JAC Board Class 10th Social Science Important Questions Geography Chapter 7 Lifelines of National Economy
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
Which is not the national highway?
(a) Grand Trunk Road
(b) Agra-Mumbai Road
(c) Mathura Road
(d) Greater Noida Express Highways
Answer:
(d) Greater Noida Express Highways
Question 2.
The name of the National Highway No. 2 is
(a) Grand Trunk Road
(b) Agra-Mumbai Road
(c) Mathura Road
(d) Delhi-Mumbai Road
Answer:
(a) Grand Trunk Road
![]()
Question 3.
National Highway connecting Delhi, Mumbai, Chennai and Kolkata is termed as
(a) Locomotives
(b) Gauge
(c) Golden quadrilateral
(d) Dock
Answer:
(c) Golden quadrilateral
Question 4.
What does BOT stands for?
(a) Bureau of Transport
(b) Bureau of Trans-communication
(c) Build, Operate and Transfer
(d) Bureaucracy Official against Terrorists
Answer:
(c) Build, Operate and Transfer
Question 5.
Kochi in Kerala is the example of which of the following ports?
(a) Tidal Port
(b) Natural Harbour
(c) Artificial Harbour
(d) Recently developed
Answer:
(b) Natural Harbour
Question 6.
Which of the following is not the factor, which-influence the distribution of railway in the country?
(a) Physiographic factors
(b) Economic factors
(c) Administrative factors
(d) Political factors
Answer:
(d) Political factors
![]()
Question 7.
Which of the following is not the devel-opment in the field of communication?
(a) Cellular phone
(b) Laptop
(c) Internet e-commerce
(d) pipeline
Answer:
(d) pipeline
Question 8.
Trade carried in cities, towns and villages is called
(a) External Trade
(b) Local Trade
(c) Internal Trade
(d) International Trade
Answer:
(b) Local Trade
Question 9.
Border Roads Organisation was established in
(a) 1950
(b) 1955
(c) 1958
(d) 1960
Answer:
(d) 1960
Question 10.
The air transport was nationalised in the year
(a) 1947
(b) 1950
(c) 1953
(d) 1957
Answer:
(c) 1953
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are the two major means of land transport?
Answer:
The two major means of land transport are:
- Roadways
- Railways
Question 2.
What are express or free highways?
Answer:
Express or free highways are the national highways with 4 to 6 lanes meant to meet the requirement of fast traffic movement across the country.
Question 3.
Name the means of mass communication.
Answer:
Books, Journals, Magazines, Newspapers, Radio, Television and Films.
Question 4.
What are the three names of Express or Freeways?
Answer:
Three names are:
- Golden Question uadrilateral
- North-South and East-West Corridors
- Connectivity of 10 major ports with Golden Question uadrilateral and Corridors
Question 5.
Why International trade is called an “Economic Barometer”?
Answer:
The economic prosperity of a country depends upon international trade. The per capita trade of a country is the index of a country’s development, hence it is called an economic barometer.
Question 6.
What comes under the category of second class mail?
Answer:
Book packets, registered newspapers and periodicals come under the category of second class mail.
![]()
Question 7.
What is a railway gauge? Name three types of gauges found in India.
Answer:
A railway gauge refers to the width between two rails. There are three types of railway gauge in India. They are:
- Broad Gauge (1.676 metres)
- Metre Gauge (1.000 metres)
- Narrow Gauge (0.762 metre and 0.610 metre).
Question 8.
Name the two navigational rivers of India.
Answer:
Ganga and the Brahmaputra.
Question 9.
Name ihe four ports which have developed recently.
Answer:
(a) New Mangalore
(b) Haldia
(c) Nhava Sheva
(d) Ennore
Question 10.
Why metalled roads are called all weather roads?
Answer:
Metalled roads are made of cement, concrete or even bitumen of coal. They do not go out of use in the rainy season. Therefore, they are called all weather roads.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are national highways?
Answer:
The highways which link all major cities of extreme parts of the country are known as national highways. These are the primary road systems. They are maintained by the Central Public Works Department (CPWD).
Question 2.
What are state highways?
Answer:
Roads linking a state capital with different district headquarters are known as State Highways. These roads are constructed and maintained by the State Public Works Department (PWD) in States and Union Territories.
![]()
Question 3.
What are border roads? Mention its importance.
Answer:
Strategically important roads in the bordering areas of the country are called border roads. These roads are in the northern and north-eastern border areas. Importance of Border roads:
- Border roads have improved accessibility in areas of difficult terrain.
- These roads have helped in the economic development of border areas.
- These are used to supply military equipment to the borders of our country.
Question 4.
Describe the importance of Railways in India.
Answer:
Indian Railways
- Is the principal mode of transportation for freight and passengers in India.
- Is suitable for long distance travel.
- Conducts multiple activities like business, sightseeing, and pilgrimage along with transportation of goods.
- Plays an important role of national integration.
- Binds the economic life of the country as well as accelerates the development of the industry and agriculture.
- Is the largest public sector undertaking in the country.
Question 5.
Mention the importance of water transport.
Answer:
Water transport is important because:
- Waterways are the cheapest means of transport.
- It is the most suitable transport for carrying heavy and bulky goods.
- It is a fuel-efficient and environment- friendly mode of transport.
Question 6.
Name three important networks of pipeline transportation in the country.
Answer:
Three important networks of pipelines are:
- Pipeline from oil field in upper Assam to Kanpur (Uttar Pradesh).
- Pipeline from Salaya in Gujarat to Jalandhar in Punjab.
- Pipeline from Hazira in Gujarat to Jagdishpur in Uttar Pradesh.
Question 7.
Describe the importance of communi-cation in modern days.
Answer:
Modem life is so complex that one has to depend on others. The same is true of the countries as well. No country today can prosper without the co-operation and assistance of others. This requires movement of goods and materials between countries. Trade provides us with our necessities and also adds to amenities and comfort of life.
Question 8:
What is mass communication?
Answer:
Mass communication plays a vital role – in creating awareness among the people about? various national programmes and policies. These provide healthy entertainment as well. Important means of mass communication are radio, television, newspapers including magazines, books and films. These means communicate with several people at a time, and, hence, are called means of mass communication.
![]()
Question 9.
The Great Plains has more railways than the Himalayan Mountains. Why?
Answer:
The distribution pattern of the railway network in the country has been .influenced by physiographic, economic and administrative factors. Level lands of the great plains of India, with high density of population and rich agriculture and greater industrial activity, have favoured development of railways in these areas. Flood plains of Bihar and Assam, and the rugged topography of the Himalayan region, have very few railway lines.
Sparsely populated sandy deserts of Rajasthan and hilly tracts of the Sahyadri are unfavourable for the development of railways.
Question 10.
Mention the importance of tourism as a trade.
Answer:
The importance of tourism as a trade is:
- Our country earns foreign exchange through Tourism.
- More than 15 million people are directly engaged in the tourism industry.
- Tourism also promotes national integration.
- It provides support to local handicrafts and cultural pursuits.
- It also helps in the development of international understanding about our culture and heritage.
- Heritage tourism, eco-tourism, adventure tourism, cultural tourism, medical tourism and business tourism promote development of all sectors of economy.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Explain why the means of transport and communication are called lifelines of our national economy.
Answer:
Transport and communication are called lifelines of our national economy because:
- They help in increasing cooperation and assistance between countries by easy movement of goods and material between countries.
- They help in trade and commerce within a country.
- They have reduced distances thus bringing the world closer.
- They help in both production and distribution of goods and movement of large number of people and over long distance.
- They provide important links between producers and consumers of goods.
- They bring people very close to one another by promoting interdependence among people.
Question 2.
‘Roadways have an edge over railways in India.’ Justify the statement with arguments.
Answer:
The growing importance of road transport vis-a-vis rail transport is rooted in the following reasons:
- Construction cost of roads is much lower than that of railway lines.
- Roads can traverse comparatively much dissected and undulating topography.
- Roads can negotiate higher gradients of slopes and as such can traverse mountains such as the Himalayas.
- Road transport is economical in transportation of few persons and relatively small amount of goods over short distances.
- It also provides door-to-door service, thus the cost of loading and unloading is much lower.
- Road transport is also used as a feeder to other modes of transport such as they provide a link between railway stations, air and sea ports.
Question 3.
Describe the factors which influence the ‘di&tiribution pattern of Railway network in India.
Answer:
The distribution pattern of the Railway network in the country has been largely influenced by physiographic, economic and administrative factors.
- The density of railway network is high in the northern plains because they are vast level land, have high population density and rich agricultural resources. But, a large number of rivers create obstacles because it requires construction of bridges across their wide beds.
- In the hilly terrains of the peninsular region, railway tracts are laid through low hills, gaps or tunnels. Therefore, it is difficult to construct railway lines.
- The Himalayan mountainous regions are unfavourable for the construction of railway lines due to high relief, sparse population and lack of economic opportunities.
- It is difficult to lay railway lines on the sandy plain of western Rajasthan, swamps of Gujarat, forested tracks of Madhya Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Odisha and Jharkhand.
- Sinking of track in some areas and landslides make it difficult for railways.
![]()
Question 4.
Describe the importance of pipelines in India.
Answer:
Pipelines are important because:
- They are used for transporting crude oil, petroleum products and natural gas from oil fields and natural gas fields to refineries, fertilizer factories and big thermal power plants.
- Solids can also be transported through a pipeline when converted into slurry.
- Refineries at Barauni, Mathura, Panipat and gas based fertilizer plants, could be located in the interiors of India due to pipelines.
- Initial cost of laying pipelines is high but subsequent running costs are minimal.
- Pipelines rule out trans-shipment (during transportation) losses or delays.
Question 5.
Mention the importance of mass communication.
Answer:
The importance of mass communication is as follows:
- Mass communication provides entertainment.
- It creates awareness among people about various national programmes and policies.
- It provides variety of programmes in national, regional and local languages for various categories of people, spread over different parts of the country.
- It strengthens democracy in the country by providing news and information to the masses.
- It helps in rural development which is suffering from illiteracy and superstitious social practices.
- It helps in agriculture sector by providing the farmers information on new agricultural practices.
Activity Based Questions
Question 1.
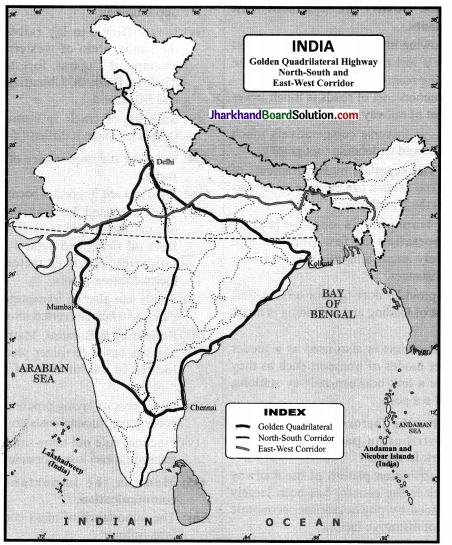
Locate the four cities came in Golden Quadrilateral and join them in a line map of India.
- Golden Question uadrilateral
- North-South Corridor, East-West Corridor.
Question 2.
Locate and label the following on an outlined map of India.
(i) Major Ports – Kandla, Mumbai, Marmagao, New Mangalore, Kochi, Tuticorin, Chennai, Vishakhapatnam, Paradip, Kolkata (Haldia).
Answer:
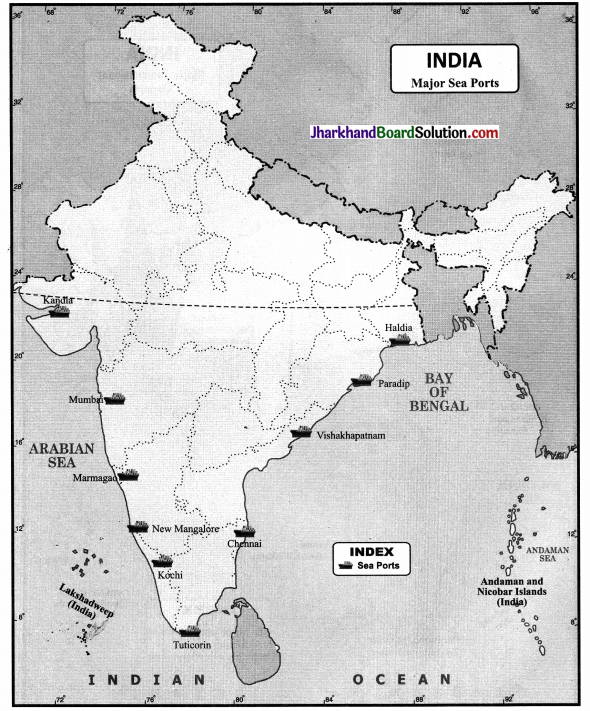
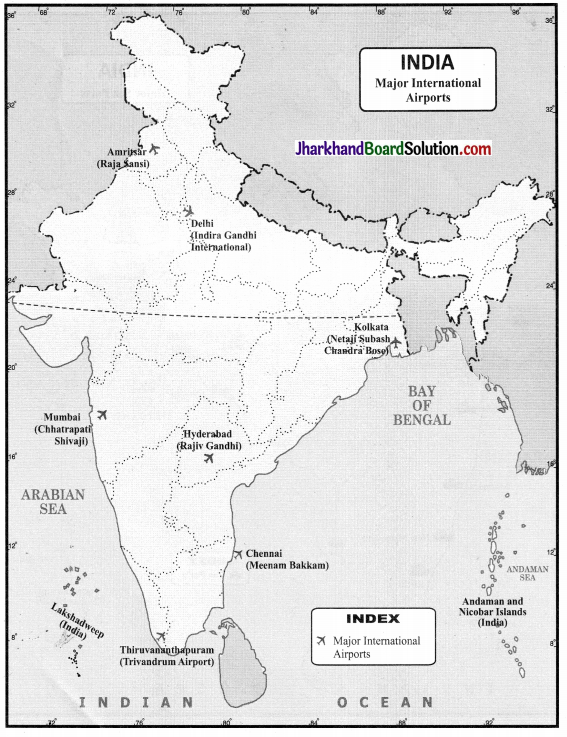
(ii) International Airports – Amritsar, Delhi, Mumbai, Thiruvananthapuram, Chennai, Kolkata, Hyderabad.