Jharkhand Board JAC Class 10 Science Solutions Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
JAC Board Class 10 Science Solutions Chapter 2 Acids, Bases and Salts
Jharkhand Board Class 10 Science Acids, Bases and Salts Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
A solution turns red litmus blue; its pH is likely to be…
(a) 1
(b) 4
(c) 5
(d) 10
Answer:
10
Question 2.
A solution reacts with crushed egg-shells to give a gas that turns lime water milky. The solution contains …
(a) NaCl
(b) HCl
(c) LiCl
(d) KCl
Answer:
HCl
Question 3.
10 mL of a solution of NaOH is found to be completely neutralised by 8 mL of a given solution of HC1. If we take 20 mL of the same solution of NaOH, the amount of HC1 solution (the same solution as before) required to neutralise it will be…
(a)4mL
(b) 8 mL
(c) 12mL
(d) 16 mL
Answer:
16 mL
[Hint: Here, 10 mL NaOH neutralises 8 mL HCl
∴ 20 mL NaOH is neutralised by = \(\frac{20 \mathrm{~mL} \times 8 \mathrm{~mL}}{10 \mathrm{~mL}}\) = 16 mL]
Question 4.
Which one of the following types of medicines is used for treating indigestion?
(a) Antibiotic
(b) Analgesic
(c) Antacid
(d) Antiseptic
Answer:
Antacid
Question 5.
Write word equations and then balanced equations for the reaction taking place when…
(a) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with zinc granules.
(b) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with magnesium ribbon.
(c) dilute sulphuric acid reacts with aluminium powder.
(d) dilute hydrochloric acid reacts with iron filings.
Answer:
(a) Zinc granules + Dilute sulphuric acid → Zinc sulphate + Hydrogen gas
Zn(s) + H2SO4(aq) → ZnSO4(aq) + H2(g)
(b) Magnesium + Dilute hydrochloric acid → Magnesium chloride + Hydrogen gas
Mg(s) + 2HCl(aq) → MgCl2(aq) + H2(g)
(c) Aluminium + Dilute sulphuric acid → Aluminium sulphate + Hydrogen gas
2Al(s) + 3H2SO4(aq) → Al2(SO4)3(aq) + 3H2(g)
(d) Iron + Dilute hydrochloric acid → Iron chloride + Hydrogen gas
Fe(s) + 2HCl(aq) → FeCl2(aq) + H2(g)
![]()
Question 6.
Compounds such as alcohols and glucose also contain hydrogen but are not categorised as acids. Describe an activity to prove it.
Answer:
Arrange the apparatus as shown in figure 2.3. Add an aqueous solution of alcohol (ethanol) in a beaker and record the observation. Thereafter, add solution of glucose instead of alcohol and record the observation.
Observation : Bulb does not glow for both the solutions, which indicate that electric current is not flowing through both the solutions.
This experiment shows that ethanol and glucose do not ionise and do not release H+ ions while in the solution of acids, H+ ions are released and allow an electric current to flow through the solution.
Thus, eventhough alcohol and glucose contain hydrogen but are not categorised as acids.
Question 7.
Why does distilled water not conduct : electricity whereas rain water does ?
Answer:
Distilled water is a pure water and it does not contain ions while rain water contains impurities like acid, which provides ions and they help in carrying electricity.
Question 8.
Why do acids not show acidic behaviour in the absence of water?
Answer:
Acids cannot release H+(aq) ions in absence of water. H+ ions are responsible for acidic character. So acids cannot release H+(aq) ions in absence of water and it does not exhibit acidic character.
Question 9.
Five solutions A, B, C, D and E, when tested with universal indicator showed pH as 4, 1, 11, 7 and 9 respectively. Which solution is …
(a) neutral? (b) strongly alkaline? (c) strongly acidic? (d) weakly acidic? (e) weakly alkaline?
Arrange the pH in increasing order of hydrogen-ion concentration.
Answer:
(i)
- Solution ‘D’ is neutral, as its pH value is 7.
- Solution ‘C’ is strongly alkaline, as its pH value is 11 (Highest pH).
- Solution ‘B’ is strongly acidic as its pH value is 1 (lowest pH).
- Solution ‘A’ is weakly acidic as its pH value is 4. S
- Solution ‘E’ is weakly alkaline as its pH value is 9.
(ii) Increasing order of H+ ion concentration based on the pH values is as follows :
pH : 11 < 9 < 7 < 4 < 1
Concentration of H+ ion = [H+ (aq)] :
10-11M < 10-9M < 10-7M < 10-4M < 10-1M
Solution :
C < E < D < A < B
Question 10.
Equal lengths of magnesium ribbons are taken in test tubes A and B. Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is added to test tube A; while acetic acid (CH3COOH) is added to test tube B. Amount and concentration taken for both the acids are same. In which test tube will the fizzing occur more vigorously and why?
Answer:
Hydrochloric acid (HCl) is a stronger l acid than acetic acid (CH3COOH). Hence, < more vigorous fizzing will occur in test tube A. Here, HC1 being a strong acid s undergoes complete ionisation giving more H+ ions.
Question 11.
Fresh milk has a pH of 6. How do you think the pH will change as it turns into curd? Explain your answer.
Answer:
When milk changes into curd, it produces lactic acid. Lactic acid is more acidic than milk, therefore, the value of pH decreases and curd tastes sour.
Question 12.
A milk man adds a very small amount of baking soda to fresh milk.
(a) Why does he shift the pH of the fresh milk from 6 to slightly alkaline ?
(b) Why does this milk take a long time to set as curd ?
Answer:
(a) When a very small amount of baking soda is added to fresh milk, then the pH value of the milk increases beyond 6, since baking soda possesses basic character and alkaline medium does not allow milk to turn sour quickly.
(b) Milk turns basic by adding a small quantity of baking soda in it and lactic acid of milk is neutralised. Therefore, milk takes a longer time to set as a curd.
![]()
Question 13.
Plaster of parts should be stored in a moisture-proof container. Explain why?
Answer:
Plaster of paris should be stored in a moisture-proof container, because it absorbs moisture and sets into hard solid mass called gypsum. As a result, it loses the characteristics of plaster of paris.
Question 14.
What is a neutralisation reaction ? Give two examples.
Answer:
The reaction between an acid and a base to form a salt and water is called a neutralisation I; reaction.
For example,
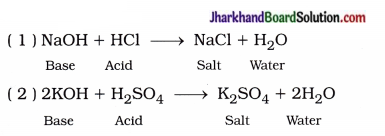
In short, neutralisation reaction can be S’ represented as follows:
Acid + Base → Salt + Water
Question 15.
Give two important uses of washing soda and baking soda.
Answer:
Uses of washing soda:
- Washing soda is used in glass, soap, textile and paper industry.
- It is used for removing permanent hardness of water.
Uses of baking soda :
- Baking soda is used as an antacid and as disinfectant.
- It is used in soda-acid fire-extinguishers.
Jharkhand Board Class 10 Science Acids, Bases and Salts InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
You have been provided with three test tubes. One of them contains distilled water and the other two contain an acidic solution and a basic solution respectively. If you are given only red litmus paper, how will you identify the contents of each test tube?
Answer:
Take three test tubes and label them as A, B and C. Add one drop of solution from test tubes A, B and C on the red litmus paper separately. The solution of a test tube which turns red litmus paper to blue contains a base.
Now, tire remaining two test tubes contain acid and distilled water. Use the above blue litmus paper to test the solution of remaining two test tubes. Add one drop of solution from two test tubes on blue litmus paper separately. The solution of a test tube which turns blue litmus paper to red contains an acid.
The solution of a test tube which does not change either red or blue litmus paper contains distilled water. Thus, solutions of three test tubes can be tested.
Question 2.
Why should curd and sour substances not to be kept in brass and copper vessels?
Answer:
Curd and sour substances are acidic in nature, which react with brass and copper vessels and form toxic substances; which are harmful to the human body.
Therefore, curd and other sour substances should not be kept in brass and copper vessels.
Question 3.
Which gas is usually liberated when an acid reacts with a metal? Illustrate with an example. How will you test for the presence of this gas?
Answer:
Reaction of a metal with an acid liberates hydrogen gas.
For example,
Zn(s) + 2HCl(aq) → ZnCl2(aq) + H2(g)
The presence of hydrogen gas can be tested by bringing a burning candle or match-stick near the mouth of the test tube, in which hydrogen gas is collected. The hydrogen gas burns with a popping sound.
Question 4.
A metal compound ‘A’ reacts with dilute hydrochloric acid to produce effervescence. The gas evolved extinguishes a burning candle. Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction, if one of the compounds formed is calcium chloride.
Answer:
The compound of metal ‘A’ is CaCO3.
Gas formed is CO2.
Balanced chemical equation:
CaCO3(s) + 2HCl(aq) → CaCl2(aq) + CO2(g) + H2O(1)
Question 5.
Why do HCl, HNO3, etc. show acidic characters in aqueous solutions while solutions of compounds like alcohol and glucose do not show acidic character?
Answer:
HCl, HNO3, etc. release H+ions in their aqueous solutions. Hence, their solutions show acidic character. While alcohol and glucose do not release H+ ions in their aqueous solutions. So, their aqueous solutions are not acidic.
Question 6.
Why does an aqueous solution of an acid conduct electricity?
Answer:
when an acid dissolves in water to form a solution, it ionises forming ions, which carry electricity.
Question 7.
Why does dry HCl gas not change the colour of the dry litmus paper?
Answer:
Dry HCl gas does not release H+ ions, so it does not possess acidic character and it does not impart any effect on dry litmus paper. As a result, the colour of the dry litmus paper does not change.
Question 8.
While diluting an acid, why is it recommended that the acid should be added to water and not water to the acid.
Answer:
When water is added to a concentrated ? acid for dilution, the heat generated may cause the mixture to splash out and may cause burns. The glass container may also break due to excessive local heating.
Therefore, for dilution of concentrated acid, instead of adding water to acid, acid is added s slowly to water with constant stirring. Hence, liberated heat energy during dilution will spread in water and does not cause harm.
Question 9.
How is the concentration of hydronium ion (H3O+) affected when a solution of an acid s is diluted?
Answer:
when the acid solution is diluted, the concentration of hydronium ions (H3O+) per unit volume decreases.
Question 9.
How is the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH–) affected when excess base is dissolved in a solution of sodium hydroxide ?
Answer:
when excess of water is added to the solution of sodium hydroxide (NaOH), i.e., solution is diluted, the concentration of hydroxide ions (OH–) per unit volume decreases.
![]()
Question 10.
You have two solutions, A and B. The pH of solution A is 6 and pH of solution B is 8. Which solution has more hydrogen ion concentration? Which of this is acidic and which one is basic?
Answer:
The pH value of solution A is 6.
∴ It is acidic and has higher concentration of hydrogen ions. (about 10-6 M)
The pH value of solution B is 8.
∴ It is basic and having lower concentration of hydrogen ions. (about 10-8M)
Question 11.
What effect does the concentration of H+(aq) ions have on the nature of the solution?
Answer:
A solution has higher concentration of H+(aq) ions (more than 10-7) is acidic in nature and the solution has lower concentration of H+ ions (less than 10-7 M) is basic in nature.
Question 12.
Do basic solutions also have H+(aq) ions? If yes, then why are these basic?
Answer:
Yes, basic solutions also possesses H+ ions, but due to more number of OH– ions than H+ ions they are basic in nature.
Question 13.
Under what soil condition do you think a farmer would treat the soil of his fields with quick lime (calcium oxide) or slaked lime (calcium hydroxide) or chalk (calcium carbonate)?
Answer:
The soil having pH value less than 6.5 is called acidic soil. Now to make this soil neutral, the farmers add basic substances such as quick lime, slaked lime or chalk to the soil.
Question 14.
What is the common name of the compound CaOCl2?
Answer:
The common name of CaOCl2 is bleaching powder.
Question 15.
Name the substance which on treatment with chlorine yields bleaching powder.
Answer:
Calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2) reacts with chlorine to form bleaching powder.
Ca(OH)2 + Cl2 → CaOCl2 + H2O
Question 16.
Name the sodium compound which is used for softening hard water.
Answer:
Sodium carbonate – Na2CO3.
Question 17.
What will happen if a solution of sodium hydrogencarbonate is heated? Give the equation of the reaction involved.
Answer:
The solution of sodium hydrogen- carbonate, on heating forms sodium carbonate, water and carbon dioxide.
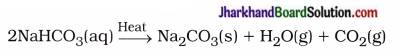
Question 18.
Write an equation to show the reaction between plaster of paris and water.
Answer:
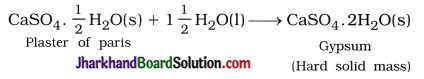
Activity 2.1 [T. B. Pg. 18]
Aim : To test acids and bases in the laboratory.
Activity:
1. Collect the solutions of hydrochloric acid (HCl), sulphuric acid (H2SO4), nitric acid (HNO3), acetic acid (CH3COOH), sodium hydroxide (NaOH), potassium hydroxide (KOH), calcium hydroxide (Ca(OH)2), magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2) and ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH) from the laboratory.
2. Put a drop of each of the above solution on a watch-glass and test with a drop of the indicators as shown in Table 1.
3. Observe the colour change with red litmus paper, blue litmus paper, phenolphthalein and methyl orange solution for each of the sample solution.
4. Write your observations in Table 1.
| Sample solution | Red litmus solution (or paper) | Blue litmus solution (or paper) | Phenolphthalein solution | Methyl orange solution |
| HCl | No colour change | Red | Colourless | Red |
| H2SO4 | No colour change | Red | Colourless | Red |
| HNO3 | No colour change | Red | Colourless | Red |
| CH3COOH | No colour change | Red | Colourless | Red |
| NaOH | Blue | No colour change | Pink | Yellow |
| KOH | Blue | No colour change | Pink | Yellow |
| Ca(OH)2 | Blue | No colour change | Pink | Yellow |
| Mg(OH)2 | Blue | No colour change | Pink | Yellow |
| NH4OH | Blue | No colour change | Pink | Yellow |
Activity 2.2 [T. B. Pg. 18-19]
Aim: To test acids and bases using olfactory > indicators.
Activity:
- Take some finely chopped onions in a plastic bag along with some strips of clean cloth. Tie up the bag tightly and leave overnight in the fridge. The cloth strips can now be used to test for acids and bases.
- Take two of these cloth strips and check their odour.
- Keep them on a clean surface and put a few drops of dilute HCl solution on one strip and a few drops of dilute NaOH solution on the other.
- Rinse both cloth strips with water and again check their odour.
- Note your observations.
- Now take some dilute vanilla extract and clove oil and check their odour.
- Take some dilute HC1 solution in one test tube and dilute NaOH solution in another. Add a few drops of dilute vanilla extract to both test tubes and shake well. Check the odour once again and record changes in odour, if any.
- Similarly, test the change in the odour of clove oil with dilute HC1 and dilute NaOH solutions and record your observations.
Questions :
Question 1.
Which among the vanilla extract, onion and clove oil can be used as olfactory indicator?
Answer:
Vanilla extract, onion and clove oil can be used as olfactory indicators.
Question 2.
What change in odour do you observe when vanilla extract, onion and clove oil are mixed with dilute HCl and dilute NaOH solutions separately?
Answer:
When dilute HCl solution is added in vanilla extract, onion and clove oil separately, their odour remains unchanged, but adding dilute NaOH solution separately in vanilla extract, onion and clove oil, their odour disappears.
Activity 2.3 [T .B. Pg. 19]
Aim: Testing of hydrogen gas formed by the reaction of zinc granules with dilute sulphuric acid (H2SO4).
Caution: This activity needs the teacher’s assistance.
Activity:
- Arrange the apparatus as shown in the figure 2.1.
- Take about 5 mL of dilute sulphuric acid in a test tube and add a few pieces of zinc granules to it.
- What do you observe around the surface of zinc granules?
- Pass the gas being evolved through the soap solution.
- Why are bubbles formed in the soap solution?
- Take a burning candle near a gas filled in bubbles.
- What do you observe?
- Repeat this activity with some more acids like HCl, HNO3 and CH3COOH.
- Are the observations in all the cases the same or different?
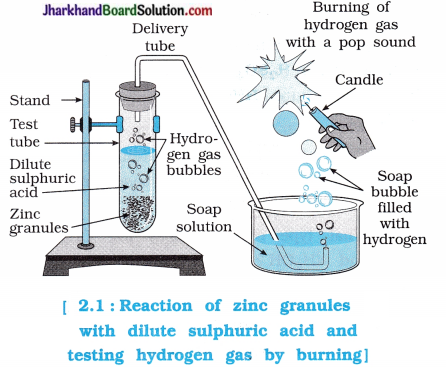
- In above reactions, metal displace hydrogen gas from acid.
- In short, when metal reacts with an acid forms salt and evolves H2 gas.
Metal + Acid → Salt + Hydrogen gas
Questions :
Question 1.
What do you observe around the surface l of zinc granules?
Answer:
Hydrogen gas is bubbled around the surface of zinc granules.
Question 2.
Why are bubbles formed in the soap? solution?
Answer:
Zinc granules reacts with H2SO4 forming hydrogen gas which, when passed through the solution of soap form bubbles.
![]()
Question 3.
What happens, when a burning candle is brought near the hydrogen gas?
Answer:
When a burning candle is brought near the s hydrogen gas, it burns with a popping sound.
Question 4.
Does zinc metal liberate hydrogen gas with dilute HCl, dilute HNO3 and CH3COOH solution? Mention it with equations of? chemical reactions.
Answer:

Question 5.
Write the balanced chemical equation of ( reaction of zinc metal with dilute H2SO4.
Answer:
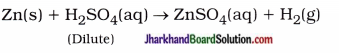
Activity 2.4 [T. B. Pg. 20]
Aim : To study the reaction of a base with metal.
Activity:
- Take a few pieces of granulated zinc metal in a test tube.
- Add about mL of sodium hydroxide solution in it and warm the mixture of the test tube.
- Repeat the rest of the steps as in Activity 2.3 and record your observations.
Questions :
Question 1.
Which gas is liberated when zinc metal reacts with sodium hydroxide solution?
Answer:
Hydrogen gas
Question 2.
State the molecular formula of sodium zincate.
Answer:
Na2ZnO2
Question 3.
Give the balanced chemical equation for the reaction of zinc with sodium hydroxide solution.
Answer:
Zn(s) + NaOH(aq) → Na2ZnO2(s) + H2(g)
Activity 2.5 [T. B. Pg. 20]
Aim : To study the reaction of metal carbonates and metal hydrogencarbonates with acids.
Activity :
- Take two test tubes, label them as A and B.
- Take about 0.5 g of sodium carbonate (Na2CO3 in test tube A 0.5 g of sodium hydrogencarbonate (NaHCO3) in test tube B.
- Add about 2mL of dilute HCl to both the test tubes.
- What do you observe?
- Pass the carbon dioxide gas formed into calcium hydroxide solution as shown in figure 2.2 and record your observations.
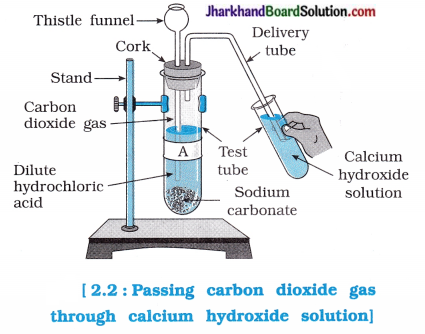
Questions :
Question 1.
Which gas is evolved, when sodium carbonate and sodium hydrogencarbonate are treated with HCl?
Answer:
Carbon dioxide gas
Question 2.
Write the general word equation for the above activity.
Answer:

Question 3.
What is the common name of Ca(OH)?
Answer:
Lime water
Question 4.
What is the solubility of Ca(HCO3)2 in water?
Answer:
Ca(HCO3)2 is highly soluble in water.
Activity 2.6 [T. B. Pg. 21]
Aim : To study the reaction takes place between acids and bases.
Activity:
- Take about mL of dilute NaOH solution in a test tube. Add two drops of phenolphthalein and observe the colour change.
- Add dilute HCl solution to the above solution drop by drop.
- Is there any colour change for the reaction mixture?
- Why did the colour of phenolphthalein change after the addition of an acid?
- Now add a few drops of NaOH to the above mixture.
- Does the pink colour of phenolphthalein reappear?
Questions:
Question 1.
What happens when an indicator phenolphthalein is added to NaOH solution?
Answer:
NaOH solution becomes pink.
Question 2.
What happens when few drops of HCl are added in the solution of NaOH and phenolphthalein indicator?
Answer:
Pink colour disappears.
Question 3.
Write only the name of the reaction occurring between acid and base.
Answer:
Neutralisation reaction.
Question 4.
Write an equation for a neutralisation reaction.
Answer:
NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + HO(l)
Activity 2.7 [T. B. Pg. 21]
Aim : To study the reaction of metal oxide with an acid.
Activity:
- Take a small amount of copper oxide in a beaker.
- Add dilute hydrochloric acid slowly while stirring.
- Note the colour of the solution. What has happened to the copper oxide?
Questions:
Question 1.
State the colour of powder of copper oxide.
Answer:
The powder of copper oxide is black.
Question 2.
What would be the colour of solution when dilute hydrochloric acid is added to copper oxide?
Answer:
Blue-green.
Question 3.
State the reason of blue-green colour of the solution.
Answer:
The blue-green colour of the solution is due to the formation of copper (II) chloride in the reaction between copper oxide and hydrochloric acid.
![]()
Question 4.
Write the molecular formula of copper (II) chloride.
Answer:
CuCl2
Question 5.
State the general equation of reaction that occurs between a metal oxide and an acid.
Answer:
Metal oxide + Acid → Salt + Water
Activity 2.8 [T. B. Pg. 22]
Aim : To study the conduction of electricity by aqueous solutions of acids and bases.
Activity:
- Arrange the apparatus as shown in the figure 2.3.
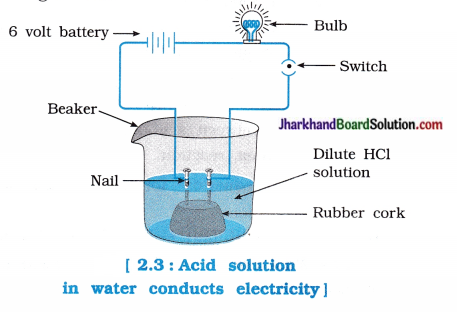
- In the given arrangement, when solutions of different compounds are added in the beaker separately, following observations were recorded :
| Solution | Bulb | Reason |
| 1. HCl | Glows | H+ ions released |
| 2. H2SO4 | Glows | H+ ions released |
| 3. Glucose (C6H12O6) | Does not | H+ or OH– ions are not released. |
| 4. Alcohol (C2H5OH) | glow | H+ or OH– ions are not released. |
| 5. NaOH | Does not glow | OH– ions released |
| 6. Ca(OH)2 | Glows | OH– ions released |
Questions :
Question 1.
What does the glowing of bulb indicate?
Answer:
Glowing of bulb indicates that electric current is passing through the solution.
Question 2.
By whom is the electric current carried through the solution?
Answer:
The electric current is carried through the solution by ions.
Question 3.
Mention the ions responsible for acidic and basic character of the compound.
Answer:
H+ ions in an aqueous solution are responsible for acidic character, while OH” ions in an aqueous solution are responsible for basic character.
Activity 2.9 [T.B.Pg.23]
Aim : To test that dry HC1 gas is not acidic but its aqueous solution is acidic.
Activity:
- Take about 1 g solid NaCl in a clean and dry test tube and set up the apparatus as shown in figure .4.
- Add some concentrated sulphuric acid to the test tube.
- What do you observe? Is there a gas coming out of the delivery tube?
- Test the gas evolved successively with dry and wet blue litmus paper.
- In which case does the litmus paper change colour?
- On the basis of the above activity, what do you infer about the acidic character of: (i) dry HCl gas and (ii) HCl solution?
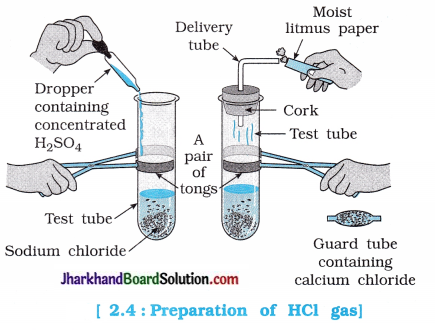
Questions:
Question 1.
Does the separation of H+ ions from HCl molecules occur in the absence of water?
Answer:
No
Question 2.
How are the hydrogen ions always represented?
Answer:
Hydrogen ions are always represented by H+(aq) or H3O+ (hydronium ion).
Question 3.
Which ion is responsible to represent the basic character of an aqueous solution?
Answer:
OH+ ion.
Question 4.
Mention the solubility of alkali (base) in water.
Answer:
Alkalis (base) are soluble in water.
Question 5.
Give two examples of alkali (base).
Answer:
NaOH, KOH
Question 6.
State the properties of alkalis (base).
Answer:
Alkalis are soapy in touch, bitter in taste and corrosive.
Question 7.
State the general equation for neutralisation reaction.
Answer:
Acid + Base → Salt + Water
or
HX + MOH → MX + H2O
Activity 2.10 [T. B. Pg. 24]
Aim: To demonstrate that dilution of a strong acid and a strong base is exothermic.
Activity:
- Take 10 mL water in a beaker.
- Add a few drops of concentrated H2SO4 to it and swirl the beaker slowly.
- Touch the base of the beaker.
- Is there a change in temperature?
- Is this an exothermic or an endothermic process?
- Repeat the above activity with sodium hydroxide pellets and record your observations.
Questions:
Question 1.
Name the process of dissolving an acid or a base in water.
Answer:
Exothermic reaction
Question 2.
What change occurs in concentration of solution by adding water to an acid or a base?
Answer:
Concentration of solution decreases.
Activity 2.11 [T. B. Pg. 26]
Aim : To test the pH values of given solutions, s
Activity:
Test the pH values of the following solutions :
- Saliva (before meal)
- Saliva (after meal)
- Lemon juice
- Colourless aerated drink
- Carrot juice
- Coffee
- Tomato juice
- Tap water
- 1 M NaOH
- 1 M HCl
| Solution | Colour of pH paper | Approxi-mate pH value | Nature of substance |
| 1. Saliva (before meal) | Light green | 7.4 | Basic |
| 2. Saliva (after meal) | Light yellow | 5.8 | Acidic |
| 3. Lemon juice | Pink-red | 2.5 | Acidic |
| 4. Colourless aerated drink | Light yellow | 6.0 | Acidic |
| 5. Carrot juice | Light orange | 4.0 | Acidic |
| 6. Coffee | Orange yellow | 5.0 | Acidic |
| 7. Tomato juice | Dark orange | 4.1 | Acidic |
| 8. Tap water | Green | 7.0 | Neutral |
| 9. 1M NaOH | Dark blue | 13-14 | Basic |
| 10. 1MHCl | Red | 1.0 | Acidic |

Activity 2.12 [T. B. Pg. 27]
Aim: To find the pH value of the soil.
Activity:
- Take about g soil in a test tube and add 5 mL water to it.
- Shake the test tube, filter the contents and collect the filtrate in a test tube.
- Check the pH of this filtrate with the help of universal indicator paper.
Questions :
Question 1.
Filtrate in a test tube turns red litmus to blue. What does it indicate about sample of soil?
Answer:
The sample of soil possess basic property.
Question 2.
What would be the property of soil having pH value less than 5.6?
Answer:
The soil possess acidic property.
Question 3.
How will you neutralise the acidic and basic soil?
Answer:
Add base like lime to neutralise the acidic soil and add acid like gypsum to neutralise the basic soil.
Question 4.
What should be the pH value of soil for healthy growth and development of plants?
Answer:
The soil should have pH value between 6.5 to 7.3.
Activity 2.13 [T. B. Pg. 28 – 29]
Aim: Identify the acids and bases required to form the given salts.
Activity:
Some salts are given in the following table. Identify the required acids and bases to form the salts :
Table 3
| Name of the Salt | Formula of the salt | Acid required | Base required |
| 1. Potassium sulphate | K2SO4 | H2SO4 | KOH |
| 2. Sodium sulphate | Na2SO4 | H2SO4 | NaOH |
| 3. Calcium sulphate | CaSO4 | H2SO4 | Ca(OH)2 |
| 4. Magnesium sulphate | MgSO4 | H2SO4 | Mg(OH)2 |
| 5. Copper sulphate | CuSO4 | H2SO4 | CU(OH)2 |
| 6. Sodium chloride | NaCl | HCl | NaOH |
| 7. Sodium nitrate | NaNO3 | HNO3 | NaOH |
| 8. Sodium carbonate | Na2CO3 | H2CO3 | NaOH |
| 9. Ammonium chloride | NH4Cl | HCl | NH4OH |
Questions:
Question 1.
What is called family of salt?
Answer:
Salts having the same positive or negative radicals (ions) are said to be family of salt.
Question 2.
Give examples of family of sodium salts.
Answer:
NaCl, NaSO4, Na2CO3, etc. are family of sodium salts.
Question 3.
State the examples of family of chloride salts.
Answer:
NaCl. KCl, NH4Cl, etc. are family of chloride salts.
Activity 2.14 [T. B. Pg. 29]
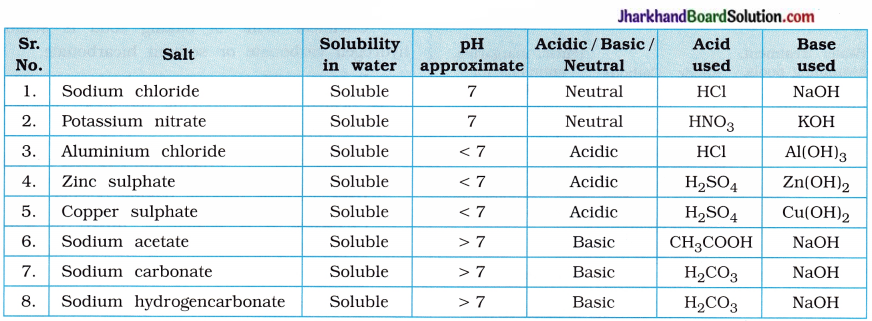
Aim: To find the pH and test the solubility of salt in water.
Activity:
- Check the solubility of given salts (in Table 4) in distilled water. Write the approximate value of their pH and mention the acids and bases from which the salts are formed.
Table 4
Activity 2.15 [T. B. Pg. 32]
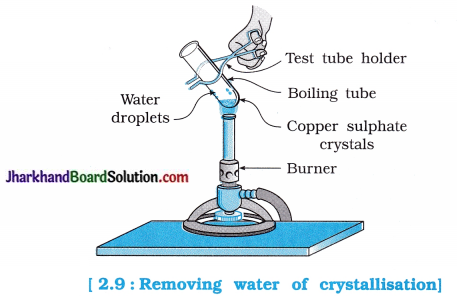
Aim: To remove the water of crystallisation.
Activity:
- Heat a few crystals of copper sulphate in a dry boiling tube.
- What is the colour of copper sulphate after heating?
- Do you observe water droplets in the boiling tube? Where have these come from?
- Add 2-3 drops of water on the sample of copper sulphate obtained after heating and observe it.
- Is the blue colour of copper sulphate restored?
Questions:
Question 1.
State the colour of copper sulphate after heating.
Answer:
It turns white from blue.
Question 2.
Do you notice the water droplets in the boiling tube?
Answer:
Yes. Copper sulphate crystals which seem to be dry contain water of crystalisation. On heating the copper sulphate crystals, water molecules are removed from the crystal and appear in the boiling tube.
Question 3.
Does the blue colour of copper sulphate solution reappear on adding 2 to 3 drops of water after heating it?
Answer:
Yes.
Question 4.
What is the chemical formula of hydrated copper sulphate?
Answer:
CuSO4.5H2O