JAC Board Class 7th Social Science Solutions Geography Chapter 6 Natural Vegetation and Wild Life
JAC Class 7th Geography Natural Vegetation and Wild Life InText Questions and Answers
Page 39
Question 1.
Salima was excited about the summer camp she was attending. She had gone to visit Manali in Himachal Pradesh along with her class mates. She recalled how surprised she was to see the changes in the landform and natural vegetation as the bus climbed higher and higher. The deep jungles of the foothills comprising sal and teak slowly disappeared.
She could see tall trees with thin pointed leaves and cone shaped canopies on the mountain slopes. She learnt that those were coniferous trees. She noticed blooms of bright flowers on tall trees. These were the rhododendrons. From Manali as she was travelling up to Rohtang pass she saw that the land was covered with short grass and snow in some places.
![]()
Question 1.
Now can you tell why Salima saw changes in the natural vegetation as she climbed higher and higher? What type of vegetations did she see in the Himalayas starting with the foothills and going to the higher altitudes?
Answer:
Salima saw changes in the natural vegetation as she climbed higher and higher because of change in climate, slope, thickness of soil. The type of vegetation she saw in the Himalayas starting with the foothills and going to the. higher altitudes are trees such as cedar, pine, chir; snow covered coniferous forests and short grass.
Question 2.
Like Salima, when you go to visit any new place, notice the type of natural vegetation occurring there and try to think of factors responsible for the growth of such vegetation in that habitat.
Answer:
Students need to do it themselves.
Question 3.
Note down if any human interference has taken place in that area in terms of deforestation, grazing, cultivation of cash crops, constructional activities etc.
Answer:
Students need to do it themselves.
Page 41
Question 4.
Where in India do tropical evergreen and tropical deciduous forests occur? Name the states.
Answer:
In India, the tropical evergreen and tropical deciduous forests occur are
- Tropical evergreen forests: Assam, West Bengal, Nagaland, Meghalaya, Tripura, Karnataka, Tamil Nadu.
- Tropical deciduous forests: Odisha, Jharkhand Chhattisgarh, Kerala.
Question 5.
Which type of forest dominates most part of India?
Answer:
The tropical deciduous forests dominates part of India.
Page 43
Question 6.
Look around in your surroundings and find out the articles made of hard wood and soft wood.
Answer:
The articles made of Hard wood Doors, windows, tables, chairs, beds, cupboards, etc. Soft wood Match boxes, packaging materials, boats, etc.
Question 7.
Find out and learn few names of trees of your locality.
Answer:
We see mango, neem, guava, peepal, jamun trees in our locality.
JAC Class 7th Geography Natural Vegetation and Wild Life Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Answer the following questions.
(i) Which are the two factors on which the growth of vegetation mostly depends?
Answer:
The temperature and moisture are the two factors on which the growth of vegetation mostly depends.
(ii) Which are the three broad categories of natural vegetation?
Answer:
Forests, grasslands and shrubs are the three broad categories of natural vegetation.
![]()
(iii) Name the two hardwood trees commonly found in tropical evergreen forest.
Answer:
Mahogany and rosewood are the two hardwood trees commonly found in tropical evergreen forest.
(iv) In which part of the world and tropical deciduous forest is found?
Answer:
The tropical deciduous forest are found in northern Australia, Central America and in large part of India.
(v) In which climatic conditions, citrus fruits cultivated?
Answer:
In hot dry summers and mild rainy winters, citrus fruits are cultivated.
(vi) Mention the uses of coniferous . forest.
Answer:
The coniferous forests are used for manufacturing paper and newsprint, match boxes, packing boxes.
(vii) In which part of the world is seasonal grassland is found?
Answer:
In the mid-latitudinal zones and in the interior parts of the continents of the world, the seasonal grasslands are found.
Tick (√) the correct answer.
Question 2.
(i) Mosses and Lichens are found in
(a) Desert vegetation
(b) Tropical evergreen forest
(c) Tundra vegetation
Answer:
(c) Tundra vegetation
(ii) Thorny bushes are found in
(a) Hot and humid tropical climate
(b) Hot and dry desertic climate
(c) Cold polar climate
Answer:
(b) Hot and dry desertic climate
(iii) In tropical evergreen forest, one of the common animals is
(a) Monkey
(b) Giraffe
(c) Camel
Answer:
(a) Monkey
(iv) One important variety of coniferous forest is:
(a) Rosewood
(b) Pine
(c) Teak
Answer:
(b) Pine
(v) Steppe grassland is found in
(a) S. Africa
(b) Australia
(c) Central Asia
Answer:
(c) Central Asia
Question 3.
Match the following.
| (i) Walrus | (a) Soft wood tree |
| (ii) Cedar | (b) An animal of tropical deciduous forest |
| (iii) Olives | (c) A polar animal |
| (iv) Elephants | (d) Temperate grassland in Australia |
| (v) Campos | (e) Thorny shrubs |
| (vi) Downs | (f) A citrus fruit |
Answer:
| (i) Walrus | (c) A polar animal |
| (ii) Cedar | (a) Soft wood tree |
| (iii) Olives | (f) A citrus fruit |
| (iv) Elephants | (b) An animal of tropical deciduous forest |
| (v) Campos | (g) Tropical grassland of Brazil |
| (Vi) Downs | (d) Temperate grassland in Australia |
Question 4.
Give reasons.
- The animals in polar region have thick fur and thick skin.
- Tropical deciduous trees shed their leaves in the dry season.
- The type and thickness of vegetation changes from place to place.
Answer:
- The animals in polar region have thick fur and thick skin to protect themselves from extreme cold climatic conditions.
- Transpiration occurs through leaves. To reduce transpiration in dry season, the tropical deciduous trees shed their leaves in dry season.
- Due to variation in temperature and moisture, the type and thickness of vegetation changes from place to place.
(For Fun)
Question 5.
In the given crossword table given below, some words are hidden. They are all about vegetation and wildlife and are to be found horizontally and vertically. Two have been worked out for you. Work in pairs with a friend
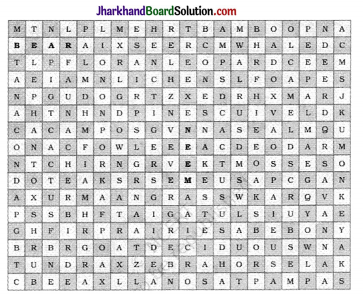
| Vegetation | Wildlife |
| 1. Neem | 1. Bear |
| 2. Bamboo | 2. Whale |
| 3. Flora | 3. Ox |
| 4. Lichen | 4. Zebra |
| 5. Pine | 5. Goat |
| 6. Chir | 6. Tiger |
| 7. Grass | 7. Yak |
| 8. Taiga | 8. Owl |
| 9. Tulsi | 9. Deer |
| 10. Fir | 10. Lion |
| 11. Tundra | 11. Fowl |
| 12. Ebony | 12. Horse |
| 13. Pampas | 13. Pig |
| 14. Llanos | 14. Camel |
| 15. Oak | Wildlife |
| 16. Mosses |
JAC Class 7th Geography Natural Vegetation and Wild Life Important Questions and Answers
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Coniferous forests are also known as
(a) Mediterranean
(b) Taiga
(c) Tundra
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Taiga
![]()
Question 2.
The forest which comprises both hard wood and softwood trees is
(a) Coniferous forest
(b) Tropical evergreen forest
(c) Temperate evergreen forest
(d) Tropical deciduous forest
Answer:
(c) Temperate evergreen forest
Question 3.
Tropical deserts are found on the margins of the continents.
(a) Northern
(b) Western
(c) Southern
(d) Eastern
Answer:
(b) Western
Question 4.
Tropical grasslands in East Africa is
(a) Campos
(b) Llanos
(c) Savannah
(d) Prairie
Answer:
(c) Savannah
Question 5.
kind of vegetation is found in steppes.
(a) Temperate grasslands
(b) Tropical evergreen forests
(c) Tropical grasslands
(d) Temperate deciduous forests
Answer:
(a) Temperate grasslands
Question 6.
The given below is a coniferous tree
(a) Teak
(b) Cedar
(c) Rosewood
(d) Pine
Answer:
(d) Pine
Question 7.
Given below tree is not a hardwood tree
(a) Rosewood
(b) Eucalyptus
(c) Ebony
(d) Mahogany
Answer:
(b) Eucalyptus
Question 8.
The most commonly found primate in India is
(a) The Rhesus Macaque
(b) The Red-faced baboon
(c) The Proboscis monkey
(d) The Grey langur
Answer:
(a) The Rhesus Macaque
![]()
Question 9.
The only species of bears found in India are
(a) Sloth bear
(b) Himalayan Black bear
(c) Asian Sun Bear
(d) None of these
Answer:
(b) Himalayan Black bear
Question 10.
Thorny bushes are mainly found in
(a) Cold polar climate
(b) Hot and humid tropical climate
(c) Hot and dry desert climate
(d) None of these
Answer:
(c) Hot and dry desert climate
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What do the term Taiga mean in Russian language?
Answer:
The term taiga means untouched or pure in the Russian language.
Question 2.
What is the reason which makes the coniferous forest unique?
Answer:
The reason which makes the coniferous forest unique is the tall and softwood evergreen trees. .
Question 3.
What is the alternate name of tropical evergreen forests?
Answer:
The alternate nathe of tropical evergreen forests is tropical rainforests.
Question 4.
Where is Veld Temperate Grassland situated?
Answer:
Veld Temperate Grassland is situated in Africa.
Question 5.
What is the main feature of polar region?
Answer:
The main feature of polar region is that it is very cold.
Question 6.
Where are Campos found?
Answer:
Campos are found in Brazil.
Question 7.
What animals are found in the tropical grasslands?
Answer:
Animals which are found in the tropical grasslands are elephants, zebras, giraffes, deer, leopards, etc.
Question 8.
Where are Savannah grasslands found?
Answer:
Savannah grasslands are found in Africa.
Question 9.
Which place is known as ‘Orchards of the World’ and why?
Answer:
Mediterranean places are known as ‘Orchards of the World’ because for their fruit cultivation.
![]()
Question 10.
In which region temperate evergreen forests are found?
Answer:
The thick forests are found in the regions near the equator and close to the tropics.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
The equatorial forests are considered as the lungs of the earth. Why?
Answer:
The tropical evergreen forest or the equatorial forests in Brazil are so enormous that it is like the lungs of the earth.
Question 2.
What are the features of Mediterranean trees?
Answer:
The features of Mediterranean trees are that they adapt themselves to dry summers with the help of their thick barks and wax coated leaves which help them to lessen the transpiration.
Question 3.
Write a note on anaconda.
Answer:
Anaconda is one of the world’s largest snakes. They are very huge and non- poisonous snakes. They are found in the tropical rainforest. Anaconda can kill and eat a large animal such as a crocodile.
Question 4.
Does altitude affect vegetation? If yes then-how?
Answer:
Yes, altitude affects vegetation. A close relationship between height of land and the character of vegetation is present. With the change in height, the climate changes and thus changes the natural vegetation.
Question 5.
Name the different types of grasslands. Answer: Different grasslands are:
- Savannah in East Africa
- Campos in Brazil
- Llanos in Venezuela
- Pampas in Argentina
- Prairie in North America
- Veld in South Africa
- Steppe in Central Asia
- Down in Australia.
Question 6.
Write the important features of tropical evergreen forests.
Answer:
Important features of tropical evergreen forests are:
- These forests are so dense and opaque that thick canopies and sunshades are developed which do not allow the sunlight to penetrate and go inside the forest.
- There is no particular dry season, hence the trees do not shed their leaves altogether. This keeps the forest evergreen.
- Hardwood trees such as rosewood, ebony and mahogany, etc., are found here.
Question 7.
Brief about the tropical grasslands.
Answer:
The tropical grasslands develop on either side of the equator and extend till the tropics. This vegetation grows in the regions of moderate to low amount of rainfall. The grass can grow very tall to a height of about 3 to 4 metres. One of this type of grasslands are Savannah grasslands of Africa. Some ; of the animals found here are elephants, zebras, giraffes, deer and leopards.
![]()
Question 8.
What are the different kinds of h natural forests found?
Answer:
The different kinds of natural forests’ found are
- Tropical evergreen forest
- Tropical deciduous forest
- Temperate evergreen forest
- Temperate deciduous forest
- Mediterranean vegetation
- Coniferous forest
Question 9:
Write a short note on the natural vegetation and wildlife found in the polar regions.
Answer:
The growth of natural vegetation is very limited here as the polar regions are extremely cold. Only mosses, lichens and very and small shrubs are found here and grow during the very short summer. This is known as Tundra type of vegetation and found in the polar regions of Europe, Asia and North America. The animals found here have thick fur and skin which protect them from the cold and harsh climatic
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 10.
Explain different types of forests.
Answer:
Different types of forests are:
- Tropical evergreen forests
- Tropical deciduous forests
- Temperate evergreen forests
- Temperate deciduous forests
- Mediterranean vegetation
- Coniferous forests
Tropical evergreen forests :
These forests are very dense and thick and found in the regions near the equator and close to the tropics. They receive heavy rain all through the year. The trees of these forests do not shed their leaves altogether and therefore they remain green all the time and called as evergreen. Hardwood trees like rosewood, ebony and mahogany are found here.
Tropical deciduous forests:
These forest are found in the areas which experience seasonal changes and trees shed their leaves in the dry season to conserve water. The hardwood trees such as sal, teak, neem and shisham are found in this region. Animals like tigers, lions, elephants, langoors and monkeys are found in these forests.
![]()
Temperate evergreen forests:
These forests are found along the eastern margin of the continents. They contains both hard and softwood trees such as oak, pine, eucalyptus, etc.
Temperate deciduousf orests:
Trees of these forests shed their leaves in dry season. Trees found here are oak, ash, beech, etc. Deer, foxes, wolves, etc., are some of the animals found in these forests.
Mediterranean vegetation :
It is found in the areas around the Mediterranean sea in Europe, Africa and Asia. Citrus fruits like oranges, figs, olives and grapes are cultivated in the Mediterranean regions.
Coniferous forests :
These forests are also known as Taiga. They are tall, softwood evergreen trees. Chir, pine, cedar are important types of trees found in these forests. Silver, fox, mink, polar bear are the some of the animals found here.