JAC Board Class 10th Social Science Important Questions Geography Chapter 6 Manufacturing Industries
Multiple Choice Questions
Question 1.
How is the industry classified on the basis of their main role?
(a) Agro-based and mineral-based industry
(b) Small-scale and large-scale industry
(c) Heavy and light industry
(d) Basic and consumer industry
Answer:
(d) Basic and consumer industry
Question 2.
Which is an example of agro-based industry?
(a) Cement industry
(b) Iron and steel industry
(c) Jute textile industry
(d) Ele’ctronics industry
Answer:
(c) Jute textile industry
Question 3.
Where was the first textile mill set up in India?
(a)’Mutnbai
(b) Gujarat
(c) Kolkata
(d) Kerala
Answer:
(a)’Mutnbai
![]()
Question 4.
Which is a private sector industry?
(a) BHEL
(b) Coal India
(c) SAIL
(d) TISCO
Answer:
(d) TISCO
Question 5.
Which country is the largest producer of raw jute and jute goods?
(a) Bangladesh
(b) Myanmar
(c) India
(d) Indonesia
Answer:
(c) India
Question 6.
Which industry is seasonal in nature?
(a) Automobile industry
(b) Sugar industry
(c) Chemical industry
(d) Fertiliser industry
Answer:
(b) Sugar industry
Question 7.
Which country is the world’s largest consumer of steel?
(a) India
(b) China
(c) Japan
(d) Germany
Answer:
(b) China
![]()
Question 8.
Which region in India has the largest concentration of iron and steel industries?
(a) South India
(b) Himalayan belt
(c) North-east India
(d) Chhotanagpur Plateau
Answer:
(d) Chhotanagpur Plateau
Question 9.
Which is the second most important metallurgical industry in India?
(a) Aluminium smelting
(b) Chemical industry
(c) Iron and steel industry
(d) Fertiliser industry
Answer:
(a) Aluminium smelting
Question 10.
Which state has emerged as the electronic capital of India?
(a) Mumbai
(b) Noida
(c) Bengaluru
(d) Chennai
Answer:
(c) Bengaluru
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are secondary activities?
Answer:
Secondary activities are those which process
Question 2.
How is the economic strength of a country measured?
Answer:
The economic strength of a country is measured by the development of its manufacturing industries.
Question 3.
What are the factors that influence the location of an industry?
Answer:
The factors that influence the location of an industry are availability of raw material, labour, capital, power, market, etc. The key to decision of the factory location is the least cost. Government policies and specialised labour also influence the location of industry.
Question 4.
What are consumer industries?
Answer:
Consumer industries produce goods for direct use by consumers, such as sugar, toothpaste, paper, sewing machines, fans, etc.
Question 5.
What are joint sector industries?
Answer:
Joint sector industries are run jointly by the state and individuals or a group of individuals. Oil India Ltd. (OIL) is jointly owned by public and private sector.
![]()
Question 6.
Which is the only industry in the country, which is self-reliant?
Answer:
The textile industry is the only industry which is self-reliant and complete in the value chain, i.e., from raw material to the highest value added products.
Question 7.
Why maximum iron and steel industries are concentrated in Chhotanagpur Plateau region?
Answer:
Maximum iron and steel industries are concentrated in Chhotanagpur Plateau region because of the relative advantages in this region for the development of this industry. This includes low cost of iron ore, high grade raw materials in proximity, cheap labour and vast growth potential in the home market.
Question 8.
Though India is an important iron and steel producing country in the world, yet it is not able to perform to its full potential. Why?
Answer:
Though India is an important iron and steel producing country in the world, yet it is not able to perform to its full potential because of
- high costs and limited availability of coking coal,
- lower productivity of labour,
- irregular supply of power, and
- poor infrastructure.
Question 9.
What has been the major impact of information technology and electronics industry? |
Answer:
The major impact of information technology and electronics industry has been on employment generation. Liberalisation resulted in the demand for new and contemporary models in the market.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Agriculture and industry move hand in hand. Discuss.
Answer:
Agriculture and industry are not exclusive of each other. They move hand in hand. For instance, the agro-industries in India have given a major boost to agriculture by raising its productivity. They depend on the latter for raw materials and sell their products, such as irrigation pumps, fertilisers, insecticides, pesticides, plastic and PVC pipes, machines and tools, etc. to the farmers. Thus, development and competitiveness of manufacturing industry has not only assisted agriculturists in increasing their production but also made the production processes very efficient.
Question 2.
Industrialisation and urbanisation go hand in hand. Explain.
Answer:
After an industrial activity starts, urbanisation follows. Sometimes, the industries are located in or near the cities. Thus, industrialisation and urbanisation go hand in hand. Cities provide markets, and services, such as banking, insurance, transport, labour, consultants and financial advice, etc. to the industry. Many industries tend to come together to make use of the advantages offered by the urban centres known as agglomeration economies. Gradually, a large industrial agglomeration takes place.
Question 3.
With the help of a flow chart describe the industry and market linkage.
Answer:
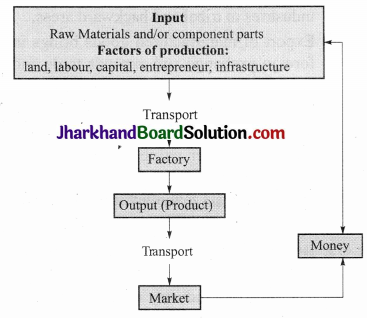
Question 4.
Discuss the classification of industries on the basis of ownership.
Answer:
On the basis of ownership, industries are classified into:
- Public sector:
Owned and operated by government agencies, e.g., BHEL, SAIL, .etc. - Private sector industries:
Owned and operated by individuals or a group of individuals. For example, TISCO, Bajaj Auto Ltd., Dabur Industries, etc. - Joint sector industries:
Jointly run by the state and individuals or a group of individuals, e.g., Oil India Ltd. (OIL). - Cooperative sector industries:
Owned and operated by the producers or suppliers of raw materials, workers or both. They pool in the resources and share the profits or losses proportionately, such as, sugar industry in Maharashtra, coir industry in Kerala, etc.
Question 5.
Explain the close link of cotton textiles with agriculture. How does it support other industries?
Answer:
The cotton textiles industry has close links with agriculture. It provides a living to farmers, cotton boll pluckers and workers engaged in ginning, spinning, weaving, dyeing, designing, packaging, tailoring and sewing. The industry by creating demands supports many other industries, such as chemicals and dyes, mill stores, packaging materials and engineering works.
Question 6.
Give the factors responsible for the location of jute textile industries in the Hugli basin.
Answer:
Factors responsible for the location of jute textile industries in the Hugli basin are proximity of the jute producing areas, inexpensive water transport, support of good network of railways, roadways and waterways to facilitate movement of raw material to the mills, abundant water for processing raw jute, and cheap labour from West Bengal, and adjoining states of Bihar, Odisha and Uttar Pradesh.
![]()
Question 7.
Why, in recent years, there is a tendency for the sugar mills to shift and concentrate in the southern and western states?
Answer:
In recent years there has been a tendency for the sugar mills to shift and concentrate in the southern and western states, especially in Maharashtra because the cane produced here has higher sucrose content and the cooler climate ensures a longer crushing season. The cooperatives are also more successful here.
Question 8.
Give the differences between mini steel plants and an integrated steel plant.
Answer:
Mini steel plants are smaller than the integrated steel plants. They have electric furnaces, use steel scrap and sponge iron. They have re-rollers that use steel ingots as well. They produce mild and alloy steel of given specifications. On the other hand, an integrated steel plant is large. It handles everything in one complex, from putting together raw material to steel making, rolling and shaping.
Question 9.
How is aluminium useful and what it is used to manufacture? Where are aluminium smelting plants located?
Answer:
Aluminium is light, resistant to corrosion, a good conductor of heat, malleable and becomes strong when it is mixed with other metals. It is used to manufacture aircraft, utensils and wires. It has gained popularity as a substitute of steel, copper, zinc and lead in a number of industries. Aluminium smelting plants are located in Odisha, West Bengal, Kerala, Uttar Pradesh, Chhattisgarh, Maharashtra and Tamil Nadu.
Question 10.
Describe the chemical industries of India.
Answer:
The chemical industry in India is fast growing and diversifying. It comprises both large and small scale manufacturing units. Rapid growth has been recorded in both inorganic and organic sectors. The chemical industry is its own largest consumer. Basic chemicals are processed to further produce other chemicals that are used in industrial application, agriculture or directly for consumer markets.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Manufacturing industry is considered the backbone of development in general and economic development in particular. Justify.
Answer:
Manufacturing sector is considered the backbone of development in general and economic development in particular because:
- Manufacturing industries not only help in modernising agriculture, but also help to reduce the heavy dependence of people on agricultural income by providing them jobs in secondary and tertiary sectors.
- Industrial development aims to eradicate unemployment and poverty. Public sector industries and joint sector ventures were started with the philosophy to bring down regional disparities by establishing industries in tribal and backward areas.
- Export of manufactured goods brings in foreign exchange and expands trade and commerce.
- Countries that transform their raw materials into a wide range of furnished goods of higher value are prosperous. India’s prosperity lies in increasing and diversifying its manufacturing industries as quickly as possible.
Question 2.
Briefly describe the fertiliser industry of India.
Answer:
The fertilizer industry is centred around the production of nitrogenous fertilizers (mainly urea), phosphatic fertilizers and ammonium phosphate (DAP) and complex fertilizers which have a combination of nitrogen (N), phosphate (P), and potash (K) Potash is entirely imported as the country does not have any reserves of commercially usable potash or potassium compounds in any form.
After the Green Revolution, the industry has spread to several other parts of the country. Half of the fertiliser production is from the states of Gujarat, Tamil Nadu, Uttar Pradesh, Punjab and Kerala. Other significant producers are Andhra Pradesh, Odisha, Rajasthan, Bihar, Maharashtra, Assam, West Bengal, Goa, Delhi, Madhya Pradesh and Karnataka.
Question 3.
Discuss the effect of industries on air and water.
Answer:
Industries are responsible for four types of pollution: air, water, land and noise. The thermal power plants also cause pollution. Air pollution: It is caused by the presence of high proportion of undesirable gases, such as sulphur dioxide and carbon monoxide. Air-bome particulate materials contain both solid and liquid particles like dust, sprays mist and smoke. Smoke is emitted by chemical and paper factories, brick kilns, refineries and smelting plants and burning of fossil fuels in big and small factories that ignore polluting norms. Toxic gas leaks are hazardous and can have long-term effects.
![]()
Water pollution:
It is caused by organic and inorganic industrial wastes and effluents discharged into rivers. Pollution is caused by paper, chemical, textile and dyeing, petroleum refineries, tanneries and electroplating industries that release dyes, detergents, acids, salts and heavy metals like lead and mercury, pesticides, fertilisers, synthetic chemicals with carbon, etc. into the water bodies. Fly ash, phospogypsum, iron and steel slags are the major solid wastes in India.
Question 4.
Explain the steps taken by NTPC to control and reduce pollution.
Answer:
NTPC, a major power providing corporation in India, has ISO certification for EMS (Environment Management System) 14001. The corporation has a pro-active approach for preserving the natural environment and resources, such as water, oil and gas, fuel in places where it is setting up power plants. They have .’ made If possible through
- Optimum utilisation of equipment adopting latest techniques and upgrading existing equipment.
- Minimising waste generation by maximising ash utilisation.
- Providing green belts for nurturing ecological balance and addressing the question of special purpose vehicles for afforestation.
- Reducing environmental pollution through ash pond management, ash water recycling system and liquid waste management.
- Ecological monitoring, reviews and online database management for all its power stations.
Activity Based Questions
Question 1.
Which industry am I?
1. I am a basic industry as all other industries heavy, medium and light, depend on me for their machinery. I am needed to manufacture a variety of engineering goods, construction material, defence, medical, telephonic, scientific equipment and a variety of consumer goods.
2. My basic ingredient is bauxite. I am a good substitute of steel, copper, zinc and lead in a number of industries.
3. Decontrol of my price and distribution since 1989 and other policy reforms have led to rapid strides in my capacity, process, technology and production. Efforts are being made to generate adequate domestic demand and supply in order to sustain me.
4. After the liberalisation, the coming in of new and contemporary models stimulated the demand for me in the market, which led to the healthy growth of my industry. I am located around Delhi, Gurugram, Mumbai, Pune, Chennai, Kolkata, Lucknow, Indore, Hyderabad, Jamshedpur and Bengaluru.
5. I cover a wide range of products from transistor sets to television, telephones, cellular telecom, telephone exchange, radars, computers and many other types of equipment.
Answer:
- Iron and steel industry
- Aluminium smelting industry
- Cement industry
- Automobile industry
- Information technology and electronics industry
Question 2.
On a political map of India, mark the major cotton textiles industries.
Answer:
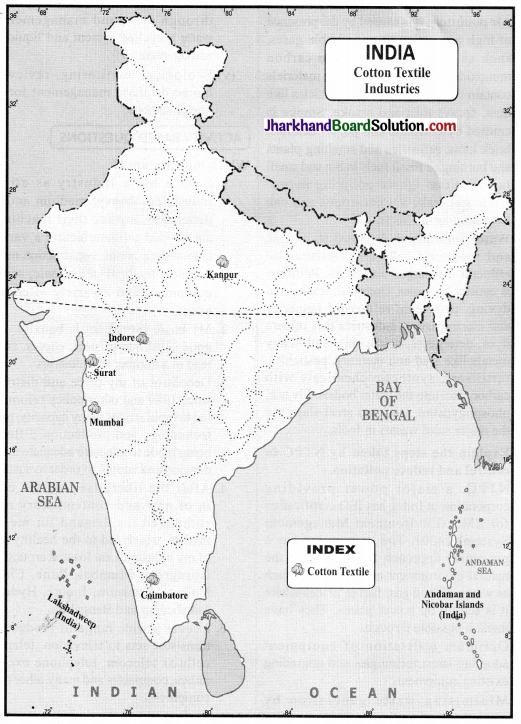
Question 3.
On a political map of India, mark the major Iron and Steel plants of India.
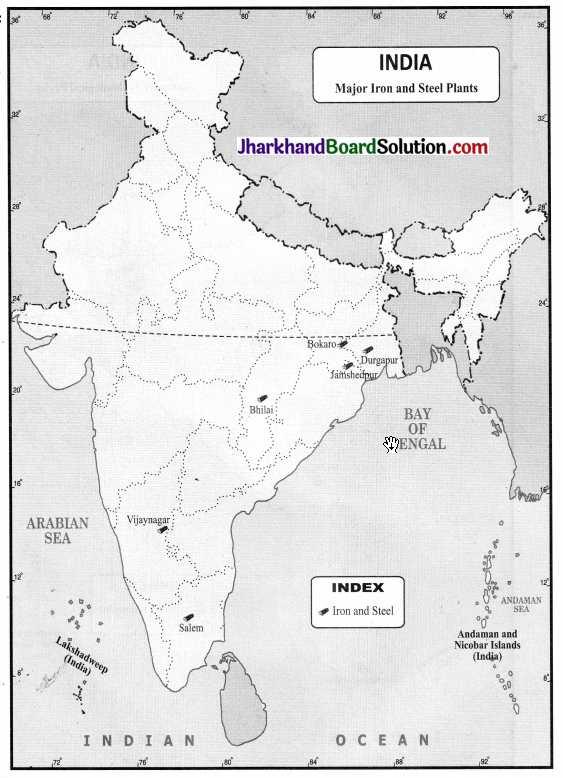
Question 4.
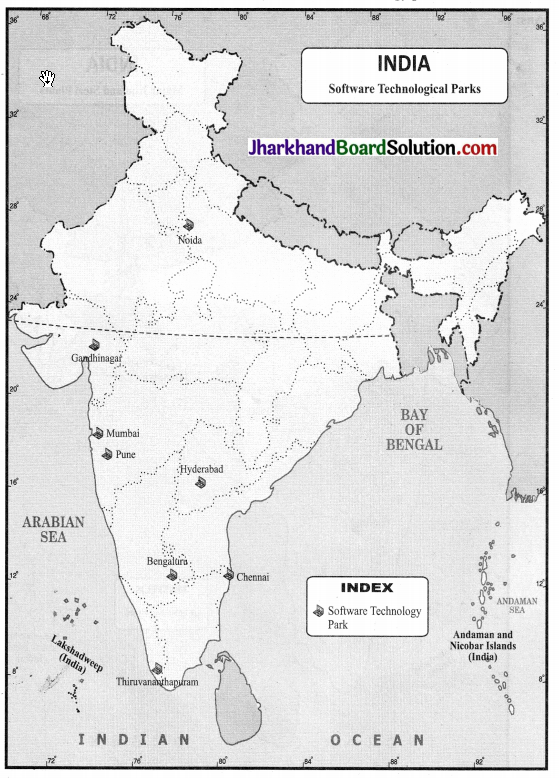
On a political map of India, mark the major software technology parks of India.