JAC Board Class 10th Social Science Important Questions Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
What proportion of the Indian population is engaged in agriculture?
(a) One-third
(b) Two-fourths
(c) Three-fourths
(d) Two-thirds
Answer:
(d) Two-thirds
Question 2.
Which of the following is a plantation crop?
(a) Rice
(b) Bajra
(c) Rubber
(d) Wheat
Answer:
(c) Rubber
![]()
Question 3.
Which of this is a zaid season crop?
(a) Maize
(b) Cucumber
(c) Groundnut
(d) Peas
Answer:
(b) Cucumber
Question 4.
Which country is the second largest producer of rice in the world after China? *
(a) India
(b) Japan
(c) Philippines
(d) Pakistan
Answer:
(a) India
5. Which crop is used both as food and fodder?
(a) Wheat
(b) Cotton
(c) Rice
(d) Maize
Answer:
(d) Maize
Question 6.
Which crop is a kharif crop in the north and rabi crop in south India?
(a) Wheat
(b) Sesamum
(c) Tea
(d) Cotton
Answer:
(b) Sesamum
Question 7.
What is the rearing of silkworms known as?
(a) Pisciculture
(b) Agriculture
(c) Sericulture
(d) Horticulture
Answer:
(c) Sericulture
![]()
Question 8.
Which was one of the strategies initiated to improve the lot of Indian agriculture?
(a) Revolution 2020
(b) White Revolution
(c) Operation Desert Storm
(d) Operation Blue Star
Answer:
(b) White Revolution
Question 9.
Which is one of the schemes introduced by the Government of India for the benefit of the farmers?
(a) Agenda 21
(b) Agglomeration economies
(c) Personal Accident Insurance Scheme (PAIS)
(d) Golden Question uadrilateral Super Highways
Answer:
(c) Personal Accident Insurance Scheme (PAIS)
Question 10.
Which movement was initiated by Vinoba Bhave?
(a) Operation Flood
(b) Bhoodan-Gramdan
(c) Green Revolution
(d) Tehri Dam Andolan
Answer:
(b) Bhoodan-Gramdan
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Why is the land productivity low in primitive subsistence farming?
Answer:
The land productivity is low in primitive subsistence farming because the farmer does not use fertilisers or other modem inputs.
Question 2.
Where is primitive subsistence farming practised?
Answer:
Primitive subsistence farming is practised in north-eastern states, such as Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram, Nagaland and Manipur; Bastar district of Chhattisgarh; Jharkhand, Andhra Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh, Odisha, Western Ghats, south-eastern Rajasthan, Himalayan belt and in Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Question 3.
In which area is intensive subsistence farming practised?
Answer:
Intensive subsistence farming is practised in the areas of high population.
Question 4.
Mention the climatic factor which helps in the success of rabi crops.
Answer:
The western temperate cyclones bring precipitation during winter months, which helps in the success of rabi crops.
![]()
Question 5.
Name the three crops of paddy grown in a year and in which states of India are they grown?
Answer:
Aus, Aman and Bow are three crops of paddy grown in a year. They are grown in Assam, West Bengal and Odisha.
Question 6.
How has it become possible to grow rice in the areas of less rainfall?
Answer:
It has become possible to grow rice in the areas of less rainfall, such as Punjab, Haryana, western Uttar Pradesh and parts of Rajasthan with the development of dense network of canal irrigation and tube wells.
Question 7.
What type of soil is required for growing bajra?
Answer:
Bajra grows well on sandy soils and shallow black soil.
Question 8.
Name the major maize-producing states.
Answer:
The major maize-producing states are Karnataka, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, Andhra Pradesh and Madhya Pradesh.
Question 9.
Why is tea processed within the tea garden?
Answer:
Tea is processed within the tea garden to restore its freshness.
![]()
Question 10.
Where is rubber grown?
Answer:
Rubber is mainly grown in Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, Garo Hills of Meghalaya, and Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe ‘slash and burn’ agriculture.
Answer:
In ‘slash and bum’ agriculture, a farmer clears’a patch of land and grows cereals and other food crops to sustain his family. When the fertility of the soil decreases, the farmer shifts to another area and clears a fresh patch of land. This shifting allows the nature to replenish the soil through natural processes. Primitive tools are used, and family or community labours are involved. Farmers depend on monsoon, natural fertility of the soil and other environmental conditions required for the crops to be grown. The productivity is low, fertilisers or other modem inputs are not used.
Question 2.
What are the various terms used for ‘slash and burn’ agriculture in various parts of the country and the world?
Answer:
It is known as Jhumming in the north¬eastern states like Assam, Meghalaya, Mizoram and Nagaland; Pamlou in Manipur, Dipa in Bastar district of Chhattisgarh and Andaman and Nicobar Islands. It is known as Dahiya or Bewar in Madhya Pradesh, Podu or Penda in Andhra Pradesh; Pama Dabi, Koman or Bringa in Odisha, Kumari in Western Ghats, Valre or Waltre in South-eastern Rajasthan, Khil in the Himalayan belt and Kuruwa in Jharkhand.
Question 3.
What is intensive subsistence farming? Why there is immense pressure on agricultural land in this type of farming?
Answer:
Intensive subsistence farming is labour-intensive farming. High doses of biochemical inputs and irrigation are used to obtain higher production. This type of farming is practised in the areas of high population. The ‘right of inheritance’ has led to division of land among successive generations, which has rendered land-holding size uneconomical. However, the farmers continue to extract maximum output from the limited land in the absence of alternative source of livelihood. Therefore, there is a tremendous pressure on agricultural land in this type of farming.
Question 4.
Discuss the characteristics of commercial farming.
Answer:
Commercial farming includes the use of higher doses of modem inputs, e.g., high yielding variety (HYV) seeds, chemical fertilisers, insecticides and pesticides in order to obtain higher productivity. The degree of commercialisation of agriculture varies from one region to another. For example, rice is a commercial crop in Haryana and Punjab, but in Odisha, it is a subsistence crop. Plantation is also a type of commercial farming.
![]()
Question 5.
What are the features of plantation agriculture?
Answer:
Plantation is a type of commercial farming. In this type of farming, a single crop is grown on a large area. It has an interface of agriculture and industry. Plantations cover large tracts of land, using capital-intensive inputs, with the help of migrant labourers. All the produce is used as raw material in respective industries. As the production is only for the market, a well-developed network of transport and communication connecting the plantation areas, processing industries and markets plays an important role in the development of plantations.
Question 6.
Give the geographical conditions required for the growth of rice. In which states is rice grown?
Answer:
Rice is a kharif crop. It grows in high temperature, above 25°C and high humidity with annual rainfall above 100 cm. In the areas of less rainfall, it grows . with the help of irrigation. Rice is grown in the plains of north and north-eastern India, coastal areas and the deltaic regions. Development of dense network of canal irrigation and tube wells has iffade it possible to grow rice in the areas of less rainfall, such as Punjab, Haryana and western Uttar Pradesh and parts of Rajasthan.
Question 7.
Why are pulses grown in rotation with other crops? What is the rank of India in the world in pulse production and name the various pulses and states growing them.
Answer:
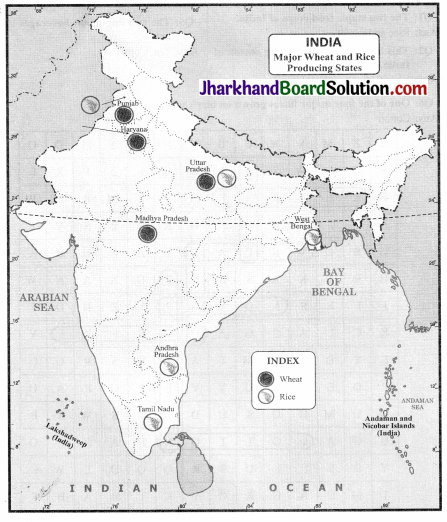
Except arhar, all pulses are leguminous crops. They help in restoring soil fertility by fixing nitrogen from the air. These pulses are grown in rotation with other crops. India is the largest producer as well as consumer of pulses in the world. These are the major sources of protein in a vegetarian diet. Major pulses grown in India are tur, urad, moong, masur, peas and gram. Major pulse producing states of India are Madhya Pradesh, Uttar Pradesh, Rajasthan, Maharashtra and Karnataka.
Question 8.
What type of soil and climatic conditions are required for growing rubber? Where is it grown and discuss its use.
Answer:
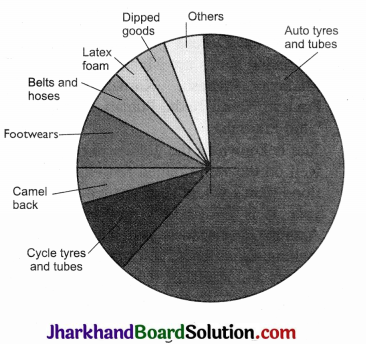
Rubber requires moist and humid climate with rainfall more than 200 cm and temperature above 25°C. It is mainly grown in Kerala, Tamil Nadu, Karnataka, and Andaman and Nicobar Islands and Garo hills of Meghalaya. Rubber has various uses. It is an important industrial raw material. It is used for making cycle tyres and tubes, auto tyres and tubes, camel back, footwears, belts and hoses, latex foam, dipped goods, and other products.
Question 9.
Specify the geographical conditions required for the growth of cotton. In which states is cotton grown?
Answer:
Cotton is a kharif crop and requires 6 to 8 months to grow. It needs high temperature, light rainfall, 210 frost-free days and bright sunshine for its growth. Cotton grows well in drier parts of the black cotton soil of the Deccan plateau. Major cotton producing states are Maharashtra, Gujarat, Madhya Pradesh, Karnataka, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, Punjab and Uttar Pradesh.
![]()
Question 10.
Write a short note on fibre crops.
Answer:
Four major fibre crops grown in India are cotton, jute, hemp and natural silk. While cotton, jute and hemp are crops grown in the soil, silk is obtained from cocoons of silkworms fed on green leaves, especially mulberry. Rearing of silkworms for the production of silk fibre is known as sericulture.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Distinguish between rabi, kharif and zaid cropping seasons.
| Rabi crops | Kharif crops | Zaid crops |
| (i) These are sown in winter from October to December. | (iii) These are sown with the onset of monsoon in different parts of the country. | (ii) In between the rabi and kharif seasons, there is a short season during summer months, known as the zaid season. |
| (ii) Wheat, barley, peas, gram, mustard are rabi crops. | (ii) Paddy, maize, jowar, bajra, tur, moong, urad, cotton, jute, groundnut, soyabean are kharif crops. | (ii) Watermelon, muskmelon, cucumber, vegetables and fodder crops are zaid crops. Sugarcane takes a year to grow. |
| (iii) These are harvested in summer from April to June. | (iii) These are harvested in September-October. |
Question 2.
Write the conditions required for growing sugarcane. What are the uses of sugarcane? Name the sugarcane producing states.
Answer:
Sugarcane is a tropical as well as a subtropical crop. ,
- It grows well in hot and humid climate with a temperature of 21°C to 27°C and an annual rainfall between 75 cm and 100 cm.
- Irrigation is required in regions of low rainfall. ‘
- It can grdw on a variety of soil.
- It needs manual labour from sowing to harvesting. It is-the main source of sugar, gur (jaggery), khandsari and molasses. The major sugarcane producing states are Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, Bihar, Punjab, and Haryana.
Question 3.
Name the different types of oilseeds grown in India and its uses. Identify the kharif and rabi oilseeds.
Answer:
Different types of oilseeds are grown covering approximately 12 per cent of the total cropped area of the country. Major oilseeds produced in India are groundnut, mustard, and coconut, sesame (til), soyabean, castor seeds, cotton seeds, linseed and sunflower seeds. Most of the oilseeds are edible and used as cooking mediums.
Some of them are also used as raw material in the production of soap, cosmetics and ointments. Groundnut is a kharif crop. Linseed and mustard are rabi crops. Sesame is a kharif crop in north and rabi crop in south India. Castor seed is grown both as rabi and kharif crop.
![]()
Question 4.
Mention the geographical conditions favourable for tea cultivation. Name the states where tea plantations are found.
Answer:
Tea grows well in tropical and subtropical climates.
- Tea requires deep and fertile well-drained soil, rich in humus and organic matter.
- Tea bushes require warm and moist frost- free climate all through the year.
- Frequent showers evenly distributed over the year ensure continuous growth of tender leaves.
- It is processed within the tea garden to restore its freshness. Major tea producing states are Assam, hills of Darjeeling and Jalpaiguri districts of West Bengal, Tamil Nadu and Kerala. Apart from these, Himachal Pradesh, Uttarakhand, Meghalaya, Andhra Pradesh and Tripura also produce tea.
Question 5.
Describe the technological and institutional reforms in agriculture in India after Independence.
Answer:
Agriculture which provides livelihood for more than 60 per cent of its population needed some serious technical and institutional reforms. Government introduced the reforms in the J 960s and 1970s.
- Collectivisation, consolidation of holdings, cooperation and abolition of zamindari, etc. were given priority to bring institutional reforms in the country after independence.
- Land teform was the main focus of the First Five-Year Plan.
- Green Revolution based on the use of package technology and White Revolution (Operation Flood) were some of the strategies initiated to improve Indian agriculture.
- In the 1980s and 1990s, a comprehensive land development programme was initiated, which included both institutional and technical reforms.
- Steps like provision for crop insurance against drought, flood, cyclone, fire and disease, establishment of Grameert banks, cooperative societies and loan facilities for farmers by banks at low interest rates were taken.
- Kisan Credit Card (KCC) and Personal Accident Insurance Scheme (PAIS) were schemes introduced by the Government of India for the benefit of the farmers.
- Special weather bulletins and agricultural programmes were broadcasted on television and radio.
- The government has also announced minimum support price, remunerative and procurement prices for important crops to check the exploitation of farmers by speculators and middlemen.
Question 6.
Discuss the Bhoodan-Gramdan movement initiated by Vinoba Bhave.
Answer:
Vinoba Bhave was one of the votaries of Gandhi’s concept of gram swarajya. In Andhra Pradesh, few landless villagers demanded land for their economic well-being. Vinoba Bhave assured that he would talk to the Government of India regarding provision of land if they undertook cooperative farming. Shri Ram Charan Reddy offered 80 acres of land to be distributed among the landless villagers. This was known as Bhoodan. Some zamindars offered to distribute villages among the landless. This was known as Gramdan. Many landowners, in fear of land ceiling act, chose to provide some part of their land to the poor farmers. This was known as Bhoodan-Gramdan movement or Blood-less Revolution.
Activity Based Questions
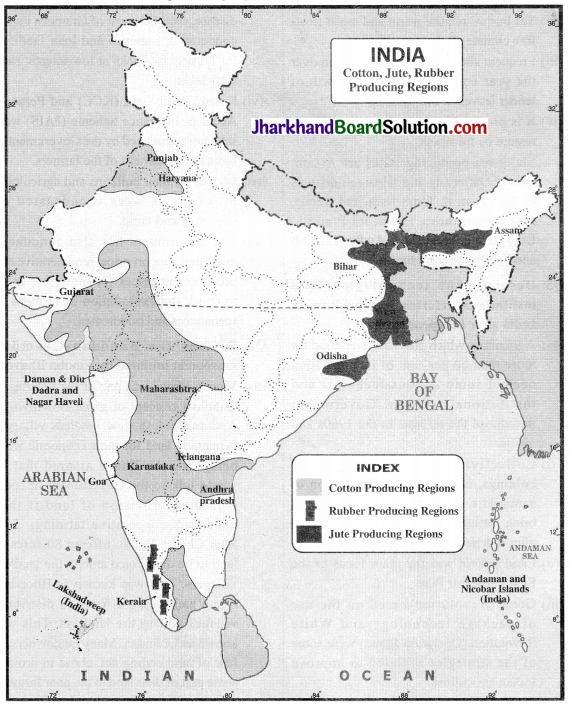
Question 1.
On a political map of India, mark the cotton, jute and rubber producing regions.
Answer:
Jute, cotton and rubber producing regions
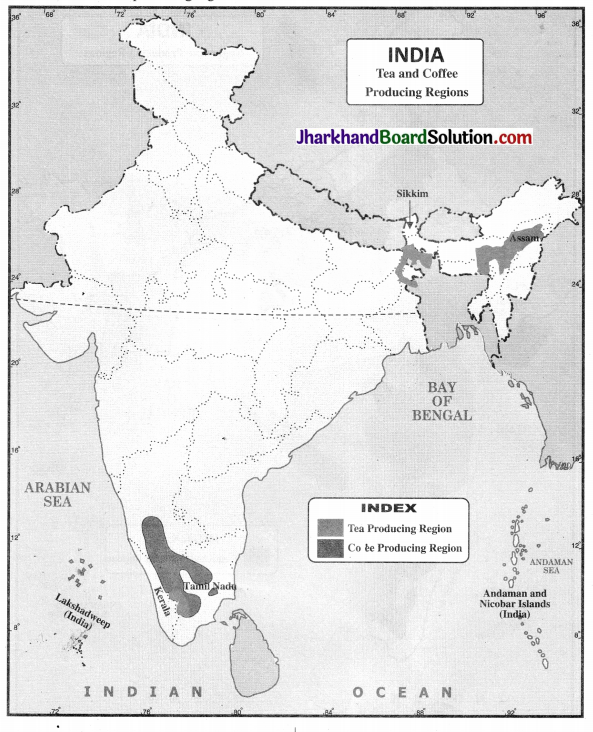
Question 2.
On a political map of India, mark the tea and coffee producing regions of India.
Answer:
Tea and coffee producing regionsg.
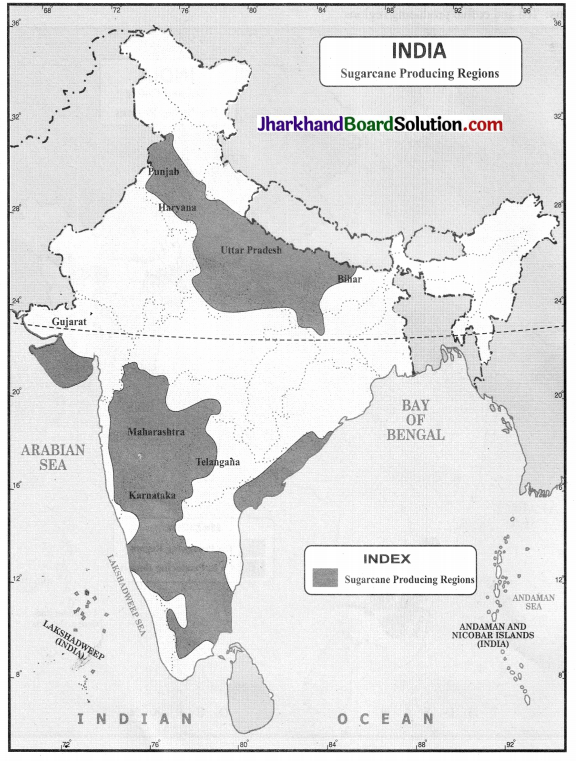
Question 3.
On a political map of India, mark the sugarcane producing regions of India.
Answer:
Sugarcane producing regions
Question 4.
Study the picture carefully and answer the following questions:

(a) Who introduced tea plantation in India?
(b) What type of labour is required for this industry or plantation?
(c) What is the rank of India in tea production in the world?
Answer:
(a) Tea cultivation was introduced in India by the British.
(b) Abundant, cheap and skilled labour is required for this industry.
(c) As per 2015-16 records, India was the second largest producer of tea after China.
Question 5.
Study the pictures carefully and answer the following questions:

(a) What is the rank of India in fruits and vegetables production in the world?
(b) Where are apples, pears, apricots and walnuts grown?
(c) Name the vegetables grown in India.
Answer:
(a) India ranks second in fruits and vegetables production in the world, after China.
(b) Apples, pears, apricots and walnuts are grown in Jammu and Kashmir, and Himachal Pradesh.
(c) India is an important producer of pea, cauliflower, onion, cabbage, tomato, brinjal and potato.