चेत् = यदि (यदि) काकः = वायसः (कौआ), दशेत = दशति (काटे), इति प्रकारेण = अनया विधया (इस प्रकार से) अस्माकंन: (हमारा), परिश्रमं = उद्यम (मेहनत), ऐक्यम् च = एकता च (और एकता), विश्व पृथितम् = संसारे प्रसिद्धम् (संसार में प्रसिद्ध है), अपि च = अन्य च (और) काकचेष्ट: = वायस इव आचरति यः (जो कौवे की तरह आचरण करता है), विद्यार्थी = ज्ञानेच्छु (विद्यार्थी), आदर्श प्रतिरूपम् (आदर्श) छात्रा (विद्यार्थी) मन्यते = मान्यः (माना जाता है)।
सन्दर्भ-प्रसङ्गश्च – यह गद्यांश हमारी पाठ्यपुस्तक ‘शेमुषी’ के ‘सौहार्दै प्रकृतेः शोभा’ पाठ से लिया गया है। इस गद्यांश में कौवा और कोयल के संवाद में दोनों वनराज पद की अपनी-अपनी योग्यता प्रतिपादित करते हैं। सिंह की सभी उपेक्षा करते हैं।
हिन्दी अनुवादः – काक-हाँ, सत्य कहते हो तुम-वास्तव में वनराज होने के लिए तो मैं ही योग्य हूँ। पिक – (उपहास करते हुए) तू वनराज होने योग्य कैसे है? जहाँ-तहाँ काँव-काँव की कर्कश ध्वनि से वातावरण को व्याकुल या बेचैन करते हो। न रूप है न ध्वनि है। काले रंग के, शुद्ध-अशुद्ध को खाने वाले तुमको हम वनराज मानें।
काक – अरे रे, तू क्यों बकवास करता है? यदि मैं काला हूँ तो तू कौन-सा गोरा है? क्या तुम लोगों के लिए मेरी सत्य प्रियता को भूल रहे होंगे। उदाहरण के रूप में है – झूठ बोले कौवा खाये इस प्रकार से। हमारा परिश्रम और एकता विश्व प्रसिद्ध है। और भी काक जैसी चेष्टा वाला विद्यार्थी ही आदर्श छात्र माना जाता है।
5. पिकः – अलम् अलम् अतिविकत्थनेन। किं विस्मर्यते यत् – काकः कृष्णः पिकः कृष्णः को भेदः पिककाकयोः। वसन्तसमये प्राप्ते काकः पिकः पिकः।।
काकः – रे परभृत! अहं यदि तव संततिं न पालयामि तर्हि कुत्र युः पिका:? अतः अहम् एव करुणापरः पक्षिसम्राट् काकः।
गजः – समीपतः एवागच्छन् अरे! अरे! सर्वं सम्भाषणं शृण्वन्नेवाहम् अत्रागच्छम्। अहं विशालकायः,बलशाली, पराक्रमी च। सिंहः वा स्यात् अथवा अन्यः कोऽपि, वन्यपशून् तु तुदन्तं जन्तुमहं स्वशुण्डेन पोथयित्वा मारयिष्यामि। किमन्यः कोऽप्यस्ति एतादृशः पराक्रमी। अतः अहमेव योग्यः वनराजपदाय।
शब्दार्थाः – अलम् अलम्-पर्याप्तं, प्रचुरम् (बस-बस), अतिविकत्थनेन = अधिकं आत्मश्लाघया (अधिक अपनी सराहना), किं विस्मर्यते यत् = अपि विस्मृतां भवान् यत् (क्या आप भूल गये हैं कि), काकः = वायसः (कौआ), पिकः = कोकिलः (कोयल) कृष्णः = श्यामः (काला), को भेदः पिककाकयोः = कोकिल-काकयो किमन्तरम् (कोयल और कौवे में क्या अम्तर है) बसन्तसमये = मधुमास काले (बसन्त ऋतु में) प्राप्ते = आगते (आने पर) काकः काकः-वायसः = वायसः (कौवा कौवा ही) पिकः पिकः = कोकिल कोकिला एव (कोयल कोयल ही रहती है) रे परभृत = अरे परेण पालित पिकः (दूसरों के द्वारा भरण = पोषण की गई कोयल) अहं यदि तव संतति = अहम् चेत् ते अपत्यान् (यदि मैं तेरी सन्तान को) न पालयामि = पालनं न करोमि (पालन न करूँ) तर्हि = तदा (तो) कुत्र = कस्मिन् स्थाने (कहाँ) स्युः भविष्यन्ति (होगी) पिका = कोकिला: (कोयल) अतः एवम् (इस प्रकार)
अहमेव करुणापर = अहमेन करुणापेतः (मैं ही दयालु हूँ) पक्षि सम्राट् = खगानां शासकः (पक्षियों का सम्राट) काकः = वायसः (बोझा) समीपत: = पार्वात् (पास से) एव = ही आगच्छन्-आगम्य (आकर) अरे = रे (अरे) सर्वं सम्पूर्णम् (सारा) सम्भाषणम् संवादम् (बातचीत) अण्वन्नेवादम् = अकर्णमन्नेव अहम् (सुनता हुआ मैं) अत्रागच्छम् = इतः आगतोऽस्मि (आया हुआ हूँ) अहम् विशालकायः = वृहत्कायः (विशाल शरीर वाला) बलशाली = शक्तियुतः (ताकतवर) पराक्रमी च = पौरुष युतः च (और पराक्रमी) सिंहः केसरी (शेर)। स्यात् = भवतु (हो) अथवा अन्यः कोऽपि अन्यो वा कश्चिदपि (अथवा और कोई) वन्यपशून् = श्वापदान (जंगली जानवरों) तुदन्तुं = कष्टं ददानम् (कष्ट देते हुए को) स्वशुण्डेन् = आत्मकरेण (अपनी सूंड से) पोथयित्वा = पीडयित्वा (पीड़ा देकर) मारयिष्यामि-हनिष्यामि (मार दूंगा) किमन्य = किमन्यत् (और तो क्या) कोऽप्यस्ति = कश्चिदास्ति (कोई है) एतादृशः ईदृशा (ऐसा) पराक्रमी = पौरुषपुत्रः (पराक्रमी) अत: अहम् एव योग्यः = अतएव अयमेव समः (मैं ही योग्य हूँ) वन राजपदायाः = मृगराज पदव्या (वन के राजा के योग्य)।
सन्दर्भ-प्रसङ्गश्च – यह गद्यांश हमारी पाठ्यपुस्तक ‘शेमुषी’ के ‘सौहार्द प्रकृतेः शोभा’ पाठ से लिया गया है। इस गद्यांश में कोयल, कौवा और हाथी अपने-अपने को वनराज पद के लिए योग्य प्रतिपादित करते हैं।
हिन्दी अनुवाद – पिक:-बस-बस अधिक आत्म-सराहना की आवश्यकता नहीं। क्या भूल रहे हो कि कौवा काला और कोयल भी काली, कौवे और कोयल में क्या अन्तर है। बसन्त का समय आने पर कौवा-कौवा होता है और कोयल कोयल।
काक – अरे! दूसरों द्वारा पाली हुई, यदि मैं तुम्हारी सन्तान को नहीं पालूँ तो कोयल कहाँ दोगे? अतः मैं कौवा ही करुणामय खग सम्राट हूँ।
हाथी – (पास से आता हुआ) अरे-अरे! सारा संवाद सुनता हुआ ही मैं यहाँ आया हूँ। मैं विशाल शरीरवाला, शक्तिशाली और पराक्रमी हूँ। चाहे सिंह हो अथवा कोई और हो, वन्य पशुओं को तंग करने वाले प्राणी को मैं सँड़ से पीड़ित करके मार डालूँगा। क्या अन्य कोई भी ऐसा पराक्रमी है। अतः मैं ही वन के राजा के योग्य हूँ।

6 वानरः – अरे! अरे! एवं वा (शीघ्रमेव गजस्यापि पुच्छं विधूय वृक्षोपरि आरोहति)
(गजः तं वृक्षमेव स्वशुण्डेन आलोडयितुमिच्छति परं वानरस्तु कूर्दित्वा अन्यं वृक्षमारोहति। एवं गजं वृक्षात् वृक्षं प्रति धावन्तः दृष्ट्वा सिंहः अपि हसति वदति च।)
सिंहः – भोः गजः मामप्येवमेवातुदन् एते वानराः।
वानरः – एतस्मादेव तु कथयामि यदहमेव योग्यः वनराजपदाय येन विशालकायं पराक्रमिणं, भयंकर चापि सिंह गजं व पराजेतुं अस्माकं जातिः। अतः वन्यजन्तूनां रक्षायै वयमेव क्षमाः।
(एतत्सर्वं श्रुत्वा नदीमध्यस्थितः एकः बकः)
शब्दार्थाः – अरे अरे रे रे (अरे अरे) एवं वा-अथवा अनेन प्रकारेण (अथवा इस प्रकार) शीघ्रमेव क्षिप्रमेव (जल्दी ही) गजस्य = करिणः (हाथी की) पुच्छं लागलं (पूँछ को) विधूय आकृष्य (खींचकर) वृक्षोपरि = तरोरुपरिष्ठात् (पेड़ के ऊपर) आरोहति = आरूढ़ोभवति (चढ़ जाता है) गजः = करि (हाथी) तं वृक्षमेव = अमुम् तरुमेव (उस पेड़ को ही) स्वशुण्डेन = आत्मकरेण (अपनी सूंड़ से) आलोडयितुमिच्छति = संक्षोभितं कर्तुमीहते (हिलाना चाहता है) परम् = परन्तु (लेकिन) वानरस्तु कपिस्तु (बन्दर तो) कूर्दित्वा = उत्प्लुत्य (उछलकर) अन्यं = अपरं (दूसरे) वृक्षं = तरुम् (पेड़ पर) आरोहरि आरूढं भवति (चढ़ जाते हैं) एवं अनेन = प्रकारेण (इस प्रकार) गजंकरिणं (हाथी को) वृक्षात् वृक्षम् = तरोः तरुम् (पेड़ एवं पेड़ पर) धावन्तम् उत्प्लुन्तं (उछलते या दौड़ते हुए को) दृष्ट्वा = वीक्ष्य (देखकर) सिंहः अपि = केसरी अपि (शेर भी) हसति वदति च = हासं करोति कथयति च (हँसता है और कहता है) भोः गजः = अरे करि (अरे हाथी)
मामप्येवमेवातुदन् = मामपि अनेन एव प्रकारेण पीडयन् (मुझे भी इसी प्रकार पीड़ित किया) एते वानराः अमी कपयः (इन बन्दरों ने) एतस्मात् एव = अतः एव (इसीलिए), कथयामि वदामि (कहता हूँ) यत् अहमेव योग्यः = यदहमेव समर्थः (मैं ही योग्य हूँ) वनराजपदाय = अरण्यस्य राज्ञः पदस्य हेतोः (जंगल के राजा पद के योग्य) येन विशालकायं = येन वृहत् शरीरं (विशालकाय को) पराक्रमिणम् पौरुषोपेतम् (पौरुषयुक्त को) भयंकरम् = भीतिकरं चापि (भय पैदा करने वाले को) सिंह गजं वा केसरिणं = करिणं वा परास्तं कर्तुम् (सिंह अथवा हाथी को हराने के लिए) अस्माकं जाति = अस्मज्जातिः (हमारी जाति) समर्था = सक्षमा (समर्थ हैं) अतः = अतएव (इसलिए) वन्यजन्तूनां = श्वापदानां (जंगली पशुओं की) रक्षायै = रक्षणाय (रक्षा के लिए) वयमेव क्षमा = वयमेव समर्थाः (मैं ही समर्थ हूँ), एतत्सर्व श्रुत्वा = इदं सर्वं, निशम्य आकर्ण्य वा (इस सबको सुनकर) नदी मध्यस्थितः = सरितः मध्ये स्थितः (नदी के बीच स्थित), एकः वकः = एकः वकुलः (एक बगुला)।
सन्दर्भ-प्रसङ्गश्च – यह गद्यांश हमारी पाठ्य-पुस्तक ‘शेमुषी’ के ‘सौहार्द प्रकृतेः शोभा’ पाठ से लिया गया है। इस गद्यांश में वानरों की लीला का वर्णन है। वानर स्वयं को हाथी और सिंह को पराजित करने में समर्थ बताता है।
हिन्दी अनुवादः – वानर-अरे अरे, यह बात है क्या (शीघ्र ही हाथी की पूँछ को खींचकर वृक्ष के ऊपर चढ़ जाता है।)
(हाथी उस वृक्ष को सँड़ से हिलाना चाहता है परन्तु वानर तो कूदकर अन्य वृक्ष पर चढ़ जाता है। इस प्रकार हाथी को वृक्ष से वृक्ष की ओर दौड़ते हुए को देखकर सिंह भी हँसता है और कहता है।)
सिंह – अरे गजराज! मुझे भी इसी प्रकार से वानर पीड़ित कर रहे हैं।
वानर – इसीलिए तो कहता हूँ कि मैं ही वनराज के पद के योग्य हूँ, जिससे कि विशालकाय पराक्रमी और भयंकर शेर अथवा हाथी को पराजित करने में हमारी जाति समर्थ है। अतः वन्य जन्तुओं की रक्षा के लिए हम भी समर्थ हैं। (इस सबको सुनकर नदी के मध्य बैठा एक बगुला)।
7. बकः – अरे! अरे! मां विहाय कथमन्यः कोऽपि राजा भवितुमर्हति। अहं तु शीतले जले बहुकालपर्यन्तम् अविचलः ध्यानमग्नः स्थितप्रज्ञ इव स्थित्वा सर्वेषां रक्षायाः उपायान् चिन्तयिष्यामि, योजना निर्मीय च स्वसभायां विविधपदमलंकुर्वाणैः जन्तुभिश्च मिलित्वा रक्षोपायान् क्रियान्वितान् कारयिष्यामि, अतः अहमेव वनराजपदप्राप्तये योग्यः।
शब्दार्थाः – अरे अरे = रे रे (अरे) माम् = मा (मुझे) विहाय = अतिरिच्य, परित्यज्य (छोड़कर) कथमन्यः = कस्मात् अपरः (दूसरा कैसे) कोऽपि = कश्चिदपि (कोई भी) भवितुमर्हति = भवितुं शक्नोति (हो सकता है) अहं तु शीतले जले = अहं तु हिमाम्बु मध्ये (ठंडे पानी में) बहुकालपर्यन्तम् = प्रचुरं समय यावत् (पर्याप्त समय तक) अविचल = अनवरुद्ध (निरन्तर) ध्यानमग्न = ध्याने तल्लीनः निमग्नः (ध्यान लगा हुआ) स्थितप्रज्ञः = स्थिरा बुद्धिः यस्य सा (जिसकी बुद्धि स्थिर है) स्थित्वा = उपविश्य (बैठकर) सर्वेषाम् = सकलानाम् (सबकी) रक्षायाः = रक्षणस्य (रक्षा के) उपायान् = उपचारान् (उपायों को) चिन्तयिष्यामि = विचारयिष्यामि (विचार या चिन्ता करूँगा)
योजनाम् = कार्यप्रारूपकल्पनां (प्रारूप) निर्माय = निर्माणं कृत्वा, रचयित्वा (बनाकर) स्वसभायाम् = आत्मनः समित्याम् (अपनी सभा या गोष्ठी में) विविधपदमलकुर्वाण: = बहुविध स्थानानि विभूषयद्भिः (अनेक पदों को सुशोभित करने वाले) जन्तुभिः = प्राणिभिः (प्राणियों द्वारा) मिलित्वा = सम्भूय (मिलकर) रक्षोएन् = रक्षणस्य उपचारान् (रक्षा के उपायों को) क्रियान्वितान् = क्रियान्विति (अनुरूप कार्य) कारयिष्यामि = कर्तुं प्रेरयिष्यामि (करवाऊँगा) अतः अहम् एव वनराज पदप्राप्तये योग्यः = अतएव अहम् एव अरण्याधिपतेः आसनं प्राप्तुं समर्थ (इसलिए मैं ही वन के राजा का पद प्राप्त करने योग्य हूँ।)
सन्दर्भ-प्रसङ्गश्च – यह गद्यांश हमारी पाठ्यपुस्तक शेमुषी के ‘सौहार्द प्रकृतेः शोभा’ पाठ से लिया गया है। इस गद्यांश में बगुला सबकी उपेक्षा करके स्वयं को वनराज पद के योग्य प्रतिपादित करता है।
हिन्दी अनुवादः – अरे, अरे! मुझे छोड़कर कैसे कोई अन्य राजा हो सकता है। मैं तो शीतल जल में बहुत समय तक बिना विचलित हुए ध्यान में मग्न हुआ स्थितप्रज्ञ की तरह बैठकर हमेशा रक्षा के उपाय सोचूँगा, योजना बनाकर अपनी सभा में विविध पदों को अलंकृत करते हुए जीवों के साथ मिलकर रक्षा के उपायों का क्रियान्वयन करूँगा। अतः मैं ही वनराज पद प्राप्त करने योग्य हूँ।

8. मयूरः – (वृक्षोपरितः-साट्टहासपूर्वकम्) विरम विरम आत्मश्लाघायाः किं न जानासि यत् –
यदि न स्यान्नरपतिः सम्यङनेता ततः प्रजा।
अकर्णधारा जलधौ विप्लवेतेह नौरिव।
को न जानाति तव ध्यानावस्थाम्। ‘स्थितप्रज्ञ’ इति व्याजेन वराकान् मीनान् छलेन अधिगृह्य क्रूरतया भक्षयसि। धिक् त्वाम्। तव कारणात् तु सर्वं पक्षिकुलमेवावमानितं जातम्।
शब्दार्थाः – वृक्षोपरित = तरोः उपरिष्ठात् (पेड़ के ऊपर से) साट्टहासपूर्वक: = उच्चैः हासेन सहितम् (जोर से हँसते हुए) विरम-विरम = तिष्ठ तिष्ठ (ठहर ठहर) आत्मश्लाघायाः = स्वकीयया प्रशंसया (बस बस अपनी प्रशंसा) किं न जानासि यत् = अपि नावगच्छसि यत् (क्या नहीं जानते कि) यदि = चेत् (यदि) न स्यात् = न भविष्यति (नहीं होगा) नरपतिः = राजा (राजा) सम्यक् = सुष्ठु (अच्छा साधु) ततः = तदा (तब) प्रजा: प्रजाजनाः (प्रजा) जलधौ = सागरे (समुद्र में) अकर्णधारा नौरिव नाविक रहित तरणी इव निमज्जेत, (बिना नाविक नौका की तरह डूब जाती है), को न जानाति = केन न ज्ञायते (किसे ज्ञात नहीं, कौन नहीं जानता) तव = ते (तेरी) ध्यानावस्थाम् = अवधानस्य स्थितिं दशां व (तुम्हारी ध्यान की स्थिति को) स्थितप्रज्ञः = स्थिर ज्ञानस्य इव (स्थित प्रज्ञ के) व्याजेन = मिषेण (बहाने से) वराकान् = दीनान् निरवलम्बान् (बेसहारों को) मीनान् = मत्स्यान् (मछलियों को) छलेन = वञ्चनेन (धोखे से) अधिगृह्य = गृहीत्वा (पकड़कर) करतया = क्रौर्येन सह (निष्ठुरता के साथ) भक्षयसि = खादसि (खा जाते हो) धिक् त्वाम् त्वम् मर्त्सनाह (तुम्हें धिक्कार है), तव = ते (तेरे) कारणात् = हेतोः (वजह से) सर्वं पक्षिकुलमेव = सकलं खगकुलम् एव (सारा खगकुल) अवमानितं = तिरस्कृतं, अवधीरणम् (अपमानित) जातम् = अभवत् (हो गई)
सन्दर्भ-प्रसङ्गश्च – यह गद्यांश हमारी पाठ्यपुस्तक शेमुषी के ‘सौहार्द प्रकृतेः शोभा’ पाठ से लिया गया है। इस गद्यांश में मोर स्वयं को न केवल पक्षिराज ही प्रतिपादित करता है अपितु वनराजपद के योग्य भी कहता है।
हिन्दी अनुवादः-मोर-(वृक्ष के ऊपर से अट्टहासपूर्वक) रुको-रुको अपनी सराहना करने से। क्या नहीं जानते कि-यदि उत्तम राजा अथवा नेता नहीं होगा तो प्रजा बिना नाविक की नौका की तरह सागर में डूब जायेगी। तुम्हारे ध्यान की स्थिति को कौन नहीं जानता। स्थितप्रज्ञ के बहाने बेचारी मछलियों को पकड़कर क्रूरतापूर्वक खा जाते हो। धिक्कार है तुम्हें! तुम्हारे कारण संसार में पक्षियों की जाति ही अपमानित हो गई है।

9 वानरः – (सगर्वम्) अतएव कथयामि यत् अहमेव योग्यः वनराजपदाय। शीघ्रमेव मम राज्याभिषेकाय तत्पराः भवन्तु सर्वे वन्यजीवाः।
मयूरः – अरे वानर! तूष्णीं भव। कथं त्वं योग्यः वनराजपदायः? पश्यतु पश्यतु मम शिरसि राजमुकुटमिव शिखां स्थापयता विधात्रा एवाहं पक्षिराजः कृतः, अतः वने निवसन्तं मां वनराजरूपेणापि द्रष्टुं सज्जाः भवन्तु अधुना। यतः कथं कोऽप्यन्यः विधातुः निर्णयम् अन्यथाकर्तुं क्षमः।
काकः – (सव्यङ्ग्यम्) अरे अहिभुक्। नृत्यातिरिक्तं का तव विशेषता यत् त्वां वनराजपदाय योग्य मन्यामहे वयम्।
शब्दार्थाः – सगर्वम् = गर्वेण सहितम्, साभिमान (अहंकार सहित) अतएव = अतः (इसलिए) कथयामि = वदामि, ब्रवीमि (कहता हूँ) यत् अहम् एव योग्य: = अहम् एव सक्षमः (कि मैं ही योग्य हूँ) वनराज पदाय = काननाधिपतेः स्थानाय (वन के राजा के पद के लिए) मममे (मेरे) राज्याभिषेकाय-राजासने स्थापयितुं स्थानाय (राज्याभिषेक के लिए) तत्पराः भवन्तु व्यग्राः सन्तु (तैयार हो जाओ) सर्वे सकलाः (सभी) वन्यजीवा = अरण्य-प्राणिन् (जंगल के जन्तु) अरे वानर!: = रे मर्कट! (अरे बन्दर) तूष्णीं भव = मौनं धारय (चुप रह) कथं त्वं गोग्य = कस्मात् भवान् क्षमः (आप कैसे योग्य हैं) वनराजपदाय = काननाधिपस्य स्थानाय (वन के राजा के पद के लिए। यतु पश्यतु = वीक्षताम् वीक्षताम् (देख-देख) मम शिरसि = मे मस्तके (मेरे शिर पर) राजमुकुटमिव = राज्ञः चूडामणिम् इव (राजा के मुकुट की तरह) शिखां = शिखरम् (चोटी) स्थापयता = स्थापितं कृत्वा (लगाकर) विधात्रा = सृष्टिकर्ता (विधाता के द्वारा)
अहमेव पक्षिराज: अहमेन खगराजः = कृताः नियुक्तः निर्मितः (बनाया हूँ) अत: = अतएव (इसलिए) वने = कानने (जंगल में) निवसन्तं माम् = निवासं कुर्वाणं (निवास करते मुझको) अधुना इदानीम् (अब) वनराज रूपेण = वनस्य राज्ञोः रूपेण (वनराज के रूप में) माम् द्रष्टुम् मामवलोकयितुं (मुझे देखने के लिए) सज्जाः भवन्तु = तत्पराः भवन्तु (तैयार हो जाओ) यतः = कस्मान् (किसलिए) कोऽन्ये = कश्चिदन्यः (कोई दूसरा) विधातुम् = कर्तुम् (करने के लिए) निर्णयम् = निश्चयम् (निर्णय को) अन्यथा = मिथ्यां कर्तुं (झूठा करने के लिए), क्षमः = समर्थः (सक्षम) सव्यङ्ग्यम् = व्यञ्जनया सहितम् (व्यंग्यपूर्वक) अरे अहिभुक = रे सर्पभक्षक (अरे सांप खाने वाले), नृत्यातिरिक्तं का तव विशेषता = नृत्ययतिरिच्य किम् ते वैशिष्ट्यम् (नाचने के अलावा और तेरी,क्या विशेषता है।) यत् त्वां = यत् भवन्तम् (कि आपको) वनराज = मृगराज (वन के राजा के) योग्यम् = क्षमम् (योग्य) वयं मन्यामहे वयं मन्यामहे (हम मानें)।
सन्दर्भ-प्रसङ्गश्च – यह गद्यांश हमारी पाठ्यपुस्तक शेमुषी के ‘सौहार्द प्रकृतेः शोभा’ पाठ से लिया गया है। इस गद्यांश में बन्दर, मोर और कौवा अपने-अपने को योग्य प्रतिपादित करते हुए विवाद करते हैं।
हिन्दी अनुवाद-वानर – (अभिमान के साथ) इसीलिए कहता हूँ कि मैं ही वनराज पद के योग्य हूँ। आप शीघ्र ही सभी वन्य जीव मेरे राज्याभिषेक के लिए तैयार हो जाओ।
मयूर – अरे वानर! चुप रह! तुम वनराज के पद के योग्य कैसे हो। देखो देखो मेरे सिर पर राज्यमुकट की तरह चोटी को स्थापित करके विधाता ने ही मुझे पक्षिराज बना दिया है। अतः वन में निवास करते हुए मुझको वनराज के रूप में अब देखने को तैयार हो जाओ। क्योंकि कोई अन्य विधाता के निर्णय को झुठला सकता है।
काकः – (व्यंग्य के साथ) अरे साँ५ खाने वाले नृत्य के अतिरिक्त और तुम में क्या विशेषता है कि तुम्हें वनराज पद के योग्य हम समझें।

10 मयूरः – यतः मम नृत्यं तु प्रकृतेः आराधना। पश्य! पश्य! मम पिच्छानामपूर्वं सौन्दर्यम् (पिच्छानुद्घाट्य नृत्यमुद्रायां स्थितः सन्) न कोऽपि त्रैलोक्ये मत्सदृशः सुन्दरः। वन्यजन्तूनामुपरि आक्रमणं कर्तारं तु अहं स्वसौन्दर्येण नृत्येन च आकर्षित कृत्वा वनात् बहिष्करिष्यामि। अतः अहमेव योग्यः वनराजपदायः।
(एतस्मिन्नेव काले व्याघ्रचित्रकौ अपि नदीजलं पातुमागतौ एवं विवादं शृणुतः वदतः च)
व्याघ्रचित्रको अरे किं वनराजपदाय सुपात्रं चीयते?
एतदर्थं तु आवामेव योग्यौ। यस्य कस्यापि चयनं तु सर्वसम्मत्या।
शब्दार्थाः – यतः = यस्मात (क्योंकि), मम = मे (मेरा) नत्यम नर्तनम् (नाच) प्रकतेः = प्रकृतितत्वस्य (प्रकृति की) आराधना: = उपासना (कृपा) पश्य = अवलोकय, ईक्षस्व (देखो) मममे (मेरी) पिच्छानाम् = पुच्छस्य (पूँछ की) अपूर्व सौन्दर्यम् = विचक्षणं सुन्दरताम् (अनोखी सुन्दरता के) पिच्छान् = पुच्छं (पंखों को) उद्घाट्य = अनावृत्य, उत्थाय (उठाकर) नृत्य मुद्रायां स्थित: नर्तनस्य स्थिति तिष्ठति (नाचने की मुद्रा में स्थित हो जाता है) न कोऽपि त्रैलोक्यं त्रिषु = लोकेषु कश्चिदपि (तीनों लोकों में कोई) मत्सदश: मादृशः (मेरे जैसा) सुन्दर = मनोरमः (सुन्दर), वन्य जन्तूनाम् = अरण्य प्राणिनाम् (जंगली जानवरों के) उपरि = उपरिष्ठात् (ऊपर) आक्रमणं कर्तारं आक्रान्तारम् (आक्रमण करने वाले को) अहम् = मैं, स्व सौन्दर्ये = आत्मनः सुन्दरतया (अपनी सुन्दरता से) नृत्येन = च-नर्तनेन च (नाचने से)
आकर्षितं = कृत्वा आकृष्य (आकर्षित करके) वनात् = काननात् (जंगल से), बहिष्करिष्यामि = बहिष्कारं विधास्यमि (बहिष्कार कर दूंगा) अत: अतएव (इसलिए) अहमेव = मैं ही। वनराजपदाय = वनराजस्य पद एव योग्य (वन के राजा के पद के योग्य हूँ)) एतस्मिन् काले तदैव (इसी समय), व्याघ्रचित्रकैः = द्वीपीमृगान्तकश्च (बाघ और चीता भी) नदीजलं = सरिज्जलम् (नदी का पानी) पातुम् = आचमिमतुम् (पीने के लिए), आगतौ = आयातौ (आ गये) एवं ईदृशं (ऐसे) विवादम् = प्रतिवादम् (विवाद को) श्रृणुतः = आकर्णत (सुनते) वदतः = कथयतः, बूतः = वः (कहते हैं) अरे = रे (अरे) किम् = अपि (क्या) वनराजपदाय = अरण्यराज्ञः आसनाय (वनराज के पद के लिए) सुपात्रम् = सत्पात्रम् (अच्छा पात्र) चीयते = चयनं क्रियते (चुना जा रहा है) एतदर्थम् = अस्य कृतं (इसके लिए) आवामेव = आवामुभावेव (हम दोनों ही) योग्यौ = क्षमौ (योग्य हैं) यस्य कस्यापि = यं कमपि प्राणिनाम् (जिस किसी प्राणी का) चयनं कुर्वन्ति = चिन्नन्तु (चुनें) सर्वसम्मत्या = सर्वेषां समान मतेन एव (सबके समान मत से चुनें)।
सन्दर्भ-प्रसङ्गश्च – यह गद्यांश हमारी पाठ्यपुस्तक ‘शेमुषी’ के ‘सौहार्दै प्रकृतेः शोभा’ पाठ से लिया गया है। इस गद्यांश में बाघ और चीता भी आ जाते हैं जो मोर को नीचा बताकर प्रत्येक स्वयं को सुयोग्य प्रतिपादित करते हैं।
हिन्दी अनुवादः – मयूर-क्योंकि मेरा नृत्य तो प्रकृति की मेहरबानी है। देखो-देखो, मेरे पंखों का अपूर्व सौन्दर्य। (पूँछ को उठाकर नृत्य की मुद्रा में स्थित होकर) तीनों लोकों में कोई भी मेरे समान सुन्दर नहीं है। वन्य पशुओं पर आक्रमण करने वाले को तो मैं अपने सौन्दर्य और नृत्य से आकर्षित करके जंगल से बहिष्कार कर दूंगा। अत: मैं ही वनराज पद के योग्य हूँ। (इस समय बाघ और चीता भी नदी का जल पान करने के लिये आ गये, इस प्रकार के विवाद को सुनते हैं और कहते हैं)
बाघ और चीता – अरे क्या वनराज पद के लिये सुपात्र चुना जा रहा है? इसके लिए तो हम दोनों ही योग्य हैं। जिस किसी का चयन करें, सर्वसम्मति से करना।

11. सिंहः – तूष्णीं भव भोः। युवामपि मत्सदृशौ भक्षको न तु रक्षको। एते वन्यजीवाः भक्षक रक्षकपदयोग्यं न मयन्ते अतएव विचारविमर्शः प्रचलित।
बकः – सर्वथा सम्यगुक्तम् सिंहमहोदयेन। वस्तुतः एव सिंहन बहुकालपर्यन्तं शासनं कृतम् परमधुना तु कोऽपि पक्षी एव राजेति निश्चेतव्यम् अत्र तु संशीतिलेशस्यापि अवकाशः एवं नास्ति। सर्वे पक्षिणः (उच्चैः)- आम् आम्- कश्चित् खगः एव वनराजः भविष्यति इति।
शब्दार्था: – तूष्णीं भव = शान्तं एधि, मौने धारय (चुप रहो)। युवामपि = भवन्तौ अपि (आप भी), मत्सदशी – मादृशौ, माम् इव (मेरे जैसे, मुझ से, मेरी तरह), भक्षको = भोजिनौ (खाने वाले ) न तु रक्षको = न च त्रातारौ (न कि रक्षक) एते = इमे (ये), वन्यजीवाः = अरण्यप्राणिन् (जंगली जानवर) भक्षक = भोजिनम्, ‘भोक्तारम् (खाने वाले को) रक्षक पद योग्यम् = त्रातुः स्थानाय सक्षम (रक्षक के पद के योग्य) न मन्यन्ते = न मन्वते (नहीं मानते हैं) अतएव = अस्मादेव (इसलिए) विचार = विमर्श = विचाराणाम् आदान प्रदान (विचारों का आदान-प्रदान) प्रचलति = चलन्नस्ति (चल रहा है) सर्वथा पूर्णतः (पूरी तरह) सम्यगुक्तम् = समीचीनमेव कथितम् (ठीक ही कहा)
सिंह महोदयेन = मृगेन्द्रेण, केसरिणा महाशयेन (सिंह जी ने) वस्तुत = यथार्थतः (वास्तव में) एव = ही। सिंहेन = केसरिणा (सिंह द्वारा), बहुकालपर्यन्तम् = दीर्घकालं यावत् (लम्बे समय तक), शासनं कृतम् = आधिपत्यं सम्पादितं (राज्य किया गया) परञ्चाधुना = परन्तु इदानीम् तु (परन्तु अब तो) कोऽपिपक्षी एव = कश्चित खगः एव (कोई पक्षी ही), राजेति = नृपेति (राजा) निश्चेतव्यम् = निश्चित एव चेतव्यम् (निश्चित करना चाहिए) अत्र = इतस्तु (यहाँ) संशीतिलेशस्यापि = सन्देह मात्रस्य (सन्देह मात्र से) अवकाशः एव = अवसर एव (अवसर ही) नास्ति = न वर्तते (नहीं है) सर्वे पक्षिणः = सकलाः खगः (सभी पक्षी) उच्चै = उच्च स्वरेण (जोर से) आम् आम् = ओम ओम (हाँ हाँ), कश्चित् = कोऽपि (कोई) कश्चन = (कोई) खगः एव = पक्षी एव (पक्षी ही) वनराज = अरण्यधिपतिः (वन का राजा) भविष्यति = नियोज्यते (नियुक्त किया जायेगा)।
सन्दर्भ-प्रसङ्गश्च – यह गद्यांश हमारी ‘शेमुषी’ पाठ्यपुस्तक के ‘सौहार्द प्रकृतेः शोभा’ पाठ से लिया गया है। इस गद्यांश में बाघ और चीता स्वयं को राजपद के लिए प्रस्तुत करते हैं और बगुला ‘सिंह ने बहुत दिन तक शासन कर लिया है’ ऐसा आरोप लगाकर किसी पक्षी को राजपद के लिये प्रस्तुत करते हैं।
हिन्दी अनुवाद – सिंह- अरे चुप हो जाओ। तुम भी मेरे समान ही भक्षक हो न कि रक्षक। ये जंगली जीव भक्षक को रक्षक पद के योग्य नहीं मानते। अतः विचार-विमर्श चल रहा है।
वक: – सिंह महोदय ने सर्वथा उचित ही कहा है। वास्तव में सिंह ने बहुत समय तक शासन किया है परन्तु अब तो कोई भी पक्षी राजा नियुक्त किया जाना चाहिए। इसमें कोई सन्देह नहीं है। सभी पक्षी (जोर से)हाँ हाँ कोई पक्षी ही वनराज होगा।

12. (परं कश्चिदपि खगः आत्मानं विना नान्यं कमपि अस्मै पदाय योग्यं चिन्तयति तर्हि कथं निर्णयः भवेत् तदा तैः सर्वैः गहननिद्रायां निश्चिन्तं स्वपन्तम् उलूकं वीक्ष्य विचारितम् यदेषः आत्मश्लाघाहीनः पदनिर्लिप्त: उलूको एवास्माकं राजा भविष्यति। परस्परमादिशन्ति च तदानीयन्तां नृपाभिषेकसम्बन्धिनः सम्भाराः इति।)
सर्वे पक्षिणः सज्जायैः गन्तुमिच्छन्ति तर्हि अनायास एव
काकः – (अट्टहासपूर्णेन-स्वरेण) सर्वथा अयुक्तमेतत् यन्मयूर-हंस-कोकिल-चक्रवाक-शुक सारसादिषु पक्षिप्रधानेषु विद्यमानेषु दिवान्धस्यास्य करालवकास्याभिषेकार्थं सर्वे सज्जाः। पूर्णं दिनं यावत् निद्रायमाणः एषः कथमस्मान् रक्षिष्यति। वस्तुतस्तु स्वभावरौद्रमत्युग्रं क्रूरमप्रियवादिनम्।
उलूकं नृपतिं कृत्वा का नु सिद्धिर्भवष्यिति।।
(ततः प्रविशति प्रकृतिमाता)।
शब्दार्था:- परं = परञ्च (लेकिन) कश्चिदपि = कश्चन् अपि (कोई भी) खगः = पक्षी (पक्षी) आत्मानं विना = स्वं विना (अपने अलावा) नान्यं कमपि = नापरं किञ्चदपि (किसी दूसरे को नहीं) अस्मै पदाय = एतस्मै स्थानाय (इस पद के लिए) योग्यं = सक्षम (समर्थ) चिन्तयन्ति = विचारयन्ति (सोचते हैं) तर्हि = तदा (तो) कथम् = कस्मात् (कैसे) निर्णयः = निश्चयः (फैसला) भवेत = स्यात् (हो) तदा = तस्मिन् काले (उस समय) सर्वे = सकलैः (सभी) गहन निद्रायाम् = प्रगाढां सुप्त्याम् (गहरी नींद में सोने पर) निश्चिन्तम् स्वपन्तम् = निश्चिन्तरूपेण शयानं। (निश्चिन्त सोते हुये) उलूकं वीक्ष्य = पेचकं अवलोक्य (उल्लू को देखकर) विचारितम् = चिंतितम् (विचार किया या सोचा),
यदेषः = यतोऽयम् (क्योंकि यह) आत्मश्लाघाविहीन = स्वस्य प्रशंसा रहितः (अपनी बड़ाई से दूर) पदनिर्लिप्त = स्थान प्राप्तुं विरक्तः (पदलोलुपता रहित) उलूके एव = धूक एव (उल्लू ही) अस्माकं राजा = अस्मन्नृपः (हमारा राजा) भविष्यति = स्यात् (होना चाहिए) परस्परमादिशन्ति च = मिथः आदेशं कुर्वन्ति च (और आपस में आदेश करते हैं।) तदा = तर्हि (तो) आनीयन्ताम् = आनेतव्यानि (लाये जाने चाहिए) नृपाभिषेक सम्बन्धिनः = राज्याभिषेकेन सम्बन्धितान् (राज्याभिषेक से सम्बन्धित) सम्भाराः = सामग्रयः (सामग्री) साधनानि वा (अथवा साधन) सर्वेपक्षिणः = सकला खगाः (सारे पक्षी), सज्जायैः गन्तुमिच्छन्ति = व्यवस्थाय प्रस्थानं कुर्वन्ति (व्यवस्था के लिए प्रस्थान करते हैं) तर्हि = तदा (तब) अनायास एव = प्रयत्न बिना एव (अनायास ही) काक: (कौआ) अट्टहासपूर्णेन = साट्टहासम् (अट्टहासपूर्वक)
स्वरेण = ध्वानेन (स्वर से) सर्वथा = सर्व प्रकारेण (सब प्रकार से) अयुक्तमेतत् = इदमनुचितम् (यह अनुचित है) यत् = यतः (क्योंकि) मयूर = हंस-कोकिल-चक्रवाक-शुक-सारिकादिषु पक्षिप्रधानेषु = बर्हि क्षीराश -पिक-कोक-कीर-पीतपादादिकाषु खग प्रमुखेषु (मोर-हंस-कोयल-चकवा-तोता, मैना आदि पक्षी प्रमुखों के) विद्यमानेषु = सत्सु (होते हुए) दिवान्धस्यास्य करालवक्त्रस्थ = एतस्याहरन्धस्य भयङ्करमुखस्य (दिन में अन्धा तथा भयंकर मुख वाले के) अभिषेकार्थम् – राजस्नाय (राज्याभिषेक) सर्वेसज्जाः = अखिलाः सकला वा तत्पराः (सभी तैयार हैं) पूर्ण: दिन यावत् = सकलं दिवसं पर्यन्त (पूरे दिनभर) निद्रायमाणः = स्वपन् उनिद्रः (सोता हुआ, उनींदा)
एष = अयं (यह) कथम् = केन प्रकारेण कस्मात् (कैसे) अस्मान् रक्षिष्यति = अस्माकं रक्षां विधास्यती (कैसे रक्षा कर सकेगा) (वास्तव में तो) स्वभाव रौद्रम् = प्रकृत्या कोपान्वितः (स्वभाव से क्रोधी) अति उग्रम् = महत् प्रचण्डम् (बहुत उग्र), क्रूरम् = जिम, कराल (वक्र) अप्रियवादिनम् = कटु वक्ताम् (कड़वा बोलने वाले) उलूकम् = घूकम् (उल्लू को), नृपतिं = राजानं (राजा) कृत्वा = विधाय (करके) का नु सिद्धिर्भविष्यति = किं साध्यं सम्भविष्यति (क्या सिद्धि होगी) ततः = तदैव (तभी) प्रकृतिमाता = निसर्ग अम्बिका (प्रकृति रूपी माता) प्रविशति = प्रवेश करोति (प्रवेश करती है)।
सन्दर्भ-प्रसङ्गश्च – यह नाट्यांश हमारी शेमुषी पाठ्य-पुस्तक के सौहार्द प्रकृतेः शोभा’ पाठ से उद्धृत है। इस नाट्यांश में सभी पक्षी मिलकर आत्मश्लाघा रहित तथा पद लोलुप न होने कारण उल्लू को राजा नियुक्त करना इसका विरोध कर देता है।
हिन्दी अनुवादः – परन्तु कोई भी पक्षी अपने अलावा अन्य किसी को इस पद के लिए नहीं सोचता तो निर्णय कैसे हो? तब उन सभी ने गहरी नींद में निश्चित सोते हुए उल्लू को देखकर विचारने लगे कि यह आत्म प्रशंसा रहित तथा पद से निर्लिप्त उल्लू ही हमारा राजा होगा। आपस में आदेश देने लगे तो राज्याभिषेक की सामग्री लाई जाये। सभी पक्षी तैयारी के लिए जाना चाहते हैं तब अनायास ही काक ने अट्टहासपूर्ण स्वर से कहा- यह पूरी तरह अनुचित है, क्योंकि मोर, हंस, कोयल, चकवा, तोता, मैना आदि पक्षियों के होते हुये भी दिन में अंधे, भयंकर मुख वाले को अभिषेक करने के लिए सभी तैयार हो। पूरे दिन तक सोता हुआ यह हमारी रक्षा कैसे करेगा। वास्तव में तो स्वभाव से क्रोधी, बहुत उग्र, कुटिल तथा कटुवादी उल्लू को राजा बनाकर तुम्हारी कौन-सी सिद्धि होगी। (तब प्रकृति माता प्रवेश करती है।)

13. प्रकृतिमाता – (सस्नेहम्) भोः भोः प्राणिनः। यूयम् सर्वे एव मे सन्ततिः। कथं मिथः कलहं कुर्वन्ति। वस्तुतः सर्वे
वन्यजीविनः अन्योन्याश्रिताः। सदैव स्मरत ददाति प्रतिगृह्णाति, गुह्यमाख्याति पृच्छति। भुङ्क्ते भोजयते चैव षड्-विधं प्रीतिलक्षणम्।।
(सर्वे प्राणिनः समवेतस्वरेण) मातः ! कथयति तु भवन्ती सर्वथा सम्यक परं वयं भवतीं न जानीमः। भवत्याः परिचयः कः?
शब्दार्थाः – सस्नेहम् = स्नेहपूर्वक (प्रेम से), भोः प्राणिनः = अरे अरे जपाः (अरे प्राणियो), यूयं सर्वे एव मे सन्ततिः = भवन्त सकलाः एव मम अपत्यानि (आप सब मेरी सन्तान हो) कथं = कस्मात् (किसलिए) मिथः = परस्परम् (आपस में) कलहं कुर्वन्ति = विवादं रचयन्ति(विवाद कर रहे हो) वस्तुतः = यथार्थतस्तु (वास्तव में तो) सर्वे = सकलाः (सभी) वन्यं जीविनः = अरण्यप्राणिनः (जंगली जीव) अन्योन्याश्रिता = परस्परम् शरण्याः सन्ति (आपस में एक दूसरे पर आश्रित हैं) सदैव = सर्वदा एव (हमेशा ही) स्मरत = स्मरणं कुरुत (याद रखो) ददाति = यच्छति (देते हो) प्रतिगृह्णाति = आदति (लेते हो) गुहयम् = गुप्तरूपेण (गुप्तरूप से)
आख्याति = कथयति (कहते हो) पृच्छति च = प्रश्नयति च (पूछते हो) भुङक्ते = खादति (खाते हो) भोजयते च= खादयति च (खिलाते हो) च एव = (और ही प्रकारकं (छः प्रकार के) लक्षणम् = लिङ्गम् (लक्षण) सर्वे = सकलाः (सभी) प्राणिनः = जन्तवः (जीव) समवेत स्वरेण = सम्भूत स्वरेण (एक साथ स्वरों में) मातः हे मातः (हे माता) भवती = त्वम् (तू) कथयति = वदति तु (कहती तो) सर्वथा सम्यक् = सर्व प्रकारेण सत्यमेव (सभी प्रकार से उचित) परं वयं भवती न जानीमः = परञ्च वयं त्वां न अवगच्छामः भवत्याः = तव (तुम्हारा) परिचयः = अभिज्ञता (पहचान परिचय) किम = किमस्ति (क्या है)।
सन्दर्भ-प्रसङ्गश्च – यह नाट्यांश हमारी शेमुषी पाठ्यपुस्तक के ‘सौहार्द प्रकृतेः शोभा, पाठ से उद्धृत है। प्रस्तुत नाट्यांश में लेखक प्रकृति माता को प्रवेश करवाता है, प्रकृति माता सभी को सौहार्द का उपदेश देती है।
हिन्दी अनुवादः – प्रकृतिमाता – (स्नेह के साथ) अरे अरे प्राणियो! तुम सब ही मेरी सन्तान हो, क्यों आपस में कलह कर रहे हो। वास्तव में सभी वन्य जीव एक दूसरे पर आधारित हैं। सदैव याद रखो-देता है, लेता है, गोपनीय को कहता है, पूछता है, खाता है, खिलाता है, ये छः प्रकार के प्रीति के लक्षण हैं। (सभी प्राणी समवेत स्वर में) हे माँ! आप पूर्णत उचित ही कहती हैं परन्तु हम आपको जानते नहीं है, आपका परिचय क्या है?
14 प्रकृतिमाता- अहं प्रकृतिः युष्माकं सर्वेषां जननी? यूयं सर्वे एव मे प्रियाः। सर्वेषामेव मत्कृते महत्त्वं विद्यते
यथासमयम् न तावत् कलहेन समयं वृथा यापयन्तु अपितु मिलित्वा एव मोदध्वं जीवनं च रसमयं कुरुध्वम्। तद्यथा कथितम्
प्रजासुखे सुखं राज्ञः, प्रजानां च हिते हितम्।
नात्मप्रियं हितं राज्ञः, प्रजानां तु प्रियं हितम्।।
शब्दार्थाः – प्रकृतिमाता = निसर्गजननी (प्रकृति माता) अहं प्रकृति = अहं निसर्ग (मैं प्रकृति हूँ) युष्माकंभवताम् (आपके) सर्वेषाम् समेषाम् (सभी की) जननी = जन्मदात्री (जन्मदायिनी) यूयं सर्वे एव मे प्रियाः = भवन्तः सर्वे एव मय स्निग्धा (आप सब मेरे प्रिय हैं) सर्वेषामेव समेषाम् (सबका) मत्कृते-मह्य (मुझे) महत्वं महनीयता (महानता) विद्यते = अस्ति (है) तावत् = तर्हि, तदा (तब) कलहेन = विवदमानः विवादेन (झगड़ते हुए) समयंकालं (समय को) वृथा = व्यर्थमेव (व्यर्थ ही) मा नहिं (नहीं) यापयन्तु व्यतीतं = मा कुरुत (व्यतीत मत कसे) अपितु अन्यथा (बल्कि) मिलित्वा = सम्भूय (मिलकर) एव = ही, मोदध्वं जीवनं च = जीवनस्य आनन्दं अनुभवत् (जीवन का आनन्द लो) रसमयं च. = मधुरं च (और रसमय जीवन) कुरुध्वम् कुरुत् (करो) तद्यथा = तदेनं (वह इस प्रकार से) कथितम् उक्तम् (कहा गया है) प्रजासुखे-प्रजा यदि सुखं लभते (प्रजा यदि सुख पाती है) (तर्हि-तो) राज्ञः सुखम् = नृपस्य अपि सौख्यम् (राजा का भी गुख होता है) प्रजानां = प्रजाजनानां (प्रजाजनों के) हिते हितम् = लाभेलाभम् (लाभ में लाभ है) नात्मप्रियंन = स्वार्थी, आत्मलाभे निरतं (अपने हित में रत) राज्ञः = नृपस्य (राजा के) प्रजानां = प्रजाजनानाम् (प्रजा का) हितम् = लाभः (लाभ) प्रियं न = प्रियं न भवति। तेभ्यः स्वार्थमेव = प्रियं भवति (उनका स्वार्थ ही प्रिय होता है)।
सन्दर्भ-प्रसङ्गश्च – यह नाट्यांश हमारी पाठ्यपुस्तक ‘शेमुषी’ के ‘सौहार्द प्रकृतेः शोभा’ पाठ से लिया गया है। इस अंश में प्रकृतिमाता अपने और प्राणियों के सम्बंध का वर्णन करती है तथा आनन्द का मार्ग दर्शाती है।
हिन्दी अनुवादः-प्रकृतिमाता- मैं प्रकृति तुम्हारी सभी की जन्मदात्री हूँ। तुम सब ही मेरे प्रिय हो। यथासमय तुम सभी को मेरे प्रति महत्व है तो कलह से व्यर्थ समय मत गँवाओ, अपितु मिलकर के ही प्रसन्न रहो और जीवन को रसमय करो। तो जैसा कहा मया है-प्रजा के सुख में ही राजा का सुख है, प्रजा के हित में ही राजा का हित है। राजा का हित आत्मप्रिय नहीं होता अपितु प्रजा का हित ही प्रिय होता है।

15 अपि च –
अगाधजलसञ्चारी न गर्वं याति रोहितः। अगुष्ठोदकमात्रेण शफरी फुफुरायते।। अत: भवन्तः सर्वेऽपि शफरीवत् एकैकस्य गुणस्य चर्चा विहाय’- मिलित्वा प्रकृतिसौन्दर्याय वनरक्षायै च प्रयतन्ताम्। सर्वे प्रकृतिमातरं प्रणमन्ति मिलित्वा दृढ़संकल्पपूर्वकं च गायन्ति प्राणिनां जायते हानिः परस्परविवादतः।
अन्योन्यसहयोगेन लाभस्तेषां प्रजायते।।
शब्दार्थाः – अपि च = और भी, अगाध अथाह (अथाह), जलसञ्चारी = तोये विचरन्ती (अथाह जल में विचरण करने वाली), रोहित: = रोहित मत्स्य, मृगमीनः (रोहित नाम की मछली) न गर्वं याति = अभिमानं न प्राप्नोति (अभिमान नहीं करती है), परञ्च = परन्तु, अङ्गुष्ठोदकमात्रेण = वृद्धाङ्गुलि मात्रेण उदकेन (अँगूठा की बराबर गहरे पानी में) शफरी = लघुमत्स्य (छोटी मछली शफरी) फुर्फरायते = गर्वेण उद्विग्ना भवति (फरफराती है) अतः = अतएव (इसलिए) भवन्तः = यूयम् (तुम) सर्वेऽपि = सकलाः एव (सभी) सफरीवत् = सफरी मत्स्य इव (शफरी मछली की तरह) एकैकस्य एकस्य एकस्य (एक एक के) गुणस्यवैशिष्ट्यम् (गुण की) चर्चा = संवादे (चर्चा को) विहायः त्यक्त्वा (त्यागकर) मिलित्वा = सम्भूय (एकत्र होकर) प्रकृति सौन्दर्या य च = प्रकृतेः निसर्गस्य वा सुन्दरतायै (प्रकृति की सुन्दरता के लिए)
वनरक्षायै च = काननं संरक्षाय, त्रातुं वा (वन की रक्षा के लिए) प्रयतन्ताम् = प्रयासं कुर्वन्तु, प्रयस्यन्ताम् (प्रयत्न करें) सर्वे सकलाः (सभी) प्रकृति मातरम् = निसर्ग जननी (प्रकृति माता को) प्रणमन्ति = नमन्ति (नमस्कार करते हैं, झुकते हैं) मिलित्वा = सम्भूय (मिलकर) दृढसङ्कल्पपूर्वकम् = वद्धपरिकरम् (कटिवद्ध हुए को) पूर्वकम् = युक्तम् (युक्त, उचित) च गायन्ति = सस्वरं उच्चरानेन (सस्वर उच्चारण करते हैं) प्राणिनो = जन्तूनाम् (प्राणियों की) हानिः = क्षया (नुकसान) जायते = भवति (होती है) परस्पर विवादतः = मिथः विवादात् (परस्पर विवाद से) अन्योन्य = परस्पर, मिथ (आपसी सहयोग से) तेषाम् = अमीषाम् (उनका) लाभ: = हित (लाभ) प्रजायते = प्रभवति (होता है)।
सन्दर्भ-प्रसङ्गश्च – यह नाट्यांश हमारी पाठ्य पुस्तक ‘शेमुषी’ के ‘सौहार्द प्रकृतेः शोभा’ पाठ से लिया गया है। इस नाट्यांश में प्रकृति माता उपदेश (सन्देश) देती है कि विवाद में लोगों की हानि तथा परस्पर सहयोग से ही लाभ है।
हिन्दी अनुवादः – और भी-अगाध जल में विचरण करने वाली रोहित मछली तो गर्व नहीं करती है (परन्तु) मात्र अँगूठे के बराबर गहरे पानी में शफरी मछली (घमण्ड से) फरफराती है। अतः आप सभी शफरी की तरह से एक-एक गुण की चर्चा त्यागकर मिल करके प्रकृति सौन्दर्य के लिए और वन की रक्षा के लिए प्रयत्न करो। सभी प्रकृति माता को प्रणाम करते हैं, मिलकर पूर्ण (दृढ़) संकल्पपूर्वक गाते हैं-आपस में विवाद करने से प्राणियों की हानि होती है तथा एक-दूसरे के सहयोग से उनका लाभ होता है।
![]()
![]()
![]()