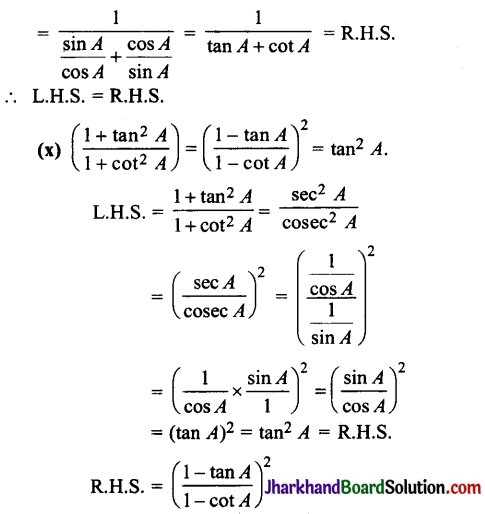
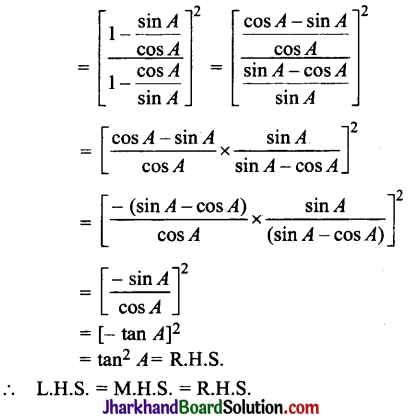
Jharkhand Board JAC Class 10 Science Important Questions Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce? Important Questions and Answers.
JAC Board Class 10 Science Important Questions Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce?
Additional Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Distinguish between :
(1) Asexual reproduction and Sexual reproduction
OR
What is the basic difference between asexual reproduction and sexual reproduction?
Answer:
| Asexual reproduction | Sexual reproduction |
| 1. In asexual reproduction, a single individual is involved, whose certain body part forms the new individual of the same kind. | 1. In sexual reproduction, two gametes of opposite sex fuse to form a fertilized egg (zygote) that develops into a new individual. |
| 2. The sex of an organism does not play any role in the reproductive process. | 2. The organisms involved are either bisexual or the two individuals are of opposite sex. |
| 3. The new organism has all the characters of the parent organism without any change in the hereditary characters. | 3. The new individual follows laws of inheritance and therefore, differs from its parent organisms. |
| 4. Asexual reproduction is of different types such as fission, regeneration, budding, sporulation, fragmentation, etc. | 4. No specific types of sexual reproduction. |
| 5. With changing environment asexual reproduction is not sufficient to sustain life. | 5. With changing environment, sexual reproduction is essential to sustain life. |
(2) Binary fission and Multiple fission
Answer:
| Binary fission | Multiple fission |
| 1. Binary fission forms only two offsprings from a single parent. | 1. Multiple fission forms many offsprings from a single parent. |
| 2. This method of reproduction occurs in normal condition. | 2. This method of reproduction occurs in unfavourable condition. |
| 3. In this method the nucleus divides once. | 3. The nucleus divides several times. |
| 4. In this cytoplasm also divides into two parts. | 4. In this, small amount of cytoplasm collects around each daughter nuclei after multiple divisions. |
| 5. The parent cell does not get destroyed but it gets divided into two parts. | 5. In this with breaking of cyst, the parent cell also break. |
(3) Budding and Sporulation
Answer:
| Budding | Sporulation |
| 1. In this method of asexual reproduction, a small part of the body of the parent animal grows out as a ‘Bud’. | 1. In this method of asexual reproduction, sporangium is produced in the parent plant. |
| 2. The forming bud grows and differentiates in daughter animal. | 2. The spore germinates to produce new plant. |
| 3. The forming bud is not a reproductive unit. | 3. The spore is the microscopic reproductive unit, which is covered by protective coat. |
| 4. Example: Hydra, Yeast. | 4. Example: Mucor, Rhizopus. |

(4) Puberty stage in male and Puberty stage in female
Answer:
| Puberty stage in male | Puberty stage in female |
| 1. Boys reach puberty at the age of 13 to 14 years. | 1. Girls attain puberty at the age of 10 to 12 years. |
| 2. Muscles grow more in boys. | 2. Muscles are soft in girls. |
| 3. Voice becomes deep. | 3. Voice remains shrilled. |
| 4. Shoulder and chest broadens. | 4. The hip region widens. |
| 5. The penis becomes larger and it is capable of becoming erect. | 5. Mammary glands, vagina and uterus are developed. |
(5) Male reproductive system and Female reproductive system
Answer:
| Male reproductive system | Female reproductive system |
| 1. Testes, vas deferens, seminal vesicle, prostate gland and penis are included in it. | 1. Ovary, oviduct, uterus and vagina are included in it. |
| 2. Male reproductive system is formed by the organs related to production of sperms and transfer of sperms to the place of fertilisation. | 2. Female reproductive system is formed by the organs related to production of ovum, implantation of embryo and child birth. |
| 3. Testes are located in the scrotal sac outside the abdominal cavity. | 3. Ovaries are located in the abdominal cavity. |
| 4. The vas deferens, joins with urinary duct coming from urinary bladder to form urethra. | 4. The oviducts from two sides open in the muscular uterus. |
| 5. The urethra is common passage for sperms and urine. | 5. In female, the urinaiy opening and genital opening are separate. |
(6) Contraceptive mechanical method and Contraceptive chemical method
Answer:
| Contraceptive mechanical method | Contraceptive chemical method |
| 1. In this method, copper-T, loop, diaphragm worn in vagina and condom are used. | 1. In this method, the pills are used which are made up of hormones. |
| 2. This method is useful for both male and female. | 2. This method is useful only for females. |
| 3. Sperms are prevented from entering in female genital tract or unable to reach in oviduct due to barrier. | 3. Release of ova is inhibited. |
| 4. This method does not affect the production of gametes. | 4. This method can disturb the balance of female sex hormones. |
Question 2.
Give scientific reasons for the following tatements:
(1) The offsprings formed through asexual : reproduction have same genetic constitution as their parent cell.
Answer:
In asexual reproduction, the union of male and female gametes does not occur.
- Single parent is involved in asexual reproduction. The process of formation of new cell begins s with the creation of DNA copies.
- Two offsprings are formed from the single parent cell which possess equal proportion of DNA.
Hence, the offsprings formed through asexual reproduction have same genetic constitution as their parent cell.
(2) Variation is necessary for the maintenance of existence of any species.
Answer:
Specific species or its population live in the particular environment or habitat which is suitable to them.
- There are changes taking place on earth e.g., fluctuation in temperature, variation in the water level, etc.
- Organisms possesing variations get a chance to urvive in the changing environment.
- Due to variation, organisms can adapt to the environment and hence they can exist through adaptations.
- With the help of variation geographical distribution of organisms increase.
Hence, variation is necessary for the maintenance of existence of any species.
(3) Testes are situated outside the abdominal cavity.
Answer:
Sperms are produced by the testis.
- The temperature of testis remains 2-3°C lower than the body temperature which is optimal for the formation of sperms.
- If testis remain in abdominal cavity, then at the higher temperature, testes are unable to produce sperms.
Hence, testes are situated outside the abdominal cavity.
(4) The number of bryophyllum keep on increasing in garden.
Answer:
In some plants, parts like root, stem and leaves can give rise to buds in dormant state which acts as reproductive unit.
- When suitable moisture and temperature are provided to these dormant structures, they form new plants.
- Buds found on the leaves of bryophyllum induce vegetative propagation.
- In garden, the detatched buds germinate under favourable conditions such as moisture, nutrients, suitable temperature.
Hence, the number of bryophyllum keep on increasing in garden.
(5) The property of vegetative propagation is useful in agricultural purposes.
Answer:
In many plants root, stem and leaves develop into new plants under appropriate condition. Such a mode of reproduction is called vegetative propagation.
Advantages of vegetative propagation are as follow:
- Vegetative propagation is used in layering or grafting methods to grow many plants like sugarcane, roses or grapes for agricultural purposes.
- Plants raised by vegetative propagation can bear flowers and fruits earlier than those produced from seeds.
- The plants that have lost the capacity to produce seeds can also be produced by vegetative propagation, e.g., banana, orange, rose, jasmine
- All plants produced by vegetative propagation are genetically similar to the parent plant.

(6) Extinction of species can be prevented in sexually reproducting organisms.
Answer:
In sexual reproduction, a zygote is formed s by the union of sexual reproductive cells through fertilisation.
- The male reproductive cell is formed in father’s body and female reproductive cell is formed in mother’s body.
- Thus, offspring gets genetic material (DNA) of two different parents. So, there is variation in offspring.
- This variation helps the individual to get adapted to the changing environment. So, organism can live better.
- Through variation and adaptation, species extinction can be prevented and continuity of life is maintained.
So, extinction of species can be prevented in sexually reproducting organisms.
(7) Contraceptive pills are helpful to prevent pregnancy.
Answer:
Pills used for contraception form contraceptive chemical method.
- The female uses oral contraceptive pills.
- The oral pills contain a combination of hormones (progesterone) which stop the release of eggs and fertilisation cannot occur.
- By using, such pills fertilisation can be prevented.
Hence, contraceptive pills are helpful to prevent pregnancy.
(8) The use of ultrasound technique should be banned for the sex determination.
OR
Prenatal sex determination has been prohibited by law.
Answer:
The ultrasound technique should be used for detection of genetic and other structural abnormalities in embryo.
- Some people use the ultrasound technique (sonography) illegally for sex determination of embryo.
- Due to preference to male child the female embryo is aborted.
- The killing of the unborn girl child is known as female foeticide. This sex-selective abortion is unethical and illegal.
- By female foeticide, female sex ratio is reducing at an alarming rate in India.
Hence, the use of ultrasound technique should be banned for the prenatal sex determination.
(9) Each new generation through sexual mode of reproduction will end up in equal number of chromosomes and the DNA content instead of double to its parents.
Answer:
In sexual mode of reproduction, each new generation is the combination of the DNA copies from two parents. Each new generation gets twice the amount of DNA compared to that with the previous generation.
But reduction division i.e., meiosis occurs during gamete formation. As a result germ cells have half the number of chromosomes and half the amount of DNA set as compared to the non- reproductive body cells.
When haploid germ cells from two parents fuse during sexual reproduction, it results in diploid zygote. Chromosomes and the DNA content in new generation is thus reestablished.
Question 3.
Carefully observe the given diagram and answer the questions related with it:
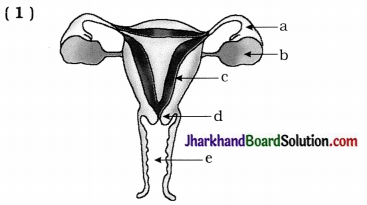
Questions :
(1) Write name of a, b, c, d and e in given diagram.
(2) Where do given events occur?
- Formation of ovum and its release
- Fertilisation
- Implantation of fertilised ovum
(3) The inner wall of uterus….
- Before ovulation and
- What happens if ovum does not get fertilised?
Answer:
(1) a-oviduct, b-ovary, c-uterus, d-cervix, e-vagina
(2)
| Event | Organ |
| (i) Formation of ovum and its release | by ovary |
| (ii) Fertilisation | in oviduct |
| (iii) Implantation of fertilised ovum | in uterus |
(3) (i) Before ovulation, the inner wall of uterus becomes thick, spongy and with full of blood supply.
(ii) If ovum does not get fertilised, then thick and spongy wall of uterus along with blood and dead ovum comes out of the vagina in the form of bleeding, i.e., Menstruation.
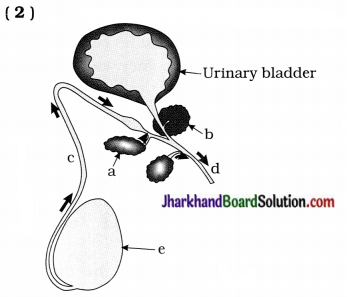
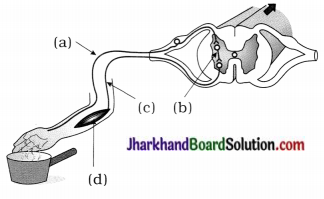
Questions:
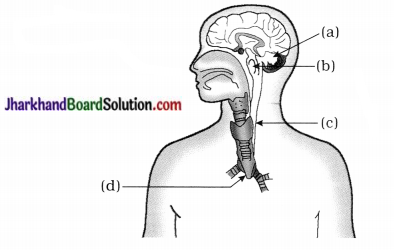
(1) Do labelling of a, b, c, d and e in given diagram.
(2) Where do the given events occur?
- Both sperms and urine pass.
- Sperms delivered through in it.
- Add their fluid secretion with sperms.
(3) ‘d’ part passes through which organ?
What changes are noticed in such organ during adolescence?
(4) State the characteristics of cells produced by e in the given diagram.
Answer:
(1) a-seminal vesicle, b-prostate gland, c – vas deferens, d – urethra, e – testis.
(2)
| Event | Related organ / part |
| (i) Both sperms and urine pass | Urethra |
| (ii) Sperms delivered in it. | Vas deferens |
| (iii) Add their fluid secretion with sperms | Seminal vesicle, Prostate gland |
(3) ‘d’ part is urethra passes through penis. The penis begins to become enlarged and erect. This changes are noticed after puberty.
(4) Sperms are produced by ‘e’ (Testis). The sperms are motile male gametes that consist of mainly genetic material and a long tail.
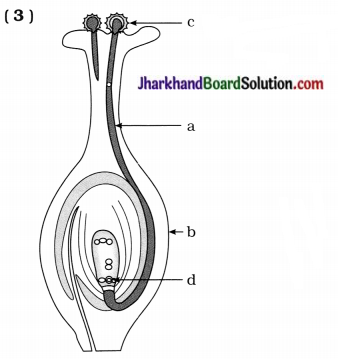
(1) Identify ‘a’ and state what it carries.
(2) Identify ‘b’ and state the changes in its structure after fertilisation.
(3) Identify ‘c’ and mention from where is it released and by which process does it reach here.
(4) Identify ‘d’ and state how seeds are formed?
Answer:
(1) a – Pollen tube, it carries male germ cell.
(2) b – Ovary, it grows rapidly and ripens to form a fruit after fertilisation.
(3) c – Pollen grain, it is released from anther of stamen and by the process of pollination it reaches on the stigma.
(4) d – Female germ cell, male germ cell fuses with it to form zygote. Zygote divides several times to form an embryo within the ovule. The ovule develops a tough coat and it is gradually converted into seed.
Objective Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Answer the following questions in short:
(1) Write down the name of different methods of asexual reproduction.
Answer:
The various methods of asexual reproduction are:
- Fission (Binary fission and multiple fission)
- Fragmentation
- Regeneration
- Spore formation and
- Vegetative propagation.
(2) Name two animals which reproduce asexually through fission.
Answer:
Animals that reproduce asexually through fission : Amoeba. Plasmodium.
(3) Name the asexual method of reproduction in (a) Hydra and (b) Plasmodium.
Answer:
- In hydra methods of asexual reproduction are regeneration and budding.
- In plasmodium method of asexual reproduction is multiple fission.
(4) What is the meaning of regeneration? Name two animals which can regenerate from their body parts.
Answer:
Meaning of regeneration : A small cut part of the body can regenerate to form a complete new organism.
Example: Hydra and Planaria.
(5) What is the meaning of vegetative propagation?
Answer:
Vegetative propagation means production of new plants from the roots, stem or leaves of parental plant without taking help of any reproductive orgAnswer:
(6) How do we know that two different individual organisms belong to the same species?
Answer:
Due to similarities among organisms it is clear that they belong to the same species.
(7) What will lead to change in body designs?
Answer:
The DNA in the cell nucleus is the information source for making proteins. If the information is changed, different proteins are formed leading changes in body designs.
(8) What does most basic level in reproduction involve?
Answer:
The most basic level in reproduction involves making of DNA copies for the blueprints of body design.

(9) When does the newly formed DNA copies separate?
Answer:
Newly formed DNA copies separate when additional cellular apparatus is formed at the time of cell division.
(10) Are the two cells formed by a cell division absolutely identical?
Answer:
No, the process of copying the DNA will have some variations each time. As a result, the DNA copies generated may not be identical to \ the original. So, the two cells are not absolutely identical.
(11) How is reproduction to be achieved from a single type, if the organism itself consists of many cell types?
Answer:
Organism may contain many cells but only specialized cells are able to perform reproduction.
(12) Why regeneration is not the same as reproduction?
Answer:
Reproduction is a complex process using specialised cells or organs but regeneration is basically a repair process in which torn out part can heal.
(13) Which parts of flowers fall off after fertilisation?
Answer:
The petals, sepals, stamens, style and stigma may shrivel and fall off after fertilisation.
(14) What are the functions of petals and sepals?
Answer:
- Function of petals : To attract insects for pollination.
- Function of sepals : To protect petals, stamens and pistils.
(15) Which part of flower persists in the fruit of which plant?
Answer:
Dry sepals persist in some fruits such as brinjals, apple, guava. Some of sepals persist in strawberry.
(16) State any two changes that can be included under the general process of growth in human beings.
Answer:
Increase in height and weight, replacement of milk teeth by permanent teeth, etc.
(17) How are new combinations of variants produced generation after generation?
Answer:
Each new variation is made in a DNA copy that already has variation accumulated from previous generations. During sexual reproduction, variations from two individuals are recombined.
(18) Name the methods in which property of vegetative propagation is used? Give the examples for the same.
Answer:
The property of vegetative propagation is used in layering and grafting methods. Sugarcane, roses, grapes are grown for agricultural purposes by this methods.
(19) By which agents is cross-pollination achieved?
Answer:
Cross-pollination is achieved by agents like wind, water or animals.
(20) State any two common changes that appear in both sexes during the period of adolescence?
Answer:
Thick hair growing in armpits and the genital area, the skin frequently becomes oily and pimples begin to develop.
(21) Secretion of which glands makes transport and nutrition of sperms easier?
Answer:
The fluid secretion of prostate gland and seminal vesicles makes transport and nutrition of sperms easier.
(22) State the difference in meaning between zygote, embryo and foetus.
Answer:
| Zygote | Embryo | Fbetus |
1. The ferti-lised egg is called zygote.
2. It is formed by fusion of sperm and egg cell. | The zygote starts dividing and form a ball of cells called embryo. | The em-bryo is implanted in the lining of the uterus where it continues to grow organs then it is called foetus. |
(23) What is called placenta?
Answer:
A disc-like special tissue embedded in uterine wall through which the embryo gets nutrition from mother’s blood is called placenta.
(24) How is body of mother designed to undertake the development of the child?
Answer:
The uterus in mother prepares itself every month to receive and nurture the growing embryo.
(25) How the transmission of sexually transmitted diseases can be prevented during the sexual act?
Answer:
Using a condom diming sexual act can help to prevent transmission of sexually transmitted diseases.
(26) State the names of STDs caused by bacteria and virus.
Answer:
Bacterial STDs : Gonorrhoea, Syphilis.
Viral STDs: Warts, HIV-AIDS
(27) What is the misuse of prenatal sex determination?
Answer:
Parents terminate the pregnancy after knowing the sex of their unborn child; usually a daughter. This is illegal and unethical to carry out prenatal sex determination for aborting female foetus.
Question 2.
Define : OR Explain the terms :
(1) Reproduction
Answer:
The process producing new organism of its own kind during their maturity stage is known as reproduction.
(2) Variation
Answer:
The difference in the characters of individuals of a same species or its population is known as variation.
(3) Asexual reproduction
Answer:
The mode of reproduction allows new generation to be created from a single individual without the formation and fusion of gametes is known as asexual reproduction.
(4) Sexual reproduction
Answer:
A mode of reproduction that depend on the involvement of two individuals (male and female) to create new generation is known as sexual reproduction.
(5) Multiple fission
Answer:
A mode of asexual reproduction in which the division of parent cell forms small, nearly equal sized daughter offsprings is known as multiple fission.
(6) Fragmentation
Answer:
The breaking up of the body of a multi-cellular organism into two or many pieces and on maturing, each piece grows to form a complete new organism is known as fragmentation.

(7) Bud
Answer:
A bulging structure that develops as an outgrowth due to repeated cell division at one specific site, which develops into tiny individual is called a bud.
(8) Vegetative propagation
Answer:
In certain plants, root, stem and leaves develop into new plants under favourable conditions. This property is called as vegetative c propagation.
(9) Sporangia
Answer:
In fungus e.g., Rhizopus, tiny blob-like structure producing spores for reproduction is called sporangia.
(10) Spore
Answer:
A microscopic reproductive unit produced in sporangia and covered by thick protective wall is called spore.
(11) Meiosis
Answer:
A type of cell division in germ cells in which chromosome number is reduced to half is called meiosis.
(12) Flower
Answer:
A sexual reproductive structure produced in flowering plants, especially in angiosperms is called flower.
(13) Seed germination
Answer:
The development of new plant from the seed upon getting favourable conditions, is known as seed germination.
(14) Pollination
Answer:
A process of transfer of pollen from anther of a stamen to the stigma of a pistil in the same or in different flower is called pollination.
(15) Puberty
Answer:
The age at which reproductive organs become functional and attaining the sexual maturity is known as ‘puberty’.
(16) Female foeticide
Answer:
Illegal sex-selective abortion of female foetuses or killing the female foetus is called female foeticide.
(17) Fertilisation
Answer:
A process of a fusion of male gamete and female gamete to form a zygote is called fertilisation.
(18) Menstruation
Answer:
Menstruation is the periodic event taking place after every 28 days in mature woman. This is a cyclic process, interrupted only by pregnancy. During menstruation there is bleeding through vaginal opening. The cell debris and unfertilised ovum is given out of the body during menstruation.
If the egg is not fertilised, it lives for about one day. Since the ovary releases one egg every month, the uterus also prepares itself every month to receive a fertilised egg. Uterine lining becomes thick, spongy and richly supplied with blood. But if fertilisation does not occur then this lining is not needed any longer. So, the lining slowly breaks and comes out through the vaginal opening as blood and mucous.
This cycle takes place roughly every month and is called menstruation. It usually lasts for about two to eight days.
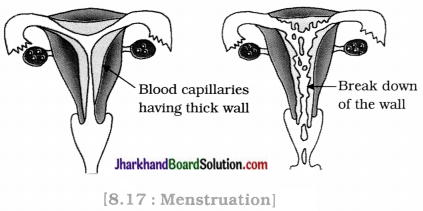
some degree of sexual maturation does not necessarily mean that the body or the mind is ready for sexual acts or for having and bringing up children.
Question 3.
Fill in the blanks :
- ……………….. undergoes continuous cell division to produce multicellular embryo.
- ……………….. is the causative agent responsible for sexual diseases like gonorrhea and syphilis.
- ……………….. type of cell division reduces chromosome number to half in germ cells.
- In plasmodium, asexual reproduction occurs through ………………..
- On the surface of potato tuber, there are many ……………….. present for the asexual reproduction.
- A small cut part of organism’s body can form complete new organism. This process is known as ………………..
- In flowering plant, fertilisation of egg cell occur in ………………..
- In sexual reproduction, creation of diversity in characters are fulfilled by ………………..
- In female, every ……………….. days ovum is released from the ovary.
- To prevent pregnancy, copper-T is placed in ………………..
- The temperature of scrotum remains ……………….. below the body temperature.
- The genetic variation created during reproduction is the basis for ………………..
- In flowering plant, ……………….. is most important part for continuity of life.
- The cells involved in sexual reproduction are known as ………………..
- When sperms reach in urethra from testes, secretions from ……………….. and ……………….. are added with them.
- If fertilisation of ovum does not occur in female, then ……………….. happens.
- The size of ……………….. is determined by the rates of birth and death.
- The uterus opens into the vagina through the ………………..
- A ……………….. is a future shoot and a ……………….. is a future root in the structure of seed.
- The DNA in the cell nucleus is the information source for making ………………..
Answer:
- Zygote
- Bacteria
- Meiosis
- multiple fission
- buds
- regeneration
- ovule
- Genetic variation
- 28
- uterus
- 2-3°C
- evolution
- ovule
- gametes/germ cells
- seminal vesicles, prostate gland
- menstruation
- population
- cervix
- plumule, radicle
- proteins
Question 4.
State whether the following statements are true or false:
- Number of organisms increase rapidly through asexual reproduction under unfavourable condition.
- Fragmentation is the simplest method of reproduction in unicellular animals like amoeba and leishmania.
- The information of protein synthesis is stored in DNA of a cell nucleus.
- Variation is useful for the survival of species.
- Budding is an asexual reproduction method observed only in animals.
- Condom is a mechanical barrier.
- In sexual reproduction, DNA content is doubled in zygote than the DNA content of parents.
- The pollen grains produced in stamen are male reproductive cells.
- Secretion of the sex hormones starts at the puberty stage.
- Fallopian tubes come out from the vas deferens.
- In human, fertilisation occurs in vagina of female and embryo development occurs in uterus.
- The ovaries contain thousands of immature eggs in newborn girl.
- Menstruation usually lasts for about two to eight days.
- Prenatal sex determination is legal in our country.
- The size of population is determined through birthrate and deathrate of organisms.
- Syphilis is a STD.
- Copying of DNA is a part of cellular reproduction.
- Plants such as banana, orange, rose and jasmine that have lost the capacity to produce s seeds can reproduce by vegetative propagation.
- Self-pollination is considered better than cross-pollination as far as variation is concerned.
- Reproduction by production of bud is a common in yeast, hydra and bryophyllum.
Answer:
- False
- False
- True
- True
- False
- True
- False
- False
- True
- False
- False
- True
- True
- False
- True
- True
- True
- True
- False
- True
Question 5.
Match the following :
(1)
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Fragmentation | p. Planar ia |
| 2. Budding | q. Potato |
| 3. Vegetative propagation | r. Spirogyra |
| 4. Regeneration | s. Yeast |
Answer:
(1 – r), (2 – s), (3 – q), (4 – p).
(2)
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Testis | p. Mouth of uterus |
| 2. Ovary | q. Testosterone |
| 3. Prostate gland | r. Fertilisation |
| 4. Cervix | s. Disc-like special tissue develops between embryo and the uterus wall. |
| 5. Oviduct | t. Progesterone |
| 6. Placenta | u. Secretory gland in the passage of sperms |
Answer:
(1 – q), (2 – t), (3 – u), (4 – p), (5 – r), (6 – s).
(3)
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Binary fission | p. Hydra |
| 2. Multiple fission | q. Amoeba |
| 3. Budding | r. Rhizopus |
| 4. Spore formation | s. Plasmodium |
Answer:
(1 – q), (2 – s), (3 – p), (4 – r).
(4)
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Ovary | p. Fertilisation of ovum by a sperm |
| 2. Oviduct | q. Passage of sperms |
| 3. Uterus | r. Secretion of sex hormones |
| 4. Vagina | s. Growth of fertilised ovum and development of embryo |
Answer:
(1 – r), (2 – p), (3 – s), (4 – q).
(5)
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Life of unfertilised egg | p. 2 to 8 days |
| 2. Puberty in girls | q. About 1 day |
| 3. Menstruation in female | r. At least 9 months |
| 4. Development of embryo in uterus of female | s. 10 to 12 years |
Answer:
(1 – q), (2 – s), (3 – p), (4 – r).
(6)
| Column I (Contraceptive methods) | Column II (Uses) |
| 1. Barrier method in male | p. Oral pills |
| 2. Chemical method | q. Condom |
| 3. Surgical method | r. Copper-T |
| 4. Barrier method in female | s. Fallopian tubes blocked |
Answer:
(1 – q), (2 – p), (3 – s), (4 – r).
Question 6.
Diagram based questions:
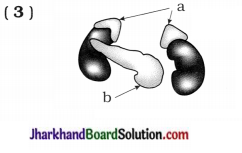
1. Identify organisms in the diagram. Which asexual reproduction method is seen? Write it.
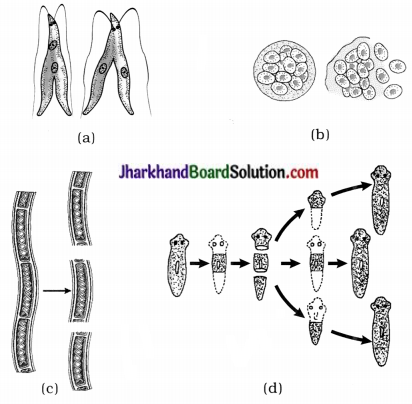
Answer:
- Leishmania – Binary fission
- Plasmodium – Multiple fission
- Spirogyra – Fragmentation
- Planaria – Regeneration
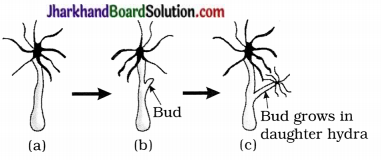
2. Draw labelled diagram of (b) and (c) steps of budding in hydra.
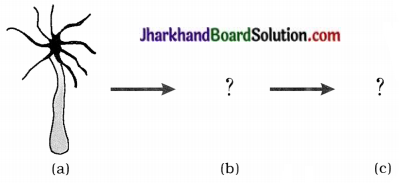
Answer:
3. In amoeba, binary fission’s some diagrams are given. Give its proper sequence.
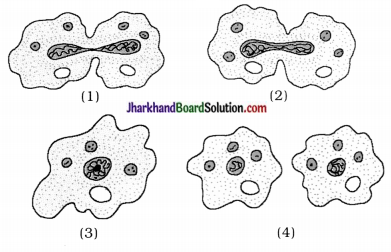
Answer:
(3) → (2) → (1) → (4)
4. Carefully observe the given diagrams and give answer of following questions:

(1) Identify organisms (a), (b), (c), (d) and write their names.
(2) Give names of biological processes seen in all the four diagrams.
(3) How is this biological process useful for organisms?
Answer:
(1)
- Hydra
- Rhizopus
- Bryophyllum
- Planaria
(2) Asexual reproduction
- Budding
- Spore formation
- Vegetative propagation
- Regeneration
(3 ) To maintain continuity of life and to increase their number
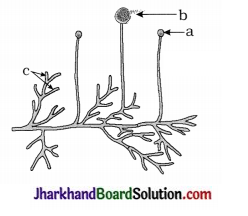
5. Identify the given diagram and label the parts a, b and c.
Answer:
Spore formation in Rhizopus
a-Sporangium, b-Spore and c-Hyphae
6. Observe the diagram and answer the questions :
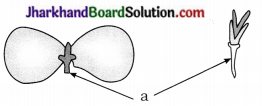
Which part give rise to shoot when seed germinates?
(1) Is the seed dicot or monocot?
(2) Which part give rise to shoot when seed germinates?
(3) Identify ‘a’ in the diagram.
Answer:
(1) Dicot
(2) Plumule
(3) a – Radicle

Question 7.
Select the correct option from those given below each question:
1. A simple multicellular animal having tentacles and lives in fresh water reproduces by the asexual method of ………………………
A. binary fission
B. spore formation
C. budding
D. fragmentation
Answer:
C. budding
2. In which of the following living organism spore formation takes place?
A. Rhizopus
B. Planaria
C. Spirogyra
D. Potato
Answer:
A. Rhizopus
3. Method of asexual reproduction in spirogyra….
A. division of a cell into two cells
B. breaking up of filaments into smaller bits
C. division of a cell into many cells
D. formation of a large number of buds
Answer:
B. breaking up of filaments into smaller bits
4. The filaments of certain algae breaks again and again and each part develops as individual algae. Which type of process is this?
A. Budding
B. Fragmentation
C. Binary fission
D. Multiple fission
Answer:
B. Fragmentation
5. Which kind of reproduction methods are fission, budding, spore formation, etc.?
A. Vegetative propagation
B. Asexual reproduction
C. Sexual reproduction
D. None of these
Answer:
B. Asexual reproduction
6. Which parts of plant produce new plant through vegetative propagation?
A. Root, stem and flower
B. Stem, flower and fruit
C. Stem, leaf and flower
D. Root, stem and leaf
Answer:
D. Root, stem and leaf
7. For how many days does the menstruation period last in woman?
A. 2 to 8
B. 10 to 12
C. 13 to 18
D. 28 to 32
Answer:
A. 2 to 8
8. Which unicellular fungus shows budding?
A. Mucor
B. Yeast
C. Amoeba
D. None of these
Answer:
B. Yeast
9. Which of the following organism shows regeneration?
A. Amoeba
B. Paramoecium
C. Hydra (or Planaria)
D. Rhizopus
Answer:
C. Hydra (or Planaria)
10. Where are testes located in male?
A. In abdominal cavity
B. In vas deferens
C. In scrotum
D. In penis
Answer:
C. In scrotum
11. If the normal temperature of the body is 37 °C, then the ideal temperature of the scrotum is ………………
A. 37 °C
B. 36 °C
C. 39 °C
D. 34 °C
Answer:
D. 34 °C
12. Where does the fertilisation of sperm and ovum occur in human?
A. In uterus
B. In cervix
C. In vagina
D. In oviduct
Answer:
D. In oviduct
13. Where does the implantation and development of the embryo take place?
A. In uterus
B. In vagina
C. In ovary
D. In oviduct
Answer:
A. In uterus
14. Duration from time of fertilisation in human female to the birth of a child :
A. 100 days
B. 180 days
C. 210 days
D. 280 days
Answer:
D. 280 days
15. Which structure develops between uterine wall and foetus to fulfill the need of nutrition?
A. Placenta
B. Umbilical cord
C. Amnion
D. Amniotic fluid
Answer:
A. Placenta
16. In asexual reproduction, offsprings are similar, because…
A. only one parent is involved in reproduction.
B. two parents are involved in reproduction.
C. reproductive cells are involved.
D. reproductive cells are not involved.
Answer:
A. only one parent is involved in reproduction.
17. From the following, which fungus does not undergo asexual reproduction through spore formation?
A. Rhizopus
B. Penicillium
C. Yeast
D. Mucor
Answer:
C. Yeast
18. What is the similarity in reproduction between amoeba and bacteria?
(1) They are multicellular.
(2) They are unicellular.
(3) They only undergo sexual reproduction.
(4) They only undergo asexual reproduction.
(5) They mainly undergo binary fission.
A. (1), (3) and (4)
B. (2) and (3)
C. (2) and (4)
D. (2), (4) and (5)
Answer:
D. (2), (4) and (5)
19. Which is a necessity of cellular reproduction?
A. Changes in niche
B. Continuity of life
C. Copying of DNA
D. Transportation of hereditary characters
Answer:
C. Copying of DNA
20. Which of the following is true for the flower?
(1) Flowers are always bisexual.
(2) They possess sexual reproductive part.
(3) They are produced in all plant groups.
(4) Its ovule after fertilisation is converted into seed.
A. (1) and (3)
B. (2) and (3)
C. (1) and (4)
D. (2) and (4)
Answer:
D. (2) and (4)
21. Variation is observed more in the offsprings produced through sexual reproduction, because…
A. sexual reproduction is a long and complicated process.
B. genetic material of two parents of different species is inherited in offspring.
C. genetic material of two parents of same species is inherited in offspring.
D. genetic material in the offspring is double than that in the parent.
Answer:
C. genetic material of two parents of same species is inherited in offspring.
22. In which part of the flower male reproductive cells and female reproductive cells are produced I respectively?
A. Pollen grain, ovule
B. Anther, Stigma
C. Stigma, style
D. Ovary, ovule
Answer:
A. Pollen grain, ovule
23. What will be produced from the fertilised egg cell In a flower?
A. Embryo
B. Spore
C. Fruit
D. All of given
Answer:
A. Embryo
24. In which type of reproduction there is seed formation?
A. Vegetative propagation
B. Asexual reproduction
C. Sexual reproduction
D. Budding
Answer:
C. Sexual reproduction
25. At the stage of puberty in boy there are secondary sexual changes. Which of the following is these?
A. Increase in height and weight
B. Hair growth in armpits
C. Hair growth in genital area
D. Larger and erect penis
Answer:
D. Larger and erect penis
26. For the formation of sperms in testes, the temperature…
A. must be lower than the body temperature.
B. must be higher than the body temperature.
C. must be same as the body temperature.
D. temperature is not an affecting factor.
Answer:
A. must be lower than the body temperature.
27. Which of the following are not the functions of testes, at puberty?
(1) Formation of reproductive cells
(2) Development of placenta
(3) Secretion of testosterone
(4) Secretion of progesterone
A. (1) and (4)
B. (2) and (4)
C. (3) and (4)
D. (2) and (3)
Answer:
B. (2) and (4)
28. Which of the following group of sexual diseases occur through the bacteria?
A. AIDS-Herpes of reproductive organs
B. Syphilis-Gonorrhea
C. Syphilis-AIDS
D. Gonorrhea-AIDS
Answer:
B. Syphilis-Gonorrhea
29. Offsprings formed by organisms showing asexual reproduction have greater range of similarity because …
(1) only one parent is involved in asexual reproduction.
(2) reproductive cells does not involve in asexual reproduction.
(3) asexual reproduction is faster than sexual reproduction.
(4) more offsprings are produced in asexual reproduction.
A. (1) and (2)
B. (1) and (3)
C. (2) and (4)
D. (3) and (4)
Answer:
B. (1) and (3)
30. Stamen in flower:
A. They produce new seeds.
B. They produce new fruit.
C. They produce pollen grains.
D. They develops fertilised ovum.
Answer:
C. They produce pollen grains.
31. The responsible factors for rapid spread of rhizopus on piece of bread are….
(1) more amount of spores.
(2) getting moist and mineral nutrients from the bread.
(3) presence of branched tubular hyphae.
(4) round spores having sporangium.
A. (1) and (3)
B. (2) and (4)
C. (1) and (2)
D. (3) and (4)
Answer:
C. (1) and (2)
32. What is indicated by the given figure?
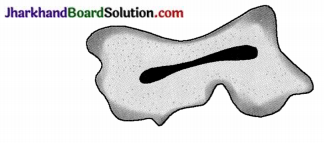
A. Budding in yeast
B. Formation of pseudopodia in amoeba
C. Binary fission in amoeba
D. Cyst-formation in amoeba
Answer:
C. Binary fission in amoeba
33. Which is the sign of initiation of reproductive maturity in girl?
A. When menstruation occurs
B. When embryo is carried
C. When she arrives at menopause stage
D. Before ovulation
Answer:
A. When menstruation occurs
34. Which part of flower becomes mature and modified into fruit?
A. Ovule
B. Carpel
C. Ovary
D. Female gamete
Answer:
C. Ovary
35. When plants lose the capacity of seed formation then how does reproduction occur in them?
A. By spore formation
B. By vegetative propagation
C. By fission
D. By regeneration
Answer:
B. By vegetative propagation
36. In which contraceptive method, condom is used?
A. Surgical method
B. Hormonal method
C. Chemical method
D. Mechanical method
Answer:
D. Mechanical method
37. Statement A: Prenatal sex determination has been prohibited by law.
Reason R : Illegal sex-selective abortion of female foetuses increased.
Which is the correct option for A and R?
A. Both A and R correct, R is correct explanation of A.?
B. Both A and R correct, but R is not explanation of A.?
C. A is correct, R is incorrect.
D. A is incorrect, R is correct.
Answer:
A. Both A and R correct, R is correct explanation of A.
Question 7.
Answer as directed : (Miscellaneous)
(1) Give full form : HIV – AIDS
Answer:
HIV : Human Immunodeficiency Virus
AIDS: Acquired Immuno Deficiency Syndrome
(2) Following events in flowering plants given below:
(a) Pollen tube develops in style
(b) Plumule develops as shoot system
(c) Ovule modified in seed
(d) Anther releases pollen and stigma receives it.
Arrange them in correct sequence.
Answer:
(d) → (a) → (c) → (b)
(3) Identify me : I am a type of cell division, significant during sexual reproduction and helping to maintain constant chromosome number generation after generation in particular species.
Answer:
Meiosis
(4) Stamen : Pollen grains : : Testes : ………………
Answer:
Sperms
(5) Find mismatched pair :
A. Hydra → Budding, Regeneration
B. Binary fission → Amoeba, Leishmania
C. Pistil → Anther, Filament
D. Sperms → Genetic material, Long tail
Answer:
C. Pistil → Anther, Filament
(6) Identify me : I am a disc like specialised tissue developed after implantation of embryo in a uterine wall.
Answer:
Placenta
(7) Arrange following events in correct sequence:
(a) Menstruation lasts for two to eight days.
(b) Ovary releases one egg every month.
(c) Uterus lining becomes thick and spongy.
(d) Egg is not fertilised.
Answer:
(b) → (c) → (d) → (a)
(8) Differentiate the word pair : Uterus and urethra
Answer:
Uterus is an elastic bag like structure in female reproductive system where embryo is implanted and nourished.
Urethra is a common passage for passing sperms and urine in males.
(9) Plasmodium : malaria : ………………….. : :
Leishmania : ………………….. : Binary fission
Answer:
Multiple fission, Kala-azar
(10) Arrange following events in correct sequence :
(a) Division of zygote to form embryo.
(b) Rhythmic contractions of muscles in the uterus.
(c) The lining of uterus thicken and richly supplied with blood.
(d) Embryo develops organs to become foetus.
(e) Embryo gets nutrition with the help of placenta.
Answer:
(c) → (a) → (e) → (d) → (b)
(11) Find mismatched pair :
(I) Viral infection Warts
(II) Bacterial infection – Syphilis
(III) Fungal infection – Kala-azar
(IV) Protozoan infection – Malaria
Answer:
(III) Fungal infection Kala-azar

(12) Identify me : I am an external organ of male reproductive system essential for sexual intercourse, but due to covering on me, unwanted pregnancy and transmission of many infection can be prevented.
Answer:
Penis
Value Based Questions With Answers
Question 1.
In higher level multicellular animals, the capacity of regeneration is seen or not? Justify your answer with an example of human body. Is it a type of reproduction?
Answer:
Yes, in human being hair and nails grow after cutting. At a site of injury, new cells are formed and healing of cut body part takes place. But this is not a type of reproduction.
Question 2.
A woman has undergone surgical contraceptive method. Will she show the menstruation or not? Justify your answer.
Answer:
Yes, she will show menstruation till 45 – 48 years. Because oviducts are surgically s blocked whereas menstruation flow takes place mainly due to breakage of lining of uterine wall. This is under the influence of ovarian hormones.
Question 3.
A man has undergone surgical contraceptive method. Will he be able to participate in sexual act? On which structure/part, surgical process s is done? Will he now be safe against sexually transmitted diseases?
Answer:
Yes, man will be able to participate in sexual act even after he has undergone surgical contraceptive method.
Vas deferens is surgically blocked.
He will not be safe against sexually transmitted diseases unless he uses condom.
Question 4.
Why in sexual reproduction variation is observed even though the DNA and chromosomes do not get doubled?
Answer:
Variation is observed in offsprings produced through sexual reproduction because off-springs receive DNA and chromosomes from two different parents.
New variation is made in DNA copying in parental generation and during gamete formation, meiosis is also responsible for new combinations.
Question 5.
Vegetative propagation is seen in which plants? Flowering or non-flowering plant?
Artificial vegetative propagation is practised in which plants? Seed bearing or seedless plants?
Answer:
Vegetative propagation is seen mainly in flowering plants. But non-flowering plants such as moss, fern also show vegetative propagation.
Artificial vegetative propagation is practised in seed bearing plants such as rose, sugarcane, grapes, jasmine, orange, etc.
Practical Skill Based Questions With Answers
Question 1.
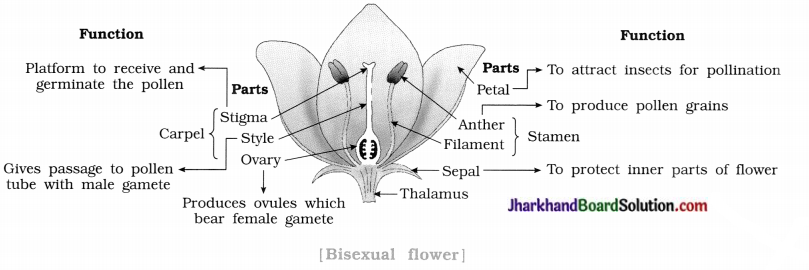
Collect different flowers such as Maize, Sunflower, Papaya, Hibiscus, Datura, Rose, Crinum, etc. Which of them are bisexual? Draw diagram of any one bisexual flower and state function of each parts.
Answer:
Bisexual flowers: Hibiscus, Sunflower, Datura, Rose, Crinum.
Question 2.
You are given following seeds :
Maize, Bean, Wheat, Green gram (Mung), Rice, Groundnut.
Classify them into monocot and dicot seeds. Select any one dicot seed and dip in water for about 4 to 5 hours. Press it and observe the part of embryo.
Questions:
(1) Are the basic structural parts of an embryo equal in all dicot seeds?
(2) What is the function of cotyledons?
(3) Is there any change in size of cotyledon as seed germination progresses?
Answer:
Monocot seeds : Maize, Wheat, Rice
Dicot seeds : Bean, Green gram (Mung). Groundnut

(1) Yes
(2) Cotyledons of dicot seeds are food storing. It provies nutrients to germinating seeds.
(3 ) The size of cotyledons is reduced as the seed germination progresses. The food stored in cotyledons is used for
Question 3.
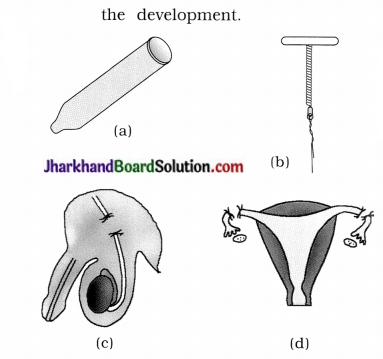
Identify diagram (a), (b), (c) and (d) and give its name.
Out of these, which one is effective for preventing unwanted pregnancy as well as for protection against sexually transmitted diseases ?
Answer:
(a) Condom
(b) Copper-T
(c) Surgical contraceptive for male (vasectomy)
(d) Surgical contraceptive for female (tubectomy).
Only condom is effective for preventing unwanted pregnancy as well as for protection against sexually transmission of diseases.
Memory Map

![]()
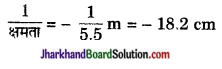
![]()
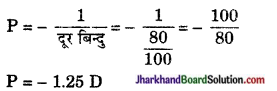
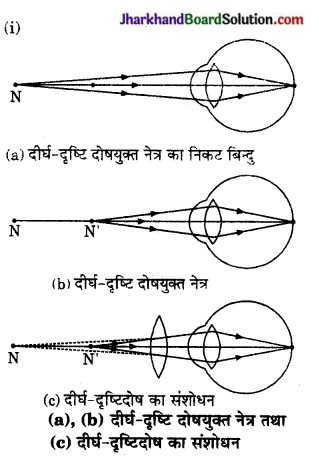
![]()
![]()