Jharkhand Board JAC Class 10 Science Important Questions Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements Important Questions and Answers.
JAC Board Class 10 Science Important Questions Chapter 5 Periodic Classification of Elements
Additional Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Answer the following questions in short:
(1) From the following elements :
20Ca, 3Li, 11Na, 10Ne
(a) Select the element which has two shells, both of which are completely filled with electrons.
(b) Select two elements of the same group.
Answer:
(a) Element in which two shells are completely filled with electrons is 10Ne (2, 8).
(b) Two elements of the same group are 3Li(2, 1) and 11Na (2, 8, 1).
(2) Answer the following questions [for an element having atomic number 17] :
(a) Name the element.
(b) In which period will you find this element?
(c) To which group of the periodic table does this element belong?
(d) State the electronic configuration of the element.
Answer:
(a) Chlorine
(b) Third period
(c) Group 17
(d) Electronic configuration : 2, 8, 7
(3) An element X (atomic number 17) reacts with an element Y (atomic number 20) to form a divalent halide.
(a) What is the position of elements X and Y in the periodic table?
(b) What will be the nature of oxide of element Y? Identify the nature of bonding in the compound formed.
Answer:
Element X is a non-metal while element Y is a metal.
Molecular formula of dihalide is YX2.
(a)
| Position | Element X | Element Y |
| In a group | 17 | 2 |
| In a period | 3 | 4 |
(b) Basic oxide : YO
Nature of the bond : Ionic
![]()
(4) Two elements M and N belong to the same period of the modern periodic table and are in group I and group II respectively. Compare their following properties:
(a) Atomic size
(b) Metallic character
(c) Valency of oxides
(d) Molecular formula of their chlorides
Answer:
(a) Element ‘M’ has larger atomic size than that of ‘N’.
(b) Element ‘M’ possess more metallic? character than that of ‘N’.
(c) Group I : Valency : 1
Group II : Valency : 2
(d) MCl, MCl2
(5) A part of the periodic table has been shown below :
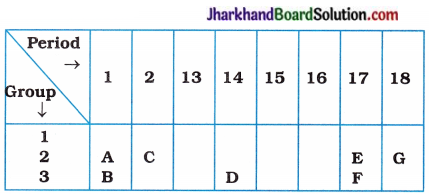
Answer the following questions on the basis of position of elements in the above table:
(a) Which element is a noble gas? Give reason.
(b) Which element is most electronegative? Give reason.
(c) Write the electronic configuration of B and E.
Answer:
(a Element G is a noble gas, because it is present in group 18 and has zero valency.
(b) Element E is the most electronegative element due to its small size and greater tendency to gain electrons.
(c) Electronic configuration of ‘B’ = 2,8, 1 Electronic configuration of ‘E’ = 2, 7
(6) The positions of elements A, B, C, D, E, F, G and H in their respective groups are as follows :
| Group | 1 | 2 | 13 | 14 | 15 | 16 | 17 | 18 |
| Element | A | B | C | D | E | F | G | H |
Answer the following questions:
(a) Which elements have the largest and smallest atomic size?
(b) Which elements have the valency 3 and 0 respectively?
Answer:
(a) Largest atomic size : A
Smallest atomic size : G
(b) Valency 3 : Element C
Valency O : Element H
(7) Consider the part of periodic table given below and answer the following questions :
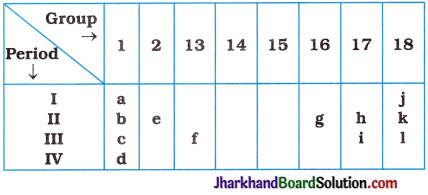
(i) State the most reactive metal.
(ii) How many shells does element d have?
(iii) Identify the element having valency 2.
(iv) Write the number of electrons in the valence shell of j.
(v) Out of h and i, which element is more non-metallic in nature?
(vi) Out of e and h, which element possess large atomic size?
Answer:
(i) d
(ii) 4
(iii) e and g
(iv) 2
(v) h
(vi) e
(8)
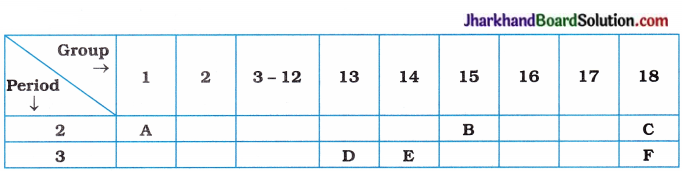
Using the above table, answer the following questions:
(i) Which element will form only covalent compounds?
(ii) Which element is a metal with valency 3?
(iii) Which element is a non-metal with valency 3?
(iv) Out of D and E, which one has a bigger atomic size?
(v) Write common name for the family of elements, C and F.
Answer:
(i) E
(ii) D
(iii) B
(iv) D
(v) Inert gases or noble gases
Question 2.
Distinguish between the following :
(1) Elements of a group and Elements of a period
Answer:
| Elements of a group | Elements of a period |
| 1. The atomic number of elements increases on moving down the group. | 1. The atomic number of elements increases on moving from left to right along a period. |
| 2. All the elements in a group have same number of valence electrons. | 2. The number of valence electrons of the elements in a period increases. |
| 3. The chemical reactivity of elements in a group are same or identical. | 3. The chemical reactivity of elements in a period are not identical. |
| 4. The atomic radius and metallic character increase on moving down the group. | 4. The atomic radius and metallic character decrease on moving from left to right along a period. |
(2) Mendeleev’s periodic table and the Modern periodic table
Answer:
| Mendeleev’s periodic table | Modern periodic table |
| 1. Mendeleev’s periodic table consists of seven periods and eight groups. | 1. Modern periodic table consists of seven periods and eighteen groups. |
| 2. Transition elements are not separated in the Mendeleev’s periodic table. | 2. Transition elements are placed in a separate groups in the modern periodic table. |
| 3. In Mendeleev’s periodic table, elements are arranged in increasing order of their atomic masses. | 3. In the modern periodic table, elements are arranged in increasing order of their atomic numbers. |
| 4. Period number and group number of an element cannot be predicted. | 4. Period number and group number of an element can be determined easily. |
| 5. Mendeleev’s periodic table has descripancies and limitations. | 5. Modern periodic table is almost errorless. |
| 6. Periodicity in the properties of elements cannot be explained. | 6. Periodicity in the properties of elements can be explained. |
(3) Metallic elements and Non-metallic elements
Answer:
| Metallic elements | Non-metallic elements |
| 1. They are electropositive elements. | 1. They are electronegative elements. |
| 2. Metals have tendency of losing the electrons during the bond formation process. | 2. Non-metals have tendency of gaining the electrons during the bond formation process. |
| 3. Oxides of metals are basic. | 3. Oxides of non-metals are acidic. |
| 4. Metals possess 1, 2 or 3 electrons in their respective valence shells. | 4. Non-metals possess 5, 6 or 7 electrons in their respective valence shells. |
Question 3.
Give scientific reasons for the following statements:
(1) Dobereiner’s triads could not arrange all the elements known at that time.
Answer:
In Dobereiner’s triads, three elements were arranged in the order of increasing atomic masses of elements in which the atomic mass of the middle element is the average of the atomic masses of the other two elements.
Dobereiner could identify triads from the elements known at that time was only a coincidence. Thus, this classification of elements into triads could not be applied to all the elements known at that time.
(2) Newlands’ law of octaves could not classify all the elements known at that time.
Answer:
Newlands’ law of octaves was applicable upto calcium. After calcium, every eighth element s did not possess properties similar to that of the first element.
- Newlands’ assumed that only 56 elements existed s in nature.
- Newlands’ law of octaves was found correct only to lighter elements.
- Thus, all the elements could not be classified s by the Newlands’ law of octaves.
(3) No fixed position can be assigned to hydrogen in the periodic table.
Answer:
Electronic configuration of hydrogen resembles with alkali metals.
- Like alkali metals, hydrogen combines with halogens, oxygen and sulphur to form compounds having similar formulae.
- Hydrogen also resembles halogens as it exists in the form of diatomic molecules.
- Hydrogen combines with metals and non-metals to form ionic and covalent bonds respectively.
- Thus, hydrogen cannot be assigned fixed position in the periodic table.
![]()
(4) The atomic size decreases in a period on moving from left to right.
Answer:
As moving from left to right in a period, the atomic number of elements increases by 1.
- As atomic number increases, nuclear charge also increases.
- Due to this increased nuclear charge, the electrons are attracted strongly towards the nucleus and hence the atomic size decreases.
(5) On moving down in a group, the atomic radii of elements increases gradually.
Answer:
On moving down in a group, the atomic number of element increases.
- A new shell of electrons is added with increase in atomic numbers of elements.
- Thus, the distance between the valence shell and nucleus increases and atomic size increases down the group inspite of the increase in nuclear charge.
Objective Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Answer the following questions in one word:
- How many elements are known till date?
- How many amongst the known elements are naturally occurring?
- In which two types the elements were classified in early attempts?
- By which name the law proposed by Dobereiner is known?
- How many elements were classified by Dobereiner’s triads?
- Cl, X and I are the elements of Dobereiner’s triad, then what would be the element X?
- Name the elements Newlands started and ended the classification of elements.
- With what Newlands’ law of octaves was compared?
- Name the element having similar property with lithium in Newlands’ law of octaves.
- Which element possess similar property with boron in Newlands’ law of octaves?
- Name two elements which were placed in the same slot in Newlands’ octaves.
- How many elements were known when Mendeleev started the classification of elements?
- Name two elements which formed compound on which Mendeleev had concentrated.
- What are the vertical columns and the horizontal rows called in Mendeleev’s periodic table?
- Which Sanskrit prefix was used by Mendeleev in the naming of elements which were not discovered at that time?
- Which element was not placed in Mendeleev’s periodic table properly?
- Which scientist proposed tire ‘periodic law’ for the modern periodic table?
- Write the number of elements present in first, third and fourth period in the modern periodic table.
- State the number of elements present in sixth period of the modern periodic table.
- How many groups are present in the modern periodic table?
- How many elements exist as gases in the modern periodic table?
- By what names the elements of group I are known in the modern periodic table?
- By which formula the maximum number of electrons that can be accommodated in a shell determines?
- Write the valency of an element having atomic number 13.
- Name the elements in the modern periodic table having lowest and highest atomic radii.
- State the radius of a hydrogen atom.
Answer:
- 118
- 98
- Metals and non-metals
- Law of Triads
- 9
- Br
- Hydrogen and thorium
- Indian musical notes
- Sodium
- Aluminium
- Cobalt and nickel
- 63
- Hydrogen and oxygen
- Groups and periods
- Eka
- Hydrogen
- Henry Moseley
- 2, 8, 18
- 32
- 18
- 11
- Alkali metals
- 2n²
- 3
- He and Fr
- 39
Question 2.
Define :
(1) Isotopes
Answer:
Atoms of the same element having same atomic number but different atomic masses are known as isotopes.
(2) Periodic properties
Answer:
Properties of the elements which are periodic function of their electronic configuration and are repeated after definite interval of atomic numbers.
OR
Properties which show the regular gradation in the same group (moving from top to bottom) or along a period (moving from left to right) are known as periodic properties.
(3) Valency
Answer:
The valency is the combining capacity of an atom of an element to acquire noble gas configuration.
(4) Atomic radius
Answer:
The distance between the centre of the nucleus and the outermost shell of an isolated atom is called atomic radius.
(5) Metalloids (Semi-metal)
Answer:
Elements which possess intermediate properties of both metals and non-metals are called metalloids or semi-metals.
Question 3.
Fill in the blanks :
- Lithium, sodium and …………………. are the members of Dobereiner’s triad.
- Newlands’ law of octaves is applicable for …………………. elements.
- According to Newlands, …………………. elements occur in nature.
- Mendeleev named scandium as ………………….
- The element known as eka-silicon is ………………….
- The position of cobalt in Mendeleev’s periodic table is prior to ………………….
- If the valency of an element is 2, then it lies in group ………………….
- The electronic configuration of an element is 2, 8, 3, then it is an element of …………………. period.
- In the modern periodic table, noble gases are placed in group ………………….
- Modern periodic table consists of …………………. periods and …………………. groups.
- Position of …………………. in the periodic table is controversial.
- The valency of noble gases is ………………….
- On moving down in any group, the metallic character of the elements ………………….
- Oxides of non-metallic elements are …………………. in nature.
- Oxides of …………………. elements are basic in nature.
Answer:
- potassium
- lighter
- 56
- eka-boron
- germanium
- nickel
- 2
- third
- 18
- 7, 18
- hydrogen
- zero
- increases
- acidic
- metallic
![]()
Question 4.
State whether the following statements are true or false:
- At present, naturally occurring elements are 98.
- The atomic masses of elements form a Dobereiner’s triad are 14 u, 31 u and 74.9 u respectively.
- Calcium, strontium and barium form a Dobereiner’s triad.
- According to the Newlands’ law of octaves, every eighth element had properties similar to that of the first element.
- Sodium is the eighth element after lithium.
- Oxygen is the eighth element after sulphur.
- Phosphorus is tire eighth element after nitrogen.
- Dobereiner’s triads are observed in Newlands’ octaves.
- Mendeleev’s periodic law was based on atomic number of element.
- Molecular formula of oxide of barium is BaO.
- Mendeleev named gallium for eka-silicon.
- An element having atomic number 3.5 can be placed between Be and B.
- There are three valence electrons present in the elements of group I.
- Electrons are filled in K, L and M shells in the elements of the third period.
- Each period starts with the filling of electrons in a new shell.
Answer:
- True
- False
- True
- True
- True
- False
- False
- True
- False
- True
- False
- False
- False
- True
- True
Question 5.
Match the following properly :
(1)
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Dobereiner | a. Law of octaves |
| 2. Newlands | b. Periodic law |
| 3. Mendeleev | c. Modern periodic table |
| 4. Henry Moseley | d. Law of triads |
Answer:
(1-d), (2-a), (3- b), (4 – c).
(2)
| Column I | Column II |
| 1. Li, Na, K | a. Metalloids |
| 2. S, E Cl | b. Noble gases |
| 3. B, Si, Ge | c. Non-metallic elements |
| 4. He, Ne, Ar | d. Metallic elements |
Answer:
(1-d), (2-c), (3-a), (4-b).
Question 6.
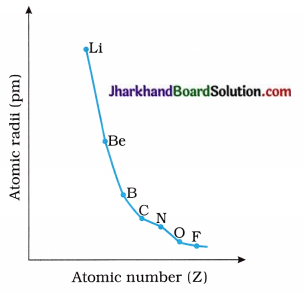
Draw the following graphs :
1. Draw the graph of Atomic radii → Atomic numbers for the elements of second period.
Answer:
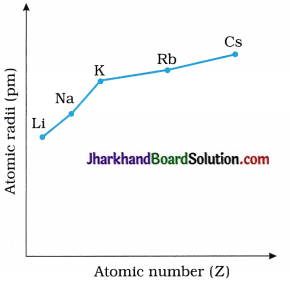
2. Draw the graph of Atomic radii → Atomic numbers for the alkali metal elements.
Answer:
Question 7.
Which one of the following depict the correct representation of atomic radius of an atom?
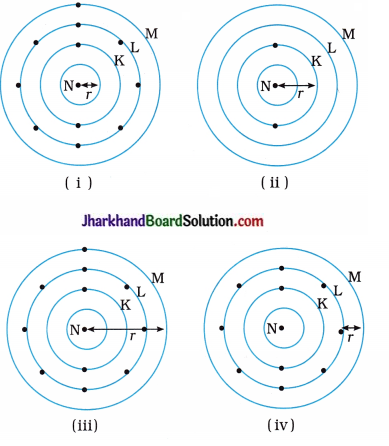
Answer:
(ii) and (iii)
Question 8.
(A) Choose the correct option from those given below each question:
1. For which of the following element, Mendeleev didn’t left gap in his periodic table?
A. Gallium
B. Beryllium
C. Germanium
D. Scandium
Answer:
B. Beryllium
2. Newlands’ law of octaves was found to be applicable upto …………………
A. nickel
B. cobalt
C. phosphorus
D. calcium
Answer:
D. calcium
3. According to Mendeleev’s periodic law, the elements were arranged in the periodic table in the order of…
A. increasing atomic number.
B. decreasing atomic number.
C. increasing atomic masses.
D. decreasing atomic masses.
Answer:
C. increasing atomic masses.
4. The elements Si, B and Ge are …………………
A. metallic elements
B. non-metals
C. metalloids
D. metal, non-metal and metalloid respectively
Answer:
C. metalloids
5. In Mendeleev’s periodic table, gaps were left for the elements to be discovered later. Which of the following elements found a place in the periodic table later?
A. Be
B. Ge
C. Si
D. Se
Answer:
B. Ge
6. The three imaginary elements X, Y and Z represent a Dobereiner’s triad. If the atomic mass of element X is 14 u and that of element Y is 46 u, then the atomic mass of element Z will be …………………
A. 28
B. 60
C. 78
D. 72
[Hint: According to the law of Dobereiner’s triad,
Atomic mass of Y

Answer:
C. 78
7. The atomic numbers of four elements R Q, R and S are 6, 8, 14 and 16 respectively. Out of these, the element known as metalloid is ……….
A. P
B. Q
C. R
D. S
[Hint: Elements in which generally four? electrons are present in outermost shell are called metalloids.]
Answer:
C. R
8. Which of the following statements is correct with regard to the classification of elements?
A. Elements in modern periodic table are arranged on the basis of increasing atomic masses.
B. Elements in modern periodic table are arranged on the basis of decreasing atomic numbers.
C. In modern periodic table, the element nickel of lower atomic mass is kept before the element cobalt of higher atomic mass.
D. In modern periodic table, the isotopes of chlorine having different atomic masses are kept in the same group.
Answer:
D. In modern periodic table, the isotopes of chlorine having different atomic masses are kept in the same group.
9. Which of the following statements about the modern periodic table is correct?
A. It has 18 horizontal rows known as periods.
B. It has 8 vertical columns known as periods.
C. It has 18 vertical columns known as groups.
D. It has 7 horizontal rows known as groups.
Answer:
B. It has 8 vertical columns known as periods.
![]()
10. An element X forms an oxide X2O3. In which : group of Mendeleev’s periodic table is this element placed?
A. Group II
B. Group III
C. Group V
D. Group VIII
Answer:
B. Group III
11. Who proposed the ‘Modern periodic law’ for the modern periodic table?
A. Dobereiner
B. Newlands
C. Henry Moseley
D. Mendeleev
Answer:
C. Henry Moseley
12. Which fundamental particle forms the real basis for the modern classification of elements?
A. Proton
B. Electron
C. Neutron
D. Nucleon
Answer:
A. Proton
13. Which of the following is not correct about the trends when going from left to right across the periods of the periodic table?
A. The elements become more non-metallic in nature.
B. The number of valence electrons increases.
C. The atoms lose their electrons easily.
D. The oxides become more acidic.
Answer:
C. The atoms lose their electrons easily.
14. The electronic configuration of the atom of an element X is 2, 8, 4. In modern periodic table, the element X is placed in
A. Group 2
B. Group 14
C. Group 4
D. Group 8
Answer:
B. Group 14
15. The atomic number of an element is 20. In modern periodic table, this element is placed in ……………..
A. 2nd period
B. 3rd period
C. 1st period
D. 4th period
Answer:
D. 4th period
16. The elements A, B, C, D and E have atomic numbers of 2, 3, 7, 10 and 18 respectively. The elements which belong to the same period of the periodic table are
A. A, B, C
B. B, C, D
C. A, D, E
D. B. D, E
Answer:
B. B, C, D
17. The elements A, B, C, D and E have atomic numbers 9, 11, 17, 12 and 13 respectively. The pair of elements which belong to the same group of the periodic table is ……………..
A. A and B
B. B and D
C. D and E
D. A and C
Answer:
D. A and C
18. Which of the following element would lose an electron easily?
A. Mg
B. Na
C. K
D. Ca
Answer:
C. K
19. Which of the following element will gain an electron easily?
A. Na
B. F
C. Mg
D. Al
Answer:
B. F
20. Where would you place the element with electronic configuration 2, 8 in the modern periodic table?
A. Group 8
B. Group 2
C. Group 18
D. Group 10
Answer:
C. Group 18
21. An element which is an essential constituent of all organic compounds belong to ……………..
A. Group 4
B. Group 10
C. Group 16
D. Group 14
Answer:
D. Group 14
22. Which of the following is the valence shell for the elements of second period of the modern periodic table?
A. M-shell
B. K-shell
C. N-shell
D. L-shell
Answer:
D. L-shell
23. The element which has the maximum number of valence electrons is ……………..
A. 15P
B. 11Na
C. 14Si
D. 13Al
Answer:
A. 15P
24. The correct increasing order of the atomic radii of the elements oxygen, fluorine and nitrogen is ……………..
A. O, F, N
B. N, F, O
C. O, N, F
D. F, O, N
Answer:
D. F, O, N
25. Which one of the following does not increase while moving down the group of the periodic table?
A. Atomic radius
B. Metallic character
C. Valence electrons
D. Basicity of oxides
Answer:
C. Valence electrons
(B) Choose more than one correct options from those given below each question:
1. Mention the drawbacks of Mendeleev’s periodic table.
A. Position of hydrogen
B. Position of isotopes
C. Arrangement of Noble gases
D. Arrangement of more than one elements in the same slot.
Answer:
A, B, C, D
2. Which of the following increase while moving down the group 17 elements?
A. Atomic radius
B. Valence electrons
C. Metallic character
D. Acidity of oxides
Answer:
A, C
3. Which of the following statements are correct for modern periodic table?
A. New elements can be easily arranged.
B. Predictions of properties of the elements become easy.
C. The elements have been divided into metals and non-metals by the thick zig-zag line running diagonally across the periodic table.
D. Atomic volume of elements decreases on moving down in the group.
Answer:
A, B, C
4. The electronic configuration of the atom of an element is 2, 8, 7. In this reference, which of the following statements are correct?
A. This element belong to group 17.
B. This element has a tendency to gain one electron.
C. This element belongs to fourth period.
D. The element fluorine is placed above this element.
Answer:
A, B, D
(C) In each of the following questions, a statement of Assertion A is given, followed by a Reason R. Read the statements carefully and choose the correct option as under:
A. Assertion A and reason R are true, and reason R is the correct explanation of assertion A.
B. Assertion A and reason R are true, but reason R is not the correct explanation of assertion A.
C. Assertion A is corret but reason R is false.
D. Assertion A is false but reason R is true.
1. Assertion A: The position of hydrogen in modern periodic table is a matter of controversy.
Reason R : The properties of hydrogen resembles with the properties of alkali metals and halogens.
Answer:
A. Assertion A and reason R are true, and reason R is the correct explanation of assertion A.
2. Assertion A: In the modern periodic table, metallic character of elements increases on moving down the group.
Reason R: In the modern periodic table, the elements are arranged in order of their increasing atomic masses.
Answer:
C. Assertion A is corret but reason R is false.
3. Assertion A : Newlands arranged the then known elements in order of musical notes.
Reason R: According to Newlands, proton is responsible for the arrangement of elements in the periodic table.
Answer:
C. Assertion A is corret but reason R is false.
4. Assertion A : Chemical reactivity of the element of group 18 is very less.
Reason R : Their outermost shell is completely filled with electrons.
Answer:
A. Assertion A and reason R are true, and reason R is the correct explanation of assertion A.
![]()
Value Based Questions With Answers
Question 1.
Six elements of periodic table A, B, C, D, E and F have atomic numbers of 2, 12, 20, S 18, 4 and 10 respectively (where A, B, C,? D, E and F are not the chemical symbols of s these elements). Based on this information, answer the following questions :
(1) Which of these elements belong to the same groups of the periodic table? Why?
(2) Which of these elements belong to the same periods of the periodic table? Why?
(3) Which of these elements are (i) metals and (ii) non-metals?
(4) Which of these elements are chemically (i) reactive and (ii) unreactive?
(5) What values are indicated in a student in answering the above questions?
Answer:
First of all, write the electronic configurations? of all the given six elements as follows :
| Element | Atomic number | Electronic configuration | |||
| K | L | M | N | ||
| A | 2 | 2 | |||
| B | 12 | 2 | 8 | 2 | |
| C | 20 | 2 | 8 | 8 | 2 |
| D | 18 | 2 | 2 | 8 | |
| E | 4 | 2 | 8 | ||
| F | 10 | 2 | 8 | ||
(1) (i) Elements B, C and E belong to the s group 2 of the periodic table because all of them have an equal number of valence electrons equal to 2.
(ii) Elements A, D and F also belong to the group 18 because they are all inert gases having completely filled outermost electron shells with 8 valence electrons.
(2) (i) Element B (2, 8, 2) and element D (2, 8, 8) belong to the third period because they both have 3 electron shells – K, L and M each.
(ii) Element E (2, 2) and element F (2, 8) belong to the second period because they both have 2 electron shells – K and L each.
(3) (i) Elements B, C and E belonging to group 2 are metals.
(ii) Elements A, D and F belonging to group 18 are non-metals (noble gases).
(4) (i) Elements B, C and E of group 2 are chemically reactive elements.
(ii) Elements A, D and F of group 18 are chemically unreactive elements.
(5) Answering these questions by a student are indicating awareness towards modern periodic classification of the elements and ability to apply his knowledge in solving the related questions.
Question 2.
In his periodic table, Mendeleev arranged all the then known 63 elements in the order of increasing atomic masses in horizontal rows but in such a way that elements having similar properties came directly under one another in the same vertical column. In the classification of the then known elements, Mendeleev was guided mainly by two factors.
In order to make sure that the elements having similar properties fall in the same vertical column, Mendeleev left some gaps in his periodic table. Though leaving gaps in the periodic table was considered to be a drawback of his classification of elements at that time but Mendeleev was firm on his decision.
Answer the following questions:
(1) What are the horizontal rows of Mendeleev’s periodic table known as? How many horizontal rows of elements were there in Mendeleev’s periodic table?
(2) What are the vertical columns of Mendeleev’s periodic table known as? How many vertical columns were there? in Mendeleev’s periodic table?
(3) What were the similar properties used by Mendeleev to classify the then known elements into vertical columns?
(4) What were the two main guiding factors for Mendeleev in the classification of the then known elements?
(5) For what purpose were some gaps left by Mendeleev in his periodic table? Does the modern periodic table also have the 5 gaps left by Mendeleev?
(6) What values were displayed by Mendeleev in presenting his classification of elements?
Answer:
(1) The horizontal rows of elements in the Mendeleev’s periodic table are called periods. There were seven periods in s Mendeleev’s periodic table.
(2) The vertical columns of Mendeleev’s periodic table are called groups. There were eight groups in Mendeleev’s periodic s table.
(3) The similar properties used by Mendeleev to classify the elements into vertical columns were the similar formulae of S their oxides and hydrides.
(4) The two main guiding factors for Mendeleev in the classification of the then known elements were
- increasing t order of atomic masses
- grouping together the elements having similar properties.
(5) These gaps were left for the elements which had not been discovered at that time. He thought that these elements would be discovered later in future. The modern periodic table does not have any gaps.
(6) The various values displayed by Mendeleev were-
- self-confidence
- courage
- foresight
- prophecy.
Question 3.
There are three elements X, Y and Z having atomic numbers of 6, 16 and 19 respectively. Based on this information, Het has been asked to answer the following questions :
(1) In which group of the periodic table would you expect to find (i) element X (ii) element Y and (iii) element Z?
(2) Which two elements will form ionic bonds? Why?
(3) What will be the formula of ionic compound formed?
(4) Which two elements will form covalent bonds? Why?
(5) What will be the formula of covalent compound formed?
(6) What values are displayed by Het in answering the above questions?
Answer:
In order to answer these questions, Het first wrote down the electronic configurations of the elements X, Y and Z by using their atomic numbers, as follows :
| Element | Atomic number | Electronic configuration | |||
| K | L | M | N | ||
| X | 6 | 2 | 4 | ||
| Y | 16 | 2 | 8 | 6 | |
| Z | 19 | 2 | 8 | 8 | 1 |
(1) (i) Element X has 4 valence electrons in its atom, so it will be placed in group 4 + 10 = 14 of the modern periodic table.
(ii) Element Y has 6 valence electrons in its atom, so it will be placed in group 6 + 10 = 16 of the modern periodic table.
(iii) Element Z has 1 valence electron in its atom, so it will be placed in group 1 of the modern periodic table.
(2) An ionic bond is formed between a metal element and a non-metal element. Here, the elements Z and Y will combine to form ionic bond.
(3) The element Z has 1 valence electron, so its valency is +1 (after losing this electron). The element Y need two electrons to complete its octet. So, element Y will gain two electrons and form Y2- ion. Here, two Z+ ions will combine with one Y-2 ion, so that the formula of ionic compound formed will be Z2Y.
(4) A covalent bond is formed between two non-metallic elements. Here, element X of group 14 is a non-metal and element Y of group 16 is also a non-metal. Therefore, the elements X and Y will combine together to form covalent bonds.
(5) The element X has 4 valence electrons, so its valency is 4. The element Y has 6 valence electrons, so its valency is 2. So, one atom of element X will combine with two atoms of element Y to form a covalent compound having the formula XY2.
(6) The values displayed by Het in answering these questions are (1) knowledge of modern classification of elements, and (2) understanding of periodic table.
Practical Skill Based Questions With Answers
Question 1.
Complete the following cross-word puzzle :
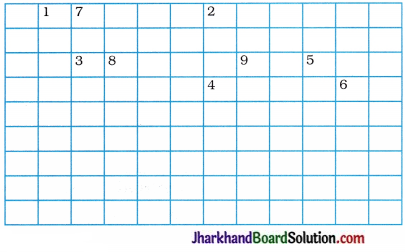
Across:
(1) An element with atomic number 12.
(3) Metal used in making cans and member of group 14.
(4) A lustrous non-metal which has 7 electrons ; in its outermost shell.
Down:
(2) Highly reactive and soft metal which imparts yellow colour when subjected to flame and is kept in kerosene.
(5) The first element of second period.
(6) An element which is used in making fluorescent bulbs and is second member of group 18 in the modern periodic table.
(7) A radioactive element which is the last member of halogen family.
(8) Metal which is an important constituent of steel and forms rust when exposed to moist air.
(9) The first metalloid in modern periodic table whose fibres are used in making bullet-proof vests.
Answer:

Question 2.
In this ladder, symbols of elements are jumbled up.
(a) Rearrange these symbols of elements in the increasing order of their atomic numbers in the periodic table.
(b) Arrange them in the order of their group also.
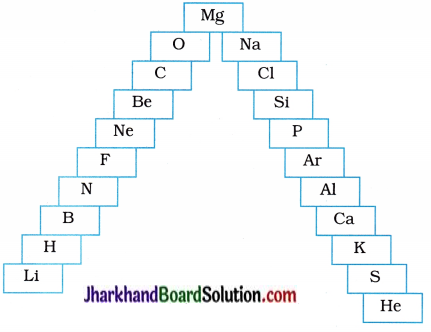
Answer:
(a) H, He, Li, Be, B, C, N, O, F, Ne, Na, Mg, Al, Si, E S, Cl, Ar, K, Ca.
(b)
| Group | Elements |
| 1 | H, Li, Na, K |
| 2 | Be, Mg, Ca |
| 13 | B, Al |
| 14 | C, Si |
| 15 | N, P |
| 16 | O, S |
| 17 | F, Cl |
| 18 | He, Ne, Ar |
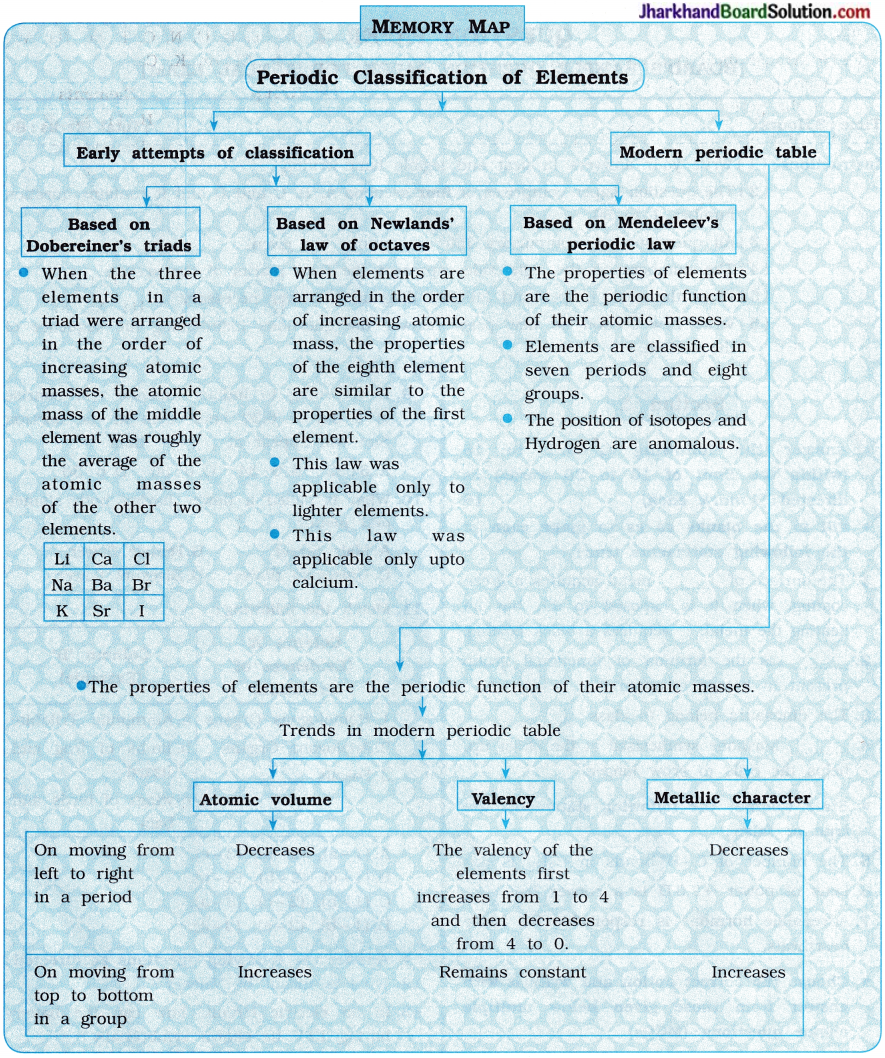
Memory Map