Students must go through these JAC Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 6 Life Processes to get a clear insight into all the important concepts.
JAC Board Class 10 Science Notes Chapter 6 Life Processes
→ Indication of life : Showing movements is an indication of life. Movements can be visible or invisible. They can be related to growth or not concerned with growth.
- Viruses are said to be connecting link between living and non-living.
→ Life processes: The main processes, that are carried out by all the living organisms in order to sustain their existence as living beings, are called life processes.
- Common life processes: The common life processes occurring in all the living organisms are nutrition, respiration, excretion or removal of metabolic wastes, growth, transportation, movement, control and coordination, reproduction, etc.
→ Nutrition: A process to transfer a source of energy from outside the body of the organism to the inside is called nutrition.
→ Modes of nutrition: There are mainly two modes of nutrition:
(i) Autotrophic nutrition : The organisms, that possess chlorophyll utilize solar energy, water and carbon dioxide and synthesize their own food as glucose -a simple form of carbohydrate. This process is called photosynthesis.
- The photosynthetic organisms show autotrophic nutrition. Green plants and certain photosynthetic bacteria are autotrophic organisms.
- Equation of photosynthesis:
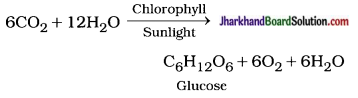
- The carbohydrates, i.e., glucose which are not used immediately are stored in . form of starch, in case of plants.
![]()
(ii) Heterotrophic nutrition : Organisms which consume complex food material prepared by other organisms are called heterotrophic organisms. They lack chlorophyll and thus cannot synthesise their own food. All animals, fungi, cuscuta, etc. are heterotrophic organisms.
→ Digestion : Process of converting complex food components into simple and soluble form with the help of enzymes is called digestion. The resulting nutrients can be easily absorbed after digestion.
- Digestion is essential for nutrition especially. for animals.
- In single celled animals example : (Amoeba, Paramoecium), intracellular digestion takes place and in human beings digestion is extracellular in alimentary canal.
- Human alimentary canal: It extends from mouth to anus consisting of buccal cavity, oesophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine. There are associated glands with alimentary canal which help in digestion.
- Salivary glands, liver and pancreas are accessory glands.
- In human beings five different digestive juices, i.e., saliva, gastric juice, bile juice, pancreatic juice and intestinal juice play significant role in the process of digestion.
- Small intestine is the longest part of the alimentary canal of a human. However the length of the small intestine depends on the food consumed by the animal. Example: Herbivores have a longer small intestine, carnivores have a shorter small intestine.
- Villi: The inner lining of the small intestine has numerous finger like projections called villi which increase the surface area for absorption of simple nutrients formed by digestion.
→ Respiration : A process of breakdown of simple carbohydrates such as glucose to liberate energy is called respiration. As this process occurs inside the living cells, it is also known as cellular respiration. The energy released during respiration is stored in ATP.
- ATP is the energy currency for most of cellular processes.
→ Types of respiration: (1) Aerobic respiration: Respiration in presence of oxygen. (2) Anaerobic respiration : Respiration in absence of oxygen.
The release of energy in the aerobic respiration is greater than in the anaerobic respiration.
- Aerobic organisms need sufficient O2 and they expell CO2 during the process.
- Plants exchange gases through stomata. Stomata are tiny pores present on the lower surface of the leaves.
- Breathing is an important process in animals for aerobic respiration. The rate of breathing in aquatic animals is much faster than that seen in terrestrial animals.
→ Human respiratory system : This system consists nostrils, pharynx, larynx, trachea bronchi and bronchioles and lungs. Each bronchiole ends in alveolus. In lungs, large number of balloon-like structure alveoli are present. The alveoli provide a surface for gaseous exchange. In human beings a respiratory pigment haemoglobin present in red blood corpuscles take up oxygen from the air in the lungs and carry it to tissues.
→ Blood : Blood is a fluid connective tissue that carries out transportation of many substances in human beings. Blood consists of plasma which is fluid in which blood corpuscles i.e., red blood corpuscles, white blood corpuscles and platlets are suspended. Red blood corpuscles carry oxygen. Platelets plug blood leakage by helping to clot the blood at the point of injury.
- Human heart is conical, muscular organ which is four chambered, consisting of two atria (auricles) and two ventricles. There is oxygenated blood in left chambers of the heart whereas there is deoxygenated blood in right chambers.
- Fishes have only two chambered heart. Amphibians and most of the reptiles have three chambered hearts.
- Blood vessels : The blood vessels are arteries, veins and blood capillaries. In the arteries, the blood flows from the heart towards different organs and in the veins, blood flows from different organs towards the heart.
→ Lymph: It is another type of fluid involved in transportation similar to the blood plasma but it is colourless and contains less protein.
![]()
→ Transportation in plants:
- In higher plants, the transportation of water and mineral elements takes place through xylem and that of synthesized organic substances takes place through phloem.
- Conducting components of xylem: Tracheids and tracheae (vessels).
- Conducting components of phloem: Sieve tubes and companion cells.
- In xylem the conduction of materials starts from the root in upward direction, while in phloem the conduction of materials occurs in both the directions viz. downward from above and upward from roots.
- In higher plants, the water in the tracheids and tracheae is pulled upwards due to the suction force created as a result of transpiration.
- The effect of root pressure in transport of water is more important at night.
- Transpiration : The loss of water in form of water vapour from the aerial parts of the plant is called transpiration.
- Translocation of organic food : The transport of soluble products of Photosynthesis through the phloem tissue is called translocation. In this process ATP is used.
→ Excretion : The biological process of removal of harmful nitrogenous metabolic wastes from body is called excretion. Many unicellular organisms remove nitrogenous wastes by simple diffusion from the body surface.
→ Human excretory system : It consists of a pair of kidneys, a pair of ureters, urinary bladder and a urethra.
Each kidney has large number of the basic filtration units called nephrons.
→ Excretion in plants: Plants use completely different strategies for excretion than those of animals.
Waste material may be stored in the cell- vacuoles or as gum and resin, removed in the falling leaves, or excreted into the surrounding soil.