JAC Board Class 10th Social Science Important Questions Geography Chapter 1 Resource and Development
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Resource which can be renewed again are
(a) National resource
(b) Potential resource
(c) Renewable resource
(d) Stock
Answer:
(c) Renewable resource
Question 2.
Balancing the need to use resources and also conserve them for the future is called
(a) sustainable development
(b) resource conservation
(c) resource development
(d) human resource development
Answer:
(a) sustainable development

Question 3.
How much percentage of land is plain in India?,
(a) 41%
(b) 45%
(c) 43%
(d) 47%
Answer:
(c) 43%
Question 4.
The thin layer of grainy substance covering the surface of the earth is called
(a) soil
(b) sand
(c) mineral
(d) organic matter
Answer:
(a) soil
Question 5.
Land degradation due to over irrigation can be seen in the states of:
(a) Punjab and Haryana
(b) Assam
(c) Odisha
(d) Mizoram
Answer:
(a) Punjab and Haryana
Question 6.
How many Economic zones are there in India? *
(a) Five
(b) One
(c) Two
(d) Ten
Answer:
(a) Five
Question 7.
Which dhe of the following resources can be acquired by a Nation?
(a) Potential resources
(b) International resources
(c) National resources
(d) Public resources
Answer:
(c) National resources
Question 8.
Which one of the following soil is the best for cotton cultivation?
(a) Red soil
(b) Black soil
(c) Laterite soil
(d) Alluvial soil
Answer:
(b) Black soil

Question 9.
Which one of the following term is used to identify the old and new alluvial respectively?
(a) Khadar & Tarai
(b) Tarai & Bangar
(c) Bangar & Khadar
(d) Tarai & Dvars
Answer:
(c) Bangar & Khadar
Question 10.
Which type of soil develops due to high temperature and evaporation?
(a) Arid Soil
(b) Forest Soil
(c) Black Soil
(d) Red Soil
Answer:
(a) Arid Soil
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is the main purpose of resources?
Answer:
Resources are a function of human activities. The main purpose of resources is to satisfy the basic needs of mankind.
Question 2.
On the basis of status of development resources are classified into how many categories?
Answer:
On the basis of status of development resources are classified into four categories – Potential, Developed, Stock and Reserved.
Question 3.
What can lead to socio-economic and environmental problems?
Answer:
Irrational consumption and over¬utilisation of resources may lead to socio¬economic and environmental problems.
Question 4.
Name four ecological crisis.
Answer:
Global warming, ozone layer depletion, environmental pollution and land degradation.
Question 5.
Name the soil which covers the largest part of India.
Answer:
Alluvial soil

Question 6.
The use of land is determined by which factors?
Answer:
The use of land is determined by both physical factors such as topography, climate, soil types and human factors such as population density, technological capability and culture and traditions, etc.
Question 7.
What is fallow land?
Answer:
It is the land cultivated once in two or three years which is then left for one or two seasons to regain its fertility.
Question 8.
How can resources contribute to development?
Answer:
Resources can contribute to development only when they are accompanied by appropriate technological development and institutional changes.
Question 9.
Name two factors responsible for the formation of soil.
Answer:
Climate and rocks are the two factors responsible for the formation of soil.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What do you mean by resources? How are resources classified?
Answer:
Everything available in our environment which can be used to satisfy our needs provided it is technologically accessible, economically feasible and culturally acceptable. Resources can be classified on the following ways:
- On the basis of origin: Biotic and abiotic.
- On the basis of exhaustibility: Renewable and non-renewable.
- On the basis of ownership: Individual, Community, National and International.
- On the basis of status of development: Potential, Developed, Stock and Reserves.
Question 2.
What is resource planning? Give three phases of resource planning?
Answer:
Resource planning means proper and judicious use of resource. Resource planning is a complex process which involves:
- Identification and inventory of resources across the regions of the country. This involves surveying, mapping and qualitative and quantitative estimation and measurement of the resources.
- Evolving a planning structure endowed with appropriate technology, skill and institutional set up for implementing resource development plans.
- Matching the resource development plans with overall national development plans.
Question 3:
What is the difference between Stock resources and reserves?
Answer:
| Stock Resources | Reserves |
| (i) The things present in the nature which have the potential to satisfy the human needs but due to non-availability of appropriate technology, these cannot be used for the time being, are called Stock. | (i) These are the subset of stock which can be put to use with the help of existing technology but they are still unused. |
| (ii) For example, water. It has oxygen and hydrogen. These can be used as a source of energy but we do not have technology _ to use it. | (ii) These can be used for meeting future generation requirements. |
Question 4.
Give two factors that determine soil fertility.
Answer:
- Soil fertility depends on its composition. Sandy soil is not suitable for agriculture as they do not retain water which is needed for survival. The ideal soils contain a mixture of sand and clay.
- The humus content determines soil fertility. Organic farm manures improve humus content.
Question 5.
Soil is the most important renewable natural resource. Explain.
Answer:
It is the medium of plant growth and supports different types of living organisms on the earth. Soil is a living system. It takes millions of years to form soil upto a few cm in depth. Relief, parent rock or bed rock, climate, vegetation and other forms of life and time are important factors in the formation of soil.
Various forces of nature such as change in temperature, actions of running water, wind and glaciers, activities of decomposers, etc., contribute to the formation of soil. Chemical and organic changes, which take place in the soil, are equally important. Soil also consists of organic (humus) and inorganic materials.

Question 6.
Give a brief note on the productivity of alluvial soil.
Answer:
Alluvial soils are very fertile. Mostly these soils contain proportion of potash, phosphoric acid and lime which are ideal for the growth of sugarcane, paddy, wheat and oth$r cereal and pulse crops. Due to its high fertility, regions of alluvial soils are intensively cultivated and densely populated. Soils in the drier areas are more alkaline and can be productive after proper treatment and irrigation.
Question 7.
What are the ways to solve the problems of land degradation?
Answer:
There are many ways to solve the problems of land degradation: Afforestation and proper management of grazing can help to some extent. Planting of shelter belts of plants, control on overgrazing, stabilisation of sand dunes by growing thorny bushes. Proper management of waste lands, control of mining activities, proper discharge and disposal of industrial effluents and wastes after treatment can reduce land and water degradation in industrial and suburban areas.
Question 8.
Explain the importance of conservation of resources.
Answer:
Conservation of resources is necessary for the following reasons:
- Resources are important for any development activity but irrational consumption and overuse of resources may lead to socio-economic and environmental problems. To overcome these problems, resource conservation at every level is necessary.
- If resources are not conserved at this point of time, then our future generation will be left with no resources at all. So it is very important to start conserving resources now.
Question 9.
What is the inter-relationship between nature, technology institutions?
Answer:
Human beings interact with nature to fulfil their needs using the resources that are available. They also transform the natural stuff into resources through technology and create institutions to accelerate their economic development.
Question 10.
State three characteristics of black soil.
Answer:
Three characteristics of black soil are:
- Black soil consists of higher proportion of clay and thus can retain moisture for a long time.
- It develops deep cracks during summer which helps in aeration.
- Black soil is sticky and when wet, it is difficult to work unless tilled immediately after the monsoon.
Question 11.
What is Agenda 21?
Answer:
It is the declaration signed by the world leaders in 1992 at the United Nations Conference on Environment and Development (UNCED), which took place at Rio de Janeiro, Brazil. It aims at achieving global sustainable development. It is an agenda to combat environmental damage, poverty, disease through global co-operation on common interests, mutual needs and shared responsibilities.
Question 12.
What is sustainable development?
Answer:
Sustainable economic development means ‘development should take place without damaging the environment, and development in the present should not compromise with the needs of the future generations.’
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Distinguish between renewable and non-renewable resources.
Answer:
| Renewable resources | Non-renewable resources |
| (i) The resources which get renewed by physical, chemical or mechanical processes are known as renewable resources. | (i) These resources occur over a very long geological time. They gradually get exhausted with use. |
| (ii) These resources are generally available throughout the world. | (ii) These resources are generally unevenly distributed on the earth. |
| (iii) Some of the examples are water, solar energy, wind energy, tidal energy and k forest. | (iii) Some of the examples are minerals, coal and petroleum. |
Question 2.
Distinguish between biotic resources and abiotic resources.
| Biotic resources | Abiotic resources |
| (i) These resources are obtained from Biosphere. – | (i) Basically, they are those things which are composed of non-living things. |
| (i) These include flora and fauna, fisheries, livestock, human beings, etc. | (ii) These include rocks, metals, lands, air, mountains, rivers, etc. |
| (iii) Minerals such as coal and petroleum are included in this category because they are , formed from decayed organic matter. | (iii) Minerals such as gold, iron, copper, silver, etc., come in this category. |
Question 3.
Describe the different types of soils in India emphasizing on any two characteristics.
Answer:
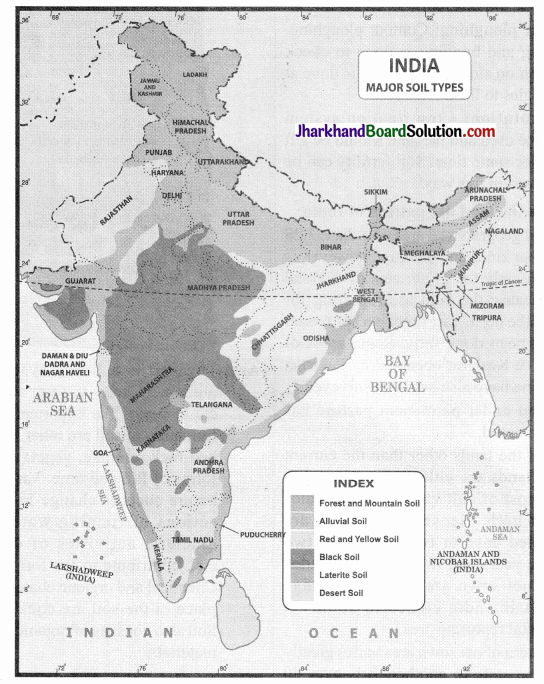
India has varied relief features, landforms, climatic realms and vegetation types. All of these have contributed in the development of various types of soils.
(i) Alluvial soil
- Alluvial soil as a whole is very fertile. Mostly this soil contains adequate proportion of potash, phosphoric acid and lime which are ideal for the growth of sugarcane, paddy, wheat and other cereal and pulse crops.
- Due to its high fertility, regions of alluvial soils are intensively cultivated and densely populated.
(ii) Black soil
- Black soil is made up of extremely fine, i.e., clayey material. It is well-known for their capacity to hold moisture. In addition, it is rich in soil nutrients, such as calcium carbonate, magnesium, potash and lime.
- This soil is black in colour and is also known as regur soil. Black soil is ideal for growing cotton and is also known as black cotton soil.
(iii) Red soil
- Red soil develops on crystalline igneous rocks in the areas of low rainfall in the eastern and southern parts of the Deccan plateau.
- This soil develops a reddish colour due to diffusion of iron in crystalline and metamorphic rocks.
(iv) Laterite soil
- Laterite soil develops in the areas with high temperature and heavy rainfall. This is the result of intense leaching due to heavy rain.
- It is suitable for cultivation with adequate doses of manures and fertilizers. After adopting appropriate soil conservation techniques particularly in the hilly areas of Karnataka, Kerala and Tamil Nadu, this soil is very useful for growing tea and coffee.
(v) Arid soil
- Arid soil ranges from red to brown in colour. It is generally sandy in texture and saline in nature. In some areas the salt content is very high and common salt is obtained by evaporating the water.
- Due to the dry climate and high temperature, evaporation is faster and the soil lacks humus and moisture.
(vi) Forest soil
- This soil is found in the hilly and mountainous areas where sufficient rain forests are available. The soil’s texture varies according to the mountain Environment where it is formed. It is loamy and silty in valley sides and coarse grained in the upper slopes.
- In the snow covered areas ofthe Himalayas, this soil experiences denudation and is acidic with low humus content.

Question 4.
Explain any four human activities which are mainly responsible for land degradation in India.
Answer:
Human activities such as deforestation, overgrazing, construction and mining have contributed significantly to land degradation.
- Mining sites are abandoned after mining work is complete leaving deep scars and traces of over-burdening.
- In the states like Jharkhand, Chhattisgarh, Madhya Pradesh and Odisha deforestation has occurred due to mining.
- In the states like Rajasthan, Gujarat, Maharashtra and Madhya Pradesh overgrazing is one of the main reasons for land degradation.
- In Punjab, Haryana and Western Uttar Pradesh, over-irrigation is one of the main reasons for land degradation due to water logging leading to increase in salinity and alkalinity in the soil.
- The mineral processing like grinding of limestone for cement industry and calcite and soapstone for ceramic industry generates huge quantity of dust in the atmosphere which retards the process of infiltration of water into the soil after it settles down on the land.
- Industrial effluents as waste have become a maj or source of land and water pollution.
Question 5.
What are the steps taken to promote soil conservation?
Answer:
Methods for soil conservation are :
- Afforestation:
In some areas the original vegetation cover has been removed, such as in the Shiwalik hills. In such areas, both afforestation and reforestation are dneeded to hold the soil. Development of deserts can be checked by planting trees along the margins of desert. - Controlled grazing:
The number of cattle to be grazed on slopes should be according to the capacity of the pastures. - Terraced farming:
Slopes can be cut into a series of terraces for cultivation, so as to slow down the flow of rain water. - River dam: River dams are built in the upper course of rivers to control floods and check soil erosion.
- Contour ploughing:
Contour ploughing, terracing and bunding is done to check soil wash on slopes. Ploughing is done at right angles to the hill slopes. - Crop rotation:
Crop rotation system should be used and the land should be left fallow for some time. Soil fertility can be maintained in this way.

Question 6.
Explain the land use pattern of India.
Answer:
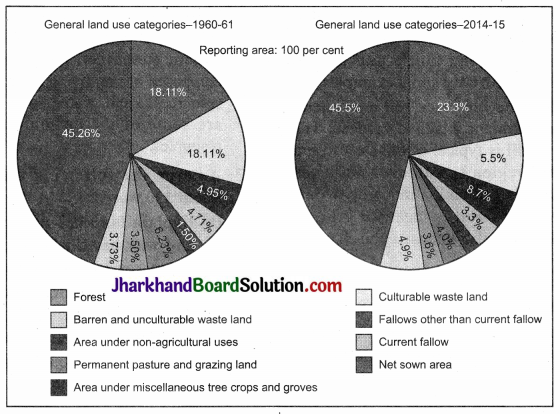
(i) Total geographical area of India is 3.28 million sq km. Land use data, however, is available only for 93 per cent of the total area because the land use reporting for most of the north-east states except Assam has not been done fully. Some areas of Jammu & Kashmir occupied by Pakistan and China have also not been surveyed.
(ii) The land under permanent pasture has also decreased.
(iii) Most of the lands other than the current fallow lands are either of poor quality or the cost of cultivation of such lands is very high. Hence, these lands are cultivated once or twice in about two to three years and if these are. included in the net sown area, the percentage of NSA in India comes to about 54 of the total reporting area.
(iv) The pattern of net sown area varies greatly from one state to another. It is over 80 per cent of the total area in Punjab and Haryana and less than 10 per cent in Arunachal Pradesh, Mizoram, Manipur and Andaman and Nicobar Islands.
(v) Forest area in the country is far lower than the. desired 33 per cent of geographical, area, as it was outlined in the National Forest Policy (1952).
Activity Based Questions
Question 1.
Look at the picture carefully and explain the formation for soil.

Answer:
The soil is a living system. It takes millions of years to form soil upto a few cm in depth. The important factors in the formation of soil are relief, parent rock or bed rock, climate, vegetation and other forms of life and time. Various forces of nature such as change in temperature, actions of running water, wind and glaciers, activities of decomposers etc., contribute to the formation of soil. Chemical and organic changes which take place in the soil are equally important. Soil also consists of organic and inorganic materials.

Question 2.
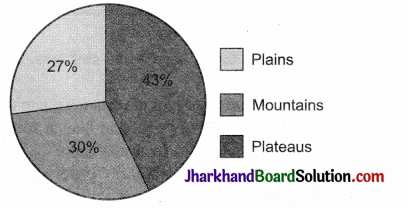
Explain the distribution of relief features in India through the diagram.
Question 3.
Explain the types of soil found in different regions of India on a map.
Answer:
See the given map of India.
![]()
![]()