JAC Board Class 10th Social Science Solutions Geography Chapter 4 Agriculture
JAC Class 10th Geography Agriculture InText Questions and Answers
Page 34
Question 1.
Can you name some industries based on agricultural raw material?
Answer:
Few industries based on agricultural raw materials are the oilseed industry, jute and cotton industry, woollen and textile industry, paper industry and food processing units.
Question 2.
Can you name some such types of farmings?
Answer:
Jhumming: The ‘slash and burn’ agriculture is known as ‘Milpa’ in Mexico and Central America, ‘Conuco’ in Venzuela, ‘Roca’ in Brazil, ‘Masole’ in Central Africa, ‘Ladang’ in Indonesia, ‘Ray’ in Vietnam. In India, this primitive form of cultivation is called ‘Bewar’ or ‘Dahiya’ in Madhya Pradesh, ‘Podu’ or ‘Penda’ in Andhra Pradesh, ‘Pama Dabi’ or ‘Roman’ or Bringa’ in Odisha, ‘Kumari’ in Western Ghats, ‘Valre’ or ‘Waltre’ in South-eastern Rajasthan, ‘Khil’ in the Himalayan belt, ‘Kuruwa’ in Jharkhand, and ‘Jhumming’ in the Northeastern region.
Poge 35
Question 3.
Rinjha lived with her family in a small village at the outskirts of Diphu in Assam. She enjoys watching her family members clearing, slashing and burning a patch of land for cultivation. She often helps them in irrigating the fields with water running through a bamboo canal from the nearby spring.
She loves the surroundings and wants to stay here as long as she can, but this little girl has no idea about the declining fertility of the soil and her family’s search for fresh a patch of land in the next season. Can you name the type of farming Rinjha’s family is engaged in?
Answer:
Rinjha’s family is engaged in ‘slash and bum’ or jhumming agriculture.
![]()
Question 4.
Can you enlist some crops which are grown in such farming?
Answer:
Crops such as jowar, millet, cassava, com, beans, etc. are grown.
Question 5.
Can you name some of the states of India where intensive subsistence farming is practised?
Answer:
Intensive subsistence farming is practised in Punjab, some parts of Rajasthan, Uttar Pradesh, Madhya Pradesh and Haryana.
Question 6.
Can you give some more examples of crops which may be commercial in one region and may provide subsistence in another region?
Answer:
While wheat is grown on a large scale as a commercial crop in Punjab, Haryana and Uttar Pradesh, it is grown as a subsistence crop in eastern states like Bihar and West Bengal.
Page 42
Question 7.
List the items w hich are made of rubber and are used by us.
Answer:
Rubber is an important industrial raw material. It is used for a variety of purposes
Page 45
Question 8.
Can you name any gene-modified seed used vastly in India?
Answer:
Cotton is the only gene-modified see vastly used in India
![]()
Question 9.
Change in cropping patterns, for example, from cereals to high-value crops will mean that India will have to import food. During 1960s this would have been seen as a disaster. But if India imports cereals while exporting high-value commodities, it will be following successful economies like Italy, Israel and Chile. These countries export farm products (fruits, olives, especially seeds and wine) and import cereals. Are we ready to take this risk? Debate the issue.
Answer:
Self-help.
Hints:
- India can take this risk with the assistance from the government.
- Some government-owned land or cooperatives can be involved in the beginning for trial.
- If the crop production is successful and there is a good sale, then gradually the cropping pattern can be changed.
- Farmers need to be educated on the techniques of cultivating high-value crops
JAC Class 10th Geography Agriculture Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Choose the right answer from the four alternatives given below.
(i) Which one of the following describes a system of agriculture where a single crop is grown on a large area?
(a) Shifting agriculture
(b) Plantation agriculture
(c) Horticulture
(d) Intensive agriculture
Answer:
(b) Plantation agriculture
(ii) Which one of the following is a rabi crop?
(a) Rice
(b) Gram
(c) Millets
(d) Cotton
Answer:
(b) Gram
(iii) Which one of the following is a leguminous crop?
(a) Pulses
(b) Jowar
(c) Millets
(d) Sesamum
Answer:
(a) Pulses
![]()
Question 2.
Answer the following questions in 30 words.
(a) Name one important beverage crop and specify the geographical conditions required for its growth.
(b) Naitte one staple crop of India and the regions where it is produced.
(c) Enlist the various institutional reform programmes introduced by the government in the interest of farmers.
(d) The land under cultivation has got reduced day by day. Can you imagine its consequences?
Answer:
(a) Tea is an important beverage crop. It grows well in tropical and sub-tropical climates having deep and fertile well- drained soil, rich in humus and organic matter. Tea bushes require warm and moist frost-free climate all through the year. Frequent showers evenly distributed over
the year ensure continuous growth of tender leaves. It is processed within the tea garden to restore its freshness.
(b) Rice is a staple crop of a majority of the people in India. It is grown in the plains of north and north-eastern India, coastal areas and the deltaic regions. Development of dense network of canal irrigation and tube wells has made it possible to grow rice in the areas of less rainfall, such as Punjab, Haryana and western Uttar Pradesh and parts of Rajasthan.
(c) The Government of India introduced several institutional reforms for the benefit of the farmers and agriculture of India. Land reform was the main focus of our first five year plan. Collectivisation, consolidation of land holdings, cooperation and abolition of zamindari, etc. were given priority to bring institutional reforms in the country after Independence. 1980s and 1990s a land development programme was initiated, which included both institutional and technical reforms.
(d) The competition for land between non- agricultural uses such as housing, etc. and agriculture has led to reduction in net sown area. This will lead to shortage of food. Food is a basic need and every citizen of the country should have access to food which provides minimum nutritional balance. There will be a huge pressure on the country’s future food security.
Question 3.
Answer the following questions in about 120 words:
(a) Suggest the initiative taken by the government to ensure the increase in agricultural production.
(b) Describe the impact of globalisation on Indian agriculture.
(c) Describe the geographical conditions required for the growth of rice.
Answer:
(a) Various initiatives taken by the government to ensure the increase in agricultural production are:
- Collectivisation, consolidation of holdings, cooperation and abolition of Zamindari, etc., were given priority to bring about institutional reforms in the country after independence.
- Laftd Reform was the main focus of our ‘First Five Year Plan’.
- The Green Revolution was based on the use of package technology and the White Revolution were some of the strategies initiated to improve the Indian agriculture.
- provision for crop insurance against drought, floods, diseases, etc.
- Grameen Banks, Kissan Credit Card and Personal Accident Insurance Scheme are some of the reforms by the Indian Government for the benefit of the farmers.
(b) Globalisation has been existent since the time of colonisation of India. After the 1990s, the Indian farmers have been exposed to new challenges as they are not able to compete with the developed countries because of the highly subsidised agriculture in those countries.
A fewveconomists think that Indian farmers have a bleak future if they keep growing foodgrains on small landholdings for ever increasing population. Despite being an important producer of rice, cottbn, rubber, tea, coffee, jute and spices, the agricultural products are unable to face the stiff competition.
Overuse of chemicals, dying aquifers and vanishing diversity has led to land degradation. It is said that Green Revolution is responsible for it.Farmers should adopt to genetic engineering, which is recognised as a powerful supplement in inventing new hybrid varieties of seeds. Organic farming has become popular. Indian farmers should diversify their cropping pattern from cereals to high-value crops. This will increase income and reduce environmental degradation simultaneously.
![]()
(c) Rice is a kharif crop. It requires high temperature, above 25°C and high humidity with annual rainfall above 100 cm. In the areas of less rainfall, it grows with the help of irrigation. Rice grows well in the plains of north and north¬eastern India, coastal areas and the deltaic regions. Development of dense network of canal irrigation and tube wells has made it possible to grow rice in the areas of less rainfall, such as, Punjab, Haryana, and western Uttar Pradesh and parts of Rajasthan.
NCERT ‘Project’ Work
Question 1.
Group discussion on the necessity of literacy among farmers.
Answer:
Self-help Hints:
- Literacy is a must for development and progress of a country.
- Farmers of a country need proper guidance to understand the quality of their land, what is required to keep their land fertile. To know and understand this, they need to be literate.
- They need to know how to run and maintain all the farming machines and implements.
- To understand what nutrients, fertilisers and pesticides are required for their soil.
- To read and understand the terms and conditions of loans taken from various sources.
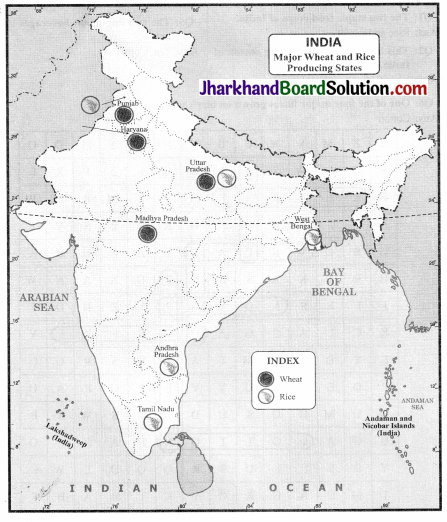
Question 2.
On an outline map of India show major wheat and rice producing states.
NCERT Activity
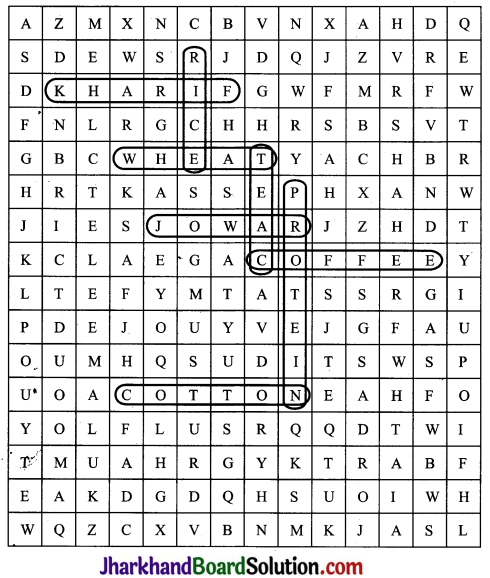
Solve the puzzle by following your search horizontally and vertically to find the hidden answers.
Question 1.
The two staple food crops of India.
Answer:
Rice and wheat
Question 2.
This is the summer cropping season of India.
Answer:
Kharif
![]()
Question 3.
Pulses like arhar, moong, gram, urad contain
Answer:
Protein
Question 4.
It is a coarse grain.
Answer:
Jo war
Question 5.
The two important beverages in India are…….
Answer:
Tea, Coffee
Question 6.
One of the four major fibres grown on black soils.
Answer:
Cotton