Jharkhand Board JAC Class 10 Science Solutions Chapter 7 Control and Coordination Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
JAC Board Class 10 Science Solutions Chapter 7 Control and Coordination
Jharkhand Board Class 10 Science Control and Coordination Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Which of the following is a plant hormone?
A. Insulin
B. Thyroxin
C. Estrogen
D. Cytokinin
Answer:
Cytokinin
Question 2.
The gap between two neurons is called a ………………..
A. dendrite
B. synapse
C. axon
D. impulse
Answer:
synapse
Question 3.
The brain is responsible for ……………….
A. thinking
B. regulating the heartbeat
C. balancing the body
D. all of the above
Answer:
all of the above
![]()
Question 4.
What is the function of receptors in our body? Think of situations where receptors do not work properly. What problems are likely to arise?
Answer:
The function of receptors : To receive collect information about changes in the environment around us in form of stimuli. This information pass to central nervous system through sensory nerves in form of impulse.
If receptors do not work properly, external stimuli cannot be received and body will not respond towards it.
Question 5.
Draw the structure of a neuron and explain its function.
Answer:
Structure of neuron:
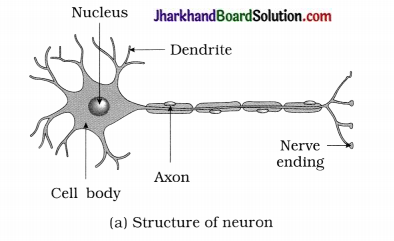
Function of neuron:
The information is acquired at the end of the dendritic tip of a nerve cell and sets off a chemical reaction that creates an electrical impulse. This impulse travels from the dendrite to the cell body and then along the axon to its end. At the end of the axon, the electrical impulse sets off the release of some chemicals (Neurotransmitters) which cross the synapse and start a similar electrical impulse in a dendrite of the next neuron.
Thus, neuron is specialised for conducting information via electrical impulses from one part of the body to another.
Question 6.
How does phototropism occur in plant?
Answer:
To observe the response of plant parts to light OR To study phototropism in plants.
Materials: Conical flask, wire mesh, cardboard box open from one side, water, two-three freshly germinated bean seeds.
Procedure:
- Fill a conical flask with water.
- Cover the neck of the flask with a wire mesh.
- Keep two-three freshly germinated bean seeds on the wire mesh.
- Take a cardboard box which is open from one side.
- Keep the flask in the box in such a manner that the open side of the box faces light coming from a window.
- Observe after two or three days and note down your observation.
- Now turn the flask and leave it undisturbed in this condition for a few days and then observe.
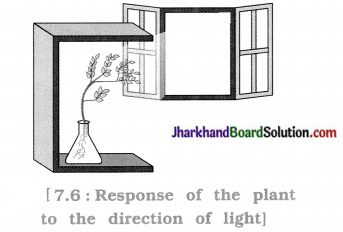
Observation: In the initial position of flask, the shoot bends towards light and roots turn away from light.
After turning the flask, position of shoot and roots change, i.e., shoot goes away from light and roots turn towards light but after a few days shoot again shows bending towards light and roots move away from light.
Questions:
Question 1.
Have the old parts of the shoot and root changed direction?
Answer:
Yes, shoot always grows towards light as it positively phototropic and root goes in opposite direction of light.
Question 2.
Are there differences in the direction of the new growth?
Answer:
No, growth pattern or direction follows environmental stimulus.
Question 3.
What can we conclude from this activity?
Answer:
We can conclude from this activity that shoot shows positive phototropism and roots show negative phototropism.
Question 7.
Which signals will get disrupted in case of a spinal cord injury?
Answer:
In case of a spinal cord injury following signals will get disrupted :
- Reflex action
- Sensory impulses from different organs of body to brain through spinal cord will not be conducted
- Motor impulses from brain to different organs of body through spinal cord will not be transmitted.
Question 8.
How does chemical coordination occur in plants?
Answer:
The chemical coordination occurs in plants by means of plant hormones. They help to coordinate growth, development and. responses to the environment. They are synthesised at places away from where they act and reach to the areas of action by simple diffusion.
Question 9.
What is the need for a system of control and coordination in an organism?
Answer:
In multicellular organisms, body organisation is complex. Different organs s and tissues perform different specialised functions. Therefore, it is necessary that all the organs work together in a proper coordinating way, it needs a system of control and coordination.
In human beings, well-developed nervous and endocrine system were evolved for control and coordination.
![]()
Question 10.
How are involuntary actions and reflex actions different from each other?
Answer:
| Involuntary actions | Reflex actions |
| These are controlled by medulla a part of hind-brain. | These are controlled by spinal cord in general. |
| Functioning of internal body parts are involuntary actions. | It is involuntary response to external stimuli without the knowledge of cerebrum. |
| Such actions go on continued under normal condition also, e.g., heartbeats, breathing, peristalsis, etc. | It is shown under a condition of emergency. Such as to pull hand away on touching to hot object. |
| It occurs in controlled rhythmic way. | It is a quick action. |
Question 11.
Compare and contrast nervous and hormonal mechanisms for control and coordination in animals.
Answer:
| Nervous mechanism | Hormonal mechanism |
| Neuron is the main functional unit in nervous mechanism. | Hormone acts as chemical messenger in hormonal mechanism. |
| Impulse is generated at dendrite and it passes along the axon through cell body. | Hormone is secreted from endocrine gland and is transported through blood circulation. |
| The neural responses are quick. | The hormonal actions are slow. |
| Its effect is short lasting. | Its effect is long lasting. |
| Impulse is delivered to other neuron, gland or muscle cells. | Information is received by target cells who have specific molecules on their surfaces. |
Question 12.
What is the difference between the manner in which movement take place in a sensitive plant and the movement in our legs?
Answer:
| Movement in a sensitive plant | Movement in our legs |
| It occurs in response to touch. | It is voluntary action as per our need. |
| Neural signals are not involved in such movement. | Neural signals from cerebellum are involved in such movements. |
| No specific protein is present in plant cells for it. | A specific protein is present in our muscle cells for it. |
| Plant cells change their shape by changing the amount of water in it. | A special proteins change both their shape and their arrangement in response to nervous impulses due to which the muscle cells shorten. |
Jharkhand Board Class 10 Science Control and Coordination InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is the difference between a reflex action and walking?
Answer:
Reflex action is an involuntary action controlled by spinal cord. Thinking is not involved in such action.
Walking is a voluntary action and is controlled by a cerebellum, a part of hind-brain. This action is shown as per wish of an individual.
Question 2.
What happens at the synapse between two neurons?
Answer:
Synapse is the gap between nerve endings of axon of one neuron and dendrites of another neuron. At the end of axon, the electrical impulse sets off the release of some chemicals. These chemicals cross the synapse and start a similar electrical impulse in a dendrite of the next neuron.
Question 3.
Which part of the brain maintains posture and equilibrium of the body?
Answer:
Cerebellum is the part of the brain that maintains posture and equilibrium of the body.
Question 4.
How do we detect the smell of an agarbatti (incense stick)?
Answer:
Olfactory receptors in our nose are stimulated by the smell of agarbatti. This causes generation of impulse which is received at dendrite of sensory neuron. Such impulse is transmited to brain. In cerebrum message is interpreted and we detect the smell.
Question 5.
What is the role of the brain in reflex action?
Answer:
Generally reflex action is shown by spinal cord and there is no active role of brain in it. However the information input also goes to the brain.
In some reflex actions such as mouth watering on seeing delicious food, heartbeats, breathing, movement of diaphragm, yawning, blinking of eyes, sneezing, etc. brain is involved.
Question 6.
What are plant hormones?
Answer:
Plant hormones are chemical compounds produced by plant itself and help to coordinate growth, development and responses to the environment.
Question 7.
How is the movement of leaves of the sensitive plant different from the movement of a shoot towards light?
Answer:
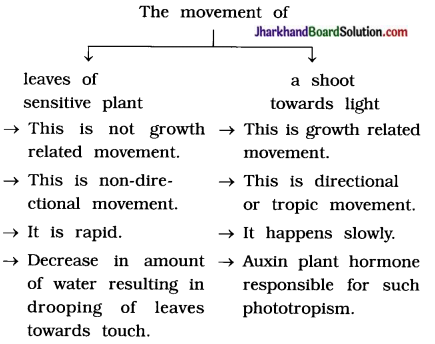
Question 8.
Give an example of a plant hormone that promotes growth.
Answer:
An example of a plant hormone that promotes growth : Auxin.
Question 9.
How do auxins promote the growth of a tendril around a support?
Answer:
Auxins are growth promoting plant hormones that induce cell elongation. When tendril comes in contact with a support, auxin stimulates faster growth on to a part of tendril away from the support. This causes the tendril to coil around the support.
![]()
Question 10.
Design an experiment to demonstrate hydrotropism.
Answer:
The type of movement of the growing plant organ, which is induced by stimulus of water is called hydrotropism.
To demonstrate hydrotropism.
Apparatus-Materials: clay, two plants, two glass
Procedure: Take two glass troughs each filled to about 1/3 with clay. Label the trough as (A) and (B). Plant two, almost equal sized cuttings, S one in each of the troughs. Add water in trough (A) and keep the clay of trough (B) dry. However in trough (B) place a small clay pot (or a cup of clay) filled with water quite close to the cutting. (See the figure) Add daily a small quantity of? water in trough (A) but not in trough (B). Dig out the clay carefully in both the troughs after about a week or more.
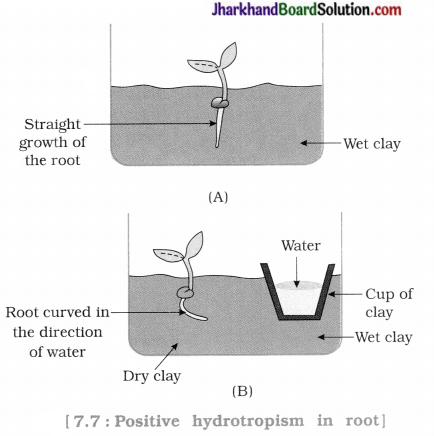
Observation : It will be seen that the cutting in trough (A) shows a simple and straight growth of the root, while that in trough (B) shows the root curved in the direction of clay pot filled with water.
Conclusion: It can be concluded that the root grows and elongates in the direction of source of water. It means that the root shows positive hydrotropism.
Question 11.
How does chemical coordination take place in animals?
Answer:
In animals, endocrine glands secretes S chemical substances (Hormones) in precise quantities. They are directly released in blood and through blood circulation they reach to their target (Functional) site. Specific cells of body have specific molecules with which hormone molecules bind and transmit information.
Thus, chemical coordination take place in animals.
Question 12.
Why is the use of iodised salt advisable?
Answer:
The use of iodised salt is advisable because iodine is essential for the synthesis of thyroxin hormone in thyroid gland. Deficiency of iodine causes goitre. Iodised salt fulfills the requirement of iodine of body and protects agains goitre disease.
Question 13.
How does our body respond when adrenaline is secreted into the blood?
Answer:
Adrenaline prepares our body in an emergency situation. When adrenaline is secreted into the blood body shows following responses:
The heart beats faster, breathing rate increases, blood pressure increases, skeletal muscles become more active, etc. This is known as fight or flight response.
Question 14.
Why are some patients of diabetes treated by giving injections of insulin?
Answer:
Insulin is a pancreatic hormone which helps in regulating blood sugar level. In the patients of diabetes, the blood sugar level rises due to deficiency of insulin. So, some patients of diabetes are treated by giving injections of insulin to maintain blood sugar level.
Activity 7.1 [T. B. Pg. 115]
To detect the taste bud (gustatory receptor) and its function.
- Put some sugar on your tongue In the mouth.
- Block your nose by pressing it between your thumb and index finger.
- Now eat sugar again.
- While eating lunch, block your nose in the same way and notice If you can fully appreciate the taste of food you are eating.
Questions:
Question 1.
How does the sugar taste?
Answer:
The taste of sugar is sweet.
Question 2.
Is there any difference in the taste of sugar while you block your nose?
Answer:
When we eat sugar after blocking our nose, we find no difference in the taste of sugar.
Question 3.
Is there a difference in how sugar and food taste If your nose Is blocked? If so, why might be happening?
Answer:
If we block our nose, we feel the taste but cannot fully appreciate because the olfactory receptors are not stimulated. We cannot feel the smell.
Question 4.
Do you come across a similar situation when you have a cold?
Answer:
Yes, when we have a cold, olfactory receptors are covered with excessive secreted mucus.
Activity 7.2 [T. B. Pg. 121]
To observe the response of plant parts to light OR To study phototropism in plants.
Materials: Conical flask, wire mesh, cardboard box open from one side, water, two-three freshly germinated bean seeds.
Procedure:
- Fill a conical flask with water.
- Cover the neck of the flask with a wire mesh.
- Keep two-three freshly germinated bean seeds on the wire mesh.
- Take a cardboard box which is open from one side.
- Keep the flask in the box in such a manner that the open side of the box faces light coming from a window.
- Observe after two or three days and note down your observation.
- Now turn the flask and leave it undisturbed in this condition for a few days and then observe.
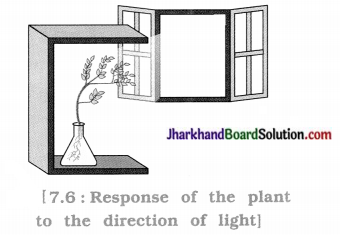
Observation: In the initial position of flask, the shoot bends towards light and roots turn away from light.
After turning the flask, position of shoot and roots change, i.e., shoot goes away from light and roots turn towards light but after a few days shoot again shows bending towards light and roots move away from light.
Questions:
Question 1.
Have the old parts of the shoot and root changed direction?
Answer:
Yes, shoot always grows towards light as it positively phototropic and root goes in opposite direction of light.
Question 2.
Are there differences in the direction of the new growth?
Answer:
No, growth pattern or direction follows environmental stimulus.
![]()
Question 3.
What can we conclude from this activity?
Answer:
We can conclude from this activity that shoot shows positive phototropism and roots show negative phototropism.
Activity 7.3 [T. B. Pg. 123]
Identify the endocrine glands mentioned in the diagram.
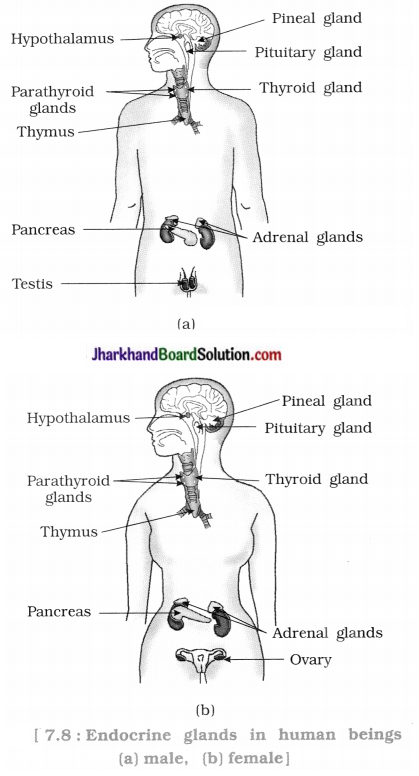
Activity 7.4 [T. B. Pg. 125]
To know some important hormones and their functions.
Complete the following given table:
| No. | Hormone | Endocrine Gland | Function |
| 1. | Growth hormone | Pituitary gland | Stimulates growth in all organs. |
| 2. | Thyroxin | Thyroid gland | Regulates metabolism for body growth. |
| 3. | Insulin | Pancreas | Regulate blood sugar level |
| 4. | Testosterone | Testes | Development of secondary sexual characters in male |
| 5. | Estrogen | Ovaries | Development of female sex organs, regulates menstrual cycle, etc. |
| 6. | Adrenaline | Adrenal gland | Prepares body for an emergency condition, i.e., either fight or flight. |
| 7. | Releasing hormones | Hypo-thalamus | Stimulates pituitary gland to release hormones |