Jharkhand Board JAC Class 9 Science Solutions Chapter 1 हमारे आस-पास के पदार्थ Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
JAC Board Class 9 Science Solutions Chapter 1 हमारे आस-पास के पदार्थ
Jharkhand Board Class 9 Science हमारे आस-पास के पदार्थ Textbook Questions and Answers
प्रश्न 1.
निम्नलिखित तापमानों को सेल्सियस इकाई में परिवर्तित करें-
(a) 300K
(b) 573K
उत्तर:
सेल्सियस K273
(a) सेल्सियस = 300 K – 273 = 27°C
(b) सेल्सियस 573K – 273 = 300°C
प्रश्न 2.
निम्नलिखित तापमानों को केल्विन इकाई में परिवर्तित करें-
(a) 25°C
(b) 373°C
उत्तर:
केल्विन = सेल्सियस + 273
(a) 25°C केल्विन (25+ 273) K 298K
(b) 373°C केल्विन (373273) K= 646K
प्रश्न 3.
निम्नलिखित अवलोकनों हेतु कारण लिखें-
(a) नैफ्थलीन को रखा रहने देने पर यह समय के साथ कुछ भी ठोस पदार्थ छोड़े बिना अदृश्य हो जाती है।
(b) हमें इत्र की गंध बहुत दूर बैठे हुए भी पहुँच जाती है।
उत्तर:
(a) नैफ्थलीन की गोलियाँ बिना कोई अवशेष छोड़ गायब हो जाती हैं क्योंकि उनका ऊर्ध्वपातन हो जाता है। अर्थात ठोस अवस्था से बिना द्रव में बदले गैसीय अवस्था में परिवर्तित हो जाता है। इस क्रिया को ऊर्ध्वपातन कहते हैं।
(b) इत्र के कण अपने-आप हवा के कणों के साथ मिलकर चारों तरफ फैल जाते हैं। इत्र के कणों के इस तरह फैलने के कारण कुछ दूरी पर बैठे होने पर भी हम इसकी गंध प्राप्त कर लेते हैं।
प्रश्न 4.
निम्नलिखित पदार्थों को उनके कणों के बीच बढ़ते हुए आकर्षण के अनुसार व्यवस्थित करें-
(a) जल
(b) चीनी
(c) ऑक्सीजन।
उत्तर:
अन्तराण्विक आकर्षण बल सबसे कम गैस में, उससे अधिक द्रव में सबसे अधिक ठोस में होता है अतः यह ऑक्सीजन में सबसे कम, फिर जल में तथा सर्वाधिक चीनी में होगा।
![]()
प्रश्न 5.
निम्नलिखित तापमानों पर जल की भौतिक अवस्था क्या है?
(a) 25°C
(b) 0°C
(c) 100°C
उत्तर:
(a) 25°C पर – द्रव अवस्था में होगा।
(b) 0°C पर ठोस अवस्था में होगा।
(c) 100°C पर वाष्प अवस्था में होगा।
प्रश्न 6.
पुष्टि हेतु कारण दें-
(a) जल कमरे के ताप पर द्रव है।
(b) लोहे की अलमारी कमरे के ताप पर ठोस है।
उत्तर:
(a) कमरे के ताप पर पानी द्रव होता है क्योंकि इसका कोई निश्चित आकार नहीं होता। यह उस बर्तन का आकार ग्रहण कर लेता है जिसमें उसे रखा जाता है तथा यह आसानी से प्रवाहित हो सकता है। अतः यह तरल है।
(b) लोहे की अलमारी एक ठोस है क्योंकि इसका आकार निश्चित होता है। यह प्रवाहित नहीं होती। अर्थात् यह ठोस है।
प्रश्न 7.
273 K पर बर्फ को ठंडा करने पर तथा जल को इसी तापमान पर ठंडा करने पर शीतलता का प्रभाव अधिक क्यों होता है?
उत्तर:
273K पर पानी के कणों की अपेक्षा बर्फ के कणों की ऊर्जा कम होती है। अतः बर्फ वातावरण से अधिक ऊष्मा अवशोषित कर सकती है। यही कारण है कि समान ताप पर होते हुए भी बर्फ पानी की अपेक्षा अधिक ठंडक पहुँचाती है।
प्रश्न 8.
उबलते हुए जल अथवा भाप में से जलने की तीव्रता किसमें अधिक महसूस होती है?
उत्तर:
373 K पर वाष्प के कणों की ऊर्जा समान ताप पर पानी के कणों की ऊर्जा से अधिक होती है। ऐसा वाष्प के कणों द्वारा वाष्पन की गुप्त ऊष्मा के रूप में अतिरिक्त ऊर्जा अवशोषित किए जाने के कारण होता है। अतः जब वाष्प त्वचा के सम्पर्क में आती है तो समान ताप पर उबलते पानी की अपेक्षा अधिक ऊर्जा मुक्त करती है। इसलिए 373 K पर वाष्प द्वारा समान ताप पर उबलते पानी की अपेक्षा अधिक जलन पैदा होती है।
प्रश्न 9.
निम्नलिखित चित्र के लिए A, B, C, D, E तथा F की अवस्था परिवर्तन को नामांकित करें :
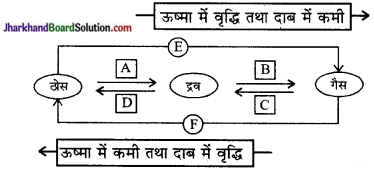
उत्तर:
- A – संगलन
- B – वाष्पन
- C – संघनन
- D – जमना
- E – ऊर्ध्वपातन
- F – निक्षेपण
Jharkhand Board Class 9 Science हमारे आस-पास के पदार्थ InText Questions and Answers
क्रियाकलाप 1.
एक 100 mL का बीकर लेकर उसे जल से आधा भरकर जल के स्तर पर निशान लगा देते हैं। अब चम्मच में रखे गए नमक या शक्कर (चीनी) को काँच की छड़ की मदद से घोल लें तथा जल के स्तर में बदलाव को देखें। (पाठ्य-पुस्तक पृ. सं. -1)
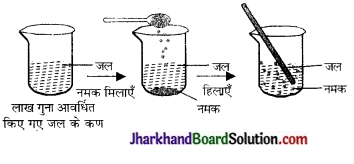
अब उत्तर दें-
प्रश्न 1.
नमक या शक्कर (चीनी) का क्या हुआ? ये कहाँ गायब हो गए?
उत्तर:
जल में नमक या शक्कर को घोलने पर इनके कण जल के कणों के बीच स्थित रिक्त स्थानों में समावेशित हो जाते हैं तथा दिखाई नहीं देते हैं।
प्रश्न 2.
क्या जल के स्तर में कोई बदलाव आया?
उत्तर:
नहीं।
क्रियाकलाप 2.
100 ml पानी को एक बीकर में लेकर उसमें 2 या 3 क्रिस्टल पोटैशियम परमैगनेट के डालकर घोल बनाइये।
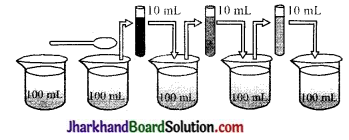
इस घोल से 10mL घोल निकालकर उसे 90mL जल में मिला दें। फिर इस घोल में से 10 ml निकालकर उसे भी 90ml जल में एक अन्य बीकर में मिला दें। इसी प्रकार इस घोल को 5 से 8 बार तनुकृत (Dilute ) करें।
अब उत्तर दें-
प्रश्न 1.
पोटैशियम परमैगनेट के एक क्रिस्टल में कितने सूक्ष्म कण होते हैं?
उत्तर:
पोटैशियम परमैगनेट के एक क्रिस्टल में बहुत से सूक्ष्म कण होते हैं तथा ये कण भी अत्यन्त छोटे-छोटे कणों में एक सीमा तक विभाजित किए जा सकते हैं।
प्रश्न 2.
जल के रंग के बारे में आपका क्या निष्कर्ष है?
उत्तर:
जल का रंग धीरे-धीरे हल्का होता जाता है फिर भी यह रंगीन ही रहता है।
क्रियाकलाप 3.
अपनी कक्षा के किसी कोने में एक बुझी हुई अगरबत्ती रख देने पर इसकी सुगन्ध लेने के लिए आपको इसके पास जाना पड़ेगा। यदि यही अगरबत्ती जल रही हो तब इसकी सुगन्ध दूर से भी आ जाती है। इस क्रियाकलाप द्वारा प्रदर्शित होता है कि पदार्थ के कण निरन्तर गतिशील होते हैं। (पाठ्य-पुस्तक पृ. सं. – 2)
![]()
क्रियाकलाप 4.
जल से भरे दो गिलास लें। पहले गिलास के एक सिरे पर सावधानी से एक बूँद लाल या नीली स्याही की डालें तथा दूसरे में शहद डालें और प्रेक्षण को नोट करें। स्याही जल में तुरन्त फैल जाती है।
(पाठ्य पुस्तक पृ. सं. – 3)
क्रियाकलाप 5.
यदि दो गिलास लेकर उसमें से एक में ठंडा पानी व दूसरे में गर्म पानी डाला जाए तथा अब इन दोनों में एक-एक क्रिस्टल पोटैशियम परमैगनेट का डाला जाए, तब हम पाते हैं कि गर्म जल वाले गिलास का पानी जल्दी रंगीन हो जाता है।
अब उत्तर दें-
प्रश्न 1.
क्या पदार्थ के कण निरन्तर गतिशील रहते हैं?
उत्तर:
हाँ, पदार्थ के कण निरन्तर गतिशील रहते हैं, अर्थात इनमें गतिज ऊर्जा होती है।
प्रश्न 2.
तापमान का पदार्थ के कणों की गतिशीलता पर क्या प्रभाव पड़ता है?
उत्तर:
तापमान बढ़ाने से पदार्थ के कणों की गतिशीलता बढ़ जाती है।
प्रश्न 3.
पदार्थ के कण अपने आप अन्तः मिश्रित क्यों हो जाते हैं?
उत्तर:
पदार्थ के कणों के बीच रिक्त स्थान होता है। इन रिक्त स्थानों में कणों के समावेश के कारण ये अन्तः मिश्रित हो जाते हैं।
प्रश्न 4.
विसरण को परिभाषित कीजिए।
उत्तर:
दो विभिन्न पदार्थों के कणों का स्वत: मिलना ही विसरण कहलाता है।
प्रश्न 5.
तापमान का विसरण पर क्या प्रभाव पड़ता है?
उत्तर:
तापमान बढ़ाने पर वि रण तेज हो जाता है।
क्रियाकलाप 6.
एक खेल के मैदान में चार समूह बनाकर मानव श्रृंखला बनाएँ। पहले समूह में ‘ईद्- मिश्मी नर्तकों’ की तरह एक दूसरे को पीछे से कसकर पकड़ लें। दूसरे समूह में एक दूसरे का हाथ पकड़कर मानव श्रृंखला बनाएँ। तीसरे समूह में केवल उंगली के सिरे से छूकर एक श्रृंखला बना लें। अब चौथे समूह द्वारा इन तीनों मानव श्रृंखलाओं को तोड़कर छोटे समूह में बाँटने का प्रयास करें। (पाठ्य पुस्तक पृ. सं. 3)
क्रियाकलाप 7.
एक लोहे की कील, एक चॉक का टुकड़ा एवं एक रबर बैंड काटकर या खींचकर उसे लेकर इन पर हथौड़ा मारकर, भंगुर करने का प्रयास करें। (पाठ्य पुस्तक पृ. सं. – 4)
क्रियाकलाप 8.
एक थाली में जल लेकर उसे उंगली से काटने का प्रयास करें एवं प्रेक्षण लें।
अब उत्तर दें-
प्रश्न 1.
क्रियाकलाप 6 में, यदि प्रत्येक समूह में उपस्थित व्यक्तियों को कणों के रूप में माना जाए तो किस समूह में कणों से आपस में सर्वाधिक बल लगता है?
उत्तर:
प्रथम समूह में सर्वाधिक बल लगता है क्योंकि इसमें प्रत्येक व्यक्ति एक-दूसरे को पीछे से कसकर पकड़ता है, अतः प्रत्येक पदार्थ में कणों के बीच एक बल कार्य करता है जो कर्णों को एक साथ रखता है।
प्रश्न 2.
क्रियाकलाप 7 में तीनों में से किसके कण अधिक बल से एक दूसरे को जकड़े हुए हैं?
उत्तर:
लोहे की कील के कण अधिक बल से एक- दूसरे को जकड़े हुए हैं।
![]()
प्रश्न 3.
क्रियाकलाप 8 में क्या जल की धारा कटती है?
उत्तर:
नहीं।
प्रश्न 4.
जल की सतह न कटने का क्या कारण है?
उत्तर:
जल के कणों के बीच आकर्षण बल अधिक है इसी कारण जल की सतह उंगली को बीच में करने से नहीं कटती है।
खंड 1.1 1.2 से सम्बन्धित पाठ्य पुस्तक के प्रश्न
प्रश्न 1.
निम्नलिखित में से कौन से पदार्थ हैं- (पाठ्य पुस्तक पृ. सं. 4)
कुर्सी, वायु, स्नेह, गंध, नींबू पानी, इत्र घृणा, बादाम, विचार, शीत, की सुगंध।
उत्तर:
कुर्सी, वायु, बादाम व नींबू पानी पदार्थ हैं।
प्रश्न 2.
निम्नलिखित प्रेक्षण के कारण बताएँ- गर्मा-गरम खाने की गंध कई मीटर दूर से ही आपके पास पहुँच जाती है, लेकिन ठंडे खाने की महक लेने के लिए आपको उसके पास जाना पड़ता है।
उत्तर:
पदार्थ के कण सदैव गतिशील रहते हैं तथा तापमान बढ़ने पर कणों की गति तेज हो जाती है। खाने की गंध विसरण विधि द्वारा हम तक पहुँचती है। गर्म खाने का तापमान अधिक होने के कारण विसरण की दर ठंडे खाने की अपेक्षा अधिक होती है अतः कई मीटर दूर से ही गंध हम तक पहुँच जाती है।
प्रश्न 3.
स्वीमिंग पूल में गोताखोर पानी काट पाता है। इससे पदार्थ का कौन-सा गुण प्रेक्षित होता है?
उत्तर:
स्वीमिंग पूल में पानी के कणों के बीच लगने वाला आकर्षण बल गोताखोर के द्वारा लगाये बल से कम होता है जिसके कारण गोताखोर पानी को काट पाता है।
प्रश्न 4.
पदार्थ के कणों की क्या विशेषताएँ होती हैं?
उत्तर:
पदार्थों के कणों के बीच निम्नलिखित विशेषताएँ होती हैं-
- पदार्थ के कणों के बीच रिक्त स्थान होता है।
- पदार्थ के कण निरन्तर गतिशील होते हैं।
- पदार्थ के कण एक-दूसरे को आकर्षित करते हैं।
अब उत्तर दें-
प्रश्न 1.
रबर बैंड को क्या हम ठोस कह सकते हैं? क्या खींचकर इसका आकार बदला जा सकता है?
उत्तर:
बाह्य बल लगाने पर रबर बैंड का आकार बदलता है तथा बल को हटा लेने पर यह पुनः उसी आकार में आ जाता है परन्तु एक सीमा से अधिक बल लगाने पर यह टूट जाता है। अतः रबर बैंड को ठोस कह सकते हैं।
प्रश्न 2.
चीनी व नमक को जिस बर्तन में रखा जाता है, वे उन्हीं बर्तनों के आकार को ग्रहण कर लेते हैं। क्या ये ठोस हैं?
उत्तर:
ये सभी ठोस हैं, क्योंकि इन्हें किसी प्लेट या जार में रखने पर इनके क्रिस्टलों के आकार में परिवर्तन नहीं होता है।
प्रश्न 3.
स्पंज एक ठोस है फिर भी इसका संपीडन संभव है, क्यों?
उत्तर:
स्पंज में बहुत छोटे-छोटे छिद्र होते हैं जिनमें वायु भरी रहती है, जब हम स्पंज को दबाते हैं तो उसमें भरी वायु बाहर निकल जाती है। इसी कारण स्पंज का संपीडन सम्भव हो जाता है।
अब उत्तर दें-
प्रश्न 1.
इन द्रवों को यदि फर्श पर डाल दिया जाए तो क्या होगा?
उत्तर:
फर्श पर डालने पर ये सभी द्रव बहने लगते हैं परन्तु इनके गाड़ेपन व पतलेपन के कारण बहने के वेग अलग-अलग होते हैं।
प्रश्न 2.
यदि किसी द्रव का 50 mL मापकर विभिन्न बर्तनों में क्रमशः एक-एक करके डाला जाए तो क्या प्रत्येक अवस्था में आयतन समान रहता है?
उत्तर:
हाँ, प्रत्येक अवस्था में आयतन समान ही रहता है।
प्रश्न 3.
क्या द्रव का आकार एकसमान रहता है?
उत्तर:
नहीं, द्रव का आकार बर्तन की आकृति के अनुसार बदलता है।
प्रश्न 4.
द्रव को एक बर्तन से दूसरे बर्तन में उड़ेलने पर क्या यह आसानी से बहता है?
उत्तर:
हाँ, यह आसानी से बहता है।
प्रश्न 5.
द्रवों में विसरण दर ठोसों से अधिक क्यों होती है?
उत्तर:
ठोस की अपेक्षा द्रव के कर्णों में रिक्त स्थान अधिक होने के कारण द्रवों में विसरण की दर ठोसों से अधिक होती है।
![]()
प्रश्न 6.
उपरोक्त क्रियाकलाप से क्या निष्कर्ष निकलता है?
उत्तर:
द्रव का आयतन निश्चित होता है लेकिन आकार अनिश्चित होता है। इन्हें जिस बर्तन में रखा जाता है ये उसी का आकार ग्रहण कर लेते हैं।
क्रियाकलाप 11.
100 mL की तीन सीरिन्ज लेकर उनके सिरों को रबर के कॉर्क से बन्द कर दें तथा सभी के पिस्टन को हटा दें। पहली सीरिज में हवा रहने दें, दूसरी सीरिज में जल तथा तीसरी में चॉक के टुकड़े भर दें। सीरिन्ज के आसानी से गतिशील होने के लिए उस पर वैसलीन लगा दें तथा पिस्टन को सिरिन्ज में डालकर संपीडित करने की कोशिश करें।
अब उत्तर दें-
प्रश्न 1.
पिस्टन किस स्थिति में आसानी से भीतर चला जाता है?
उत्तर:
पिस्टन हवा के सिरिन्ज में रहने पर आसानी से भीतर चला जाता है।
प्रश्न 2.
इस प्रेक्षण से क्या पता चलता है?
उत्तर:
इससे यह पता चलता है कि हवा (गैसों) को ठोसों व द्रवों की अपेक्षा अधिक दबाया जा सकता है। इसका अर्थ है कि गैसों की संपीड्यता (Compressibility) बहुत अधिक होती है।
नोट- संपीड्यता के गुण का उपयोग घरों में खाना बनाने में उपयोग की जाने वाली सिलिण्डर में भरी जाने वाली गैसों में किया जाता है। सिलिण्डर में भरी गैस द्रवीकृत पेट्रोलियम गैस (LPG) को संपीड्य करके ही भरा जाता है, आजकल वाहनों में संपीडित प्राकृतिक गैस (CNG) का उपयोग किया जाता है। संपीड्यता अधिक होने के कारण गैस के अधिक आयतन को कम आयतन में संपीडित किया जा सकता है।
खंड 1.3 से सम्बन्धित पाठ्य पुस्तक के प्रश्न (पा.पु. पृ. सं. – 6)
प्रश्न 1.
किसी तत्व के द्रव्यमान प्रति इकाई आयतन को घनत्व कहते हैं।
(घनत्व = द्रव्यमान / आयतन) बढ़ते हुए घनत्व के क्रम में निम्नलिखित को व्यवस्थित करें-वायु, चिमनी का धुआँ, शहद, जल, चॉक, रुई और लोहा।
उत्तर:
वायु, चिमनी का धुआँ, रुई, जल, शहद, चॉक, लोहा।
प्रश्न 2.
(a) पदार्थ की विभिन्न अवस्थाओं के गुणों में होने वाले अन्तर को सारणीबद्ध कीजिए। (b) निम्नलिखित पर टिप्पणी कीजिए -दृढ़ता, संपीड्यता, तरलता, बर्तन में गैस का भरना, आकार, गतिज ऊर्जा एवं घनत्व।
उत्तर:
(a) पदार्थ की विभिन्न अवस्थाओं के गुणों में होने वाले अर-
| ठोस | द्रव | गैस |
| 1. ठोसों का निश्चित आयतन व आकार होता है। | द्रव का आयतन तो निशिचत होता है किन्तु आकार निशिचत नहीं होता। | गैसों का आयतन तथा आकार निश्चित नहीं होता। गैसें जिस बर्तन में रखी जाती हैं, उसी का आयतन तथा आकार ग्रहण कर लेती हैं। |
| 2. इन्हें दबाया नहीं जा सकता। | द्रव उच्च तल से निम्न तल की ओर बहते हैं। | इन्हैं दबाया जा सकता है। |
| 3. इनके गलनांक व क्वथनांक कक्षताप से अधिक होते हैं। | इनमें गलनांक कक्षताप से कम तथा क्वथनांक कक्षतताप से अधिक होते हैं। | इनके गलनांक तथा क्वथनांक क क्षताप अधिक होते हैं। |
| 4. इन्हें संपीडित नहीं किया जा सकता। | इन्हें संपीडित नहीं किया जा सकता है। | इन्हें संपीडित किया जा सकता है। |
| 5. कणों के बीच आकर्ष ण बल अधिक होता है। | कणों के बीच आकर्षण बल ठोसों से कम होता है। | कणों के बीच आकर्षण बल द्रवों से कम होता है। |
| 6. ठोस में विसरण द्रव तथा गैसों की अपेक्षा कम होता है। | विसरण तीव्र होता है। | विसरण द्रवों से अधिक होता है। |
(b) दृढ़ता – ठोस पदार्थों के कण आपस में अत्यधिक आकर्षण बल से जुड़े होते हैं जिससे उन्हें तोड़ना या दबाना कठिन होता है, इसे दृढ़ता कहते हैं।
संपीड्यता – द्रव व गैसीय पदार्थों के कणों के बीच अत्यधिक रिक्त स्थान होता है, जिसमें हवा भरी होती है, जिससे वह दबाये जा सकते हैं। इस गुण को संपीड्यता कहते हैं।
तरलता – पदार्थों के बहने के गुण को तरलता कहते हैं।
बर्तन में गैस का भरना – गैसों के बीच काफी रिक्त स्थान होता है इसीलिए उन्हें काफी दबाया जा सकता है। इस प्रकार एक छोटे बर्तन में काफी गैस भरी जा सकती है।
आकार – कोई वस्तु जितना स्थान घेरती है, उसे उस वस्तु का आकार कहते हैं।
गतिज ऊर्जा – वस्तुओं में गति के कारण जो ऊर्जा या कार्य करने की क्षमता होती है, उसे गतिज ऊर्जा कहते हैं।
K.E. = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 }\) mv²
(जहाँ m वस्तु का द्रव्यमान तथा वस्तु का वेग है)
घनत्व – किसी वस्तु के इकाई आयतन के द्रव्यमान को घनत्व कहते हैं।

प्रश्न 3.
कारण बताएँ – (a) गैस पूरी तरह उस बर्तन को भर देती हैं, जिसमें इसे रखते हैं। (b) गैस बर्तन की दीवारों पर दबाव डालती हैं। (c) लकड़ी की मेज ठोस कहलाती है। (d) हवा में हम आसानी से अपना हाथ चला सकते हैं लेकिन ठोस लकड़ी के टुकड़े में हाथ चलाने के लिए हमें कराटे में दक्ष होना पड़ेगा।
उत्तर:
(a) गैस के कणों के बीच आकर्षण बल नगण्य होता है। गैस के कण एक-दूसरे से दूर-दूर होते हैं और उसमें बहने का गुण होता है जिससे वह जिस बर्तन में रखे जाते हैं, उस पूरे बर्तन में फैल जाते हैं।
(b) गैस के अणु तीव्र गति से इधर-उधर घूमते रहते हैं और जिस बर्तन में होते हैं, उसकी दीवारों से टकराते हैं। जिससे बर्तन की दीवारों पर दबाव डालते हैं।
(c) लकड़ी के कण पास-पास होते हैं और अत्यधिक बल से जुड़े होते हैं जिससे उनका आयतन तथा आकार निश्चित होता है, जो ठोस का गुण हैं अतः लकड़ी ठोस है। इसलिए लकड़ी की मेज ठोस कहलाती है।
(d) हवा के कणों के बीच में आकर्षण बल बहुत कम होता है, (लगभग नगण्य )। इसलिए हवा के अणु आसानी से काटे जा सकते हैं और हवा में हाथ आसानी से चला सकते हैं। जबकि लकड़ी के कणों के बीच में आकर्षण बल अधिक होता है तथा लकड़ी के कण पास-पास होते हैं। अतः हाथ चलाने के लिए कराटे में दक्ष होना चाहिए।
प्रश्न 4.
सामान्यतया ठोस पदार्थों की अपेक्षा द्रवों का घनत्व कम होता है। लेकिन आपने बर्फ के टुकड़ों को पानी पर तैरते देखा होगा। पता लगाइए ऐसा क्यों होता है?
उत्तर:
बर्फ का टुकड़ा अपने अधिक आयतन के कारण अपने द्रव्यमान से अधिक पानी हटा देता है। इसलिए बर्फ का टुकड़ा पानी पर तैरता रहता है। बर्फ का आयतन जल से अधिक होता है।
अब उत्तर दें-
प्रश्न 1.
बर्फ क्यों पिघल जाती है?
उत्तर:
बर्फ को दी गई ऊष्मा उसके कणों की गतिज ऊर्जा में वृद्धि कर देती है, इस कारण कण अपने नियत स्थान को छोड़कर अधिक स्वतन्त्र होकर गति करने लगते हैं। एक अवस्था ऐसी आती है, जब ठोस (बर्फ) पूर्णतः पिघलकर द्रव में परिवर्तित हो जाता है।
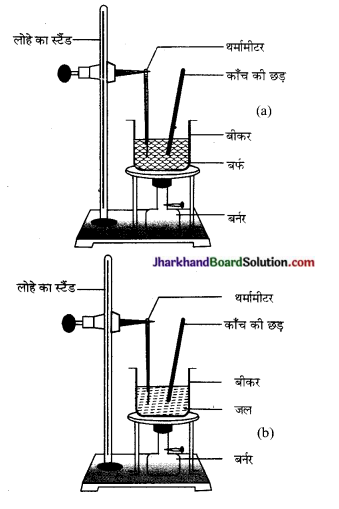
चित्र:
(a) बर्फ़ का जल में बदलने की प्रक्रिया
(b) जल से जलवाष्प में बदलने की प्रक्रिया।
प्रश्न 2.
गलनांक किसे कहते हैं?
उत्तर:
वह निश्चित तांपमान जिस पर ठोस पिघलकर द्रव बन जाता है, वह इसका गलनांक कहलाता है।
प्रश्न 3.
किसी ठोस का गलनांक क्या दर्शाता है?
उत्तर:
किसी ठोस का गलनांक उसके कणों के बीच के आकर्षण बल के सामर्थ्य को दर्शाता है।
प्रश्न 4.
बर्फ का गलनांक कितना होता है?
उत्तर:
273.15 K।
प्रश्न 5.
गुप्त ऊष्मा से आप क्या समझते हो?
उत्तर:
गलने की प्रक्रिया के दौरान जब तक सम्पूर्ण बर्फ पिघल नहीं जाती है तापमान नहीं बदलता है, तापमान में बिना किसी तरह की वृद्धि दर्शाए इस ऊष्मीय ऊर्जा को बर्फ अवशोषित कर लेती है। यह ऊर्जा बीकर में ली गई सामग्री में छुपी रहती है, इसे ही गुप्त ऊष्मा कहते हैं।
प्रश्न 6.
गुप्त ऊष्मा को परिभाषित कीजिए।
उत्तर:
वायुमण्डलीय दाब पर किग्रा ठोस को उसके गलनांक पर द्रव में बदलने के लिए आवश्यक ऊर्जा की मात्रा को गुप्त ऊष्मा कहा जाता है।
![]()
प्रश्न 7.
जल के वाष्पीकरण की गुप्त ऊष्मा क्या है?
उत्तर:
373 K (100°C) वाष्पीकरण की गुप्त ऊष्मा है। (पा. पु. पृ. सं. 8)
क्रियाकलाप 13.
चीनी की प्याली में थोड़ा सा कपूर या अमोनियम क्लोराइड (NH4 Cl) लिया तथा इसका चूर्ण बनाया। एक कीप को उल्टा करके इस प्याली के ऊपर रख दिया तथा इसे गर्म किया तब हम पाते हैं कि कपूर या अमोनियम क्लोराइड बिना द्रव अवस्था में परिवर्तित हुए सीधे गैस में बदल गया। इस क्रिया को ऊर्ध्वपातन कहते हैं।
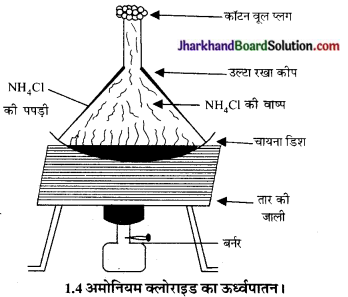
अब उत्तर दें-
प्रश्न 1.
ऊर्ध्वपातन किसे कहते हैं?
उत्तर:
द्रव अवस्था में परिवर्तित हुए बिना ठोस अवस्था से सीधे गैस अवस्था में बदलने की प्रक्रिया को ऊर्ध्वपातन कहते हैं। गैस के सीधे ठोस में बदलने की प्रक्रिया निक्षेपण कहलाती है।
खंड 1.4 से सम्बन्धित पाठ्य पुस्तक के प्रश्न (पा. पु. पू. सं. १)
प्रश्न 1.
निम्नलिखित तापमान को सेल्सियस में बदलें-
(a) 300K
(b) 573 K
उत्तर:
सेल्सियस K – 273
(a) सेल्सियस- 300K 273 27°C
(b) सेल्सियस = 573K – 273300°C
प्रश्न 2.
निम्नलिखित ताप पर जल की भौतिक अवस्था क्या होगी?
(a) 250°C
(b) 100°C
उत्तर:
(a) 250°C पर जल वाष्प अवस्था में होगा।
(b) 100°C पर जल द्रव अवस्था में होगा तथा उबल रहा होगा एवं वाष्प में परिवर्तित हो रहा होगा।
प्रश्न 3.
किसी भी पदार्थ की अवस्था परिवर्तन के दौरान तापमान स्थिर क्यों रहता है?
उत्तर:
किसी पदार्थ का तापमान बढ़ाने पर वह दूसरी अवस्था में परिवर्तित होना प्रारम्भ कर देता है। एक निश्चित ताप के बाद ताप स्थिर हो जाता है क्योंकि अब समस्त ऊर्जा, अवस्था परिवर्तन के काम आती है। ऐसा तब तक होता रहता है जब तक पदार्थ एक अवस्था से दूसरी अवस्था में पूर्ण रूप से परिवर्तित न हो जाए, इस ऊष्मा को पदार्थ की गुप्त ऊष्मा कहते हैं।
प्रश्न 4.
वायुमण्डलीय गैसों को द्रव में परिवर्तन करने के लिए कोई विधि सुझाइए।
उत्तर:
पदार्थों की अवस्थाएँ दाब व तापमान पर निर्भर होती हैं। अतः वाष्प अवस्था में ताप कम करके व दाब बढ़ाकर अवस्था परिवर्तन किया जा सकता है। वायुमण्डलीय गैसें ऊँचाई पर होती हैं जहाँ ताप कम होता है। ताप कम होने के कारण गैसें संघनित होकर बादलों में बदल जाती हैं जो द्रव की छोटी-छोटी बूँदों से मिलकर बना होता है।
क्रियाकलाप 14.
एक परखनली में 5 mL जल लेकर इसे खिड़की के पास या पंखे के नीचे रखें खुली रखी चीनी मिट्टी की प्याली में जल रखकर उसे खिड़की के पास या पंखे के नीचे रख दें। एक अन्य चीनी मिट्टी की प्याली में 5 mL जल रखकर उसे अपनी कक्षा की किसी अलमारी के अन्दर रख दें। कमरे का तापमान नोट करके सभी में वाष्पीकरण में लगे समय को नोट करें।
इस क्रियाकलाप को बारिश में भी दोहराएँ।
निष्कर्ष-इसमें निष्कर्ष निकलता है कि वाष्पीकरण की दर निम्नलिखित के साथ बढ़ती है-
- सतह का क्षेत्रफल बढ़ने पर वाष्पीकरण की दर भी बढ़ जाती है जैसे कपड़े सुखाने के लिए हम उन्हें फैला देते हैं।
- तापमान में वृद्धि होने से वाष्पीकरण में वृद्धि होती है।
- वायु में आर्द्रता कम होने पर वाष्पीकरण अधिक हो जाता है। आर्द्रता होने पर वाष्पीकरण की दर घट जाएगी।
- वायु की गति बढ़ने पर भी जलवाष्प के कण वायु के साथ उड़ जाते हैं। इससे आस पास के जलवाष्प की मात्रा घट जाती है।
खंड 1.5 से सम्बन्धित पाठ्य पुस्तक के प्रश्नोत्तर (पा.पु. पृ.सं.-11)
प्रश्न 1.
गर्म, शुष्क दिन में कूलर अधिक ठंडा क्यों करता है?
उत्तर:
गर्म, शुष्क दिनों में वायुमण्डल में जलवाष्प बहुत कम होती है। इस कारण वाष्पीकरण की दर बढ़ जाती है जब कूलर चलता है तो उसका जल अपनी वाष्पीकरण की ऊर्जा अपने वातावरण से लेता है तथा तेजी से वाष्पित होता है। वाष्पन के कारण कूलर अधिक ठंडा करता है।
प्रश्न 2.
गर्मियों में घड़े का जल ठंडा क्यों होता है?
उत्तर:
गर्मियों में वायुमण्डल में जलवाष्प कम होती है। जो वाष्पन की दर को बढ़ा देती है। घड़े में छोटे-छोटे छिद्र होते हैं जिनसे पानी धीरे-धीरे रिसता रहता है जो वाष्पन के लिए ऊष्मा जल से व वायुमण्डल से लेता है। जिससे घड़े के आस-पास का वातावरण ठंडा हो जाता है और घड़े का पानी ठंडा हो जाता है।
प्रश्न 3.
ऐसीटोन / पेट्रोल या इत्र डालने पर हमारी हथेली ठंडी क्यों हो जाती है?
उत्तर:
ऐसीटोन / पेट्रोल या इत्र वाष्पशील पदार्थ हैं। जब इन्हें हथेली पर रखते हैं तो हाथ की गर्मी के कारण इनका वाष्पन तेज हो जाता है। इसके लिए यह ऊर्जा हथेली से लेते हैं जिससे वह ठंडी हो जाती है।
![]()
प्रश्न 4.
कप की अपेक्षा प्लेट से हम गर्म दूध या चाय जल्दी क्यों पी लेते हैं?
उत्तर:
कप का क्षेत्रफल कम होने के कारण चाय या दूध का वाष्पन धीरे होता है और वह देर में ठंडी होती है तथा पीने में देर लगती है, जबकि प्लेट का क्षेत्रफल अधिक होने के कारण वाष्पन तेजी से होता है और चाय या दूध जल्दी ठंडे हो जाते है अतः प्लेट में दूध या चाय जल्दी पी लेते हैं।
प्रश्न 5.
गर्मियों में हमें किस प्रकार के कपड़े पहनने चाहिए?
उत्तर:
गर्मियों में हमें सूती कपड़े पहनने चाहिए क्योंकि इनके द्वारा पसीने का अधिक अवशोषण हो जाता है जो वायुमण्डल में आसानी से वाष्पीकृत हो जाता है।