JAC Board Class 9th Social Science Important Questions Geography Chapter 6 Population
I. Objective Type Questions
1. What is the counting of people in a country known as?
(a) census
(b) migration
(c) birth rate
(d) death rate.
Answer:
(a) census
2. Which of the following is calculated as the number of persons per unit area?
(a) population distribution
(b) population density
(c) total population
(d) None of the these.
Answer:
(b) population density
3. The population is generally grouped into which of the following categories?
(a) Aged (Above 59 years)
(b) Children (generally below 15 years)
(c) Working Age (15-59 years)
(d) All of the above.
Answer:
(d) All of the above.
4. From which of the following years, the birth rates started declining, resulting in a gradual decline in the birth of India?
(a) 1976
(b) 1990
(c) 1981
(d) 1988.
Answer:
(c) 1981
5. Which of the following along with basic sanitation amenities is available to only one- third of the rural population?
(a) Food Security
(b) Health
(c) Education
(d) Safe Drinking Water.
Answer:
(d) Safe Drinking Water.
II. Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What is census?
Answer:
The census is the process of collection, compilation and publication of information relating to different aspects of people living in a country at a specific point of time.
![]()
Question 2.
When was the first census held in India?
Answer:
The first census in India (on a limited scale) was held in 1872. The first complete census was taken in 1881 and subsequently it has been taken every 10 years.
Question 3.
What is the total population of India according to 2011 Census?
Answer:
1,210.6 million.
Question 4.
What is India’s share in world population?
Answer:
About 17.5%.
Question 5.
Name the state having highest population in India.
Answer:
Uttar Pradesh.
Question 6.
Which are the most populated and least populated states in India?
Answer:
The most populated state in India is Uttar Pradesh and least populated is Sikkim.
Question 7.
Almost 50% of India’s population lives in five states. Write their names.
Answer:
Almost 50% of India population lives in the five states of Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Bihar, West Bengal and Andhra Pradesh.
![]()
Question 8.
Name the less populated states of India.
Answer:
Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Assam, Tripura, Naga-land, Meghalaya, Manipur, Mizoram, Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh.
Question 9.
Name the states of India having high density of population.
Answer:
Uttar Pradesh, Maharashtra, Bihar, West Bengal and Andhra Pradesh.
Question 10.
What is the population density of India according to 2011 Census?
Answer:
It is 382 persons per square kilometre.
Question 11.
What is the major reason for the state of Kerala having a very high population density?
Answer:
Kerala has a very high population density because it has fertile soil and gets abundant rainfall, thus resulting in good prospects for agriculture.
Question 12.
What is called as annual growth rate?
Answer:
The rate or the pace of population increase per annum is called as the annual growth rate.
Question 13.
Mention the factors responsible for the population change.
Answer:
- Death Rate,
- Birth Rate,
- Migration.
Question 15.
What kind of migration does not change the size of the population in a country?
Answer:
Internal migration from one city to another or from rural areas to urban areas within a country does not change the size of the population.
Question 16.
What type of migration leads to changes in the distribution of population within the nation?
Answer:
Internal migration leads to changes in the distribution of population within the nation.
![]()
Question 17.
What are the three divisions of age composition?
Answer:
- Children (0-14 years age group),
- Working Age (15-59 years), and
- Aged (Above 59 years).
Question 18.
What is the sex-ratio in India according to 2011 Census?
Answer:
It is 943 females per 100 males.
Question 19.
Which states of India have the highest and the lowest sex ratio?
Answer:
Kerala has the highest sex ratio of 1084 and Haryana has the lowest sex ratio of 877 (as per the 2011 census).
Question 20.
In which state of India the sex ratio is favourable to women?
Answer:
Kerala.
Question 21.
Who is called a literate?
Answer:
A person aged 7 years and above, who can read and write with understanding in any language, is treated as literate. ‘
Question 22.
What is the literacy rate for the country as a whole?
Answer:
It is about 73 per cent.
Question 23.
What is the male and female literary rate and the general literacy level in India as per census 2011?
Answer:
As per census of 2011, the male literacy rate is 80.90% female literacy rate is 64.6% and general literacy rate is 74.04%.
Question 24.
Name the state having the highest literacy rate in India.
Answer:
Kerela.
Question 25.
What is known as occupational structure?
Answer:
The distribution of working population of an economy according to different occupations is known as occupational distribution of population or occupational structure.
![]()
Question 26.
What are the three sectors of occupations?
Answer:
- Primary sector,
- Secondary sector,
- Tertiary sector.
Question 27.
What are primary activities?
Answer:
Primary activities include agriculture, animal husbandary, forestry, fishing, mining and quarrying etc.
Question 28.
What are secondary activities?
Answer:
Secondary activities include manufacturing industry, building and construction work etc.
Question 29.
What are tertiary activities?
Answer:
Tertiary activities include transport, communication, commerce, banking, administration and other services.
Question 30.
What is adolescent population?
Answer:
Adolescents are generally grouped in the age-group of 10 to 19 years. It constitutes one-fifth of the total population of India.
Question 31.
When was the comprehensive Family Planning Programme launched?
Answer:
In 1952.
Question 32.
When did the National Population Policy come into effect?
Answer:
The National Population Policy come into effect in the year 2000.
III. Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
What are the three major aspects of population study?
Answer:
1. Population size and distribution:
First of all, we have to see how many people are there in India and where they are located. Then we have to see which states are the most populated states and which are sparsely populated states.
2. Population growth and processes of population change: The second major aspect of population study is how the population has grown and how it has changed overtime.
3. Characteristics or qualities of the population: It includes the study of age, sex composition, literacy, occupational structure and health conditions of the people.
![]()
Question 2.
How is population density calculated? Where does India stand as compared to other countries with respect to population?
Answer:
The population density is calculated as the number of persons per unit of area. India’s stand in population density with respect to other countries is discussed below: India is one of the most densely-populated countries in the world.
As per census report 2011, the population density of India was 382 persons per sq. km. Due to change in climatic conditions, economic opportunities and other geographical factors, India has very regular distribution of population ranging from 1102 persons per sq. km. in Bi’ ar to only 17 persons per sq. km in Arunachal Pradesh. India is the third most dense country in the world after Bangladesh and Japan.
Question 3.
What is the growth of population?
Answer:
Growth of population refers to the change in the number of inhabitants of a country territory during a specific period of time, say during the last ten years. It can be expressed in two ways:
- In terms of absolute numbers,
- In terms of percentage change per year.
Question 4.
Describe the term annual growth rate of population. How is it affected by the birth rate?
Answer:
1. Annual Growth Rate: The rate at which the number of individuals in a population increase in one year as a fraction of the initial population is called annual growth rate of population. Effects of Birth
2. Rate on Annual Growth Rate: The annual growth rate is affected by the birth rate in the following ways.
- With the increase in birth rate, the annual growth rate generally increases.
- For a larger population even having a lower birth rate, the annual growth rate keeps on increasing.
- For example, since 1981, the birth rate declined rapidly; still, 182 million people were added to the total population in 1990s alone. If we calculate annual growth rate based on this data, it becomes very high.
Question 5.
What are the causes of migration in India from rural to urban areas?
Answer:
Migration from rural to urban areas in India has taken place mainly due to:
- Rising population in rural areas.
- Poverty and unemployment in rural areas.
- Lack of demand for labour in agriculture.
- Increased employment opportunities, better education and living standard in urban areas.
- Expansion of industrial and service sectors in the urban areas.
Question 6.
Explain the categorisation of the population of a nation on the basis of age composi¬tion.
Answer:
The population of a nation is generally grouped into three categories :
- Children (below 15 years), who are economically unproductive and need to be provided with food, clothing, education and healthcare.
- Working age (15 to 59 years), who are economically productive and biologically reproductive. They comprise the working population.
- The aged or elderly (60 years and above), who can be economically productive though they may have retired. They may be working voluntarily, but they are not available for employment through recruitment.
![]()
Question 7.
What is the relationship between age composition and dependency ratio ? Briefly explain.
Answer:
Relationship between age composition and dependency ratio is as follows :
- Children below 15 years of age are economically unproductive and people aged above 59 years do not get employment through recruitment.
- The percentage of children and the aged affects the dependency ratio because these groups are not producers but are usually only consumers.
Question 8.
What are the reasons for low literacy rate among women in India?
Answer:
- In India, women generally look after domestic work and are left with no time to get education, which leads to low literacy rate among them, mostly in rural areas of the country.
- Lack of awareness and economic backwardness are other reasons for low literacy rate among women.
Question 9.
What do you understand by occupational structure? Briefly describe the occupational structure of India.
Answer:
1. Occupational structure: The distribution of population according to different types of occupations is referred to as the occupational structure.
2. Occupational Structure of India: In India, about 64 percent of the population is engaged only in agriculture. The proportion of population dependent on secondary and tertiary sectors is about 13 and 20 percent respectively. There has been an occupational shift in favour of secondary and tertiary sectors because of growing industrialisation and urbanisation in recent times.
Question 10.
Into how many categories are occupations generally classified?
Answer:
Occupations are generally classified into three categories:
- Primary occupations: These include agriculture, animal husbandry, forestry, fishing, mining and quarrying etc.
- Secondary occupations: These include manufacturing industry, building and construction works etc.
- Tertiary occupations: These include transport, communication, commerce, banking, administration and other services.
III. Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Write an essay on the population distribution in India.
Answer:
Population of our country is not evenly distributed. Some regions have high density of population. The population density of India in 2011 was 382 persons per sq. km. Bihar has the highest density of population about 1,102 per sq. km, whereas Arunachal Pradesh has the lowest density of population, i.e. 17 persons per sq.km.
- Densely Populated Areas: These are those areas which have population of more than 300 persons per sq. km. The population is dense in these areas due to fertile soil and good rainfall.
- Areas: Sutlej and Gangetic plain; Malabar coastal plain, Coromandel coast.
- States: Punjab, Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, West Bengal, Kerala, Tamil Nadu.
- Medium Density:
These are those areas which have population about 100-300 persons per sq. km.- Areas: Brahmaputra valley, industrial areas, areas around the main ports.
- States: Gujarat, Maharashtra, Goa, Karnataka, Odisha, Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu.
- Thinly or Sparsely Populated Areas:
These are areas which have population less than 100 persons per sq. km. These are the areas of low unreliable and of hilly terrain where there is less levelled land for agriculture.- Areas: Great Indian Desert, Hills of north-eastern states.
- States: Rajasthan, Madhya Pradesh, Kashmir, Himachal Pradesh, Assam, Tripura, Nagaland, Meghalaya, Manipur, Mizoram, Sikkim and Arunachal Pradesh.
![]()
Question 2.
What is age composition ? Why does it affect the population’s social and economic structure?
Answer:
The age composition of a population refers to the number of people indifferent age groups in a country. It affects the population’s social and economic structure because:
- Children (0-14 years) do not contribute to the economy in any way. They require resources for their health, education etc.
- Adults (15-59 years) contribute to the nation’s economy by earning money. They are the working population as they feed and look after the two age groups.
- Aged (60 + years) do not contribute to the economy in any way. The depend on their children or their own saving. However, sometimes people belonging to this age group do work, but it is for private agencies as they are not considered for recruitment after that age.
Question 3.
What is sex ratio? Why has sex ratio been unfavourable to females? Explain it.
Answer:
Sex ratio: It is defined as the number of females per 1000 males in the population. This information is an important social indicator to measure the extent of equality between males and females in a society at a given time.
Reasons for unfavourable sex ratio for females:
- The infant mortality rate in India is high and female infant mortality rate is still higher.
- Preferential treatment is given to a male child and female children get neglected in most Indian homes.
- People go though prenatal sex determination test. In case of a girl child, they abort the child.
- Women generally have lower social political and economic status in the Indian society. We find dowry, murder, opposition to widow remarriage and low nutritional levels in women.
- Lack of social awareness programmes among females, especially in rural areas.
Question 4.
Define the term ‘literate’. Describe the features of literacy rate in India.
Answer:
Definition of Literate: According to the census of 2001, a person aged 7 years and above, who can read and write with understanding in any language, is termed as literate. Features of Literacy Rate in India
- The literacy rate is steadily improving in India.
- As per census 2011, the literacy rate of India is 74.04 per cent.
- The male literacy rate is 80.9 per cent.
- The female literacy rate is 64.6 per cent.
- India has a large gap in literacy rate between male and female population.
- It also exhibits social inequality between males and females.
- This gap in literacy rate is further increased by the declining sex ratio. Literacy is an important quality of population. For overall development and economic progress of the country, there should be high literacy rate among both males and females.
Question 5.
What is the health status of people at present? What measures have been taken to improve the health of the people? Why is the health situation still an issue of major concern for India?
Answer:
Health is an important component of population and composition, which affects the process of development. Following efforts of government programmes have registered significant improvement in the health conditions of the people :
- Death rate has declined from 25 per 1000 population in 1951 to 7.2 per 1000 in 2011.
- Life expectancy at birth has increased from 36.7 years in 1951 to 67.9 years in 2012.
- This substantial improvement is the result of many factors, including improvement in public health, prevention of infectious diseases and application of modern medical practices in diagnosis and treatment of ailments.
However, despite considerable achievements, the health situation is still an issue of major concern for India due to the following reasons:
(a) The per capita calorie consumption is much below the recommended levels and malnutrition affects a large percentage of our population.
(b) Safe drinking water and basic sanitation amenities are available to only one- third of the rural population.
(c) These problems need to be tackled through an appropriate population policy.
Question 6.
Explain any six significant characteristics of the adolescent population of India.
Answer:
Six significant characteristics of the adolescent population of India are as follows:
- Adolescent population is generally categorised in the age group of 10 to 19 years.
- They constitute one-fifth of the total population of India.
- They are the most important future resource.
- Nutritional requirements of adolescents are higher than those of normal children or adults.
- In India, a large number of adolescent girls suffer from anaemia.
- The adolescent girls have to be sensitised to the problems they confront.
![]()
Question 7.
What is the National Population Policy (NPP 2000) ? Why was NPP 2000 initiated by the government?
Answer:
National Population Policy (NPP 2000) It is a comprehensive family planning programme initiated by the government of India. It provides a reliable and relevant policy framework for improving family welfare services and for measuring and monitoring the delivery of family welfare services and their demographic impact in future.
Reasons for Initiations NPP 2000: It was initiated by the government:
- To improve healthcare quality and coverage, measuring and monitoring the delivery of family welfare programme.
- To enable the increasingly literate and aware families to achieve their reproductive goals in the country.
- To achieve rapid population stabilisation.
- To promote synergy with the on-going educational, info-technology and socio¬economic transition.
- To achieve rapid population stabilisation and sustainable development as well as improvement in economic, social and human development in the new millennium.
Question 8.
Write a note on National Population Policy (NPP) 2000 and Adolescents.
Answer:
NPP 2000 identified adolescents as one of the major sections of the population that need greater attention. Besides nutritional requirements, the policy provides greater emphasis on other important needs of adolescents, including protection from unwanted pregnancies and Sexually Transmitted Diseases (STDs) like AIDS.
It called for programmes that aim towards encouraging delayed marriage and child bearing, education of adolescents about the risks of unprotected sex, making contraceptive services accessible and affordable, providing food supplements, and strengthening legal measures to prevent child marriages.
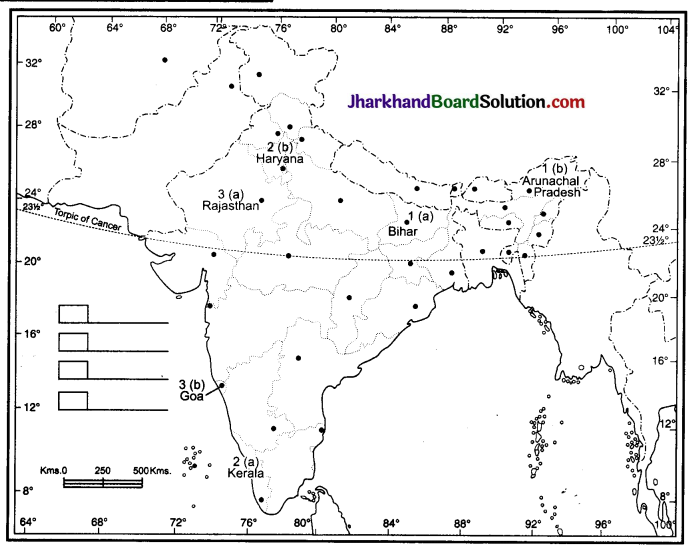
Location and Labelling
1. The state having highest and lowest density population.
2. The state having highest and lowest sex ratio.
3. Largest and smallest state according to area.
Answer:
1. (a) The state having the highest density of population is Bihar.
(b) The state having the lowest density of population is Arunachal Pradesh.
2. (a) The state having highest sex ratio-Kerala.
(b) The state having lowest sex ratio-Haryana.
3. (a) Largest state – Rajasthan.
(b) Smallest state – Goa.