JAC Board Class 7th Social Science Solutions Civics Chapter 1 On Equality
JAC Class 7th Civics On Equality InText Questions and Answers
Page 6
Question 1.
Do you think Kanta has enough reason to doubt whether she really is equal? List three reasons from the story above that might make her feel like this.
Answer:
Yes, Kanta has enough reason to doubt whether she really is equal. The three reasons from the story above that might make her feel like this are as follows : Kanta cannot take a leave from work when she needs to as she required money to take her daughter to the doctor. She cannot attend a private hospital but has to attend a government hospital. She needs to stand in a queue and wait for her turn to come to show her daughter to the doctor who was very ill. She lives in a slum area which is never cleaned.
![]()
Page 7
Question 2.
Circle the reference to caste in the matrimonial advertisements given below.

Answer:
The references are Caste no bar. SC/ST excuse Gupta boy Tamil Brahmin
Page 8
Question 3.
Why do you think Omprakash Valmiki was being treated unequally by his teacher and his classmates? Imagine yourself as Omprakash Valmiki and write four lines about how you would feel if you were in the same situation as him.
Answer:
Omprakash Valmiki was being treated unequally by his teacher and his classmates because he was from lower caste or we can say a dalit boy.If I were in the same situation as him, I would have : Felt very humiliated and sad. As every human beings have the right to live a life with dignity, there my dignity would have been violated. Felt very disappointed and questioned my identity. Since we are dalits, they made us feel that we have no access to education.
Question 4.
Why do you think the Ansaris were being treated unequally? What would you do if you were in the Ansaris’ position and could not find a place to live because some people did not want to live next to you because of the religion you practice?
Answer:
The Ansaris were being treated unequally because they were of different religion. If I were in the Ansari’s position then I would have stood for my religion and make them understand the ethics and values. Would have made them understand that all religions lead to one God only.
Page 9
Question 5.
If you were one of the Ansaris how would you have responded to the suggestion that you change your name?
Answer:
If I were one of the Ansaris then I would have decided not to change the name. The decision to change the name would hurt my self respect and its very insulting as well.
![]()
Question 6.
Can you think of an incident in your life in which your dignity was violated? How did this make you feel?
Answer:
Students need to answer on their own.
Page 11
Question 7.
What is the midday meal programme? Can you list three benefits of the programme? How do you think this programme might help promote greater equality?
Answer:
The midday meal programme is a scheme made by the government and launched on 15th August, 1995. This programme has been introduced in all government elementary schools to provide children with cooked lunch. Three benefits of the programme :
- The scheme helped to improve the attendance of children. Their mothers who earlier had to come back to home from their work to feed their children now no longer need to do so.
- More underprivileged children have begun to enrolling and regularly attending school.
- This scheme has also helped reduce caste prejudices because both lower and upper caste children in the school eat this midday meal together.
- I don’t think that this programme would be more effective. Huge differences can be seen between schools that the rich attend and those that the poor attends. Inequalities still exist. But then also, this programme proved to be a one step ahead in the direction of establishing equality in the country.
Question 8.
Find out about one government scheme in your area. What does this scheme do? Whom is this scheme set up to benefit?
Answer:
Students need to do it on their own
JAC Class 7th Civics On Equality Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
In a democracy why is universal adult franchise important?
Answer:
In a democracy, Universal Adult Franchise is important because every citizen of a country is equal in democracy and Universal Adult Franchise is based on equality. Under Universal Adult Franchise every adult person is allowed to vote irrespective of caste, creed, religion, sex, etc.
Question 2.
Re-read the box on Article 15 and state two ways in which this Article addresses inequality.
Answer:
F.xcerpt from Article 15 of the N Indian Constitution Prohibition of discrimination on grounds of religion, race, caste, sex or place of birth.
(1) The State shall not discriminate against any citizen on grounds only of religion, race, caste, sex, place of birth or any of them.
(2) No citizen shall, on grounds only of religion, race, caste, sex, place of birth or any of them, be subject to any disability, liability, restriction or condition with regard to
(a) access to shops, public restaurants, hotels and places of public entertainment;
or
(b) the use of wells, tanks, bathing ghats, roads and places of public resort maintained wholly or partly out of State funds or dedicated to the use of the general public. This article addresses inequality in terms of
- Access to shops, public restaurants, hotels and place of public entertainment.
- the use of wells, tanks, bathing ghats, roads and places of public resort maintained wholly or partly out of State funds or dedicated to the use of the general public.
Question 3.
In what ways was Omprakash Valmiki’s experience similar to that of the Ansaris?
Answer:
Omprakash Valmiki’s experience is similar to that of the Ansaris as both of them were discriminated and humiliated. Both of them faced violation of dignity. While Omprakash Valmiki has to clean and sweep the school since he was a dalit boy, Ansaris were denied the apartments on rent due to their religion.
![]()
Question 4.
What do you understand by the term “all persons are equal before the law”? Why do you think it is important in a democracy?
Answer:
The term “all persons are equal before the law” means that all person should be treated equally. Every person from President of the -country to a domestic servant has to obey the same law. No one can be discriminated or feel biased against on the basis of their caste, creed, sex, religion, etc. Every person has the access to all public places such as playgrounds, hotels, markets and shops.
Apart from these, every person can use publicly available roads, wells, bathing ghats, etc.In democracy, equality is the main ingredient. Democracy is a form of government which gives equal rights, importance and recognition to all. Democracy would never happen and flourish if inequalities continues to exist. It will perish soon.
Question 5.
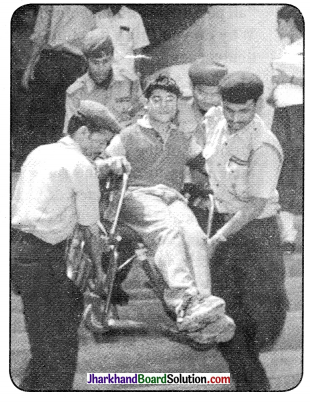
According to the Rights of Person with Disabilities Act, 2016, persons with disabilities have equal rights, and that the government should make possible their full participation in society, The government has to provide free education and integrate children with disabilities into mainstream schools. This law also states that all public places including buildings, schools, etc., should be accessible and provided with ramps.
Look at the photograph and think about the boy who is being carried down the stairs. Do you think the above law is being implemented in his case? What needs to be done to make the building more accessible for him? How7 would his being carried down the stairs affect his dignity as well as his safety?
Answer:
We can see that the boy in the above photograph is disabled. The Disabilities Act in 1955 is not fully implemented. Apart from stairs, there should be ramp as well. He is being carried down by security people through stairs which is dangerous and risky7. The boy’s dignity is hurt and will feel inferior as well. He is recognized as unequal in front of others.
JAC Class 7thCivics On Equality Important Questions and Answers
Multipie Choice Questions
Question 1.
Omprakash Valmiki wrote
(a) Godan
(b) Joothan
(c) Geetanjali
(d) Gaban
Answer:
(b) Joothan
Question 2.
The first state to introduce the Midday Meal Scheme was
(a) Tamil Nadu
(b) Manipur
(c) Karnataka
(d) Maharashtra
Answer:
(a) Tamil Nadu
![]()
Question 3.
The Civil Rights Act w as passed in
(a) 1955
(b) 1962
(c) 1964
(d) 1978
Answer:
(c) 1964
Question 4.
The right to vote in India is called as
(a) Universal Adult Franchise
(b) One vote-one value
(c) Right to vote
(d) None of these
Answer:
(a) Universal Adult Franchise
Question 5.
We should not discriminate for the colour of the skin say, w hites or blacks on the basis of
(a) Gender
(b) Race
(c) Caste
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Answer:
(d) Both (b) and (c)
Question 6.
The midday meal scheme was first started in the year
(a) 1995
(b) 2001
(c) 2005
(d) 2009
Answer:
(a) 1995
Question 7.
The main feature of democracy influences all areas of the government’s work is
(a) Liberty7
(b) Equality7
(c) Discrimination
(d) none of these
Answer:
(b) Equality7
Question 8.
Based on the idea of Universal Adult Franchise, the number of time/s a person can vote in a general election is/ are
(a) 4
(b) 3
(c) 1
(d) as many times according to his wish
Answer:
(c) 1
Question 9.
The most common forms of inequality in most of the cities and villages are
(a) cultural discrimination
(b) food habits
(c) biased in the use of public places
(d) the caste system
Answer:
(d) the caste system
![]()
Question 10.
…… has been traditionally considered a lower or inferior caste by many in India.
(a) Dalits
(b) Rajputs
(c) Kshatriyas
(d) Vaishyas
Answer:
(a) Dalits
Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Which type of government does India have?
Answer:
India has a democratic type of government.
Question 2.
In which year the Supreme Court asked all the states to start the midday meal scheme in India?
Answer:
In 2001, the Supreme Court asked all the states to start the midday meal scheme in India.
Question 3.
Which people have been employed to cook the meal under the midday meal scheme?
Answer:
Dalit women have been employed to cook the meal under the midday meal scheme.
Question 4.
Name the African American w oman who has an important role in starting the Civil Rights Movement.
Answer:
Rosa Parks was the African American woman who has an important role in starting the Civil Rights Movement.
Question 5.
What is the minimum age to cast a vote in an election?
Answer:
The minimum age to cast a vote in an election is 18 years and above means they are considered as adult.
Question 6.
Whose autobiography is ‘Joothanf?
Answer:
Omprakash Valmiki’s autobiography is ‘joothan
Question 7.
What are the common form of inequalities that exist in India?
Answer:
The caste system and religion are the common forms of inequalities that exist in India.
Question 8.
What do you mean by Constitution?
Answer:
Constitution is a document that lays down the basic and important rules and regulations -for people and the government in the country to follow and abide by it.
![]()
Question 9.
Why Omprakash Valmiki was being treated unequally by his teacher and his classmates?
Answer:
Omprakash Valmiki is being treated unequally on the basis of differences of caste as he was from lower caste.
Question 10.
What is Civil Rights Movement?
Answer:
In the late 50s, a movement took place in the USA for equal rights for the Afro- American people. This movement later came to be known as the Civil Rights Movement.
Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Dalit people are not considered as equal even though the law says it. Why?
Answer:
Dalit people are not considered as equal even though the law says it because of attitudes change very slowly. It will happen only when people begin to believe that no one is inferior, lower and that every person deserves to be treated with dignity.
Question 2.
In which way does the government assures equality?
Answer:
Equality is assured through:
- Government schemes and programmes for the disadvantaged communities or groups.
- Laws specified in the Constitution.
Question 3.
What are the reasons for unequal treatment?
Answer:
The reasons for unequal treatment are:
- Gender of a person (male or female)
- The caste we have
- The religion we practice and follow
- The background of our class from where we come
Question 4.
What was the effect and outcome of Civil Rights Movement?
Answer:
The effect and outcome of Civil Rights Movement was:
- It forbids andprohibits discrimination on the basis of religion, race and national origin.
- It also stated that the schools would be open to the Afro-American children and that they would no longer have to attend the separate schools specially opened for them.
Question 5.
Briefly describe equality in Indian democracy.
Answer:
The Indian Constitution considers and recognises every person as equal. This means that every individual in the country including male and female persons irrespective of their castes, religions, tribes, educational and economic backgrounds are recognised as equal. Though inequality still exists in our society yet the principle of equality of all person is recognised. Earlier, law was not there to protect people from discrimination and bad behaviour but now a days there are many that actually work to see that people are treated with dignity.
![]()
Question 6.
What do you understand by the Disability7 Act which was passed in 1995?
Answer:
The Government of India passed the Disabilities Act in 1995. This law states that persons with disabilities have equal rights and that the government should make possible of their full participation in society7. The government has to provide free education and integrate children with disabilities into mainstream schools. This law also states that all public places including buildings, schools, etc., should be accessible and provided with ramps so that they can move around easily.
Question 7.
Explain the Civil Rights Movement.
Answer:
On 1st December 1955, an African American woman named Rosa Parks who was tired from a long day at work and refused to give up her seat on a bus to a white man. Her refusal that day started a huge agitation against the unequal ways in which African-Americans were treated and which came to be known as the Civil Rights Movement.
Question 8.
Which formal documents recognises every person’s democratic right to equality in India? What is the place called where the elected leaders meet to discuss the problems and matters of national importance?
Answer:
The formal documents recognises eveiy person’s democratic right to equality in India in the Constitution. The place is called the Parliament where the elected leaders meet to discuss the problems and matters of national importance.
Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Describe in brief the provisions made in the Constitution for the recognition of equality.
Answer:
Provisions made in the Constitution for the recognition of equality are:
- Every person from the President of the country to a domestic worker has to obey and abide by the same laws.
- No person can be discriminated against on the basis of their religion, race, caste, place of birth or whether they are female or male.
- Every person has access to all public places which consists of playgrounds, hotels, shops and markets. All persons can use publicly available wells, roads and bathing ghats.
- Untouchability has been abolished.
Question 2.
What are the benefits of the midday meal programme?
Answer:
Benefits of the midday meal programme are:
- More poor children have begun enrolling in the school and regularly attending school.
- It has also helped to reduce caste prejudices because both lower and upper caste children in the school eat this meal together.
- In few places, Dalit women have been employed to cook the meal.
- The midday meal programme also helps reduce the hunger of poor students who often come to school and cannot concentrate because they are hungry as their stomachs are empty.