Jharkhand Board JAC Class 10 Science Important Questions Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds Important Questions and Answers.
JAC Board Class 10 Science Important Questions Chapter 4 Carbon and Its Compounds
Additional Questions and Answers
Question 1.
(1) Write the IUPAC names of the following compounds using their structural formulae:
1. CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – Cl
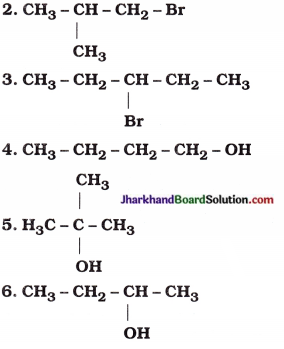
7. CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CHO
8. CH3 – CHO
9. CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – CHO
10. CH3 – CO – CH3
11. CH3 – CH2 – CO – CH3
12. CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CO – CH3
13. CH3 – CH2 – COOH
14. CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – COOH
15. CH3 – COOH
16. CH3 – CH = CH2
17. CH3 – CH2 – CH = CH2
18. CH3 – C ≡ CH
19. CH3 – CH2 – C ≡ CH
20. CH ≡ CH
Answer:
| Structural formula | IUPAC name |
| 1. CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – Cl | 1-Chloropropane |
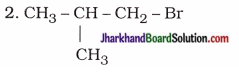 |
1-Bromo-2-methylpropane |
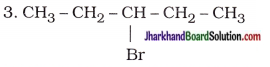 |
3-Bromopentane |
| 4. CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – OH | Butan-l-ol(Butanol) |
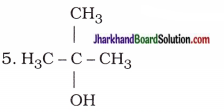 |
2-Methylpropan-2-ol |
 |
Butan-2-ol |
| 7. CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CHO | Butanal |
| 8. CH3 – CHO | Ethanal |
| 9. CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – CHO | Pentanal |
| 10. CH3 -CO-CH3 | Propanone |
| 11. CH3 – CH2 – CO – CH3 | Butanone |
| 12. CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CO – CH3 | 2-Pentanone |
| 13. CH3 – CH2 – COOH | Propanoic acid |
| 14. CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – COOH | Butanoic acid |
| 15. CH3 – COOH | Ethanoic acid |
| 16. CH3 – CH = CH2 | Propene |
| 17. CH3 – CH2 – CH = CH2 | 1-Butene (or But-l-ene) |
| 18. CH3 – C = CH | 1-Propyne |
| 19. CH3 – CH2 – C = CH | 1-Butyne (or But-l-yne) |
| 20. CH = CH | Ethyne |
(2) Give structural formulae of the following compounds using their IUPAC names:
1. 2-Chloropropane
2. 1-Bromopentane
3. 2-Bromo-2-methylpropane
4. 1-Pentanol
5. Ethanol
6. Methanol
7. Methanal
8. Ethanal
9. 3-Pentanone
10. Propanone
11. Methanoic acid
12. Pentanoic acid
13. Ethene
14. 2-Butene
15. 1-Pentyne
Answer:
| IUPAC name | Structural formula |
| 1. 2-Chloro-propane |  |
| 2. 1-Bromo-pentane | CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – Br |
| 3. 2-Bromo-2-methyl-propane | 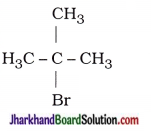 |
| 4. 1-Pentanol | CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – OH |
| 5. Ethanol | CH3 – CH2 – OH |
| 6. Methanol | CH3 – OH |
| 7. Methanal | H – CHO |
| 8. Ethanal | CH3 – CHO |
| 9. 3-Pentanone | CH3 – CH2 – CO – CH2 – CH3 |
| 10. Propanone | CH3 – CO – CH3 |
| 11. Methanoic acid | HCOOH |
| 12. Pentanoic acid | CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – CH2 – COOH |
| 13. Ethene | CH2 = CH2 |
| 14. 2-Butene | CH3 – CH = CH – CH3 |
| 15. 1-Pentyne | CH3 – CH2 – CH2 – C ≡ CH |
Question 2.
Distinguish between:
(1) Ionic compounds and Covalent compounds
Answer:
| Ionic compounds | Covalent compounds |
| 1. The compounds formed by transfer of electrons between two atoms are known as ionic compounds. | 1. The compounds formed by sharing of electrons between two atoms are known as covalent compounds. |
| 2. They are mostly solids. | 2. They may be solid, liquid or gases. |
| 3. They have comparatively high melting point and boiling point. | 3. They have comparatively low melting point and boiling point. |
| 4. They conduct electricity through a solution or in molten state. | 4. They are generally non-conductors of electricity. |
(2) Diamond and Graphite
Answer:
| Diamond | Graphite |
| 1. In diamond, each carbon atom is covalently bonded to four other carbon atoms forming a hard and three-dimensional tetrahedral structure. | 1. In graphite, each carbon atom is covalently bonded to three other carbon atoms forming two-dimensional hexagonal structure. |
| 2. It is the hardest natural substance known. | 2. It is soft and greasy. |
| 3. It is non-conductor of electricity. | 3. It is good conductor of electricity. |
| 4. Chemically, diamond is unreactive. | 4. Chemically, graphite is reactive. |
(3) Saturated carbon compounds and Unsaturated carbon compounds
Answer:
| Saturated carbon compounds | Unsaturated carbon compounds |
| 1. Compounds of carbon which have only single covalent bonds between carbon atoms are called saturated carbon compounds. | 1. Compounds of carbon which have double or triple bonds between carbon atoms are called unsaturated carbon compounds. |
| 2. They are less reactive. | 2. They are more reactive. |
| 3. For example, compounds of alkanes. | 3. For example, compounds of alkenes and alkynes. |
| 4. They burn with blue flame. | 4. They burns with yellow sooty flame and produce black smoke. |
Question 3.
Give scientific reasons for the following statements:
(1) Candle burns with a yellow flame.
Answer:
Candle is made-up of wax, which consists of saturated hydrocarbons containing 18 to 20 carbon atoms.
- When a candle is lighted (ignited), the wax melts s which rises up the wick and gets covered by vapour. As a result, there is no proper mixing of O2 of air and wax vapours.
- Therefore, here incomplete combustion of wax takes place, and complete combustion of wax does not take place.
- Furthermore, incomplete combustion of wax s produces unburnt carbon particles, which rise up in the flame, get heated and imparts yellow colour to the flame.
![]()
(2) Burning substances (fuels) burn with or without a flame.
Answer:
When the gaseous substances are heated, a luminous flame is seen and they start to glow.
- Some liquid and solid fuels burn with a flame because on heating, their atoms easily get converted into vapours; and burn with a luminous flame starting with glow.
- When volatile substances present in this type of fuel vapourises, then the fuel just glows red and gives out heat without flame.
(3) Diamond has high melting point, in spite of having covalent bonds.
Answer:
In diamond, each carbon atom is attached to four other carbon atoms by strong covalent bonds and forms three-dimensional tetrahedral structure.
- A large amount of energy is needed to break the network of large number of covalent bonds.
- Hence, diamond has high melting point.
Objective Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Answer the following questions in one word or in one sentence:
- State the proportion of carbon in the earth’s crust in the form of minerals.
- Mention the percentage proportion of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere.
- Write the number of electrons in shell of carbon, oxygen and nitrogen respectively.
- Mention the major component of biogas and CNG.
- Are the boiling points and melting points of covalent compounds high or low in comparison to ionic compounds?
- Write the property of electrical conductivity of carbon compounds.
- Which allotrope of carbon is very hard?
- Name the element which is next to carbon according to catenation property.
- What is the number of carbon compounds estimated approximately?
- State the general formula of saturated alkane compounds.
- State the general formula of unsaturated alkene compounds.
- Mention the general formula of unsaturated alkync compounds.
- Compare the chemical reactivity of saturated and unsaturated compounds.
- State the minimum number of carbon atoms required to form the ring structure.
- How many isomers are possible for hexane?
- Write the structural formula of functional groups (i) aldehyde, (ii) ketone and (iii) carboxylic acid respectively.
- What is the difference of molecular masses between two successive compounds of homologous series?
- State the elements used as catalyst in hydrogenation reaction.
- Which ions are present in hard water?
- Identify the functional groups in butanone and butanal respectively.
Answer:
- 0.02 %
- 0.03 %
- 4, 6 and 5
- Methane
- Melting points and boiling points of covalent compounds are comparatively lower than the melting points and boiling points of ionic compounds.
- Carbon compounds are non-conductor of electricity.
- Diamond
- Sulphur
- Three million
- CnH2n+2
- CnH2n
- CnH2n-2
- Unsaturated compounds are more reactive chemically than the saturated compounds.
- Three
- Five
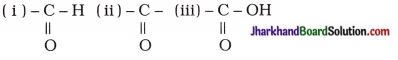
- 14u
- Nickel, palladium
- Calcium (Ca2+), magnesium (Mg2+)
- Ketone, aldehyde
Question 2.
Define:
(1) Covalent bond
Answer:
A chemical bond formed between two or more atoms by mutual sharing of valence electrons is known as a covalent bond.
(2) Catenation
Answer:
Carbon has the unique ability to form bonds with other atoms of carbon, giving rise to a large number of molecules. This property of carbon is called catenation.
(3) Saturated carbon compounds
Answer:
Compounds of carbon which are linked by only single covalent bonds between carbon atoms are called saturated carbon compounds.
(4) Unsaturated carbon compounds
Answer:
Compounds of carbon which have double or triple bonds between carbon atoms are called unsaturated carbon compounds.
(5) Hydrocarbons
Answer:
The compounds containing carbon and hydrogen only are called hydrocarbons.
(6) Functional group
Answer:
An atom or a group of atoms which imparts specific properties to the compound is called a functional group.
(7) Homologous series
Answer:
A series of organic compounds in succession which differ by a definite group (like – CH2 -) is called homologous series.
(8) Combustion reaction
Answer:
Carbon (or most of the organic compounds), in all its allotropic forms, burns in air to give carbon dioxide along with the release of heat and light. This is called combustion reaction.
(9) Oxidising agent
Answer:
Some substances are capable of adding oxygen to other substances. These substances are known as oxidising agents.
(10) Addition reaction
Answer:
The reaction in which unsaturated hydrocarbons add hydrogen in the presence of catalysts such as palladium or nickel to form saturated hydrocarbons is called an addition reaction.
(11) Substitution reaction
Answer:
The reaction in which H-atoms of saturated hydrocarbons are displaced by another atom or functional group is called a substitution reaction.
(12) Esterification reaction
Answer:
A reaction in which a carboxylic acid and an alcohol react in the presence of acid catalyst forming esters and water is known as an esterification reaction.
(13) Saponification reaction
Answer:
The reaction of forming alcohol and sodium salt of carboxylic acid from ester is known as saponification.
Question 3.
Fill in the blanks :
- All living structures are based on …………………
- The earth’s crust has ………………… carbon in the form of minerals.
- Carbon possesses ………………… electrons in its outermost shell.
- The atomic number of chlorine is
- The molecular formula of ammonia is …………………
- ………………… is a major component of biogas and CNG.
- Carbon atoms are linked together with a ………………… in saturated carbon compounds.
- Fuels such as coal and petroleum contain some amount of ………………… and ………………… in them.
- The molecular formula of propane is …………………
- The general formula of alkene is …………………
- Most of the carbon compounds release a large amount of ………………… and ………………… on burning.
- Unsaturated hydrocarbons gives a ………………… flame with lots of ………………… smoke.
- Alcohols are oxidised to …………………
- ………………… are substances that cause a reaction to proceed at a higher rate without the reaction itself being affected.
- ………………… catalyst is used in hydrogenation of vegetable oils.
- Animals fats contain esters of …………………
- Substitution of hydrogen of methane by chlorine in the presence of sunlight forms …………………
- ………………… is used in the preparation of tincture iodine.
- Reaction of alcohol with sodium forms …………………
- Concentrated H2SO4 is a …………………
- Reaction of ethanoic acid with ethanol in presence of acid catalyst forms …………………
- The molecules of soap are ………………… salts of long chain carboxylic acids.
- Micelles forms an ………………… in water.
- Unsaturated hydrocarbons add hydrogen in the presence of catalyst such as ………………… to give saturated hydrocarbons.
- Compound made-up of only carbon and hydrogen is called …………………
Answer:
- carbon
- 0.02 %
- four
- 17
- NH3
- Methane
- single bond
- nitrogen, sulphur
- C3H8
- CnH2n
- heat, light
- yellow, black
- carboxylic acids
- Catalysts
- Nickel (Ni)
- saturated fatty acids
- CH3Cl
- Ethanol
- hydrogen gas (H2)
- dehydrating agent
- ester (ethyl acetate) and water
- sodium/ potassium
- emulsion
- palladium, nickel (Pd/Ni)
- hydrocarbon
Question 4.
State whether the following statements are true or false:
- Propene is a saturated hydrocarbon.
- Alkenes or alkynes are more reactive than their corresponding alkane.
- The difference in number of atoms or molecular formula between two successive members in homologous series is – CH2.
- The solution of ethanol containing 5 % water is called as an absolute alcohol.
- The molecular formula of formaldehyde is HCHO.
- IUPAC name of CH3CH2COOH is butanoic acid.
- Detergents are used to prepare shampoos and products for cleaning clothes.
- Non-polar end of soap is hydrophilic while the polar end (head) is hydrophobic.
- Soap solution appears cloudy because micelles scatter the light.
- Reaction of carboxylic acid with sodium carbonate produces carbon dioxide.
- Dyes are added to colour the alcohol blue. This is called denatured alcohol.
- Dehydration of ethanol gives propene.
- Coal and petroleum have some amount of nitrogen and sulphur in them, hence, their combustion causes pollution in environment.
Answer:
- False
- True
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
- False
- True
- True
- True
- False
- True
Question 5.
Match the following:
(1)
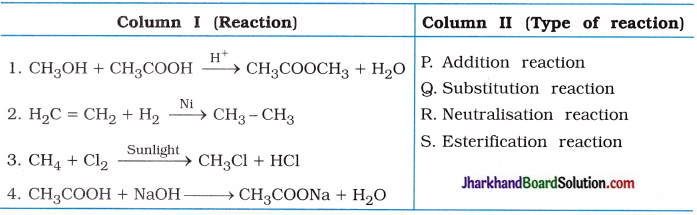
Answer:
(1 → S), (2 → P), (3 → Q), (4 → R).
(2)
| Column I (Molecule) | Column II (Number of bonds) |
| 1. Molecule of hydrogen | P. Double bond and single bond |
| 2. Molecule of nitrogen | Q. Only single bond |
| 3. Molecule of oxygen | R. Triple bond |
| 4. Benzene | S. Only double bond |
Answer:
(1 → Q), (2 → R), (3 → S), (4 → P).
(3)
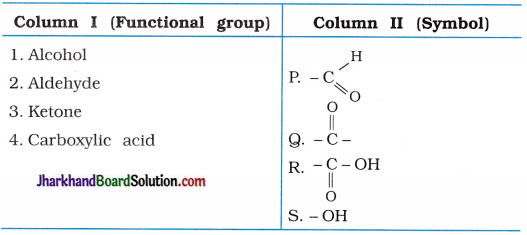
Answer:
(1 → S), (2 → P), (3 → Q), (4 → R).
Question 6.
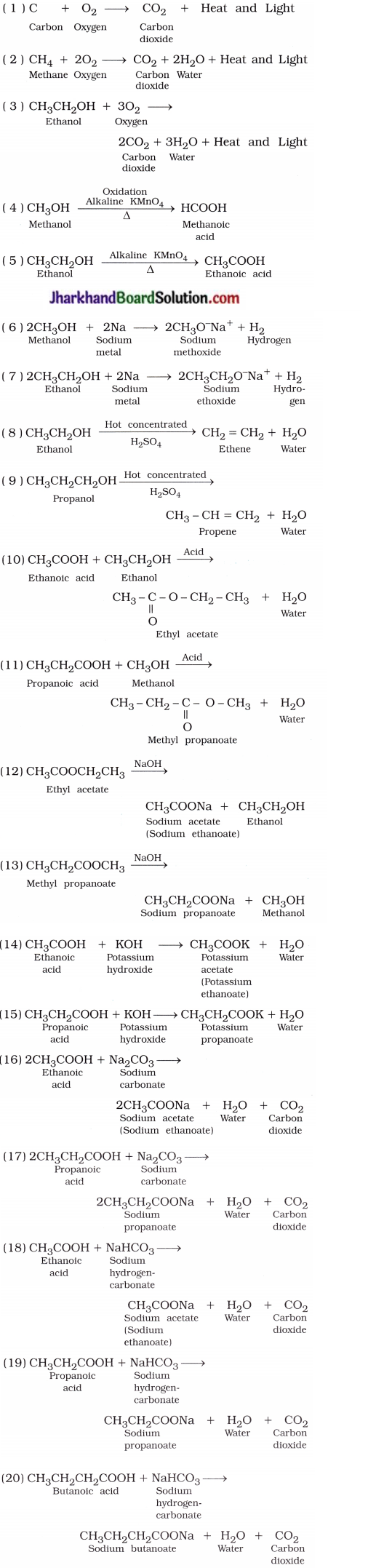
Mention the formulae, and names of the products in the following reactions:
( 1 ) C + O2 →
( 2 ) CH4 + O2 →
( 3 ) CH3CH2OH + O2 →
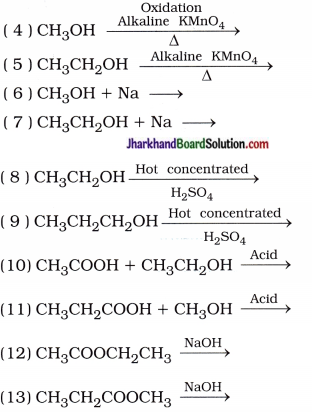
( 14 ) CH3COOH + KOH →
( 15 ) CH3CH2COOH + KOH →
( 16 ) CH3COOH + Na2O3 →
( 17 ) CH3CH2COOH + Na2CO3 →
( 18 ) CH3COOH + NaHCO3 →
( 19 ) CH3CH2COOH + NaHCO3 →
( 20 ) CH3CH2CH2COOH + NaHCO3 →
Answer:
Question 7.
Choose the correct option from those given below each question:
1. By which name the compounds containing functional group – CHO are known?
A. Amide
B. Aldehyde
C. Ketone
D. Alcohol
Answer:
B. Aldehyde
2. Which functional group is present in carboxylic acid?
A. ![]()
B. – COOH
C. – CHO
D. – OH
Answer:
B. – COOH
3. Which functional group is to be given suffix -ol in the nomenclature?
A. – CHO
B. ![]()
C. – OH
D. – X
Answer:
C. – OH
4. Which functional group is present in meyhyl ethanoate?
A. Alcohol
B. Halide
C. Ketone
D. Ester
Answer:
D. Ester
5. Which of the following is obtained by the reduction of methanal?
A. Ethanol
B. CO2 and O2
C. Methanol
D. All of the given
Answer:
C. Methanol
![]()
6. Which of the following reaction takes place between the reaction of alcohol and carboxylic acid in the presence of concentrated H2SO4?
A. Hydrolysis
B. Beta elimination
C. Saponification
D. Esterification
Answer:
D. Esterification
7. In order to form a compound, which of the following functional group possess minimum three carbon atoms?
A. – COOH
B. – CHO
C. ![]()
D. – C – O –
Answer:
C. ![]()
8. Which functional group is present in ketone?
A. ![]()
B. – COOH
C. – CHO
D. – OH
Answer:
A. ![]()
9. Which functional group is present in aldehyde?
A. ![]()
B. – COOH
C. – CHO
D. – OH
Answer:
C. – CHO
10. Name the substance having functional group – OH.
A. Alcohol
B. Ketone
C. Ester
D. Carboxylic acid
Answer:
A. Alcohol
11. How many carbon atom/s are present in formic acid?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
Answer:
A. 1
12. Which of the following is used as food preservator?
A. CH3OH
B. CH3COOH
C. CH3CHO
D. CH3COCH3
Answer:
B. CH3COOH
13. In soap and detergent, non-polar tail is attracted towards ………………. and an anionic head is attracted towards ……………….
A. stain, glycerol
B. water molecules, stain
C. stain, water molecules
D. water molecules, glycerol
Answer:
C. stain, water molecules
14. Write the common name of ethanoic acid.
A. Formic acid
B. Acetic acid
C. Propanoic acid
D. Butanoic acid
Answer:
B. Acetic acid
15. A molecule of NH3 (ammonia) has …
A. only single bonds.
B. only double bonds.
C. only triple bonds.
D. two double bonds and one single bond.
Answer:
A. only single bonds.
16. Fullerene is an allotropic form of…
A. phosphorus.
B. sulphur.
C. carbon.
D. tin.
Answer:
C. carbon.
17. Which of the following are correct structural isomers of butane?
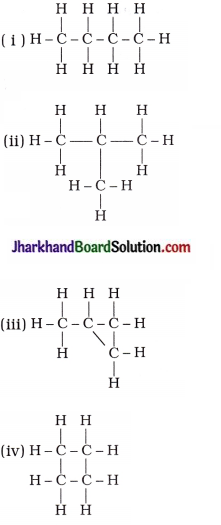
A. (i) and (iii)
B. (ii) and (iv)
C. (i) and (ii)
D. (iii) and (iv)
Answer:
C. (i) and (ii)
18. ![]()
In the above given reaction, alkaline KMnO4 acts as …
A. reducing agent.
B. oxidising agent.
C. catalyst.
D. dehydrating agent.
Answer:
B. oxidising agent.
19. Oils on treating with hydrogen in the presence of palladium or nickel catalyst form fats. This is an example of…
A. addition reaction.
B. substitution reaction.
C. rearrangement reaction.
D. oxidation reaction.
Answer:
A. addition reaction.
20. Structural formula of ethyne is …
A. H – C ≡ C – H
B. H3C – C ≡ CH
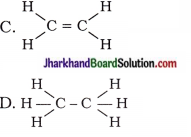
Answer:
A. H – C ≡ C – H
21. Which of the following are unsaturated compounds ?
(i)Propane
(ii) Propene
(iii) Propyne
(iv) Chloropropane
A. (i) and (ii)
B. (ii) and (iv)
C. (iii) and (iv)
D. (ii) and (iii)
Answer:
D. (ii) and (iii)
22. In which condition, chlorine reacts with saturated hydrocarbons at room temperature?
A. In the absence of sunlight
B. In the presence of sunlight
C. In the presence of water
D. In the presence of hydrochloric acid
Answer:
B. In the presence of sunlight
23. Which products are formed by the reaction between ethanol and sodium?
A. Sodium ethanoate and hydrogen
B. Sodium ethanoate and oxygen
C. Sodium ethoxide and hydrogen
D. Sodium ethoxide and oxygen
Answer:
C. Sodium ethoxide and hydrogen
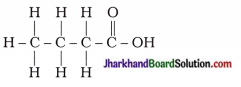
24. The correct structural formula of butanoic acid is …
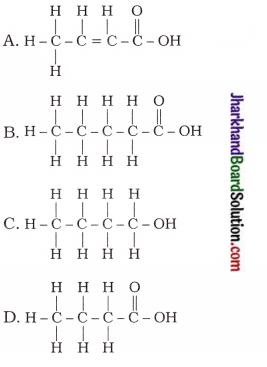
Answer:
25. Vinegar is a solution of…
A. 50%-60% acetic acid in alcohol.
B. 5%-8% acetic acid in alcohol.
C. 5%-8% acetic acid in water.
D. 50%-60% acetic acid in water.
Answer:
C. 5%-8% acetic acid in water.
26. Carbon forms four covalent bonds by sharing its four valence electrons with four univalent atoms, for example, hydrogen. After the formation of four bonds, carbon attains the electronic configuration of….
A. helium
B. neon
C. argon
D. krypton
Answer:
B. neon
27. Which of the following compounds does not belong to the homologous series?
A. CH4
B. C2H6
C. C3H6
D. C4H8
Answer:
D. C4H8
28. The first member of alkyne homologous series is … .
A. ethyne
B. ethene
C. propyne
D. methane
Answer:
A. ethyne
29. Which of the following represents saponification reaction?
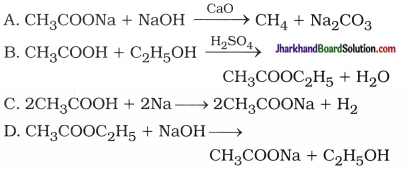
Answer:
CH3COOC2H5 + NaOH → CH3COONa + C2H5OH
30. The number of covalent bonds present in pentane is –
A. 5
B. 12
C. 16
D. 17
Answer:
C. 16
![]()
Question 8.
Choose more than one correct options from those given below each question:
1. Which of the following are not correct for carbon compounds?
A. Three hydrocarbon compounds can be represented by a general formula.
B. Three hydrocarbon compounds are isomers of each other.
C. Three hydrocarbon compounds are unsaturated hydrocarbons.
D. Chemical reactions of three hydrocarbon compounds are similar.
Answer:
B, D.
2. Which of the following are unsaturated compounds?
A. Ethene, ethyne, propene, propyne
B. Ethyne, butyne, propanol, butanol
C. Ethene, propene, butene, pentene
D. Ethyne, propyne, butyne, pentyne
Answer:
A, C, D
3. Which of the following statements are correct for the given hydrocarbon compounds?
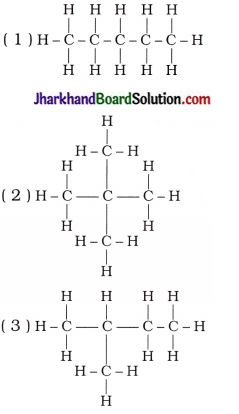
A. Three hydrocarbon compounds can be represented by a general formula.
B. Three hydrocarbon compounds are isomers of each other.
C. Three hydrocarbon compounds are unsaturated hydrocarbons.
D. Chemical reactions of three hydrocarbon compounds are similar.
Answer:
A, B, D
4. Which of the following are isomers of butane?
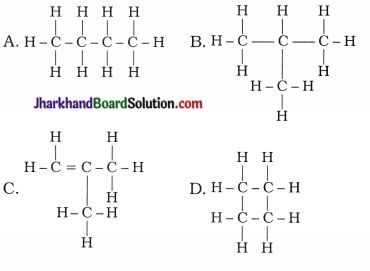
Answer:
A, B
5. Which of the following reactions are correct?
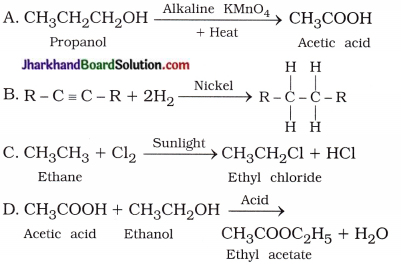
Answer:
B, C, D
Question 9.
In each of the following questions, two statements are given. A statement of Assertion (A) is followed by another statement of Reason (R). Study the statements carefully and choose the correct option:
A. Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true, and reason (R) is the true explanation of the assertion (A).
B. Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true, but reason (R) is not the true explanation of the assertion (A).
C. Assertion (A) is true and reason (R) is false.
D. Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are false.
1. (A) A mixture of oxygen and ethyne is burnt for welding.
(R) Burning of the mixture releases a large amount of heat.
Answer:
A. Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true, and reason (R) is the true explanation of the assertion (A).
2. (A) Acidified K2Cr2O7 is used in oxidation of ethanol.
(R) Acidic K2Cr2O7 is a reducing agent.
Answer:
C. Assertion (A) is true and reason (R) is false.
3. (A) Animal fats should be chosen for cooking.
(R) Animal fats are not harmful for health.
Answer:
D. Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are false.
4. (A) Carbon could not form C4- anion by gaining four electrons.
(R) It would be difficult for carbon atom with six protons in its nucleus to accomodate ten electrons.
Answer:
A. Both assertion (A) and reason (R) are true, and reason (R) is the true explanation of the assertion (A).
5. (A) C2H5OH, C3H7OH and C4H9OH are members of homologous series.
(R) These compounds do not have same functional group.
Answer:
C. Assertion (A) is true and reason (R) is false.
Value Based Questions With Answers
Question 1.
One day Mudra was talking to her mother who was cooking vegetables in a stainless steel? utensils. Mudra observed that the bottom of cooking utensils was getting blackened from outside. She showed this to her mother. The mother told Mudra that the bottoms of all the cooking utensils kept on the gas stove were getting blackened for the last few days and she had tough time cleaning these utensils.
Being a science student of class X, Mudra S checked the gas stove thoroughly and could understand the reason for this problem. She explained everything to her mother. As Mudra S was getting late for school, she asked her mother to take a particular step to stop the blackening of cooking utensils. Mudra’s mother S did the same. The mother was glad that the? bottoms of cooking utensils kept on gas burner were no longer being blackened.
Questions:
- Why is the bottom of cooking utensils getting blackened? Explain.
- Apart from blackening the utensils, state two other disadvantages in this condition.
- What did Mudra find on checking the gas stove thoroughly which was causing this problem?
- What step was taken by Mudra to get rid of this problem?
- What type of flame was produced by the gas stove burner after the required step was taken by Mudra’s mother?
- What values are shown by Mudra in this act?
Answer:
- The fuel LPG is burning incompletely in the gas stove producing yellow, sooty flame. The unburnt particles present in sooty flame stick to the bottom of the cooking utensils and blacken it.
- Since the fuel is not burning completely, there is wastage of fuel. and The incomplete combustion of LPG puts unburnt carbon particles into the air and pollutes the environment.
- Mudra had found that the air holes of the gas stove were partially blocked.
- Mudra had suggested her mother to clean the holes of the gas burner properly to bring in free flow of air sufficient for the complete combustion of fuel.
- After the air holes of the gas stove were opened fully by proper cleaning, then sufficient air was made available for the complete combustion of fuel to produce smokeless, blue flame.’
- The values shown by Mudra are : (1) Good observation skills, (2) Understanding of combustion of fuels, (3) Application of knowledge in everyday life and (4) Concern for the environment.
Question 2.
Yug studies in tenth standard. One day his science teacher was discussing about oils and fats in the class. During this discussion, Yug came to know many facts about oils and fats which he did not know earlier. When Yug came back home from school, he asked his mother about oil she used to prepare food for the family.
His mother replied that she was using vegetable ghee for cooking food. Yug requested his mother not to use vegetable ghee because it is harmful for health. He asked her to use vegetable oil for cooking the food because vegetable oil is good for health. Yug’s mother agreed to do the same; and she started the use of vegetable oil.
Questions :
- Write the physical states of vegetable ghee and vegetable oil.
- How do vegetable oils and fats differ chemically?
- By which method, the vegetable oil is converted into vegetable ghee?
- Why is vegetable ghee not considered good for health?
- Name the most common animal fat consumed by people.
- Why is vegetable oil better for health?
Answer:
- Vegetable ghee is a solid and vegetable oil is a liquid at room temperature.
- Vegetable oils are unsaturated organic compounds while fats are saturated organic compounds.
- Vegetable oil is converted into vegetable ghee by hydrogenation of vegetable oil.
- Vegetable ghee consists of saturated fatty acids, which raise the level of bad cholesterol in blood after a long time use and increase the risk of heart disorder. Hence vegetable ghee is not good for health.
- Butter is the most common animal fat consumed by people.
- Vegetable oil contains unsaturated fatty acids, which does not increase the level of bad cholesterol in blood and reduces the risk of heart disorder. Therefore, vegetable oil is preferable and good for health.
Practical Skill Based Questions With Answers
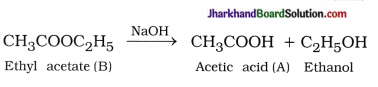
Question 1.
An organic compound A’ is widely used to preserve the pickles and has a molecular formula C2H4O2. This compound reacts with ethanol to form a sweet smelling compound ‘B
( 1 ) Identify the compound A.
( 2 ) Write the chemical equation for the reaction of A with ethanol in the presence of acid.
(3 ) Which gas is produced when compound A reacts with washing soda? Write the chemical equation.
(4) How can we obtain compound A from ‘B’?
Answer:
( 1 ) Compound A is acetic acid (CH3COOH).
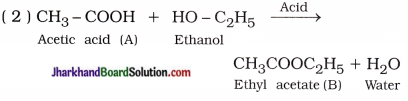
( 3 ) Carbon dioxide gas is produced :
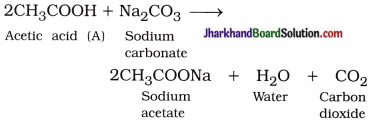
( 4 ) Saponification :
Question 2.
Identify the compounds A, B, C, D, E and F in the following reactions:
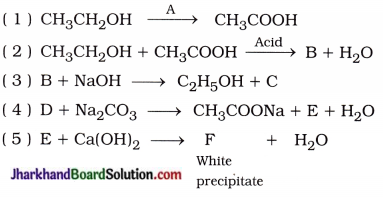
Answer:
( 1 ) A = Alkaline KMnO4 or Acidic K2Cr2O7
( 2 ) B = CH3COOC2H5
( 3 ) C = CH3COONa, B = CH3COOC2H5
( 4 ) D = CH3COOH, E = CO2
( 5 ) E = CO2, F = CaCO3
Question 3.
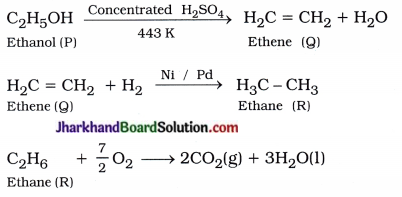
An organic compound P when heated with excess concentrated H2SO4 at 443 K produced compound Question The number of carbon atoms in P and Q are same. Compound Q when treated with hydrogen in presence of nickel or palladium formed compound R. One mole of ‘R’ when reacts with sufficient O2 gives two moles of carbon dioxide and three moles of water. Identify the compounds P, Q and R. Write chemical equations for the reactions.
Answer:
P : C2H5OH (Ethanol)
Q : H2C = CH2 (Ethene)
R : H3C – CH3 (Ethane)
Chemical reactions :
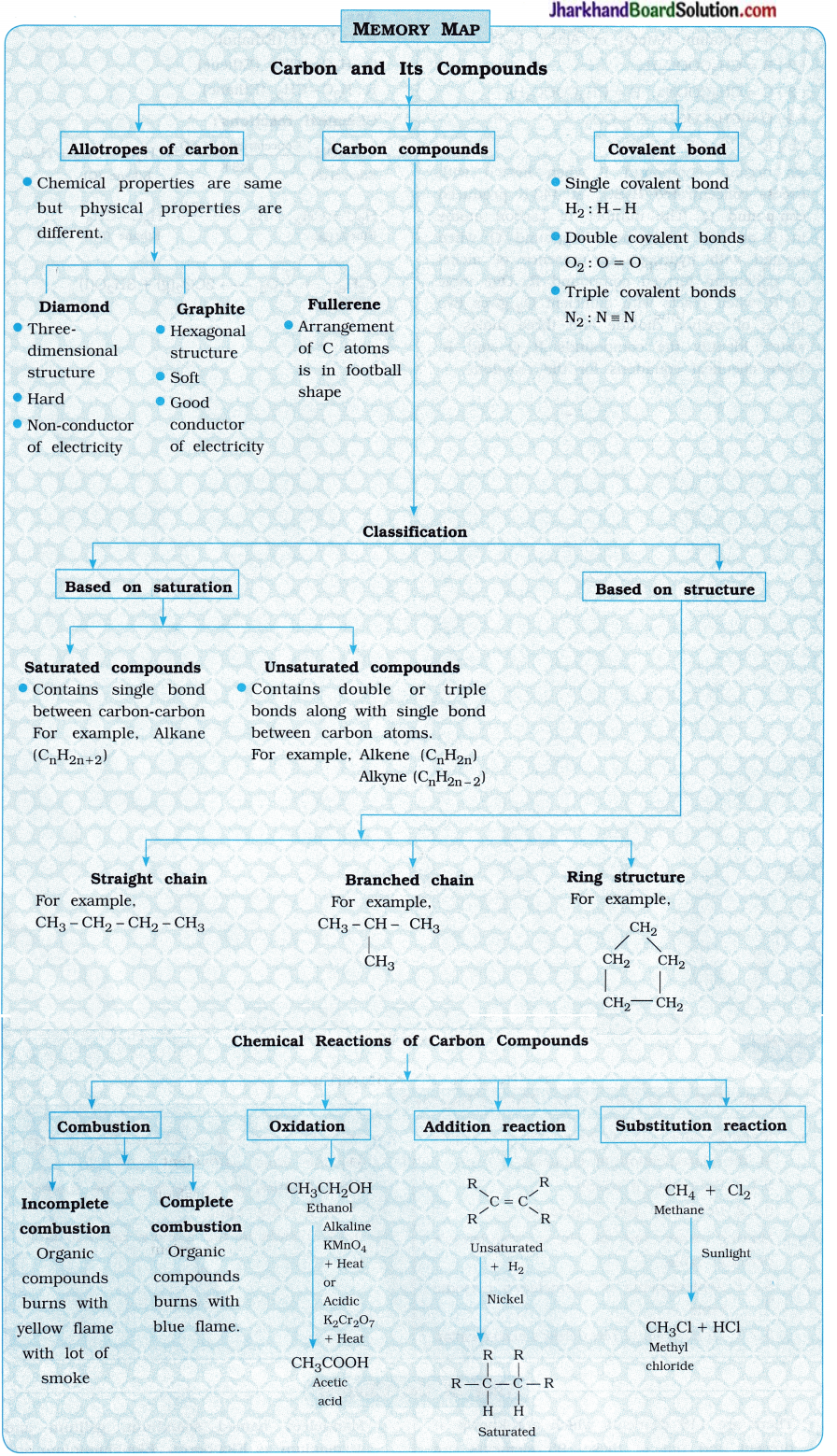
Memory Map