JAC Board Class 8th Social Science Solutions Civics Chapter 2 Understanding Secularism
JAC Class 8th Civics Understanding Secularism InText Questions and Answers
Page 19
Question 1.
Re-read the introduction to this chapter. Why do you think retaliation is not the proper response to this problem? What would happen if different groups followed this path?
Answer:
Retaliation is not the proper response to this problem because it generates lots of negative effects in the society. The security of the nation would break if different groups follow this way.
![]()
Page 20.
Question 2.
Discuss in class: Can there be different views within the same religion?
Answer:
Yes, there can be different views within the same religion. Can discuss with examples in the class answer given by the teacher.
Page 22
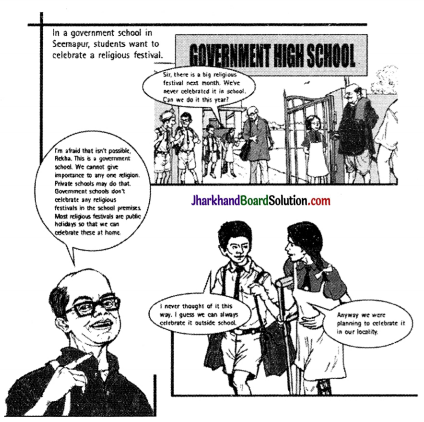
Answer:
The teacher answered that the school declares holidays on the occasions of national festivals and no religious ceremony is organized in the school. This is not done because we can not give importance to only one festival or religion. Though people are free to celebrate there festivals on their own way.
Question 4.
Government schools often have students from different religious backgrounds. Re-read the three objectives of a secular State and write two sentences on why it is important that government schools do not promote any one religion?
Answer:
It is important that government schools do not promote any one religion because if the government itself does not follow the rules in the Constitution, a nonnal citizen will also not understand the importance of following it. Also, it results in the discrimination between the students belonging to different religious backgrounds.
Page 25
Question 5 .
Can you think of a recent incident, from any part of India, in which the secular ideals of the Constitution were violated and persons were persecuted and killed because of their religious backgrounds?
Answer:
Students can do it on their own with the help of journals, old newspaper and internet.
Hint:
Communal riots in 2002 where there is a clear violation of secular ideas of the constitution).
JAC Class 8th Civics Understanding Secularism Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
List the different types of religious practice that you find ¡n your neighbourhood. This could be different forms of prayer, worship of ditTerent gods, sacred sites, different kinds of religious music and singing, etc. Does this indicate freedom of religious practice’?
Answer:
The different types of religious practices that we can see in our neighbourhood are as follows:
- Hindus visit Temple. They perform puja and worship the idols of their Gods and Goddesses. They do kirtans, satsang, jagran and yagna.
- Muslims visit mosque and worship their sacred book the Question uran. They offer namaaz.
- Sikhs visit Gurudwara. worship their sacred book Guru Granth Sahib by offering prayers and listening to shabad-kirtan.
- Christians visit Church and worship Jesus Christ. They sing carols. Yes, this indicates freedom of religious practice as the people in India have the freedom to practice the religion of their choice while living together in peace and harmony.
Question 2.
Will the government intervene if some religious group says that their religion allows them to practise infanticide? Give reasons for your answer.
Answer:
Yes, the Government will intervene if some religious group says that their religion allows them to practice infanticide. Infanticide involves the killing of an infant (a small child) which is clearly a cruel and harsh crime. This practice violates the human right ‘Right to Life’.
![]()
Question 3.
Complete the followig table:
| Objective | One religious community does not dominate another. |
| Why is this important? | The State does not enforce any particular religion nor take away the religious freedom of individuals. |
| Example of a violation of this objective | That some members do not dominate other members of the same religious community. |
Answer:
| Objective | Why is this important? | Example of a violation of this objective |
| One religious community does not dominate another. | This is important for maintain peace and harmony in the country. | A hindu religious procession was not allowed to cross the roads passing through the mosque. |
| The State does not enforce any particular religion nor take away the religious freedom of individuals. | This is important to uphold the ideals of a democratic nation which gives freedom to citizens to follow any religion. | Demolition of Babri Masjid Lower caste people are discouraged to enter the temple. |
| That some members do not dominate other members of the same religious community. | This is important to establish the sense of equality. | Example of a violation of this objective |
Question 4.
Look up the annual calendar of holidays of your school. How many of them pertain to different religions? What does this indicate?
Answer:
The annual calendar of our school marks several holidays that pertain to different religions. Various festivals for which holidays are declared are mentioned below:
| Religion | Holidays |
| Hindu festivals | Diwali, Holi, Dussehra, Shivratri, Ram Navmi |
| Muslim festivals | Id-ul-zuha, Id-ul-fitar, Muharram |
| Sikh festivals | Gum Nanak Jayanti. Gum Gobind Singh Jayanti, Vaisakhi, Lohri |
| Christian festivals | Christmas, Good Friday |
This clearly proves that India is a secular country and here all the religions are equally respected.
Question 5.
Find out some examples of different views within the same religion.
Answer:
Many religions in our country are further divided into groups and communities that hold opinions differing from each other. Some examples of such groups and communities existing within the same religion are given below:
- In Hindu religion, there are hundreds of gods and goddesses that are worshipped by different groups of people and in different forms.
- Jains are divided into Shwetambar and Digambar.
- Muslims are divided into Shias and Sunnis.
- Buddhist followers are divided into Mahayana and Hinayana.
Question 6.
The Indian State both keeps away from religion as well as intervenes in religion. This idea can be quite confusing. Discuss this once again in class using examples from the chapter as well as those that you might have come up with.
Answer:
The Indian state both keeps away from religion, as well as intervenes in religion. The central as well as state governments declare holidays on the occasions of festivals belonging to different religions, but no religious function is celebrated by any of the governments. People of the country are free to celebrate these religious festivals in their own way. However, the Indian state comes to intervene only if any religious practice disturbs the peace and harmony of the country. If some section of the people belonging to the same religion are denied the right to enter their place of worship then the state can intervene to resolve the issue and help the deprived section regain its rights.
![]()
Question 7.
This poster alongside highlights the need for ‘Peace’. It says, “Peace is a never-ending process…. It cannot ignore our differences or overlook our common interests.” Write in your own words what you think the above sentences are trying to convey? How does it relate to the need for religious tolerance?

This chapter had three drawings on religious tolerance made by students of your age. Design your own poster on religious tolerance for your peers.
Answer:
This poster gives us a message for the establishment of peace and harmony. It clarifies that peace is a long-cherished process and we cannot ignore the differences or interests. Only after establishing a coordination between the common interests, peace can be maintained. It relates to the religious tolerance because it is the most sensitive issue. Students need to do this part on their own as they have to draw posters on religious tolerance.
JAC Class 8th Civics Understanding Secularism Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Only a secular State can realise its objectives to ensure the following which is according to the Constitution:
(a) One religious community does not dominate another.
(b) Some members do not dominate other members of the same religious community.
(c) The State does not enforce any particular religion nor take away the religious freedom of individuals.
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 2.
Secularism is important because
(a) Acts of discrimination take place more easily when one religion is given official recognition by the State at the expense of other religions.
(b) Acts of discrimination does not take place more easily when one religion is given official recognition by the other countries at the expense of other religions.
(c) Acts of discrimination take place more easily when one religion is not given official recognition by the State at the expense of other religions.
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Acts of discrimination take place more easily when one religion is given official recognition by the State at the expense of other religions.
![]()
Question 3.
India follows a strategy of non interference because:
(a) For faster economic development of the country.
(b) To achieve objectives of a truly religious State.
(c) To achieve objectives of a secular State.
(d) All of these
Answer:
(c) To achieve objectives of a secular State.
Question 4.
The term secularism refers to the separation between the power of and the power of the State.
(a) law
(b) religion
(c) science
(d) colonisation
Answer:
(b) religion
Question 5.
Everyone should wear helmets while riding a two-wheeler but Sikh people are not wearing helmets because
(a) Pagri (turban) protects person’s head equal to helmet.
(b) the Indian State recognises that wearing a pagri (turban) is central to a Sikh religious practice and inorder not to interfere with this, allows an exception in the law.
(c) the Indian State recognises that wearing a pagri (turban) is in fashion to a Sikh religious practice and in order not to interfere with this, allows an exception in the law.
(d) All of these
Answer:
(b) the Indian State recognises that wearing a pagri (turban) is central to a Sikh religious practice and inorder not to interfere with this, allows an exception in the law.
Question 6.
Untouch ability is an old age practice of……..
(a) Islam
(b) Sikhism
(c) Hinduism
(d) Buddhism
Answer:
(c) Hinduism
Question 7.
………….. can not be done in government schools.
(a) Celebrate religious festivals
(b) Celebrate national festivals
(c) Sing the national song
(d) All of these
Answer:
(a) Celebrate religious festivals
Question 8.
………is not in Indian Constitution.
(a) Fundamental Rights
(b) Reservations
(c) Equality
(d) Discrimination
Answer:
(d) Discrimination
Question 9.
During Hitler’s rule, in Germany.
(a) assassination of Mahatma Gandhi
(b) killing of Jews
(c) end of World War
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) killing of Jews
![]()
Question 10.
Majority of the population of Israel is ……
(a) Jewish
(b) Muslim
(c) Christian
(d) Buddhism
Answer:
(a) Jewish
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What do you understand by ‘freedom to interpret’?
Answer:
‘Freedom to interpret’ means an individual’s liberty to develop his own understanding and meaning of the religious teachings.
Question 2.
What do you mean by the concept of ‘principled distance’?
Answer:
The concept of ‘principled distance’ means that any interference in religion by the State has to be based on the ideals laid out in the Constitution.
Question 3.
How are non-Muslims treated in Saudi Arabia?
Answer:
In Saudi Arabia, non-Muslims are not allowed to build a temple, church, etc., nor can they gather in a public place for prayers.
Question 4.
Define the word ‘establishment’.
Answer:
The word ‘establishment’ means that the legislature cannot declare any religion as the official religion. Nor can they give preference to one religion.
Question 5.
State the most important aspect of secularism.
Answer:
The most important aspect of secularism is its separation of religion from State power. This is important for a country to function democratically.
Question 6.
List the former French colonies.
Answer:
The former French colonies are Morocco, Algeria and Tunisia.
![]()
Question 7.
Can anyone criticize the unpopular laws? If yes, by which medium?
Answer:
Yes, anyone criticize the unpopular laws. The medium can be newspaper, journals, social media, Television, etc.
Question 8.
What do you mean by controversial law?
Answer:
A law when it supports a group or community or disregard a group or community is called as a controversial law.
Question 9.
What do you mean by coercion?
Answer:
Coercion is a process in which we the people make other people do something forcefully or oppressing them with power.
Question 10.
Define majority.
Answer:
The people who are more in number in a fixed geographical area or in a fixed demography is known as majority.
Question 11.
When does a Bill become an Act?
Answer:
A Bill becomes an Act after the assent of the President.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What provision has been made by the government to follow religious equality in government spaces, schools and offices?
Answer:
In India, government spaces like law courts, police stations, government schools and offices are not supposed to display or promote any one religion. Government schools cannot promote any one religion either in their morning prayers or through religious celebrations.
![]()
Question 2.
How the act of discrimination took place?
Answer:
The act of discrimination takes place when members of one religious community either oppress, ill-treat or discriminate against members of other religious communities. These occurs more easily when one religion is given official recognition by the State at the expense of other religions.
Question 3.
For what reason government schools are not allowed to celebrate religious festival?
Answer:
Government schools are not allowed to celebrate religious festival because the celebration would be a violation of the government’s policy of treating all religions equally. Government schools cannot promote any one religion either in their morning prayers or through religious celebrations.
Question 4.
What is secularism in Indian context?
Answer:
Secularism refers to the separation of religion from the State. The Indian Constitution allows individuals the freedom to live by their religious beliefs and practices as they interpret these ideas. In keeping with this idea of religious freedom for all, India had adopted a strategy of separating the . power of religion and the power of the State.
Question 5.
When was law passed by French government banning religious symbols in school? What was its impact?
Answer:
In February 2004, France passed a law banning students from wearing any conspicuous religious or political signs or symbols such as the Islamic headscarf, the Jewish skullcap, or large Christian crosses. This law has encountered a lot of resistance from immigrants who are mainly from the former French colonies of Algeria, Tunisia and Morocco.
Question 6.
How does the Indian constitution ensure its objectives of secular state?
Answer:
The Indian Constitution ensures its objectives of a secular state in the following manner:
- One religious community does not dominate another.
- Some members do not dominate other members of the same religious community.
- State does not enforce any particular religion nor take away the religious freedom of individuals.
Question 7.
With the help of a situation prove that the Indian secular state can intervene to prevent the religious domination concerning different groups of the same religion.
Answer:
Where members of the same religion, the upper-caste Hindus dominate other members the lower castes within it. In order to prevent this religion-based and excludes and that violates the Fundamental Rights of people who are citizens of this country. exclusion and discrimination of lower castes, the Indian Constitution banned untouchability. In this situation, the State is intervening in religion in order to end a social practice that it believes discriminates and excludes that violates the Fundamental Rights of lower castes who are citizens of the country.
![]()
Question 8.
State Article 17 in the Right to Equality, in the Indian constitution.
Answer:
Article 17 in the Right to Equality is related to the ‘Abolition of Untouchability’ in the Indian constitution.
It states that ‘Untouchability’ is abolished and its practice in any form is forbidden. The enforcement of any disability rising out of Untouchability shall be an offence punishable in accordance with law.”
Question 9.
In which way the different laws are made by the government?
Answer:
When the government feels the necessity to implement certain rules and regulations inside the country for the people, it derives a law and passes it in both the parliament houses. Finally with the assent and approval from the President this becomes the law and act as a force.
Question 10.
What do you understand by Indian Secularism.
Answer:
India Secularism can be understood by the following ways:
(i) Here, one religion community does not dominate the other religion community.
(ii) Some groups of religious community does not dominate the another group of same religious community.
(iii) The States provides security to every religious community and does not imposes their own religion to other community.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
How does the Indian state work to prevent domination of the majority religious group?
Answer:
The Indian State works in various ways to prevent the domination of the majority religious groups in the following manner:
(i) First, it uses a strategy of distancing itself from religion. The Indian State is not ruled by a religious group and nor does it support any one religion. In India, government spaces like law courts, police stations, government schools and offices are not supposed to display or promote any one religion.
(ii) Secondly, Indian secularism works to prevent the above domination is through a strategy of non¬interference. This means that in order to respect the sentiments and give respect to all religions and not interfere with religious practices, the State makes certain exceptions for particular religious communities.
(iii) Third, Indian secularism works to prevent the domination listed earlier is through a strategy of intervention. The State intervenes in religion in order to end a social practice that it believes discriminates and excludes and that violates the Fundamental Rights of people who are citizens of this country.
![]()
Question 2.
Explain the Hindu Succession Amendment Act, 2005.
Answer:
The Hindu Succession (Amendment) Act, 2005 was enacted to remove gender discriminatory provisions in the Hindu Succession Act, 1956. According to the Hindu Succession Amendment Act, 2005 sons, daughters and their mothers can get an equal share of family property after the death of their father. Before this act, only the son of the family was eligible to inherit the property of his father.
There were several cases in front of the court of law regarding the discrimination taking places in families ‘ for the properties of their father. To tackle this gender discrimination and biasedness, the government brought the Hindu Succession Amendment Act, 2005. This was applied on all the religions – Hindus, Jains, Sikhs, and Buddhists. This Act enabled comprehensive system of inheritance without any sort of discrimination.