JAC Board Class 7th Social Science Solutions Geography Chapter 3 Our Changing Earth
JAC Class 7th Geography Our Changing Earth InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Find out the names of a few rivers of the world that form a delta?
Answer:
Some of the rivers of the world that form a delta are Niger, Mississippi, Nile, Rhine, Ganga, Brahmaputra.
JAC Class 7th Geography Our Changing Earth Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Answer the following questions.
(i) Why do the plates move?
Answer:
There is a movement of the molten magma inside the earth hence the plates move. .
(ii) What are exogenic and endogenic forces?
Answer:
Exogenic forces are the forces that act on the surface of the earth. Endogenic forces are the forces that act in the interior of the earth.
(iii) What is erosion?
Answer:
Wearing away of the landscape by different agents such as wind, water and ice is known as erosion.
![]()
(iv) How are flood plains formed?
Answer:
Layers of fine soil and other materials called sediments are deposited on the river bank during floods. This leads to the evolution of a flat fertile and productive flood plains.
(v) What are sand dunes?
Answer:
In the desert, the low-hill like structures formed by the deposition of sand are known as sand dunes.
(vi) How are beaches formed?
Answer:
When the sea waves deposits sediments along the shores of the sea, the beaches are formed.
(vii) What are ox-bow lakes?
Answer:
Ox-bow lakes are formed when the meander loop is cut-off from the main river, it forms a cut-off lake and the shape is like an ox-bow.
Tick (√) the correct answer.
Question 2.
(i) Which is not an erosional feature of sea waves?
(a) Cliff
(b)Beach
(c) Sea cave
Answer:
(b)Beach
(ii) The depositional feature of a glacier is:
(a) Flood plain
(b) Beach
(c) Moraine
Answer:
(c) Moraine
(iii) Which is caused by the sudden movements of the earth?
(a) Volcano
(b) Folding
(c) Flood plain
Answer:
(a) Volcano
(iv) Mushroom rocks are found in:
(a) Deserts
(b) River valleys
(c) Glaciers
Answer:
(a) Deserts
(v) Ox bow lakes are found in:
(a) Glaciers
(b) River valleys
(c) Deserts
Answer:
(b) River valleys
![]()
Question 3.
Match the following.
| (i) Glacier | (a) Sea shore |
| (ii) Meanders | (b) Mushroom rock |
| (iii) Beach | (c) River of ice |
| (iv) Sand dunes | (d) Rivers |
| (v) Waterfall | (e) Vibrations of earth |
| (vi) Earthquake | (f) Sea cliff |
| (g) Hard bed rock | |
| (h) Deserts |
Answer:
| (i) Glacier | (c) River of ice |
| (ii) Meanders | (d) Rivers |
| (iii) Beach | (a) Sea shore |
| (iv) Sand dunes | (h) Deserts |
| (v) Waterfall | (g) Hard bed rock |
| (vi) Earthquake | (e) Vibrations of earth |
Question 4.
Give reasons.
(i) Some rocks have a shape of a mushroom.
Answer:
Winds usually erode the lower section of the rock much more than the upper portion in desert. Hence, such hocks take the shape of a mushroom which have narrower base and wider top.
(ii) Flood plains are very fertile.
Answer:
The deposition of fine soil and other materials called sediments on the river banks helps in the formation of flood plains. By flood water, the soil and sediments are brought hence they are very fertile.
(iii) Sea caves are turned into stacks.
Answer:
At the rocks, sea waves strikes. Cracks develops as a result and it becomes bigger over the period and hollow like caves are formed on the rocks. These are the sea caves. These cavities becomes bigger and bigger and a times come when only the roof of the caves remain to make sea arches. To some extent, erosion breaks the roof and only walls are left. These wall like features are called stacks hence, in this manner sea waves are turned into stacks,
(iv) Buildings collapse due to earthquakes.
Answer:
Most of the buildings are not earthquake proof and safe enough to withstand the pressure of the vibrations of the earthquake. They collapse tearing apart due to insubstantial foundation and lack of adequate good materials such as steel in the interior design.
Activity
Question 5.
Observe the photographs given below. These are various features made by a river. Identify them and also tell whether they are erosional or depositional or landforms formed by both.

Answer:
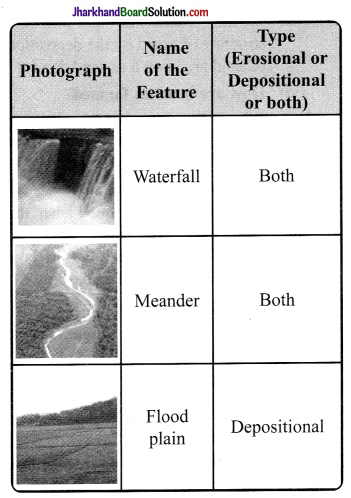
(For Fun)
Question 6.
Solve the crossword puzzle with the help of given clues.
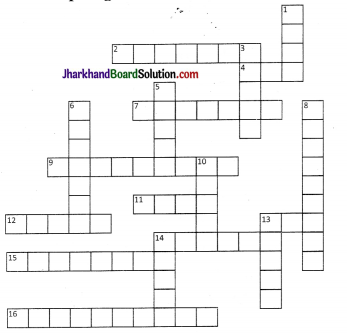
Across:
2. Loop like bend of river 4. Solid form of water
7. Moving mass of ice
9. Sudden descent of water in bed of river
11. Natural cavity on weak rocks formed by action of waves
12.Embankment on river that keeps river in its channel
13. Large body of sea water
14. Dry area where sand dunes are found
15. Small hill of sand piled by action of wind
16. Flat plain formed by river depoits during time of flood
Down:
1. Rise and fall of water caused by friction of wind on water surface
3. Flow of water in channel
5. Steep perpendicular face of rock along sea coast
6. Debris of boulder and coarse material carried by glacier
8. Crescent shaped lake formed by river meander
10. Fine sand deposited by action of wind
13. Isolated mass of rising steep rock near coastline
14. Alluvial tracts of land at mouth of river formed by river deposits
| Across | Down |
| 2. Meander | 1. Wave |
| 4. Ice | 3. River |
| 7. Glacier | 5. Cliff |
| 9.Waterfall | 6. Moraine |
| 11. Caves | 8. Ox Bow lakes |
| 12. Levee | 10. Loess |
| 13. Sea | 13. Stack |
| 14. Desert | 14. Delta |
| 15. Sand dune | |
| 16. Flood Plain |
JAC Class 7th Geography Our Changing Earth Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
The earthquake is measured with the help of
(a) Compass
(b) Seismograph
(c) Thermometer
(d) Lactometer
Answer:
(b) Seismograph
Question 2.
Sand dunes are
(a) hill like structure
(b) cave like structure
(c) wall like structure
(d) none of these
Answer:
(a) hill like structure
![]()
Question 3. Inside the earth, the molten magma moves in a……manner.
(a) circular
(b) vertical
(c) horizontal
(d) spiral
Answer:
(b) vertical
Question 4.
The highest waterfall in the world is
(a) Jog Falls
(b) Victoria Falls
(c) Niagra Falls
(d) Horseshoe Falls
Answer:
(c) Niagra Falls
Question 5.
Loess is found in
(a) mountains
(b) sea
(c) plains
(d) deserts
Answer:
(d) deserts
Question 6.
Colour of infrared images that represent sandy areas, sand dunes and beaches is
(a) yellow
(b) white – cream
(c) red magenta
(d) pink – white
Answer:
(b) white – cream
Question 7.
Broken plates are known as
(a) Farallon plate
(b) Scotia plate
(c) Tectonic plate
(d) Lithospheric plate
Answer:
(d) Lithospheric plate
Question 8.
The forces which act in the interior of the earth is known as
(a) Endogenic Force
(b) Magnetic Force
(c) Exogenic Force
(d) Gravitational Force
Answer:
(a) Endogenic Force
Question 9.
One of the Endogenic Force is theSudden Force. These include/s
(a) Volcano
(b) Landslides
(c) Earthquake
(d) All of these
Answer:
(d) All of these
Question 10: The activity in a river which erodes the landscape is
(a) Swimming of humans
(b) Growth of weeds
(c) Running water
(d) Boating
Answer:
(c) Running water
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
During an earthquake we should keep away from which places?
Answer:
During an earthquake we should keep away from the places such as chimneys, windows that shatter including mirrors and picture frames and fire places.
Question 2.
Name the major agents of erosion.
Answer:
The major agents of erosion are wind, water and ice.
Question 3.
What do you meant by vent?
Answer:
Vent is the narrow opening of the volcano.
![]()
Question 4.
Name the scale that is used to measurethe earthquake.
Answer:
The Richter Scale is used to measure themagnitude of the earthquake.
Question 5.
What do you mean by distributaries?
Answer:
When the river begins to break up to a number of streams are known as distributaries.
Question 6.
Which are the two methods that wear away the landscape?
Answer:
The two methods that wear away the landscape are weathering and erosion.
Question 7.
What are the activities on the surface of the earth that create different landforms?
Answer:
The activities on the surface of the earth that create different landforms are the process of erosion and deposition.
Question 8.
What do you mean by focus?
Answer:
The focus is the place in the crust where the movement starts.
Question 9.
When the river tumbles at the steep angle over very hard rocks or down a steep valley side then what is formed?
Answer:
When the river tumbles at the steep angle over very hard rocks or down a steep valley side then waterfall is formed.
Question 10.
What is formed when the river enters the plain and twists and turns forming large bends?
Answer:
Meander is formed when the river enters the plain and twists and turns forming large bends.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
In which manner glacial morains form?
Answer:
The materials which are carried by the glacier such as rocks small and big; sand and silt gets deposited. These depositions form glacial moraines.
Question 2.
What do you understand by the term delta?
Answer:
A feature is formed when river drops off the sediments in low-lying areas usually as they enter the sea, ocean or estuary is known as delta. It has triangular shape sometimes.
![]()
Question 3.
What are the three types of earthquake waves?
Answer:
The three types of earthquake waves are
- Longitudinal waves or P waves
- Transverse waves or S waves
- Surface waves or L waves
Question 4.
Where are Victoria Falls and Niagra Falls located?
Answer:
Victoria Falls is located on the borders of Zambia and Zimbabwe in Africa. Niagra Falls is situated on the borders of United States of America and Canada.
Question 5.
List the important lithospheric plates.
Answer:
The important lithospheric plates are
- The Indo-Australian Plate
- The Eurasian Plate
- The North American Plate
- The South American Plate
- The African Plate
- The Pacific Plate
- The Antarctic Plate
Question 6.
What are the agents of denudation?
Answer:
Denudation is the effect of two main processes – Endogenous and Exogenous.
- The agents of denudation are
- Wind
- Running water
- Sea waves
- Glaciers
Question 7.
How do we measure the intensity of an earthquake?
Answer:
Seismograph is a machine which helps to measure an earthquake and the magnitude is measured on the Richter Scale. Hence, the intensity of the earthquake is measured in the following way:
| Magnitude | Affect |
| 4.0 or less | only little can be felt |
| Over 5.0 | cause damages such as things falling |
| 6.0 or more | feel very strong |
| 7.0 or higher | major damage of this earthquake |
Question 8.
When does ox-bow lakes form?
Answer:
When there is a continuous erosion and deposition occurs along the sides of the meander, the ends of the meander loop come very closer. Hence, in due period of time the meander loop cuts off from the river and forms a cut-off lake which is known as ox-bow lakes.
Question 9.
What are the two types of tectonic movement?
Answer:
The two types of tectonic movements are Vertical earth movement and Horizontal earth movement.
![]()
Question 10.
Where do you think volcanoes are found?
Answer:
The place where the tectonic plates are pulled apart or come together, the volcanoes are found there. These are also found where there is thinning and stretching of earth’s crust happens such as in the rift valley (Africa).
Long Answer Type Questions
- Due to continuous erosion and deposition along the sides of the meander, the ends of the meander loop come very close. In due period of time the meander loop cuts off from the river and forms a cut-off lake which is also called as an oxbow lake.
- At times the river overflows its banks and and this leads to the flooding of the neighbouring areas. As it floods heavily, it deposits
Question 1.
Discuss the work of a river.
Answer:
Work of a river:
1. In the river, the running water erodes the landscape. When the river tumbles at steep angle over very hard rocks or down a steep valley side it forms a waterfall.layers of fine soil and other materials which is known as sediments along its banks. This leads to the formation of a flat fertile flood plain. This raised banks are known as levees.
2. As the river proceeds towards the sea, the speed of the flowing water
decreases and the river begins to break up into a number of streams which are known as distributaries. The river becomes so slow that it begins to deposit its load. And, each distributary forms its own mouth. The collection of sediments from all the mouths hence forms a delta.
![]()
Question 2.
Write short note on the work of sea waves.
Answer:
Work of sea waves:
- The sea waves gives rise to coastal landforms with the help of erosion and deposition. Sea waves . continuously strike at the rocks and the cracks develop. Over the period, they become larger and wider. Hence, hollow like caves are formed on the rocks. They are known as sea caves.
- As these cavities become bigger and bigger only the roof of the caves remain at last and thus forms the sea arches.
- Furthermore, erosion breaks the roof and only the walls are left. These walls like features are known as stacks.
- Above sea water, the steep rocky coast rises almost vertically is known as sea cliff”.
- The sea waves which deposits sediments along the shores forms beaches.