JAC Board Class 10th Social Science Important Questions Geography Chapter 5 Minerals and Energy Resources
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
A homogenous naturally occurring substance with a definable interior structure is called?
(a) Minerals
(b) Iron ore
(c) Diamond
(d) None
Answer:
(a) Minerals
![]()
Question 2.
Where minerals are usually found?
(a) In rocks
(b) In earth crust
(c) In ores
(d) In earth core
Answer:
(c) In ores
Question 3.
Which one of the following is a non- metallic mineral?
(a) Copper
(b) Iron ore
(c) Limestone
(d) None
Answer:
(a) Copper
Question 4.
Which of the following metallic minerals is obtained from veins and lodes?
(a) Zinc
(b) Limestone
(c) Rutile
(d) Mica
Answer:
(a) Zinc
Question 5.
Which of the following minerals is formed as a result of evaporation in the arid regions?
(a) Gypsum
(b) Zinc
(c) Coal
(d) Copper
Answer:
(a) Gypsum
Question 6.
What is Rat Hole Mining?
(a) Mining in a place where there are lots of rats
(b) Mining done by family members in the form of a long narrow tunnel
(c) Mining that kills rats
(d) None of the above
Answer:
(b) Mining done by family members in the form of a long narrow tunnel
![]()
Question 7.
Which state is the largest producer of manganese ore?
(a) Jharkhand
(b) Madhya Pradesh
(c) Maharashtra
(d) Odisha
Answer:
(b) Madhya Pradesh
Question 8.
Which metal has a very high content of iron up to 70 per cent?
(a) Magnetite ore
(b) Limonite ore
(c) Haematite ore
(d) Siderite ore
Answer:
(a) Magnetite ore
Question 9.
Which is India’s oldest oil producing state?
(a) Jharkhand
(b) Arunachal Pradesh
(c) Karnataka
(d) Assam
Answer:
(d) Assam
Question 10.
Which place in India is ideal for utilizing tidal energy?
(a) Gulf of Kachchh
(b) Puga valley
(c) Gulf of Mannar
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Gulf of Kachchh
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is an ore?
Answer:
The term ore is used to describe an accumulation of any mineral mixed with other elements. Minerals are usually found in “ores”.
Question 2.
How do minerals occur in igneous and metamorphic rocks?
Answer:
Minerals occur in igneous and metamorphic rocks in cracks, crevices, faults and joints.
Question 3.
Name some minerals formed in beds and layers.
Answer:
Coal and some forms of iron ore, gypsum
![]()
Question 4.
Which rock consists of a single mineral only?
Answer:
Limestone consists of a single mineral only.
Question 5.
Name four manganese ore producing states of India.
Answer:
Madhya Pradesh, Maharashtra, Odisha, Karnataka and Andhra Pradesh
Question 6.
What are ferrous minerals? Give two examples.
Answer:
The minerals which contain iron ore are called ferrous minerals. Manganese and Iron ore are examples of ferrous minerals.
![]()
Question 7.
What are non-ferrous minerals? Give two examples.
Answer:
The minerals which do not contain iron ore are called non-ferrous minerals. Copper and bauxite are examples of non- ferrous minerals.
Question 8.
What are conventional sources of energy?
Answer:
The sources of energy used on a large scale are conventional sources of energy. These are: wood, coal, petroleum, hydroelectricity and natural gas.
Question 9.
What are commercial sources of energy?
Answer:
The commercial sources of energy are: coal, petroleum, natural gas, hydroelectricity and nuclear energy. In India 60% of energy are obtained by commercial energy.
Question 10.
Name six non-commercial sources of energy.
Answer:
- Firewood
- Cowdung
- Biomass
- Charcoal
- Tidal
- Geothermal.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Differentiate between metallic and non-metallic minerals.
| Metallic minerals | Non-metallic minerals |
| (i) These occur in igneous rocks. | (i) These are found in sedimentary rocks. |
| (i) The rocks have crystalline structure. | (ii) The rocks are stratified. |
| (iii) These are found in impure form of ores. | (iii) These are found in pure form of ores. |
| (iv) These are malleable and ductile. | (iv) These are brittle. |
| (v) These shine, e.g. iron, copper, silver, | (v) These are dull, e.g. coal, salt, etc. |
Question 2.
Differentiate between Natural gas and Biogas.
| Natural gas | Biogas |
| (i) It is associated with or without petroleum. | (i) It is obtained by the decomposition of organic matter. |
| (ii) Natural gas is used in urban areas. | (ii) Biogas is used in rural areas. |
| (iii) This gas is exhaustible. | (iii) This gas is inexhaustible. |
| (iv) Natural gas is non-replenishable. | (iv) Biogas is replenishable. |
| (v) This is used for domestic and industrial purposes. | (v) This is used for domestic purposes only. |
| (vi) Gives less thermal energy. | (vi) Gives higher thermal energy. |
Question 3.
Differentiate between thermal and hydro electric energy.
| Thermal electricity | Hydro electricity |
| (i) This electricity is generated by coal and petroleum. | (i) It is generated by the force of running water. |
| (ii) It causes atmospheric pollution. | (ii) It does not cause atmospheric pollution. |
| (iii) It is a limited resource. | (iii) It is an unlimited resource. |
Question 4.
Name the non-metallic mineral which can split easily into thin sheets. Mention its uses.
Answer:
Mica is the non-metallic mineral which can split easily into thin sheets.
- Mica is used in electric and electronic industries due to its excellent dielectric strength, low power loss factor, insulating properties and resistance to high voltage.
- Plastic industry also uses mica as an extender and filler.
Question 5.
Why coal is called the most important source of energy even today in India? Explain giving three reasons.
Answer:
Coal is the most important source of energy because:
- It provides substantial part of nation’s energy needs.
- It is used as a power resource in many industries and domestic needs.
- It is.used for generating thermal electricity in thermal power plants.
- Many industries use coal as a raw- material.
- India is highly dependent on coal for commercial energy requirements.
Question 6.
Why petroleum is called the next major energy source in India after coal?
Answer:
Petroleum or mineral oil is the next major energy source in India after coal because it provides fuel for heat and lighting, lubricants for machinery and raw materials for a number of manufacturing industries. Petroleum refineries act as a “nodal industry” for synthetic textile, fertiliser and numerous chemical industries.
![]()
Question 7.
How will you use and conserve energy efficiently?
Answer:
To conserve energy we should:
- use public transport system as far as possible.
- switch off electricity if not required.
- use power saving devices.
- regularly check our power equipment.
- emphasise greater use of conventional sources of energy.
Question 8.
“Hydel power is more important source of energy than thermal power.” Discuss this fact with four examples?
Answer:
Hydel power is a renewable source as it is produced from water moving with a great speed. On the other hand coal, petroleum and natural gas are non-renewable. Hydel power is neat and clean and pollution free with less maintenance cost. It is transported easily through wires.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Elaborate the main types of formations in which minerals occur.
Answer:
Minerals generally occur in the following forms:
(i) In igneous and metamorphic rocks minerals occur in the cracks, crevices, faults or joints. The smaller occurrences are called veins and the larger are called lodes. Mostly, they are formed when minerals in liquid/molten and gaseous forms are forced upward through cavities towards the earth’s surface. They cool and solidify as they rise. Major metallic minerals like tin, copper, zinc and lead, etc. are obtained from veins and lodes.
(ii) In sedimentary rocks a number of minerals occur in beds or layers. They have been formed as a result of deposition, accumulation and concentration in horizontal strata. Coal and some forms of iron-dre have been concentrated as a result of long periods under great heat and pressure. Another group of sedimentary minerals includes gypsum, potash salt and sodium salt. These are formed as a result of evaporation especially in arid regions.
(iii) Another mode of formation involves the decomposition of surface rocks, and the removal of soluble constituents, leaving a residual mass of weathered material containing ores. Bauxite is formed this way.
(iv) Some minerals occur as alluvial deposits in sands of valley floors and the base of hills. These deposits are called ‘placer deposits’ and generally contain minerals, which are not corroded by water. Gold, silver, tin and platinum are most important among such minerals.
(v) The ocean waters contain vast quantities of minerals, but most of these are too widely diffused to be of economic significance. However, common salt, magnesium and bromine are largely derived from ocean waters. The ocean beds, too, are rich in manganese nodules.
![]()
Question 2.
Describe distribution, production and reserves of iron ore in India.
Answer:
Iron ore is the basic mineral and the backbone of industrial development. India is rich in good quality iron ores. Magnetite is the finest iron ore with a veiy high content of iron up to 70 per cent followed by haematite ore which contains 50 to 60 per cent. Odisha, Chattisgarh and Jharkhand produce about 75% of the total production of iron ore in India. The major iron ore belts in India are:
(i) Odisha-Jharkhand belt:
In Odisha high grade haematite ore is found in Badampahar mines in the Mayurbhanj and Kendujhar districts. In the adjoining Singhbhum district of Jharkhand haematite iron ore is mined in Gua and Noamundi.
(ii) Durg-Bastar-Chandrapur belt:
This belt lies in Chhattisgarh and Maharashtra. Very high grade haematites are found in the famous Bailadila range of hills in the Bastar district of Chhattisgarh. The range of hills comprises 14 deposits of super high grade haematite iron ore.
(iii) Ballari-Chitradurga-Chikkamagaluru- Tumakuru belt:
This belt in Karnataka has large reserves of iron ore. Kudremukh deposits are known to be one of the largest in the world. The Kudremukh mines located in the Western Ghats of Karnataka are a 100 per cent export unit.
(iv) Maharashtra-Goa belt:
This belt includes the state of Goa and Ratnagiri district of Maharashtra. Though, the ores are not of very high quality, yet they are efficiently exploited. Iron ore is exported through Marmagao port.
Question 3.
Why conservation of mineral resources is necessary? Explain any three methods to conserve them.
Answer:
Mineral resources are, finite and non-renewable. Minerals are important for the development of a country. We are rapidly consuming mineral resources that require millions of years to be created and concentrated. The geological processes of mineral formation are so slow that the rates of replenishment are infinitely small in’comparison to the present rates of consumption.
Three methods for conserving minerals are:
- Mineral resources should be used in planned and sustainable manner.
- Improved technology needs to be constantly evolved to allow use of low grade ores at low costs.
- Recycling of metals, using scraps, metals and other substitutes are steps in conserving our mineral resources for future.
Question 4.
Describe different types of coal with their distribution.
Answer:Coal is of different types, varying according to the amount of carbon content. They can be classified as:
- Peat:
It has low carbon, high moisture content and low heating power. It has less than 40% carbon content. - Lignite:
It is a low grade, brown coal. It is soft with high moisture content. In India, the main lignite reserves are in Neyvelli (Tamil Nadu) and are used for the generation of electricity. - Bituminous coal:
It is the most popular coal in commercial use. It is used for smelting iron in blast furnaces. It has 60% carbon content. - Anthracite coal:
It is the highest quality hard coal with a carbon content of 90%.
Question 5.
Describe in detail the types of non- conventional sources of energy.
Answer:
Non-conventional energy or Renewable energy is generally defined as energy that comes from resources which are naturally replenished on a human time scale such as sunlight, wind, rain, tides, waves and geothermal heat. These sources include the following:
(i) Wind energy:
Wind turbines are the most popular structures that are used to convert the speed of wind into usable electricity. They can be found on land, usually near the coast in areas where there is a constant strong wind, or in the ocean. The largest wind farm cluster is located in Tamil Nadu from Nagercoil to Madurai. Apart from these, Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Gujarat, Kerala, Maharashtra and Lakshadweep have important wind farms. Nagarcoil and Jaisalmer are well . known for effective use of wind energy in the country.
(ii) Solar energy:
Solar power, has been around for some time now. Photovoltaic technology convert sunlight into electricity. Solar energy is fast becoming popular in rural and remote areas. Some big solar power plants are being established in different parts of India which will minimise the dependence of rural households on firewood and dung cakes, which will contribute to environmental conservation and adequate supply of manure in agriculture.
![]()
(iii) Tidal energy:
Oceanic tides can be used to generate electricity. Floodgate dams are built across inlets. During high tide water flows into the inlet and gets trapped when the gate is closed. After the tide falls outside the flood gate, the water retained by the floodgate flows back to the sea via a pipe that carries it through a power-generating turbine. In India, the Gulf of Khambhat, the Gulf of Kachchh in Gujarat on the western coast and the Gangetic delta in the Sunderban regions of West Bengal provide ideal conditions for utilizing tidal energy.
(iv) Nuclear energy:
It is obtained by altering the structure of atoms. When such an alteration is made, much energy is released in the form of heat and this is .used tp’generate electric power. Uranium and thorium are available in Jharkhand and the Aravalli ranges of Rajasthan are used to generate atomic or nuclear power. The Monazite sands of Kerala are also rich’in thorium.
(v) Biogas:
Biogas, farm waste, animal and human waste are being used to produce electricity. Biogas plants using cattle dung are known as Gobar Gas Plants in rural India. These provide energy and improved manure to the farmers.
(vi) Geothermal energy:
Geothermal energy refers to the heat and electricity produced by using the heat from the interior of the Earth. Geothermal energy exists because the Earth grows hotter with increasing depth. There are several hundred hot springs in India, which could be used to generate electricity. Two experimental projects have been set up in India to harness geothermal energy. One is located in the Parvati valley near Manikaran in Himachal Pradesh and the other is located in the Puga Valley, Ladakh.
Question 6.
Why do we need to conserve energy resources?
Answer:
We need to conserve energy resources because:
- Energy is a basic requirement for economic development. Every sector of the national economy – agriculture, industry, transport, commercial and domestic needs inputs of energy.
- There is an urgent need to develop a sustainable path of energy development. Promotion of energy conservation and increased use of renewable energy sources are the two characteristics of sustainable energy.
- India is presently one of the least energy efficient countries in the world. We have to adopt a cautious approach for the judicious use of our limited energy resources.
Activity Based Questions
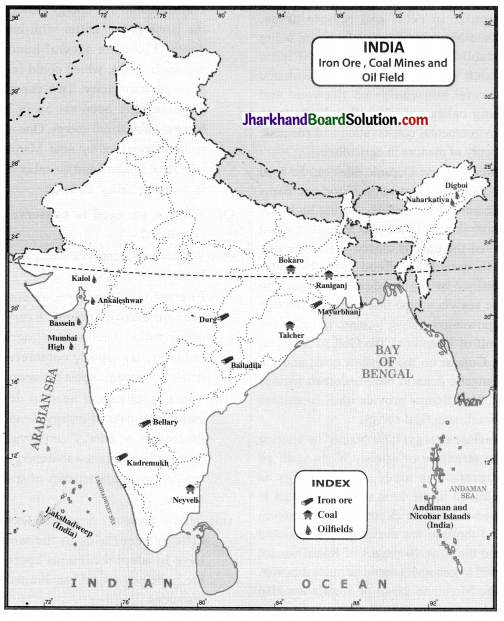
Question 1.
Locate and label the following Minerals and Energy resources.
(a) Iron ore mines
- Mayurbhanj
- Bellary
- Durg
- Kudermukh
- Bailadila
(b) Coal Mines
- Raniganj
- Talcher
- Bokaro
- Nayveli
(c) Oil Fields
- Digboi
- Bassien
- Naharkatia
- Kalol
- Mumbai High
- Ankaleshwar
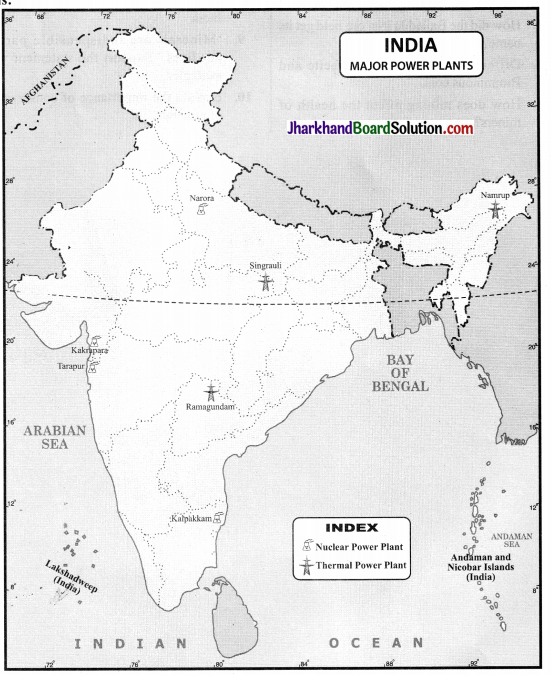
Question 1.
Locate and label the following Thermal and Nuclear Plants.
(a) Thermal
- Namrup
- Ramagundam
- Singrauli
(b) Nuclear Plants
- Narora
- Tarapur
- Kakrapara
- Kalpakkam