JAC Board Class 7th Social Science Solutions Geography Chapter 2 Inside Our Earth
JAC Class 7th Geography Inside Our Earth InText Questions and Answers
Page 9
Question 1.
Collect pictures of some monuments and find out which are the rocks used to build them.
Answer:
Students can collect pictures of monuments which are made of
- White marbles: Victoria Memorial in Kolkata; Lake Palace in Udaipur; Taj Mahal in Agra.
- Red Sandstones: Hawa Mahal in Jaipur; Buland Darwaza in Fatehpur Sikri near Agra Red Fort in Delhi.
Page 10
Question 2.
What are the minerals found in your state? Collect some samples to show in your class.
Answer:
Students need to do it on their own.
![]()
JAC Class 7th Geography Inside Our Earth Questions and Answers
Answer the following questions.
Question 1.
- What are the three layers of the earth?
- What is a rock?
- Name three types of rocks.
- How are extrusive and intrusive rocks formed?
- What do you mean by a rock cycle?
- What are the uses of rocks?
- What are metamorphic rocks?
Answer:
1. The three layers of our earth are Mantle
2. A rock is made up of a natural mass of mineral matter that makes up the earth’s cmst. They can be of different shape, colour, size and texture.
3. Three types of rocks are:
- Igneous rocks and primary rocks
- Sedimentary rocks
- Metamorphic rocks
4. When the molten lava comes down, it cools down very fast and becomes solid. In this way, the rocks formed on the crust are called the extrusive rocks. For example – basalt. Sometimes the molten magma cools down deep inside the crust of the earth. So, the solid rocks are thus formed and called the intrusive rocks. For example – granite.
5. One certain type of rock changes to another type under certain conditions in a cyclic way. This process of transformation of the rock from one to another is called the rock cycle such as igneous rocks change into sedimentary rocks. When the igneous and sedimentary rocks exposed to extreme heat. and pressure, they change into metamorphic rocks. The metamorphic rocks which are still under heat and pressure meet down to form molten magma. This again cool down and solidify into igneous rocks.
6. The rocks are used for making houses, buildings, roads. Stones are used in many games such as hopscotch (stapu / kitkit), five stones (gitti), seven stones (pitthoo) etc.
7. The igneous and the sedimentary rocks are exposed to heat and pressure, they changes into metamorphic rocks. Such as clay changes into slate, limestone changes into marble.
Tick (√) the correct answer.
Question 2:
(i) The rock which is made up of molten magma is
(a) Igneous
(b) Sedimentary
(c) Metamorphic
Answer:
(a) Igneous
(ii) The innermost layer of the earth is
(a) Crust
(b) Core
(c) Mantle
Answer:
(b) Core
![]()
(iii) Gold, petroleum and coal are examples of
(a) Rocks
(b) Minerals
(c) Fossils
Answer:
(b) Minerals
(iv) Rocks which contain fossils are
(a) Sedimentary rocks
(b) Metamorphic rocks
(c) Igneous rocks
Answer:
(c) Igneous rocks
(v) The thinnest layer of the earth is
(a) Crust
(b) Mantle
(c) Core
Answer:
(c) Core
Question 3.
Match the following.
| (i) Core | (a) Changes into slate |
| (ii) Minerals | (b) Used for roads and buildings |
| (iii) Rocks | (c) Made of silicon and alumina |
| (iv) Clay | (d) Has definite chemical composition |
| (v) Sial | (e) Innermost layer |
| (f) Changes into slate | |
| (g) Process of transformation of the rock |
Answer:
| (i) Core | (e) Innermost layer |
| (ii) Minerals | (d) Has definite chemical composition |
| (iii) Rocks | (b) Used for roads and buildings |
| (iv) Clay | (f) Changes into slate |
| (v) Sial | (c) Made of silicon and alumina |
Question 4.
Give reasons.
- We cannot go to the centre of the earth.
- Sedimentary rocks are formed from sediments.
- Limestone is changed into marble.
Answer:
1. We cannot go to the centre of the earth because we need to dig around 6000 km under the ocean bed which is not possible. Also, the centre of the earth has very high temperature and pressure.
2. Rocks break down into small pieces called the sediments. These sediments are transported and deposited by water, wind, etc. These loose sediments are composed and hardened to form layers of rocks called the sedimentary rocks.
3. Limestone is changed to marble because sedimentary rocks changes into metamorphic rocks under a extensive pressure and heat. (For Fun)
![]()
Question 5.
- What are the minerals most commonly used in the following objects?
- Identify some more objects made up of different minerals.
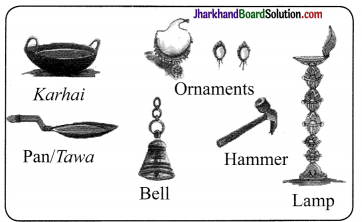
Answer:
- Karhai, Pan, Taw CL Hammer – Iron, steel Bell, lamp – brass, iron Ornaments – gold, pearl
- Utensils – aluminium, steel, copper, brass Wires – copper, aluminium Almirah – Iron Doors – Iron Windows – Iron, glass, aluminium
JAC Class 7th Geography Inside Our Earth Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
The continental mass of the crust is about km and km on the ocean floor.
(a) 5,65
(b) 45,10
(c) 35, 5
(d) 10, 50
Answer:
(c) 35, 5
Question 2.
……… is the deepest mine in the world.
(a) South Africa
(b) Australia
(c) South America
(d)Asia
Answer:
(a) South Africa
Question 3.
Rock sediments are transported and deposited by
(a) wind
(b) water
(c) Both ‘a’ and ‘b’
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Both ‘a’ and ‘b’
Question 4.
We use the following as fuel /s:
(a) petroleum
(b) coal
(c) natural gas
(d) all of these
Answer:
(d) all of these
![]()
Question 5.
The Deccan plateau is made up of
(a) clay and sandstone
(b) granite and basalt
(c) limestone
(d) basalt
Answer:
(d) basalt
Question 6.
From the sand grains is made.
(a) silicon
(b) sandstone
(c) limestone
(d) granite
Answer:
(b) sandstone
Question 7.
Below the crust, the mantle extends upto a depth of
(a) 2900 km
(b) 2000 km
(c) 2100 km
(d) 3900 km
Answer:
(a) 2900 km
Question 8.
The thickness of the outer layer of the earth is
(a) 40 km
(b) 60 km
(c) 70 km
(d) 100 km
Answer:
(b) 60 km
Question 9.
The main mineral constituents of the continental mass are
(a) silica and magnesium
(b) nickel and iron
(c) silica and alumina
(d) nickel and magnesium
Answer:
(c) silica and alumina
Question 10. The oceanic crust mainly consists of silica and magnesium called as
(a) sial
(b) sima
(c) nife
(d) nima
Answer:
(b) sima
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is the radius of the core of the earth?
Answer:
The radius of the core of the earth is 3500 km.
Question 2.
What is the crust of the earth made up of?
Answer:
The crust of the earth is made up of different types of rocks.
![]()
Question 3.
In which rock igneous and sedimentary rocks change?
Answer:
In metamorphic rocks the igneous and sedimentary rocks changes.
Question 4.
What are the main components of the core?
Answer:
The main components of the core are nickel and iron. It is generally called as nife.
Question 5.
What is the special trait of the uppermost layer of the earth?
Answer:
The special trait of the uppermost layer of the earth is that it is the thinnest of all the layers.
Question 6.
What are the components of the oceanic crust?
Answer:
The components of the oceanic crust are silica and magnesium.
Question 7.
What do you mean by lava?
Answer:
A raging and fiery red molten magma coming out from the interior of the earth on its surface is called as lava.
Question 8.
What do you mean by volcano?
Answer:
Volcano happens when magma from deep below forces its way upto earth’s outer surface.
Question 9.
What are minerals?
Answer:
Naturally occurring substances which have specific physical and definite chemical properties and composition are called the minerals.
Question 10.
What do you understand by crust?
Answer:
Crust is the uppermost layer of the earth’s surface.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Why the igneous rocks are called the primary rocks or the basic rocks?
Answer:
Our earth consists of a hot molten material which have high temperatures and pressure deep below. Igneous rocks are formed on cooling and solidification of the matter and they make up about two-thirds of the earth’s crust. Hence, they are called primary or basic rocks.
![]()
Question 2.
Volcanic ashes are found after the volcano’s eruption. What are these volcanic ashes?
Answer:
The material that comes out of the volcano are generally of three types; they are solid, liquid and gases. The solid materials are large and small fragments and pieces of rocks which are known as cinder and fine particles of these are called volcanic ashes.
Question 3.
Why formation of rocks is a slow process?
Answer:
Formation of rocks is a slow process because:
- Climate and weather breaks the parent rocks into numerous smaller pieces.
- Plants and animals organism helps in weathering of rocks.
- Elevation or topography also helps in weathering of rocks.
- Time and period also plays major role in the slow process.
Question 4.
Give examples of each of the following:
(a) Igneous rocks
(b) Sedimentary rocks
(c) Metamorphic rocks
Answer:
Examples of each of the following:
(a) Igneous rocks – basalt
(b) Sedimentary rocks – limestone, coal, sandstone, shale
(c) Metamorphic rocks – marble, slate, gnesis
Question 5.
What do you mean by fossils?
Answer:
Fossils are the remains of the dead plants and animals trapped and confined in the layer of rocks. They generally formed from the hard parts bones or shells of living things.
Question 6.
How minerals are useful for mankind?
Answer:
Some of the minerals such as coal, natural gas and petroleum are used as fuels and also in industries. Iron, aluminium, gold, uranium, etc., are used in medicine, in fertilizers, etc. Hence, minerals are very useful for mankind.
Question 7.
What do you mean by mantle?
Answer:
The intermediate layer which lies between the crust and the core of the earth is called the mantle. Its average thickness is about 2900 km and is believed to comprises of solid ultra basic rocks which are rich in iron and magnesium.
Question 8.
Why the outer crust is important to us?
Answer:
The outer crust is important to us because the solidified outer crust of the earth is having a thin crust forms the base on which human life and civilization have developed. It also consists of the valuable soil and gives us most of our minerals.
![]()
Question 9.
Differentiate between mantle and core.
Answer:
| Mantle | Core |
| • Just underneath the crust means it is the middle or centric layer of the earth. | • The innermost layer of the earth. |
| • It has a density of 3.5 km. | • It has a density of 5.1 km. |
| • The main components of minerals are silica and magnesium i.e.; SIMA. | • The main components of minerals are nickel and ferrous (iron) i.e; NIFE. |
Question 10.
Differentiate between minerals and rocks.
| Minerals | Rocks |
| • Minerals have atomic structure and contains ore. | • Rock is a collection and cluster of minerals. |
| • They have a specific and definite chemical composition. | • -They does not have a definite chemical composition. |
| • There are about 2000 types of minerals. | • Mainly they are of three types – igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic rocks. |
| • It is the natural inorganic compound which forms in the rocks. | • It is a solid natural material formed in the earth’s crust. |
| Minerals | Rocks |
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write and describe the different types and features of the rocks.
Answer:
The different types of rocks are:
- Igneous rocks
- Sedimentary rocks
- Metamorphic rocks
Igneous Rocks :
When the molten magma cools down it solidifies and rocks formed in this way are called igneous rocks. They are also known as primary rocks. These are mainly of two types:
Extrusive rocks :
When the molten lava comes on the surface of the earth, „ it cools down very fast and solidifies. Thus, rocks formed in this way on the crust are called extrusive rocks such as basalt.
Intrusive rocks:
When the molten magma cools down deep inside the earth’s crust and solidifies. Thus, rocked formed in this way are called intrusive rocks such as granite. They cool down slowly and form large grains.
Sedimentary rocks:
Small and tiny pieces of rocks are called sediments. These sediments are carried from and deposited by wind, water, etc. These ‘ loose sediments are compressed and hardened to form sedimentary rocks such as sandstone.
![]()
Metamorphic rocks:
When igneous and sedimentary rocks are exposed to enormous heat and pressure they gradually change into metamorphic rocks such as clay changes into slate.
Important Features of Rocks:
- They are found in different shapes, sizes, textures and colours.
- On the earth’s crust, different types of rocks are found.
- They can be as soft as clay or chalk and hard as granite.
Question 2:
Differentiate between crust and core.
Answer:
| Crust | Core |
| • Crust is the uppermost layer of the earth’s surface. | • Core is the innermost layer of the earth’s surface. |
| • The main mineral components are silica and alumina i.e; SIAL. | • The main mineral components are nickel and iron (ferrous) i.e; NIFE. |
| • The density is only 1.5 km. | • The density is only 5.1 km. |
| • The temperature is between 50 degree to 55 degree Celcius. | • It has pressure and the temperature is much higher than the crust. |
| • On continental mass the crust is about 35 km and on the ocean floors it is about 5 km. | • It has a radius of 3500 km. |