JAC Board Class 8th Social Science Solutions Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture
JAC Class 8th Geography Agriculture InText Questions and Answers
Page 43
Question 1.
Who discovered the coffee plant?
Answer:
In about AD 850, Kaldi, an Arab goat- herder, who was puzzled by the queer antics of his flock, tasted the berries of the evergreen bush on which the goats were feeding. On experiencing a sense of exhilaration, he proclaimed his discovery to the world.
JAC Class 8th Geography Agriculture Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Answer the following questions.
(i) What is agriculture?
Answer:
Agriculture is a primary activity which includes growing crops, fruits, vegetables, flowers and rearing of livestock. It is also known as farming.
(ii) Name the factors influencing agriculture?
Answer:
The factors influencing agriculture are the climate and topography of soil.
(iii) What is shifting cultivation? What are its disadvantages?
Answer:
Shifting cultivation is also known as slash and bum agriculture. In this cultivation a plot of land is cleared by felling the trees and burning them. Then the ashes are mixed with the soil and crops are grown. The land is abandoned after the soil loses its fertility and the cultivator moves to a new plot. The disadvantages are deforestation occurs and trees are burnt which are not good for environment.
![]()
(iv) What is plantation agriculture?
Answer:
Commercial farming where only a single type of crop is grown such as banana, coffee, tea, sugarcane is known as plantation agriculture. In this type of agriculture, large amount of capital and labour are required The produce is either processed in the farm itself or in i nearby factories.
(v) Name the fibre crops and name the climatic conditions required for their growth.
Answer:
The fibre crops are cotton and jute. The climatic conditions required for their growth are:
Cotton requires high temperature, light rainfall, 210 days and bright sunshine for its growth. Jute requires high temperature, heavy rainfall and humid climate.
Tick the correct answer.
Question 2.
(i) Horticulture means
(a) growing of fruits and vegetables
(b) primitive farming
(c) growing of wheat
Answer:
(a) growing of fruits and vegetables
(ii) Golden fibre refers to
(a) tea
(b) cotton
(c) jute
Answer:
(c) jute
(iii) Leading producers of coffee
(a) Brazil
(b) India
(c) Russia
Answer:
(a) Brazil
Question 3.
Give reasons.
- In India agriculture is a primary activity.
- Different crops are grown in different regions.
Answer:
1. In India agriculture is a primary activity because two third of the population depends on agriculture and it provides around 65% of work to labour force. It is also responsible for 25% of Gross Domestic Product and total value of nation’s export is 16%.
2. Since different crops require different climatic and geographical conditions hence different crops are grown in different regions. Certain human factors also play an important role such as labour, demand of yield and technology level.
Question 4.
Distinguish between the followings.
- Primary activities and tertiary activities.
- Subsistence farming and intensive farming.
Answer:
1.
| Primary activities | Tertiary Activities |
| It includes all those connected with extraction and production of natural resources. | It provides support to the primary and secondary sectors through services. |
| Agriculture, fishing and gathering are examples of this activity. | Transport, trade, banking, insurance and advertising are examples of this activities. |
2.
| Subsistence Farming | Intensive Farming |
| It is practised to meet the needs of the farmer’s family. | The farmer cultivates a small plot of land using simple tools and more labour. |
| Low levels of technology and household labour are used to produce on vsmall output. | In this type of farming, quality seeds, rich manure and fertilisers are used |
Question 5.
Activity
- Collect seeds of wheat, rice, jowar, bajra, ragi, maize, oilseeds and pulses available in the market. Bring them to the class and find out in which type of soil they grow.
- Find out the difference between the life style of farmers in the USA and India on the basis of pictures collected from magazines, books, newspapers and the internet.
Answer:
- Type of soil in which the following grows:
Rice – Alluvial clayey Wheat – Alluvial soil Jowar, bajra and ragi – Desert Maize, oilseeds – Alluvial, Black Pulses- Red, Alluvial - Students need to do on their own.
Question 6.
For Fun.
Solve the crossword puzzle with the help of given ciues
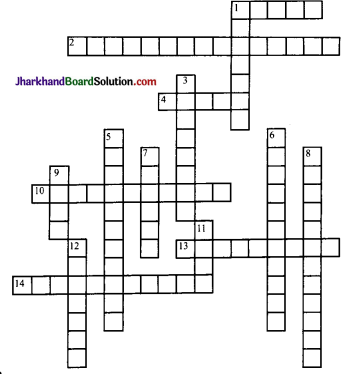
Across:
1. Crop that needs well drained fertile soils, moderate temperatures and lots of sunshine (5)
2. Increasing production through use of HYV seeds, chemical fertilisers and pesticides (5,10)
4. USA, Canada, Russia, Australia are major producers of this crop (5)
10. Type of farming to meet family needs (11)
13. Rearing of animals for sale (9)
14. Growing grapes for wines (11)
Down:
1. Coarse grains are also called (7)
3. Cultivation involving slash and bum (8)
5. Growing of crops, fruits and vegetables (11)
6. Tea, coffee, sugarcane and mbber are grown in (11)
7. Requires 210 frost-free days for growth (6)
8. Growing of flowers (12)
9. Also called ‘Golden Fibre’ (4)
11. Also known as paddy (4)
12. Activity concerned with extraction of natural resources (7)
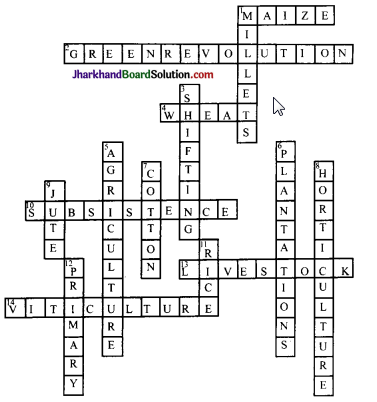
Answer:
JAC Class 8th Geography Agriculture Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
The process in which farmers use organic manure and natural pesticides instead of chemicals is called
(a) Mechanical farming
(b) Non-organic farming
(c) Organic farming
(d) All of these
Answer:
(c) Organic farming
Question 2.
Thescienceofcommercially cultivating grapes is called .
(a) Viticulture
(b) Horticulture
(c) Sericulture
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Viticulture
![]()
Question 3.
Tertiary activities are……
(a) provide support to only primary activities.
(b) provide support to only secondary activities.
(c) provide support to both primary and secondary activities.
(d) none of these
Answer:
(c) provide support to both primary and secondary activities.
Question 4.
Coarse grains are….. .
(a) rice
(b) millets
(c) wheat
(d) all of these
Answer:
(b) millets
Question 5.
The word ‘agriculture’ origins from
a. Latin term agri means soil.
(b) Latin term culture means cultivation.
(c) Neither a nor b
(d) Both a and b
Answer:
(d) Both a and b
Question 6.
The inputs of a farm system are…….
(a) seeds and fertiisers
(b) labour
(c) machinery
(d) all of these
Answer:
(d) all of these
Question 7.
Out of the following which is not a cropping season of India?
(a) Kaffir
(b) Rabi
(c) Kharif
(d) Zaid
Answer:
(a) Kaffir
Question 8.
Jhumming, Ladang, Milap, Roca & Ray are also known as:
(a) Shifting Farming
(b) Commercial Farming
(c) Nomadic Farming
(d) Intensive Farming
Answer:
(a) Shifting Farming
Question 9.
………. is……. grown in winter. It requires rainfall during growing season and bright sunshine at the time of harvest.
(a) Rice
(b) Watermelon
(c) Wheat
(d) Bajra
Answer:
(c) Wheat
Question 10.
The land on which crops are grown is known as:
(a) Wet Land
(b) Arable Land
(c) Dry Land
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Arable Land
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by agricultural development?
Answer:
Agricultural development refers to efforts made to increase the production of farm in order to meet the growing demand of the increasing population.
Question 2.
What is the science of commercial silk worm rearing known as?
Answer:
The science of commercial silk worm rearing is known as Sericulture.
![]()
Question 3.
What is the position of India in terms of rice production in the world?
Answer:
India is the second largest producer of rice in the world.
Question 4.
What percentage of world’s coffee production does India produce?
Answer:
The percentage of world’s coffee production does India produce is 3.2%.
Question 5.
Name the two most important staple food crops of the world.
Answer:
The two most important staple food crops of the world are rice and wheat.
Question 6.
What requires high temperature, light rainfall, 210 frost-free days and bright sunshine?
Answer:
Cotton requires high temperature, light rainfall, 210 frost-free days and bright sunshine.
Question 7.
List some animals reared by nomadic herders.
Answer:
Sheep, camel, yak and goats are most commonly reared animals by nomadic . herders.
Question 8.
How many types of subsistence farming is present?
Answer:
Two types of subsistence farming are there. They are intensive subsistence and primitive subsistence farming.
Question 9.
What do you mean by mixed farming?
Answer:
n mixed farming the land is used for growing food and fodder crops and rearing livestock.
![]()
Question 10.
Where is wheat grown extensively and substantially?
Answer:
Wheat is grown extensively and substantially in USA, Canada, Argentina, Russia, Ukraine, Australia and India.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1. What are the activities under the secondary sector?
Answer:
All activities connected with the manufacturing of goods with natural resources comes under secondary activities. Steel manufacturing, weaving cloth are the examples of secondary activities.
Question 2.
There are different kinds of cultivation. What are they?
Answer:
The different kinds of cultivation are Agriculture, Horticulture, Viticulture, Sericulture and Pisciculture.
- Agriculture is cultivation on the soil.
- Horticulture is growing vegetables, fruits and flowers for commercial use.
- Viticulture is cultivation of grapes.
- Sericulture is rearing of silk worms to extract silk.
- Pisciculture is breeding of fish in specially constructed tanks and ponds.
Question 3
Shifting cultivation is known by different names in different regions of the world What are they?
Answer:
Shifting cultivation is known by different names in different parts of the world They are:
- Jhumming – North-East India
- Milpa -Mexico
- Roca – Brazil
- Ladang – Malaysia
Question 4.
When does food security exist?
Answer:
Food security exists when all people, at all times, have access to sufficient, safe and nutritious food to meet their dietary needs and food preferences for an active and healthy life.
Question 5.
What are the climatic conditions required for growing maize? In which countries they are grown?
Answer:
Maize requires moderate temperature, rainfall and lots of sunshine. It also needs well drained fertile soil. They are grown in North America, Brazil, China, Russia, India, Canada and Mexico.
Question 6.
What are the climatic conditions required for growing tea?
Answer:
Tea is a beverage crop grown on plantations. This requires cool climate and well distributed high rainfall throughout the year for the growth of its tender leaves. It needs well-drained loamy soils and gentle slopes. To pick the leaves, labour in large number is required.
![]()
Question 7.
Can agricultural development be achieved? How?
Answer:
Yes, agricultural development can be achieved in many ways such as increasing the cropped area, the number of crops grown, improving irrigation facilities, use of fertilisers and high yielding variety of seeds. Mechanisation of agriculture is also another aspect of agricultural development.
Question 8.
What type of agriculture is practiced in developing countries?
Answer:
Developing countries with large populations usually practise intensive agriculture where crops are grown on small holdings mostly for subsistence.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are the different types of subsistence farming?
Answer:
The different types of subsistence farming are intensive subsistence and primitive subsistence farming:
(i) Intensive subsistence agriculture:
In intensive subsistence agriculture the farmer cultivates a small plot of land using simple tools and more labour. The main crop is rice. Other crops include wheat, maize, pulses and oilseeds. Intensive subsistence agriculture is prevalent in the thickly populated areas of the monsoon regions of south, south-east and east Asia.
(ii) Primitive subsistence agriculture:
It includes shifting cultivation and nomadic herding.Shifting cultivation is practised in the thickly forested areas of Amazon basin, tropical Africa, parts of south-east Asia and north-east India. A plot of land is cleared by felling the trees and burning them. The ashes are then mixed with the soil and crops like maize, yam, potatoes and cassava are grown. After the soil loses its fertility, the land is abandoned and the cultivator moves to a new plot.
Nomadic herding is practised in the semi-arid and arid regions of Sahara, Central Asia and some parts of India, like Rajasthan and Jammu and Kashmir. In this type of farming, herdsmen move from place to place with their animals for fodder and water, along defined routes.