Jharkhand Board JAC Class 9 English Solutions Grammar Narration Exercises Questions and Answers.
JAC Board Class 9 English Grammar Narration Exercises
साधारणतः हम किसी के द्वारा कही गई बात को दो प्रकार से व्यक्त कर सकते हैं :
(1) वक्ता के द्वारा कहे गये शब्दों को ज्यों का त्यों लिखकर या बोलकर।
(2) वक्ता द्वारा कही गई बात को अपनी भाषा में लिखकर या बोलकर। उपर्युक्त प्रथम प्रकार से की गई अभिव्यक्ति को प्रत्यक्ष कथन या Direct Speech कहते हैं तथा दूसरे प्रकार से व्यक्त किये जाने वाले कथन को अप्रत्यक्ष कथन या Indirect Speech कहते हैं; जैसे :
He said, “I can go there.” He said that he could go there. आप इसे इस तरह समझिये। मान लीजिए आप किसी लड़के से पूछते हैं – ‘Where is your father ?’ लड़का आपसे
(Direct Speech) कहता है – ‘My father is at home.’ अब मैं आपसे पूछता हूँ – ‘उस लड़के ने आपसे क्या कहा ?’ ‘What did the boy tell you ?’) आप मुझे उस लड़के की बात दो तरह से कह सकते हैं-
(1) He said to me, “My father is at home.” लड़के का यह कथन जो आप मुझसे कह रहे हैं, Direct Narration का उदाहरण हैं।
(2) यदि आप मुझसे यह कहते हैं | The boy told me that his father was at home, तो यह Indirect Narration का उदाहरण है।

Direct Speech के भाग
इसके दो भाग होते हैं :
(1) Reporting Part – यह भाग inverted commas (“……”) के बाहर होता है। इसकी मुख्य क्रिया Reporting Verb कहलाती है।
(2) Reported Part (Reported Speech) – यह वह कथन होता है जो वक्ता व्यक्त करता है। इसे inverted commas (“……………………..”) के अन्दर रखते हैं। जैसे –
1. Maya said, “Radha is my friend.”
2. Anoop said to me, “Sit down, there.”
उपर्युक्त दोनों Sentences में “said’ Reporting Vero है और “Radha is my friend” तथा “Sit down, there” दोनों ही जो inverted commas’ के अन्दर हैं, Reported Speech हैं।
हम Direct Speech से Indirect Speech में बदलने के नियमों को निम्नलिखित भागों में बाँट सकते हैं :
(A) Assertive Sentences
(B) Interrogative Sentences
(C) Imperative Sentences
(D) Optative Sentences
(E) Exclamatory Sentences.
(A) Statements या Assertive Sentences को बदलना
1. Indirect Speech में inverted comma.s (“……………..”) को हटा देते हैं।
2. Reporting Verb के बाद comma (,) या कभी-कभी full stop (.) का प्रयोग होता है, जिसे हटा देते हैं।
3. Reporting Verb का Tense कभी नहीं बदलता। यदि Reporting Verb के पश्चात् कोई Object (कर्म) आया हो तो said to को told में तथा say to को tell में बदल देते हैं। परन्तु यदि said के बाद कोई Object न हो तो said का said ही रहता है तथा say का say ही रहता है।
4. Reporting Verb को Reported Speech से जोड़ने के लिए ‘that’ Conjunction लगाते हैं।
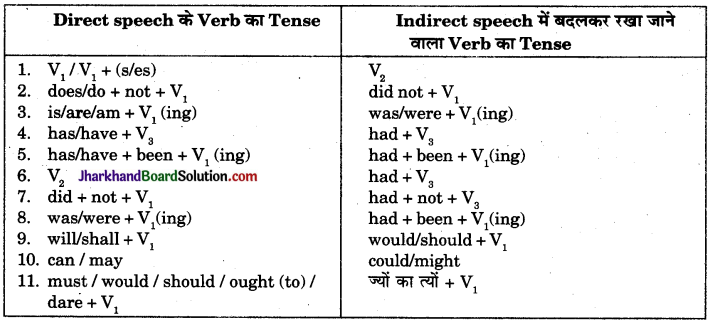
5. काल (Tenses), सर्वनाम (Pronouns) तथा समय अथवा स्थिति की निकटता (nearness of time or position) सूचक शब्दों में परिवर्तन करते हैं। इन परिवर्तनों के लिए नियमों की विस्तृत व्याख्या इस प्रकार है :
1. Tense में परिवर्तन सम्बन्धी नियम
नियम 1. अगर Reporting Verb, Present Tense या Future Tense में हो तो Reported Speech का Tense नहीं बदलता है। जैसे –
(i) Direct : He says, “Hari is not well.”
Indirect: He says that Hari is not well.
(ii) Direct : He will say, “Ram writes a letter.”
Indirect: He will say that Ram writes a letter.
(iii) Direct : Ram has said to me, “Ravi will join the camp.”
Indirect : Ram has told me that Ravi will join the camp.
नियम 2. यदि Reporting Verb, Past Tense में हो तो Reported Speech के Tense में परिवर्तन निम्न प्रकार से होता है। जैसे –
(a) Simple Present को Simple Past में बदल देते हैं। जैसे –

(i) Direct . : Mohan said to me, “Hari tells a lie.”
Indirect : Mohan told me that Hari told a lie.
(ii) Direct : Sita said to me, “Hari does not tell a lie.”
Indirect : Sita told me that Hari did not tell a lie.
(b) Present Continuous को Past Continuous में बदल देते हैं। जैसे –
[is / am / are was / were]
Direct : She said to me, “Sita is writing a letter.”
Indirect : She told me that Sita was writing a letter.

(c) Present Perfect को Past Perfect में बदल देते हैं। जैसे –
[has / have → had]
Direct : The boy said, “Mohan has done his work.”
Indirect : The boy said that Mohan had done his work.
(d) Present Perfect Continuous को Past Perfect Continuous में बदल देते हैं। जैसे –
[has / have → had]
Direct : They said, “The boys have been living in the house for five months.”
Indirect : They said that the boys had been living in the house for five months.
(e) Simple Past को Past Perfect में बदल देते हैं। जैसे –
(i) Direct : Sita said, “Madhu wrote a letter.”
Indirect : Sita said that Madhu had written a letter.
(ii) Direct : I said, “She did not go home.”
Indirect : I said that she had not gone home.
(f) Past Continuous को Past Perfect Continuous में बदल देते हैं। जैसे
[was / were → had been]
Direct : He said, “It was raining.”
Indirect : He said that it had been raining.
(g) Past Perfect तथा Past Perfect Continuous में कोई परिवर्तन नहीं होता है। जैसे –
- Direct : He said, “Ram had gone there.”
Indirect: He said that Ram had gone there. - Direct : He said, “Rekha had been reading for two hours.”
Indirect : He said that Rekha had been reading for two hours.
(h) Reported Speech का can बदलकर could, may बदलकर might, shall बदलकर should तथा will बदलकर would कर देते हैं और उनके साथ Verb की First form ही लगाते हैं। लेकिन would, might, could, should, ought को नहीं बदलते हैं। must को had to में बदल देते हैं या must का must ही रहने देते हैं।
जैसे –
(i) Direct : He said, “Hari can do that work.”
Indirect: He said that Hari could do that work.
(ii) Direct : The teacher said, “The boys may go home.”
Indirect: The teacher said that the boys might go home.
(iii) Direct : She said, “Mohan must see the picture.”
Indirect : She said that Mohan had to/must see the picture.
(यहाँ must या had to किसी का भी प्रयोग कर सकते हैं।)
(iv) Direct : I said, “I shall go to Agra.”
Indirect : I said that I should go to Agra.
(v) Direct : They said, “The clerk will not attend the office.”
Indirect : They said that the clerk would not attend the office.

Chart Showing Changes in the Verbs
( क्रियाओं में होने वाले परिवर्तन सम्बन्धी चार्ट)
Tenses
नीचे लिखी दशाओं में Reporting Verb के Past Tense में होते हुए भी Reported Speech का Tense नहीं बदलता है –
(a) Universal Truth (सार्वभौमिक सत्य) – जब Reported Speech में कोई सार्वभौमिक सत्य (Universal Truth) कहा गया हो तो उस वाक्य के Tense में किसी प्रकार का परिवर्तन नहीं होता है। जैसे –
(i) Direct : My father said, “The sun rises in the east.”
Indirect : My father said that the sun rises in the east.
(ii) Direct : The teacher said, “The earth is round.”
Indirect : The teacher said that the earth is round.
(b) Habitual Action (आदतन कार्य ) – जब Reported Speech में कोई आदतन कार्य हो तो उसका Present Tense भी नहीं बदलता है। जैसे –
(i) Direct : The teacher said, “When the cat is away the mice will play.”
Indirect : The teacher said that when the cat is away the mice will play.
(ii) Direct : He said, “Dogs bark at strangers.”.
Indirect : He said that dogs bark at strangers.
(c) Historical Present (ऐतिहासिक वर्तमान ) – Reported Speech में आये हुए ऐतिहासिक तथ्य का Present Tense भी नहीं बदलता।जैसे -Direct : The history teacher said, “Samudragupta is called the Napoleon of India.”
Indirect : The history teacher said that Samudragupta is called the Napoleon of India.
(d) यदि time-clause past में हो तो यह अपरिवर्तित रहता है।
Direct : He said, “When I was at Delhi, I visited the Red Fort.”
Indirect : He said that when he was at Delhi, he visited/had visited the Red Fort.

Exercise 1.
Change the following sentences into indirect speech :
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को Indirect Speech में बदलिये :
1. My father said, “The sun rises in the east.”
2. Hari said to Anil, “Prem Chand wrote many novels.”
3. The leader said, “Many students have died in the agitation.”
4. The teacher said, “God helps those who help themselves.”
5. He says, “Mohan is delivering a fine speech.”
6. Sarita said to Poonam, “Archana was playing very well.”
7. Ram will say, “Hari is a thief.”
8. My Sanskrit teacher said, “Kalidas is the Shakespeare of India.”
9. They said, “The clerk will not come to school.”
10. The teacher said, “Good boys ought to obey their elders.”
Answers:
1. My father said that the sun rises in the east.
2. Hari told Anil that Prem Chand had written many novels.
3 . The leader said that many students had died in the agitation.
4. The teacher said that God helps those who help themselves.
5. He says that Mohan is delivering a fine speech.
6 . Sarita told Poonam that Archana had been playing very well.
7. Ram will say that Hari is a thief.
8. My Sanskrit teacher said that Kalidas is the Shakespeare of India.
9. They said that the clerk would not go to school.
10. The teacher said that good boys ought to obey their elders.
Exercise 2.
Change the following sentences into indirect speech :
निम्नलिखिंत वाक्यों को Indirect Speech में बदलिये :
1. Kanan says, “Mohan is a naughty boy.”
2. Gopal will say, “Manu is a good player.”
3. The teacher said to the boy, “Two and two makes four.”
4. He said, “The horse had died in the night.”
5. His sister said, “Shanu likes to swim in the river.”
6. Mahesh said, “Mira is reading a book.”
7. She said, “Raju can read Sanskrit.”
8. Rekha said, “It may rain just now.”
9. My mother said to me, “Every rose has a thorn.”
10. My father said, “Honesty is the best policy.”
Answers:
1. Kanan says that Mohan is a naughty boy.
2. Gopal will say that Manu is a good player.
3. The teacher told the boy that two and two makes four.
4 . He said that the horse had died in the night.
5. His sister said that Shanu liked to swim in the river.
6. Mahesh said that Meera was reading a book.
7. She said that Raju could read Sanskrit.
8. Rekha said that it might rain just then.
9. My mother told me that every rose has a thorn.
10. My father said that honesty is the best policy.

2. Pronouns के Person में परिवरनि सम्बन्धी नियम
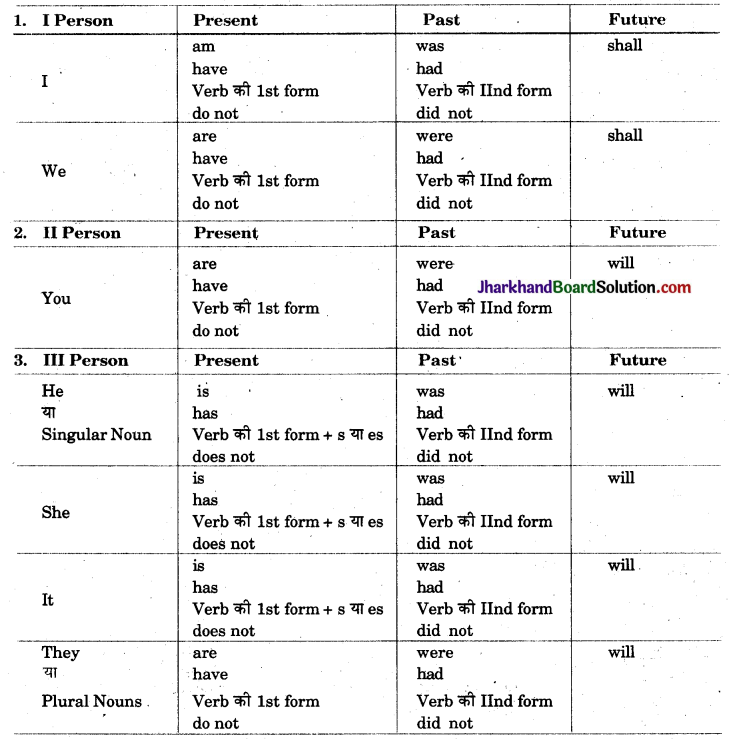
Pronouns के तीन Persons होते हैं – (i) First Person, (ii) Second Person, (iii) Third Person । वाक्य में इनका प्रयोग चार रूपों में होता है – (i) Subject के रूप में, (ii) Object के रूप में, (iii) Reflexive के रूप में तथा (iv) Possession (अधिकार) प्रकट करने के लिए। इसके प्रयोग को भली-भाँति समझने हेतु अग्रलिखित तालिका का अध्ययन करें व याद करें :
Pronouns की सारणी:
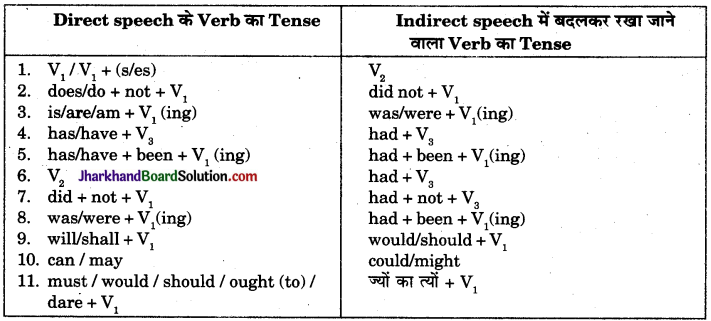
नियम 1. Reported Speech में आये हुए First Person के Pronouns (I, me, my, mine, myself, we, us, our, ours, ourselves) को Indirect बनाते समय Reporting Verb के कर्त्ता (Subject) के Person, Number और Gender के अनुसार बदल देते हैं। जैसे –

नोट – यदि Direct Speech में या we के साथ shall का प्रयोग किया गया हो और Indirect Speech में बदलते समय के स्थान पर he तथा we के स्थान पर they का प्रयोग किया गया हो तो shall के स्थान पर should का प्रयोग न करके would का प्रयोग करना चाहिए।
नियम 2. Reported Speech में आये हुए Second Person के Pronouns (you, your, yours, yourself, yourselves) को Indirect बनाते समय Reporting Verb के Object के Person, Number और Gender के अनुसार बदलते हैं। जैसे –

नोट – यदि Reporting Verb के बाद किसी Object का प्रयोग नहीं हुआ है, तो Reporting Verb के पश्चात् First Person अथवा Third Person के Pronoun का प्रयोग करके Object बना देते हैं तथा उसी के अनुसार Reported Speech में प्रयुक्त Second Person के Pronoun को First Person अथवा Third Person में बदल देते हैं; जैसे-

(i) Direct : Ram said, “You should work hard.”
Indirect : Ram told her that she should work hard.
(ii) Direct : Mother said, “You should go there soon.”
Indirect : Mother told me that I should go there soon.
अतः स्पष्ट है कि Reporting Verb का Object न होने पर Reported Speech के Second Person के Pronoun को आशय अथवा सन्दर्भ के अनुसार First Person यां Third Person किसी में भी बदल देते हैं । यदि वाक्य से यह स्पष्ट होता है कि you का प्रयोग किसके लिए है, तो उसे उसके Person के अनुसार बदल देते हैं। जैसेDirect : The old man said, “You can go to your house, Anand.”
Indirect : The old man told Anand that he could go to his house.
नियम (i) यदि किसी Sentence में कोई Proper Noun सम्बोधन कारक (Vocative case) में हो तो उस Noun को tell/told का object बना देते हैं। जैसे –
(i) Direct : The father said, “Sarla, you have become lazy.”
Indirect : The father told Sarla that she had become lazy.
(ii) Direct : The policeman said, “You must keep to the left, boys.”
Indirect : The policeman told the boys that they must keep to the left.
नियम (ii) यदि सम्बोधन कारक में कोई अन्य संज्ञा; जैसे – friend, gentleman, father, mother आदि हो तो इन शब्दों से पहले addressed as जोड़कर Reporting Verb के पूर्व प्रयोग करते हैं। जैसे –
Direct : The stranger said to me, “Gentleman, I have lost my way.”
Indirect : The stranger addressed me as gentleman and said that he had lost his way.
Or Addressing me as gentleman the stranger said that he had lost his way.
नियम 3. Direct से Indirect में परिवर्तन करते समय Reported Speech में आये हुए Third Person के Pronouns (he, she, it, they, his, her, its, their, him, them, himself, herself, themselves, hers, theirs) में कोई परिवर्तन नहीं करते हैं। जैसे –
(i) Direct : Suresh said, “He is a clerk.”
Indirect : Suresh said that he was a clerk.
(ii) Direct : I said, “She is not a good player.”
Indirect : I said that she was not a good player.

Note (i) Noùn को सदैव Third Person में मानते हैं ।
(ii) अगर Reporting Verb के कर्ता और कर्म दोनों Third Person और same Gender में हों, तो Indirect में परिवर्तन करते समय उनके सामने कोष्ठक में उन व्यक्तियों का नाम लिख देते हैं । जैसे –
Direct – Nirmala said to Mira, “I shall always help you.”
Indirect – Nirmala told Mira that she (Nirmala) would always help her (Mira).
Exercise 3.
Change the following sentences into indirect speech :
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को Indirect Speech में बदलिए :
1. He said to me, “I have completed my work.”
2. She said to him, “You are very busy.”
3. The teacher said to Hari, “You always tell a lie.”
4. Mohan said to them, “You are good players.”
5. The doctor said to you, “You are out of danger.”
6. He said, “You can take rest for a while.”
7. Rakesh said to his friends, “My parents are going to Kashmir.”
8. He said, “I lived there for a month.”
9. Hari said to Vinod, “I am glad to meet you.”
10. The mother said to Kamala, “You should not go out in the party.”
Answers:
1. He told me that he had completed his work.
2. She told him that he was very busy.
3 . The teacher told Hari that he (Hari). always told a lie.
4. Mohan told them that they were good players.
5. The doctor told you that you were out of danger.
6 . He told me that I could take rest for a while.
7. Rakesh told his friends that his parents were going to Kashmir.
8. He said that he had lived there for a month.
9. Hari told Vinod that he (Hari) was glad to meet him (Vinod).
10. The mother told Kamala that she (Kamala) should not go out in the party.

Exercise 4.
Change the following sentences into indirect speech :
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को Indirect Speech में बदलिए :
1. Dinesh said, “I am enjoying my new job.”
2. She said, “My father is not very well.”
3. Sarah and Tim said, “We are going to buy a house.”
4. Peter said, “I have to go early.”
5. He said, “My sister has gone to America.”
6. Ann said, “I cannot find a job.”
7. Satish said, “I will phone you.”
8. Anuradha said, “I do not like my job.”
9. She said, “My son does not like school.”
10. Mohit said, “You look tired.”
Answers:
1. Dinesh said that he was enjoying his new job.
2. She said that her father was not very well.
3. Sarah and Tim said that they were going to buy a house.
4. Peter said that he had to go early.
5. He said that his sister had gone to America.
6. Ann said that she could not find a job.
7. Satish told (her) that he would phone her.
8. Anuradha said that she did not like her job.
9. She said that her son did not like school.
10. Mohit told (her) that she looked tired.
3. समय तथा स्थिति की निक्ता करो अकर करने वाले शब्दो में परिवर्त केनियम
नियम 1. Direct Speech को Indirect Speech में बदलने में समय तथा स्थिति की निकटता दिखाने वाले शब्दों को दूरी प्रकट करने वाले शब्दों में बदल देते हैं। जैसे –
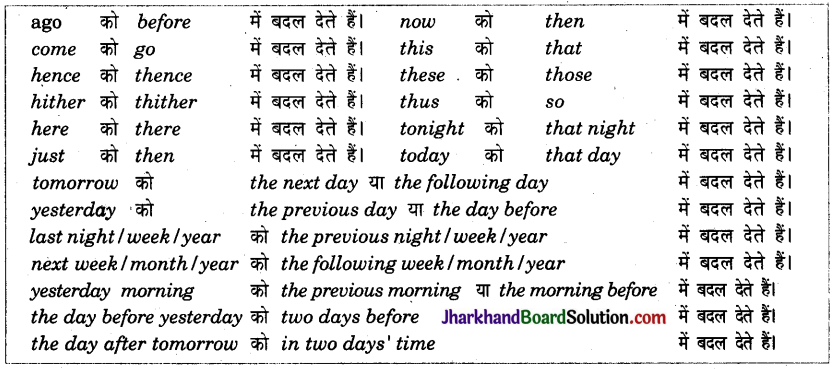
उदाहरण :
(i) Direct : He said to them, “I will leave you now.”
Indirect : He told them that he would leave them then.
(ii) Direct : Krishṇa Kumar said, “I cannot accompany you till next week.”
Indirect : Krishna Kumar said that he could not accompany me till the following week.
(iii) Direct : He said to me, “I shall see you tomorrow.”
Indirect : He told me that he would see me the next day.
(iv) Direct : The teacher said, “I feel weak today.”
Indirect : The teacher said that he felt weak that day.
नियम 2. यदि this, here आदि किसी ऐसी वस्तु या स्थान या समय की ओर संकेत करते हैं, जो कहते समय वक्ता के सामने उपस्थित हो, तो Indirect बनाते समय उनमें कोई परिवर्तन नहीं होता है, बल्कि उन्हें ज्यों का त्यों रख देते हैं-
(i) Direct – He said to me, “This is my house.”
Indirect – He told me that this (the house before him) was his house.
(ii) Direct – The leader says, “I am glad to be here this morning.”
Indirect – The leader says that he is glad to be here this morning.
(iii) Direct – Hari said, “They will do it now.”
Indirect – Hari said that they would do it now.

नियम 3. This तथा these का प्रयोग यदि समय की ओर संकेत के लिये होता हो, तो Indirect में इनको that तथा those में ही बदलते हैं।.
(i) Direct – They said, “We are going for a picnic this week.”
Indirect – They said that they were going for a picnic that week.
(ii) Direct – Hari said, “I am preparing for the examination these days.”
Indirect – Hari said that he was preparing for the examination those days.
परन्तु यदि this तथा these का प्रयोग Adjective (this/these + noun) की भाँति हुआ है, तो Indirect बनाते समय that तथा those के स्थान पर the का प्रयोग भी कर सकते हैं। जैसे –
(i) Direct – Sita said, “I have brought this stick from Udaipur.”
Indirect – Sita said that she had brought that stick from Udaipur.
Or
Sita said that she had brought the stick from Udaipur.
(ii) Direct – The typist said, “I have typed all these letters.”
Indirect – The typist said that he had typed all those letters.
Or
The typist said that he had typed all the letters.
Exercise 5.
Change the following sentences into indirect speech :
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को Indirect Speech में बदलिये :
1. He said, “I shall do my work.”
2. Mohan said to them, “You are good people.”
3. I said to you, “You can go home.”
4. He said, “I have passed the examination.”
5. She said to me, “It has been raining since daybreak.”
6. He said, “I shall give you this book tomorrow.”
7. She said, “I was taking bath when he called me.”
8. Nandini said, “They returned all the books yesterday.”
9. Everyone says, “Stars twinkle at night.”
10. My brother said to me, “You may take my car.”
11. He will say, “I know my duty well.”
Answer:
1. He said that he would do his work.
2. Mohan told them that they were good people.
3. I told you that you could go home.
4 . He said that he had passed the examination.
5. She told me that it had been raining since daybreak.
6 . He told me that he would give me that/the book the next day.
7. She said that she was/had been taking bath when he called her.
8 . Nandini said that they had returned all the books the previous day.
9. Everyone says that stars twinkle at night.
10. My brother told me that I might take his car.
11. He will say that he knows his duty well.
(B) Questions या Interrogative Sentences
Interrogative Sentences से प्रश्न का बोध होता है । इस प्रकार के Sentences को Indirect में बदलते समय निम्नलिखित बातों का ध्यान रखना चाहिए-
नियम 1. Reporting Verb ‘said to’ को asked या enquired of में तथा ‘say to’ को ask में बदल देते हैं।
नियम 2. Interrogative Sentences में ‘that’ Conjunction का प्रयोग नहीं किया जाता।
नियम 3. Indirect में प्रश्नवाचक वाक्य को साधारण वाक्य (Assertive Sentence) बना देते हैं। प्रश्नवाचक चिह्न (?) हटा दिया जाता है और उसके स्थान पर Full Stop (.) का प्रयोग किया जाता है। जैसेः
Direct : He said to me, “Where is she ?”
Indirect : He asked me where she was.
नियम 4. Reported Speech के Pronoun, Verb तथा अन्य शब्दों को साधारण वाक्यों के नियमों के अनुसार बदलते हैं।
(I) Yes/No Answer Type Questions को Indirect में बदलना
नियम 1. जब Direct Speech में ऐसा प्रश्न हो जिसका उत्तर ‘हाँ’ या ‘ना’ ( yes या no) में दिया जा सके अर्थात् Reported Speech किसी Auxiliary Verb (सहायक क्रिया); जैसे – is, are, am, was, were, do, does, did, shall, will, has, have, had, can, may आदि से शुरू हुई हो तो Indirect Speech में Connective Word ‘if’ या ‘whether’ का प्रयोग किया जाता है। जैसे –

(i) Direct : Hari said to me, “Are you reading a book?”
Indirect: Hari asked me if was reading a book.
(ii) Direct : Ram said to Hari, “Will you go to school today?”
Indirect : Ram asked Hari if he would go to school that day.
(iii) Direct : I said to him, “Can you tell me what the time is ?”
Indirect : I asked him if he could tell me what the time was.
नियम 2. अगर Reporting Verb, Past में हो व
(a) Reported Speech में सहायक क्रिया do या does हो और उसके बाद not न हो तो Indirect बनाते समय उनको हटा देते हैं और मुख्य क्रिया को Second form में बदल देते हैं। जैसे –
(i) Direct : She said to me, “Do you know Sohan ?”
Indirect : She asked me if I knew Sohan.
(ii) Direct : Sita said to Hari, “Do you understand English ?”
Indirect : Sita asked Hari if he understood English.
(b) अगर Reported Speech में do या does के बाद not हो तो do या does के स्थान पर did कर दिया जाता है और उसके साथ Verb के First form का ही प्रयोग करते हैं। जैसे –
(i) Direct : Father said to me, “Do you not obey me ?”
Indirect : Father asked me if I did not obey him.
(ii) Direct : Ramesh said to his friend, “Don’t you go to college today?”
Indirect : Ramesh asked his friend if he didn’t go to college that day.
(c) अगर Reported Speech में ‘did’ Helping Verb हो तो उसे हटाकर Main Verb को Past Perfect Tense (had की III form) में बदल देते हैं। जैसे –
Direct : He said to me, “Did you lend me your book ?”
Indirect: He asked me whether I had lent him my book.
(d) जब वाक्य में choice ( विकल्प) पूछने के लिए or दिया हो तो connective के रूप में whether का ही प्रयोग किया जाता है। जैसे –
Direct : He said, “Are you coming with me or not?”
Indirect : He asked me whether I was going with him or not.
(e) जब Reported Speech के उत्तर ‘Yes’ या ‘No’ में दिए गए हों तो इन्हें Indirect में प्रश्न के Subject के pronoun + Helping Verb द्वारा लिखा जाता है। जैसे –
अर्थात् –
Yes = प्रश्न के Subject का pronoun + H.V.
No = प्रश्न के Subject का pronoun H.V. not
जैसे –
(i) Direct : I asked Hari, “Do you know Urdu ?” Hari said, “Yes.”
Indirect : I asked Hari if he knew Urdu. Hari replied that he did.
(ii) Direct : I said to Ravi, “Are you going to Mumbai ?” Ravi said, “No.”
Indirect : I asked Ravi if he was going to Mumbai. Ravi replied that he was not.
नोट-Yes को replied in affirmative तथा No को replied in negative में भी बदला जा सकता है परन्तु अब इनका प्रयोग अच्छा नहीं समझा जाता है।
Exercise 6.
Change the following sentences into indirect speech :
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को Indirect Speech में बदलिये :
1. The old woman asked me, “Do you live in that house ?”
2. Father said to his son, “Have you brought sweets from the market?”
3. “Can you sing a song for me ?” the fox asked the crow.
4. She said to Gopal, “Are you going to see the fair with my brother today?”
5. Mohan ‘said to his brother, “Will you give me some money tomorrow ?”
6. He said to me, “Should you beat him ?”
7. My brother said to me, “Did you go to see your friend in the hospital ?”
8. Ravina said to Pawan, “Can you show me your pocket?”
9. Hari said to Shankar, “Will you go to see the zoo today?”
10. Bill said to me, “Are you sure of success this time ?”
Answer:
1. The old woman asked me if I lived in that house.
2. Father asked his son if he had brought sweets from the market.
3. The fox asked the crow if it (crow) could sing a song for him (fox).
4. She asked Gopal if he was going to see the fair with her brother that day.
5. Mohan asked his brother if he would give him some money the next day.
6 . He asked me if I should beat him.
7. My brother asked me if I had gone to see my friend in the hospital.
8. Ravina asked Pawan if he could show her his pocket.
9. Hari asked Shankar if he would go to see the zoo that day.
10 . Bill asked me if I was sure of success that time.

(1) Wh Word type frestions को Ladirect मैं बदलना
नियम 1. यदि Reported Speech प्रश्नवाचक शब्द (what, who, which, whom, whose, when, where, why, how, आदि) से शुरू होता है तो Indirect Speech में कोई अन्य Connective नहीं लगाया जाना चाहिए। ये शब्द ही स्वयं Connective का कार्य करते हैं। इनके बाद Subject, फिर Verb का प्रयोग करते हैं। जैसे-
(i) Direct : I said to her, “Who are you ?”
Indirect : I asked her who she was.
(ii) Direct : The teacher said to Hari, “Why did you not do your homework yesterday ?”
Indirect : The teacher asked Hari why he had not done his homework the previous day.
(iii) Direct : He said to me, “Where do you live ?”
Indirect : He asked me where I lived.
नोट – यदि प्रश्नकर्ता के पास उत्तर देने वाला जाता हो तो वैसी स्थिति में come का come ही रहता है, go नहीं होता; जैसे-
(i) Direct : He said to me, “Why did you come to me ?”
Indirect : He asked me why I had come to him.
(ii) Direct : She said, “Mohan came in the morning.”
Indirect : She said that Mohan had come in the morning.
Exercise 7.
Change the following sentences into indirect speech :
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को Indirect Speech में बदलिये :
1. The policeman said to the man, “Where do you want to go ?”
2. She asked the girl, “What is your name ?”.
3. Hari said to Shyam, “Whose pen is this ?”
4. Rajesh said to Hari, “Where will you go tomorrow ?”
5. She said to me, “Which pen do you like to have ?”
6. The hunter asked the boy, “When did you see the tiger ?”
7. He said to Mohan, “Why did you go to my house yesterday ?”
8. My father said to Mohan, “Are you happy with your new job ?”
9. Richa said to Raj, “Do I work very hard ?”
10. The policeman said to me, “Can you speak Tamil ?”
11. John said, “Will she have lunch with me ?”
12. Ramesh said to me, “How much will you pay me ?”
Answer:
1. The policeman asked the man where he wanted to go.
2. She asked the girl what her name was.
3. Hari asked Shyam whose pen that/it was.
4. Rajesh asked Hari where he (Hari) would go the next day.
5 . She asked me which pen I liked to have.
6 . The hunter asked the boy when he had seen the tiger.
7. He asked Mohan why he had gone to his house the previous day.
8. My father asked Mohan if he was happy with his new job.
9. Richa asked Raj if she worked very hard.
10. The policeman asked me if I could speak Tamil.
11. John asked if she would have lunch with him.
12. Ramesh asked me how much I would pay him.
(C) Commands And Requests या Imperative Sentences
जब किसी Sentence में आज्ञा (order), परामर्श (advice) या अनुरोध (request) प्रकट किया गया हो तो उसे Imperative Sentence कहते हैं। इसमें Subject ‘you’ छिपा रहता है तथा Sentence मुख्य Verb से आरम्भ होता है। इनको Direct से Indirect में बदलने के नियम निम्नलिखित हैं –
नियम 1. Reporting Verb ‘said’ को Reported speech के भाव के अनुसार इस प्रकार बदलते हैं –
(a) यदि order हो तो उसे ordered, commanded आदि में।
(b) यदि advice हो तो उसे advised, urged आदि में ।
(c) यदि request हो तो उसे requested, begged, implored आदि में।
नियम 2. Reported Speech के Verb के पहले ‘to’ जोड़ देते हैं तथा to लग जाने पर verb में कोई परिवर्तन नहीं होता है। जैसे –
(i) Direct – The teacher said to us, “Listen to me when I teach.”
Indirect – The teacher ordered us to listen to him when he taught.
(ii) Direct – He said to his friend, “Work hard.”
Indirect – He advised his friend to work hard.

नियम 3. Reported Speech के Vocative Case के Noun को Reporting Verb का कर्म (Object) बना देते हैं। जैसे –
Direct – The teacher said, “Sit down, boys.”
Indirect – The teacher ordered the boys to sit down.
नियम 4. जब Reported Speech Negative हो अर्थात् ‘Do not’ से आरम्भ हो तो इसके परिवर्तन की दो विधियाँ हैं –
(a) पहली विधि में Reporting Verb को forbade में बदल दिया जाता है। इससे Reported Speech में आये हुए dono tको समाप्त करके क्रिया से पहले to लगा देते हैं। जैसे –
Direct – The teacher said to the boy, “Do not abuse anyone.”
Indirect – The teacher forbade the boy to abuse anyone.
(b) दूसरी विधि में Reporting Verb ‘said’ को भाव के अनुसार ordered, advised या requested में बदल दिया जाता है किन्तु इसमें Reported Speech में से केवल do not को not to में बदल देते हैं। जैसे –
(i) Direct – My father said to me, “Do not waste your time.”
Indirect – My father advised me not to waste my time.
(ii) Direct – She said to him, “Don’t disturb me.”
Indirect – She asked him not to disturb her.
नियम 5. Reported Speech जब never से आरम्भ हो तो Reporting Verb को भाव के अनुसार ordered, advised आदि में बदल देते हैं और never तथा Verb के बीच में to का प्रयोग करते हैं। जैसे –
Direct – The teacher said to the student, “Never waste your time.”
Indirect – The teacher advised the student never to waste his time.
नोट – Never वाले Sentences में forbade का प्रयोग नहीं होता है।
नियम 2. Reported Speech के Verb के पहले ‘to’ जोड़ देते हैं तथा to लग जाने पर verb में कोई परिवर्तन नहीं होता है। जैसे –

(i) Direct – The teacher said to us, “Listen to me when I teach.”
Indirect – The teacher ordered us to listen to him when he taught.
(ii) Direct – He said to his friend, “Work hard.”
Indirect – He advised his friend to work hard.
नियम 3. Reported Speech के Vocative Case के Noun को Reporting Verb का कर्म (Object) बना देते हैं। जैसे –
Direct – The teacher said, “Sit down, boys.”
Indirect – The teacher ordered the boys to sit down.
नियम 4. जब Reported Speech Negative हो अर्थात् ‘Do not’ से आरम्भ हो तो इसके परिवर्तन की दो विधियाँ हैं –
(a) पहली विधि में Reporting Verb को forbade में बदल दिया जाता है। इससे Reported Speech में आये हुए donot को समाप्त करके क्रिया से पहले to लगा देते हैं। जैसे –
Direct – The teacher said to the boy, “Do not abuse anyone.”
Indirect – The teacher forbade the boy to abuse anyone.
(b) दूसरी विधि में Reporting Verb ‘said’ को भाव के अनुसार ordered, advised या requested में बदल दिया जाता है किन्तु इसमें Reported Speech में से केवल do not को not to में बदल देते हैं। जैसे –
(i) Direct – My father said to me, “Do not waste your time.”
Indirect – My father advised me not to waste my time.
(ii) Direct – She said to him, “Don’t disturb me.”
Indirect – She asked him not to disturb her.
Imperative Sentences में let को बदलने के नियम
let मुख्य रूप से दो बातें प्रकट करने के लिए प्रयोग में आता है –
(1) कोई प्रस्ताव करने के लिए,
(2) अनुमति (permission) प्राप्त करने के लिए।
1. प्रस्ताव – यदि let का प्रयोग प्रस्ताव करने के लिए होता है तो –
(i) Reporting Verb को proposed या suggested में बदल देते हैं। यदि Reporting Verb के साथ Object दिया हो तो Reporting Verb को proposed to या suggested to में बदलते हैं।
(ii) let को हटाकर Connective word ‘that’ का प्रयोग करते हैं।
(iii) Let us Let’s को हटाकर we / they should का प्रयोग करते हैं।
[Let’s V1 we/they should V1]
(i) Direct – Girraj said to Kishore, “Let us go for a walk.”
Indirect – Girraj proposed to Kishore that they should go for a walk.
(ii) Direct – The girls said, “Let’s play a hockey match today.”
Indirect – The girls suggested that they should play a hockey match that day.
नोट – जिन वाक्यों में ‘let’ के पश्चात् us आता है, उनसे साधारणतया प्रस्ताव का बोध होता है तथा इन्हें इसी प्रकार से बदला जाता है।

2. अनुमति – यदि let का तात्पर्य अनुमति से होता है तो Reporting Verb को भाव के अनुसार requested में बदलकर let को Infinitive ‘to let’ में बदल देते हैं। दूसरी विधि यह है कि let के स्थान पर that का प्रयोग करते हैं, फिर Noun या Pronoun, उसके बाद might be allowed to और फिर क्रिया की First form लगाते हैं; जैसे –
Direct – He said to his friend, “Let me go home.”
Indirect – He requested his friend to let him go home.
He requested his friend that he might be allowed to go home.
नोट – यदि Reporting Verb में object I Person का (me, us) हो और Reported Speech में let के बाद us दिया हो तो उसे (us को) we/they में बदल देते हैं। उसे Reporting Verb के subject के अनुसार नहीं बदला जाता है।
Exercise 8.
Change the following sentences into indirect speech :
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को Indirect Speech में बदलिये :
1. The teacher said to the boys, “Do not make a noise.”
2. The officer said to the servant, “Bring me a cup of milk.”
3. My father said to me, “Do not sleep in the day.”
4. “Sit down and learn your lesson, boys,” said the teacher.
5. The commander said to the soldiers, “Fire.”
6. The mother said to me, “Give me a glass of water.”
7. Rani said to Kamala, “Never visit my house.”
Answer:
1. The teacher ordered the boys not to make a noise.
OR
The teacher forbade the boys to make a noise.
2. The officer ordered the servant to bring him a cup of milk.
3. My father forbade me to sleep in the day.
OR
My father advised me not to sleep in the day.
4. The teacher ordered the boys to sit down and learn their lesson.
5. The commander ordered the soldiers to fire.
6. The mother ordered me to give her a glass of water.
7. Rani warned Kamala never to visit her (Rani’s) house.

Exercise 9.
Change the following sentences into indirect speech :
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को Indirect Speech में बदलिये :
1. Ram said to me, “Let’s sing together.”
2. Sita said to me, “Let me finish my work.”
3. He said to me, “Let’s start tomorrow.”
4. I said to Hari, “Let’s go out for a walk.”
5. The two cats cried, “Let the case be closed.”
6. The boy said to his father, “Let me try once more.”
7. Socrates said, “Let me meet death like a man.”
Eownd More Bramples of Indircet Command, Thequed, Advice
Answer:
1. Ram suggested to me that they/we should sing together.
2. Sita requested me to let her finish her work.
OR
Sita requested me that she might be allowed to finish her work.
3. He suggested to me that they/we should start the next day.
4. I suggested to Hari that we should go out for a walk.
5. The two cats proposed that the case should be closed.
6. The boy requested his father to let him try once more.
OR
The boy requested his father that he might be allowed to try once more.
7. Socrates requested to let him meet death like a man.
OR
Socrates requested that he might be allowed to meet death like a man.
कुछ Imperative sentence दिखने में Interrogative जैसे लगते हैं पर ये वास्तव में Interrogative नहीं होते हैं। ऐसे वाक्यों की Indirect बनाते समय इनके Reporting Verb को वाक्य के भाव के अनुसार बदल देते हैं।
1. Direct – “Would you please give me your pen ?” he said to me.
Indirect – He requested me to give him my pen.
2. Direct – He said, “Could I use your phone ?”
Indirect – He requested me to allow him to use my phone.
3. Direct – He said, “Would you have a sandwich ?”
Indirect – He offered me a sandwich.
4. Direct – She said, “Would you like to have tea ?”
Indirect – She invited me to have tea.
5. Direct – “If I were you, I would buy this pen,” I said.
Indirect – I advised him to buy the pen.
6. Direct – “Why don’t you buy this pen ?” I said.
Indirect – I advised him to buy the pen.
7. Direct – “Go on, work hard for the exam,” said Isha.
Indirect – Isha encouraged me to work hard for the exam.
8. Direct – “Don’t forget to tell him,” said Anand.
Indirect – Anand reminded me to tell him.
9. Direct – He said, “What about going home ?”
Indirect – He suggested going home.

10. Direct – He said, “Thank you.”
Indirect – He thanked me.
11. Direct – He said, “Happy Holi.”
Indirect – He wished me a happy Holi.
12. Direct – He said, “Liar.”
Indirect – He called me a liar.
Exercise 10.
Change the following sentences into indirect speech:
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को Indirect Speech में बदलिये –
1. “Would you like to play with us ?” they said.
2. “Would you like a lift?” said Nadeem.
3. “Could we see the manager, please ?” said the men.
4. He said, “Would you like a drink ?”
5. “Why don’t you take this foreign money to the bank ?” said my friend.
6. “Could I have your name and address, please ?” said the receptionist.”
7. “Would you like to sleep here ?” he asked us.
Answer:
1. They offered us to play with them.
2. Nadeem offered me a lift.
3. The men requested to see the manager.
4. He offered me a drink.
5. My friend suggested taking that/the foreign money to the bank.
6. The receptionist asked for my name and address.
7. He asked us if we would like to sleep there.
(D) Optative Sentences
अगर Reported Speech में प्रार्थना, कामना, आशीर्वाद या शाप के अर्थ में ‘may’ का प्रयोग हो तो वह Optative Sentence कहलायेगा। इनके Indirect बनाने के निम्नलिखित नियम हैं-
नियम . 1. इसमें Reporting Verb said को wished, blessed, cursed या prayed में बदलकर Sentence को Assertive Sentence में बदल देते हैं। Reporting Verb यदि Past Tense में हो तो Reported speech के May को might में बदल देते हैं। Connective ‘that’ लगाते हैं तथा Interjection के चिह्न (!) को हटा देते हैं जैसे-
(i) Direct : He said to me, “May you live long !”
Indirect : He wished that I might live long.
(ii) Direct : The hermit said, “May you all go to hell !”
Indirect : The hermit cursed that they all might go to hell.
नोट – (i) शुभकामना व्यक्त करने के लिए wished तथा शाप के लिये cursed का प्रयोग होता है।
(ii) prayed का प्रयोग ईश्वर से प्रार्थना करने पर होता है। जैसे-
Direct : He said to me, “May God help you !”
Indirect : He prayed that God might help me.
नियम 2. यदि Report Speech में Goodbye या Good night का प्रयोग होता है, तो said के स्थान पर bade का प्रयोग करते हैं तथा Good morning/afternoon/evening का प्रयोग हो, तो said के स्थान पर wished लिखते हैं। जैसे-
(i) Direct : Anand said, “Good night, Krishna ! We will meet again tomorrow.”
Indirect : Anand bade good night to Krishna and said that they would meet again the next day.
(ii) Direct : He said, “Goodbye, my friends!”
Indirect : He bade goodbye to his friends.
Or
He bade his friends goodbye.

(iii) Direct: Ravi said, “Good morning, my friend!”
Indirect: Ravi wished his friend good morning.
Or
Ravi wished good morning to his friend.
(iv) Direct: He said to me, “Good morning, my friend !”
Indirect: He cordially wished me good morning.
(v) Direct: He said to, “Good morning, sir !”
Indirect: He respectfully wished Mr X good morning.
Exercise 11.
Change the following sentences into indirect speech :
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को Indirect Speech में बदलिये –
1. I said to Anand, “May you always be happy !”
2. The beggar said to me, “May you prosper in life !”
3. He said to her, “Goodbye, my sister !”
4. She said, “May God bless Hari with a son !”
5. The teacher siad, “May you get first position !”
6. I said, “May God pardon you !”
7. Mohan said to her, “May you have a happy journey !”
8. She said, “Good morning, my friend !”.
9. They said, “Long live the Prime Minister !”
10. He said to me, “Happy New Year !”
11. Ravi said, “May your enemy go to hell !”
Answer:
1. I wished Anand that he might always be happy.
2. The beggar wished that I might prosper in life.
Or
The beggar wished me a prosperous life.
3 . He bade goodbye to his sister.
4. She prayed that God might bless Hari with a son.
5. The teacher wished that I might get first position.
6. I prayed that God might pardon her/him.
7. Mohan wished that she might have a happy journey.
Or
Mohan wished her a happy journey.
8. She wished her friend good morning.
9.They wished that the Prime Minister might live long.
Or
They wished the Primer Minister a long life.
10. He wished me a Happy New Year.
11. Ravi cursed that my enemy might go to hell.
(E) Exclanatola Sentence
ऐसे वाक्यों में प्रसन्नता (joy), शोक (regret), दुःख (sorrow) या आश्चर्य (surprise) आदि प्रकट किये जाते हैं। इनके Indirect बनाने के नियम हैं-
नियम 1. Interjections (विस्मयादिबोधक शब्दों ) को समाप्त कर देते हैं, क्योंकि इनके भाव Reporting Verb से ही स्पष्ट हो जाते हैं। Interjections Hurrah से joy, Alas से sorrow, What a एवं How से surprise तथा Bravo से approval प्रकट होता है।
नियम 2. Reported Speech को Connective ‘that’ से जोड़ते हैं।
नियम 3. Note of Exclamation (!) के बदले Full Stop (.) का प्रयोग करते हैं अर्थात् Exclamatory Sentence को Assertive Sentence में बदल देते हैं।
नियम 4. Person और Tense का परिवर्तन Assertive Sentence की तरह होता है.।
नियम 5. Reporting Verb said को आशय के अनुसार निम्न प्रकार बदलते हैं –
(a) यदि वाक्य में प्रसन्नता प्रकट की गई है, तो exclaimed with joy या exclaimed with delight का प्रयोग करते हैं। जैसे-
Direct : He said, “Hurrah ! My old friend has come.”
Indirect : He exclaimed with delight that his old friend had come.
(b) यदि वाक्य में शोक प्रकट किया गया हो, तो exclaimed with sorrow या exclaimed with grief का प्रयोग करते हैं जैसे-
Direct : He said, “Alas ! I am ruined.”
Indirect : He exclaimed with sorrow that he was ruined.
(c) यदि वाक्य में किसी की प्रशंसा की गई है, तो praised या applauded शब्दों का प्रयोग करते हैं। जैसे-
Direct : He said, “Bravo ! You have done well.”
Indirect : He applauded us saying that we had done well.
(d) Exclamatory Sentences जब what a या how से प्रारम्भ हों, तो इनके द्वारा विस्मय या अधिकता का भाव प्रकट होता है। इन भावों को प्रकट करने के लिए Indirect में इनके स्थान पर very या great इस प्रकार लगाते हैं-
(i) what a या how के बाद यदि Noun आता है, तो इन्हें great में बदलते हैं।
(ii) what a या how के बाद यदि Adjective आता है, तो इन्हें very में बदलते हैं। जैसे-

(i) Direct : Ram said, “How fast you are walking !”
Indirect : Ram exclaimed with surprise that I was walking very fast.
(ii) Direct : He said, “What a fool I am !”
Indirect : He exclaimed with regret that he was a great fool.
Note – आधुनिक नियमों के अनुसार what a तथा how से प्रारम्भ होने वाले वाक्यों को Indirect में बदलते समय said के स्थान पर केवल exclaimed का प्रयोग ही उपयुक्त माना जाता है। अतः उपर्युक्त वाक्यों को इस प्रकार भी लिखा जा सकता है-
(i) Direct : Ram said, “How fast you are walking !”
Indirect : Ram exclaimed that I was walking very fast.
(ii) Direct ‘He said, “What a fool I am !”
Indirect : He exclaimed that he was a great fool.
(e) यदि वाक्य में Good Heavens का प्रयोग हो, तो Reporting Verb को exclaimed with surprise में बदल देते हैं। जैसे-
Direct : “Good Heavens ! I have dropped my key somewhere,” he said.
Indirect : He exclaimed with surprise that he had dropped his key somewhere.
Exercise 12.
Change the following sentences into indirect speech :
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को Indirect Speech में बदलिये –
1. The student said, “Alas ! My friend is dead.”
2. The boys said, “Hurrah ! We shall have a jolly holiday tomorrow.”
3. He said, “How well she sings !”
4. Sita said, “Alas ! My house is on fire.”
5. The child said, “How beautiful the flower is !”
6. He said, “Hurrah !I have passed the examination.”
7. The teacher said, “What a lazy boy you are !”
8. The captain said to the players, “Bravo ! Well done.”
9. The teacher said, “What a pity ! She has not learnt good manners.”
10. The old man said, “Good Heavens ! The hut has caught fire.”
[Glossary : jolly = खुशी का। lazy = आलसी। manners = आदतें। caught fire = आग पकड़ ली।]
Answer:
1. The student exclaimed with sorrow that his friend was dead.
2. The boys exclaimed with delight that they would have a jolly holiday the next day.
3. He exclaimed with joy that she sang very well.
Or
He applauded her saying that she sang very well.
4. Sita exclaimed with sorrow that her house was on fire.
5. The child exclaimed with joy that the flower was very beautiful.
6. He exclaimed with delight that he had passed the examination.
7. The teacher exclaimed with disgust that I was a very lazy boy.
Or
The teacher exclaimed that I was a very lazy boy.
8. The captain applauded the players saying that they had done well.
9. The teacher exclaimed with pity/regret that she had not learnt good manners.
10. The old man exclaimed with sorrow that the hut had caught fire.
Chart Of Changes in indirect speech
(With Past Tense)
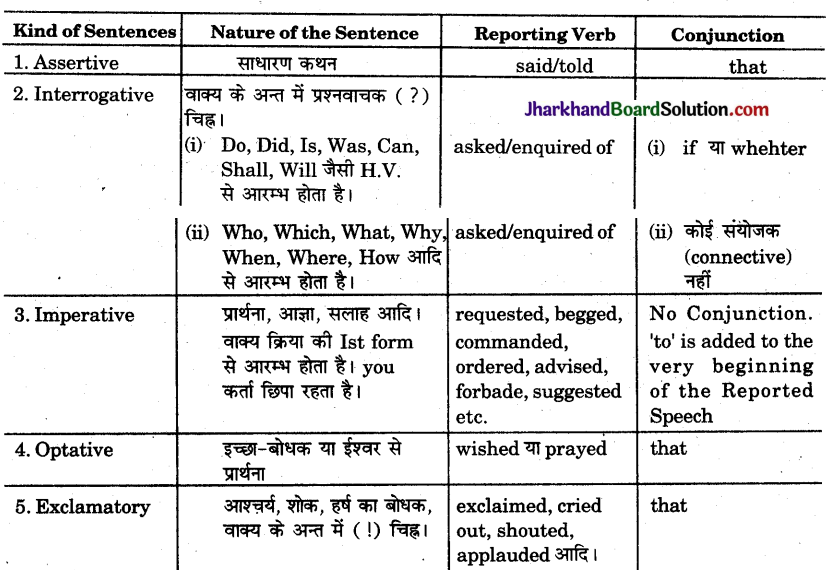
Exercise 13.
Change the following sentences into indirect speech :
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को Indirect Speech में बदलिये –
1. She said to Tommy, “Where did you find it?”
2. She said. “What’s it about?”
3. Margie said to Tommy, “What is there to write about school?”
4. He said to her mother, “It’s not the little girl’s fault.”
5. She said to Tommy, “Why would anyone write about school?”
6. She said to Tommy, “How could a man be a teacher?”
7. She said, “I wouldn’t want a strange man in my house to teach me.’
8. Margie said quickly, “I didn’t say I didn’t like it.”
9. Margie said to Tommy, “Can I read the book some more with you after school?”
10. Isabel Glennie says, “I suddenly realized she hadn’t heard.”
Answer:
1. She asked Tommy where he had found it.
2. She asked what it was about.
3. Margie asked Tommy what there was to write about school.
4 . He told her mother that it was not the little girl’s fault.
5. She asked Tommy why anyone whould write about school.
6. She asked Tommy how a man could be a teacher.
7. She said that she would not want a strange man in her house to teach her.
8. Margie said quickly that she hadn’t said she hadn’t liked it.
9. Margie asked Tommy if she could read the book some more with him after school.
10. Isabel Glennie says that she suddenly realized she hadn’t heard.

Exercise 14.
Change the following sentences into indirect speech :
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को Indirect Speech में बदलिये –
1. Evelyn says, “Everything suddenly looked black.”
2. He would say to her, “Don’t listen through your ears.”
3. She laughed and said, “Men with bushy beards give me trouble.”
4. She says, “My speech is clear because I could hear till I was eleven.”
5. The Beethoven Fund for Deaf Children says, “She is a shining inspiration for deaf children.”
6. People say, “If she can do it, we can.”
7. Ustad Faiyaz Khan said to Bismillah Khan, “Work hard and you shall make it.”
8. He says with emphasis, “I just can’t come to terms with the artificiality and glamour of the film world.”
9. He said, “Bring me tea into the drawing room.”
10. Mother would call to Kezia, “If you’re a good girl you can come and take off father’s boots.”
Answer:
1. Evelyn says that everything suddenly looked black.
2. He would forbid her to listen through her ears./He would tell her not to listen through her ears.
3. She laughed and said that men with bushy beards give her trouble.
4. She says that her speech is clear because she could hear till she was eleven.
5. The Beethoven Fund for Deaf Children says that she is a shining inspiration for deaf children.
6. People say that if she can do it, they can.
7. Ustad Faiyaz Khan advised Bismillah Khan to work hard and he would make it.
8 . He says with emphasis that he just can’t come to terms with the artificiality and glamour of the film world.
9. He ordered to bring him tea into the drawing-room.
10. Mother would call to Kezia that if she was a good girl she could come and take off father’s boots.
Exercise 15.
Change the following sentences into indirect speech :
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को Indirect Speech में बदलिये –
1. She said, “I tore up them for my surprise.”
2. He said to Kezia, “Did you do that?”
3. He said to her, “I am going to beat you for this.”
4. He ordered, “Sit up.”
5. She sobbed. “What did God make fathers for?”
6. She asked, “What’ll I do if I have a nightmare?”
7. Alice said to Kezia, “You just go to sleep.”
8. He said, “What’s the matter?”
9. Her father said to Kezia, “Rub your feet against my legs and get them warm.”
10. His mother said to Einstein, “She is a book like you.”
Answer:
1. She said that she had torn up them for her surprise.
2. He asked Kezia if she had done that.
3. He told her that he was going to beat her for that.
4. He ordered to sit up.
5. She sobbed what God had made fathers for.
6 . She asked what she would do if she had a nightmare.
7. Alice told Kezia that she just went to sleep.
8. He asked what the matter was.
9. Her father asked Kezia to rub her feet against his legs and get them warm.
10. His mother told Einstein that she was a book like him.
Dialogue in Indirect Speech
आजकल परीक्षा में dialogue को ही Indirect Speech में बदलने के लिए दिया जाता है। इनके परिवर्तन के नियम भी वही हैं जिन्हें हम यहाँ पर देख चुके हैं। फिर भी विभिन्न प्रकार के वाक्यों वाले dialogues को Indirect में बदलने के कुछ नियम इस प्रकार से हैं :
नियम 1. Direct Speech के दोनों speakers को Reporiing Speech में बदलकर प्रश्न में ही दिया हुआ रहता है।
नियम 2. Colon (:) के चिह्न के दार्यीं ओर वाला भाग ही Reported Speech होता है।
नियम 3. Reported Speech के वाक्य को देखकर सबसे पहले यह पता लगाओ कि वाक्य किस प्रकार का है तथा उसी के अनुसार Conjunction का प्रयोग किया जाता है। जैसे – Assertive Sentences में that का प्रयोग किया जाता है।
(A) Dialogues in Assertive
उदाहरण –
1. Teacher : You are late today.
Student : I was busy in completing my homework.
The teacher told the student
The student said
Answer:
The teacher told the student that he was late that day.
The student said that he had been busy in completing his homework.
2. Rajat : I saw you at the party.
Rani : I was not there.
Rajat told Rani ……………… . Rani said
Answer:
Rajat told Rani that he had seen her at the party. Rani said that she had not been there.
(B) Dialogues in Interrogative
Interrogative Sentences को Direct से Indirect में बदलने के नियम देखें।
1. Shanti : Do you live here ?
Sourabh : Yes.
Shanti asked Sourabh ……………… Sourabh said …………………
Answer:
Shanti asked Sourabh if he lived there. Sourabh said that he did.
2. Teacher : Do you know the answer ?
Student : No.
The teacher asked the student ………………
The student said
Answer:
The teacher asked the student if he knew the answer. The student said that he did not.

3. Arpit : Where are you going ?
Arpita : Kota.
Arpit asked Arpita …………….. Arpita said …………………..
Answer:
Arpit asked Arpita where she was going.
Arpita said that she was going to Kota.
4. Anil : When will you return ?
Sunita : Tomorrow.
Anil asked Sunita …………………… Sunita said ……………………….
Answer:
Anil asked Sunita when she would return.
Sunita said that she would return the next day.
(C) Dialogues in Imperative
Imperative Sentences को Direct से Indirect में बदलने के नियम देखें।
1. Teacher : Sit down, boys.
Boys : What will you teach, Sir?
The teacher asked the boys ……………….. . The boys asked the teacher
Answer:
The teacher asked the boys to sit down. The boys asked the teacher what he would teach.
2. Arun : Let’s go to party.
Aruna : Yes, let’s.
Arun suggested
Aruna agreed
Answer:
Arun suggested that they should go to party. Aruna agreed that they should go.
3. Ramesh : Don’t play here.
Kavita : Where should I play?
Ramesh forbade Kavita ……………….. . Kavita asked Ramesh …………………….
Answer:
Ramesh forbade Kavita to play there.
Kavita asked Ramesh where she should play.
(D) Dialogues in Optative
Optative Sentences को Direct से Indirect में बदलने के नियम देखें ।
1. Rajesh : May you live long!
Ranjeeta : Thank you.
Rajesh wished ……………………. Ranjeeta …………………….
Answer:
Rajesh wished that Ranjeeta might live long. Ranjeeta thanked him.
(E) Dialogues in Exclamatory
Exclamatory Sentences को Direct से Indirect में बदलने के नियम देखें।
1. John : How fast you are walking!
Mary : It is my usual speed.
John exclaimed …………………….. Mary said …………………….
Answer:
John exclaimed that Mary was walking very fast.
Mary said that it was her usual speed.
2. Sunil : What a terrible noise!
Reena : I have not heard it.
Sunil exclaimed ……………………. Reena said …………………….
Answer:
Sunil exclaimed that it was a terrible noise.
Reena said that she had not heard it.
3. Sarika : Oh ! I have cut my finger.
Sudhir : I’ll get you a bandage.
Sarika exclaimed
Answer:
Sarika exclaimed with pain that she had cut her finger.
Sudhir said that he would get her a bandage.
Exercise 16.
Rewrite the following sentences by transforming from Direct to Indirect speech :
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को Direct से Indirect Speech में बदलकर पुन: लिखिये :
1. Kavita : I don’t know the way.
Kavish : Don’t worry I’ll show you.
Kavita told Kavish ……………… (i) ………. Kavish told Kavita ……………… (ii) ……………… (iii) ………………
2. Rajan : I don’t like this colour.
Ravina : I’ll change it.
Rajan told Ravina ……….(i)……… Ravina said …………….. (ii) ………………
3. Jaya : Where are you going ?
Jayesh : I am going to market.
Jaya asked Jayesh ………………. (i) …………………. Jayesh told her ……………. (ii)……….
4. Jyoti : What are you doing, Raghav ?
Raghav : I am trying to find my book.
Jyoti asked Raghav ……….. (i) ………. Raghav told her ……….. (ii) ……….
5. Renuka: What is the boy doing, Ranjeet?
Ranjeet : He is making a science model.
Renuka asked Ranjeet …………(i)………….. Ranjeet told her ……………. (ii) ………..
6. Meghna: Who lives in Jaipur?
Karan: My uncle lives in Jaipur.
Meghna asked Karan ……….. (i) ………. Karan told Meghna ……….. (ii) ……….
7. Jayant: Have you ever gone to the Ajanta Caves?
Anita: I have been there twice.
Jayant asked Anita ……….(i)………. Anita told him ………… (ii) ………….
8. Ramesh : Have you finished your dinner ?
Pooja : Yes, I have just taken my dinner.
Ramesh asked Pooja ………..(i)………. Pooja told in affirmative …………. (ii)………..
9. Ranveer : Where have you put my pen ?
Rani : I forgot it at home.
Ranveer asked Rani (i)……….. Rani told Ranveer ……… (ii) ……..
10. Praveen: Are you watching TV ?
Parinita : No, I am studying.
Praveen asked Parinita …………. (i) …….. Parinita replied ………. (ii) …….. and said ………… (iii) …………
Answers:
1.(i) that she didn’t know the way (ii) not to worry (iii) and further told that he would show her the way.
2.(i) that he did not like the colour (ii) that she would change it.
3.(i) where he was going (ii) that he was going to market:
4.(i) what he was doing (ii) that he was trying to find his book.
5.(i) what the boy was doing. (ii) that he was making a science model.
6.(i) who lived in Jaipur. (ii) that his uncle lived in Jaipur.
7.(i) if she had ever gone to the Ajanta Caves. (ii) that she had been there twice.
8:(i) if she had finished her dinner. (ii) that she had just taken her dinner.
9.(i) where she had put his pen. (ii) that she had forgotten it at home.
10. (i) if she was watching TV. (ii) in negative (iii) that she was studying.
Exercise 17.
Rewrite the following Sentences by transforming from Direct to Indirect speech :
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को Direct से Indirect Speech में बदलकर पुनः लिखिये :
1. Mohan : Let me see the movie.
Sita: You can see the movie tomorrow.
Mohan requested Sita ………….. (i)……………. Sita told Mohan ………….. (ii)…………….
2. Vinay. : How are you, Sunidhi ?
Sunidhi : I am fine, thank you.
Vinay asked Sunidhi …………… (i) ………. Sunidhi thanked Vinay saying ………….. (ii)……………
3. Mother : Rakesh, where did you go ?
Rakesh : Mom, I went to my friend’s house.
Mother asked Rakesh ……….(i)………. Rakesh told his mother …………(ii)…………
4. Mohini : Have you seen the library, Rohan ?
Rohan : Yes, I have seen.
Mohini asked Rohan (i)…………. Rohan replied …………….. (ii)………………..
5. Sharada : What is your father ?
Sharad : My father is a teacher.
Sharada asked Sharad ………….. (i)………. Sharad told Sharada …………… (ii) …………..
6. Wolf : Why are you making the water dirty ?
Lamb : Sir, the water is flowing from your side.
The wolf asked the lamb ……….(i)………. The lamb replied respectfully ……………. (ii) …………..
7. Headmaster: What is your name ?
Student : Sir, my name is Rohan.
The headmaster asked the student …….. (i)……. The student respectfully said …….. (ii) …………..
8. Rachana: What do you want?
Raman : I want to see your father.
Rachana asked Raman …………. (i)……. Raman told Rachana ……………. (ii) ………………
9. Mukesh : Did you go to the market ?
Mona : No, I could not.
Mukesh asked Mona ………….(i)………. Mona replied ……….. (ii) ……………..
10. Anuradha : Are you going to the exhibition, Anil ?
Anil : No, I don’t want to go to the exhibition, Anuradha.
Anuradha asked Anil ………(i)……… Anil told Anuradha ………(ii)……….
Answer:
1.(i) to let him see the movie. (ii) that he could see the movie the next day.
2.(i) how she was (ii) that she was fine.
3.(i) where he had gone (ii) that he had gone to his friend’s house.
4.(i) if he had seen the library. (ii) that he had seen.
5.(i) what his father was. (ii) that his father was a teacher.
6.(i) why he was making the water dirty. (ii) that the water was flowing from his side.
7.(i) what his name was. (ii) that his name was Rohan.
8.(i) what he wanted. (ii) that he wanted to see her father.
9.(i) if she had gone to the market. (ii) that she could not.
10. (i) if he was going to the exhibition. (ii) that he didn’t want to go to the exhibition.

Exercise 18.
Rewrite the following sentences by transforming from Direct to Indirect speech :
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को Direct से Indirect Speech में बदलकर पुन: लिखिये :
1. Travel agent : Do you want to go by air or sea?
Sarika : I would like to go by air.
The travel agent asked …………….. (i)………. Sarika said ………. (ii) ……………….
2. Policeman: Did you see the accident?
Traveller : Yes, I saw.
The policeman asked the traveller ……… (i)…………… The traveller replied ………………… (ii) ………………
3. Anushka : Why don’t you buy this book?
Anukul : I have no money.
Anushka advised Anukul (i)………. Anukul said …………… (ii)……………….
4. Teacher : Would you show me your homework?
Student : Sir, I have forgotten my note-book at home.
The teacher asked the student ……………… (i)…………………… The student respectfully replied …………… (ii)……………….
5. Raman : Sit down.
Ragini : No, thanks.
Raman asked Ragini ……………….. (i)…………. Ragini thanked saying ……………. (ii)……………….
6. Shyam : Don’t forget to order the tea?
Shruti : O.K. I’ll do.
Shyam reminded Shruti …………. (i) …………. Shruti said ……… (ii)………………..
7. Pankaj : This year I failed.
Poonam : Try again.
Pankaj told Poonam …………(i)………. Poonam encouraged him ………. (ii)………………
8. Chirag : I have lost my job.
Chinki : Go on apply for another job.
Chirag told Chinki ………….. (i)…………… Chinki encouraged Chirag …………. (ii)…………
9. Vivek : Don’t open the door.
Vinita : I will not open the door.
Vivek told Vinita ……….(i)……….. Vinita told Vivek ………. (ii)………..
10. Dinesh : Let’s go home.
Damini : Let’s not.
Dinesh suggested to Damini ……….(i)……….. Damini said ……….(ii)………..
Answer:
1.(i) whether she wanted to go by air or sea. (ii) that she would like to go by air.
2.(i) if he had seen the accident. (ii) that he had seen.
3.(i) to buy the book. (ii) he had no money.
4.(i) to show him his home work. (ii) that he had forgotten his note-book at home.
5.(i) to sit down (ii) that she would not.
6.(i) to order the tea. (ii) that she would order.
7.(i) that that year he had failed (ii) to try again.
8.(i) that he had lost his job. (ii) to apply for another job.
9.(i) not to open the door. (ii) that she would not open the door.
10. (i) that they should go home. (ii) that they should not.

Exercise 19.
Rewrite the following sentences by transforming from Direct to Indirect speech :
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को Direct से Indirect Speech में बदलकर पुनः लिखिये :
1. Hari : We are late, Shanti.
Shanti : We will manage.
Hari told Shanti ……….(i)………. Shanti said ………. (ii) …………..
2. Sunita: I want to speak to you, Sharad.
Sharad : But I don’t.
Sunita told Sharad ……… (i)……….. Sharad told her ………. (ii) …………..
3. Gagan : I will answer the phone.
Shashi : I will wait.
Gagan told Shashi ……… (i)……….. Shashi said ………. (ii) …………..
4. Ratna : I am giving a party this week to all my friends.
Ratan : Will you invite me?
Ratna told Ratan …………….. (i)………. Ratan asked her ………. (ii) …………..
5. Rani : Drive as fast as you can.
Driver : Don’t worry, madam. I am trying my best.
Rani asked the driver . (i)……… The driver respectfully asked her ……….. (ii) …………..
6. Komal : You have an excellent cook.
Kumar : I hired him from Jodhpur.
Komal told Kumar ………… (i) ………….. Kumar said ………… (ii) …………..
7. Teacher : Do it again.
Student: Yes, sir.
The teacher asked the student ………(i)………. The student respectfully said …………. (ii) …………..
8. Ruchi : You have bought yourself a new hat.
Aman : I bought it from a fair.
Ruchi told Aman ……….(i)………. Aman said …………. (ii) …………..
9. Son : Give me another, Mom.
Mother : I don’t have.
The son asked his mother …………. (i)…………. The mother said ………….. (ii) …………..
10. Mother : Wash your face.
Daughter : There is no water.
The mother told the daughter ………….. (i)………… The daughter said. ………….. (ii) …………..
Answer:
1.(i) that they were late. (ii) that they would manage.
2.(i) that she wanted to speak to him. (ii) that he didn’t.
3.(i) that he would answer the phone. (ii) that she would wait.
4. (i) that she was giving a party that week to all her friends. (ii) if she would invite him.
5. (i) to drive as fast as he could (ii) not to worry as he was trying his best.
6. (i) that he had an excellent cook. (ii) that he had hired him from Jodhpur.
7. (i) to do it again (ii) that he would.
8. (i) that he had bought himself a new hat. (ii) that he had bought it from a fair.
9. (i) to give him another. (ii) that she didn’t have.
10. (i) to wash her face. (ii) that there was no water.
Exercise 20.
Rewrite the following sentences by transforming from Direct to Indirect speech:
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को Direct से Indirect Speech में बदलकर पुन: लिखिये :
1. Babita : Where will you be tomorrow ?
Jayesh : I shall be in my office.
Babita asked Jayesh ……….(i)………. Jayesh told her
2. Chirayu : Chinki, what shall I do with this broken pen?
(ii) Chinki : Throw it away.
Chirayu asked Chinki ……(i)…… Chinki advised him …………. (ii)…………..
3. Suresh : What time do you start working, Mary?
Mary : I usually start at 9 o’clock in the morning.
Suresh asked Mary ………..(i)………. Mary said ………… (ii)…………
4. Umang : What are you preparing, Gunjan ?
Gunjan : I am preparing tea.
Umang asked Gunjan ……….(i)……… Gunjan said ………… (ii)………….
5. Rashmi : What are you doing ?
Pulkit : I am putting these papers in a file.
Rashmi asked Pulkit ……….(i)………. Pulkit said ………… (ii)…………
6. Alan : Are you going to the exhibition, Helan ?
Helan : No, I do not want to go to the exhibition.
Alan asked Helan ………(i)………. Helan replied. …………. (ii)…………
7. Sharad : What is your father ?
Preeti : He is a teacher in Ajmer.
Sharad asked Preeti ……….(i)………. Preeti said ………… (ii) …………
8. Teacher : What have I drawn on the blackboard ?
Boy : You have drawn the picture of a peacock, sir.
The teacher asked the boy ……….(i)………. The boy respectfully said ………… (ii) …………
9. Shyam : Do you want any work ?
Youngman : Yes, if you have any.
Shyam asked the yougman …………. (i)……… The young man said …………. (ii)………….
10. Teacher : Give leave application for that.
Student : Sir, I have already applied for it …………. (i) …………
The teacher told the student ………… (ii) ………… The student respectfully said.
Answer:
1. (i) where he would be the next day. (ii) that he would be in his office.
2. (i) what he would do with that broken pen (ii) to throw it away.
3. (i) what time she started working. (ii) that she usually started at 9 o’clock in the morning.
4. (i) what she was preparing. (ii) that she was preparing tea.
5. (i) what he was doing (ii) that he was putting those papers in a file.
6. (i) if she was going to the exhibition.
(ii) in negative saying that she did not want to go to the exhibition.
7. (i) what her father was. (ii) that he was a teacher in Ajmer.
8. (i) what he had drawn on the blackboard. (ii) that he had drawn the picture of a peacock.
9. (i) if he wanted any work. (ii) that he did if he had any.
10. (i) to give leave application for that. (ii) that he had already applied for it.

Exercise 21.
Rewrite the following sentences by transforming from Direct to Indirect speech : निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को Direct से Indirect Speech में बदलकर पुन: लिखो।
1. Radha :What will Mr Sharma teach us today?
Ramesh : Mr Sharma will teach us grammar today.
Radha asked Ramesh ……….. (a) ………….
Ramesh told Radha that ………… (b) ………….
(b) Meera : Tell me what you did today.
Sohan : Didi, I read two lessons of Geography today.
Meera asked Sohan to ……….. (a) ………….
Sohan addressed Meera as didi and replied that …………. (b) ………….
3. Radha : Where did you go this morning ?
Mohan : I went to the grocer to buy things.
Radha asked Mohan ………. (a) ………….
Mohan told Radha that …………. (b) ………….
4. Mother : Go to the market and bring vegetables.
Son : I can’t go now because I have to complete my homework.
Mother asked her son ………. (a) ………….
The son replied his mother …………. (b) ………….
5. Mr Sharma : Mr Verma ! What is your son, Amit doing these day?
Mr Verma : Sir, Amit is studying in the USA this year.
Mr Sharma asked Mr Verma………. (a) ………….
Mr Verma politely replied Mr Sharma ……………. (b) ………….
Answers:
1. (a) what Mr Sharma would teach them that day.
(b) that Mr Sharma would teach them grammar that day.
2. (a) tell her what he had done that day.
(b) he had read two lessons of Geography that day.
3. (a) where he had gone that morning.
(b) he had gone to the grocer to buy things.
4. (a) to go to the market and bring vegetables.
(b) that he could not go then because he had to complete his homework.
5. (a) what his son Amit, was doing those days.
(b) that Amit was studying in the USA that year.
Exercise 22.
Rewrite the following sentences by transforming from Direct to Indirect speech :
निम्नलिखित वाक्यों को Direct से Indirect Speech में बदलकर पुन: लिखो :
1. (i) Mother : Don’t go near the fire, children.
Children : O.K. Mama, we won’t.
The mother warned the children ……………(a)…………..
The childern replied in affirmation ………. (b)…………..
(ii) Ram : I plan to leave for the USA next week.
Raghav : Please bring a laptop for me.
Ram said that …………(a)………………
Raghav requested Ram ………….. (b)………………
2. (i) Rita said to Amar, “Have you seen my diary ?”
Rita asked Amar ………..(a)……………….
(ii) Amar said, “Is it the one with a brown cover ?”
Amar asked ………(b)………
(iii) Rita said to Amar, “Oh yes, brother !”
Rita ……..(c)………..
(iv) Amar said to Rita, “I saw it lying on the new shelf in our drawing room.”
Amar told Rita that. ………..(d) …………..

3. (i) Gopal said to the bookseller, “Please provide me some new books.”
Gopal requested the bookseller ……………………………………………….
(ii) The bookseller asked Gopal, “Which book do you want ?”
The bookseller asked Gopal ……………………………………………….
(iii) Gopal said, “I want some English Grammar books.”
Gopal said ……………………………………………….
(iv) The bookseller said, “I have got a lot of new books.”
The bookseller replied ……………………………………………….
4. (i) The young seagull said, “I am too young to fly.”
The young seagull said ……………………………………………….
(ii) Santosh said to me, “Will you bring me a gift?”
Santosh asked me ……………………………………………….
(iii) The doctor said to the lady, “Take the medicines daily.”
The doctor advised the lady ……………………………………………….
(iv) Vivek said to Ajay, “Where do you live ?”
Vivek asked Ajay ……………………………………………….
Answer:
1. (i) (a) not to go near the fire. (b) and said that they wouldn’t.
(ii) (a) he planned to leave for the USA the following week. (b) to bring a laptop for him.
2. (i) if he had seen her diary.(ii) if it was the one with a brown cover. (iii) Rita asserted with surprise. (iv) he had seen it lying on the new shelf in their drawing room.
3. (i) to provide him some new books. (ii) which book he wanted. (iii) that he wanted some English Grammar books. (iv) that he had got a lot of new books.
4. (i) that he was too young to fly. (ii) if I would bring him a gift. (iii) to take the medicines daily. (iv) where he lived.
![]()
![]()

![]()
![]()