Jharkhand Board JAC Class 10 Science Solutions Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce? Textbook Exercise Questions and Answers.
JAC Board Class 10 Science Solutions Chapter 8 How do Organisms Reproduce?
Jharkhand Board Class 10 Science How do Organisms Reproduce? Textbook Questions and Answers
Question 1.
Asexual reproduction takes place through budding in…
A. amoeba
B. yeast
C. plasmodium
D. leishmania
Answer:
yeast
Question 2.
Which of the following is not a part of the female reproductive system in human beings?
A. Ovary
B. Uterus
C. Vas deferens
D. Fallopian tube
Answer:
Vas deferens
Question 3.
The anther contains
A. sepals
B. ovules
C. pistil
D. pollen grains
Answer:
pollen grains
![]()
Question 4.
What are the advantages of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction?
Answer:
The advantages of sexual reproduction over asexual reproduction are as follows:
- Sexual reproduction involves fusion of male and female gametes from male and female parents to form zygote. Thus, new generation shows variation as DNA copies from two different individuals are received.
- Sexual reproduction involves gamete formation. During male and female gamete formation, meiosis takes place. New combination of genes occur during meiosis. This also leads to variation. Combining variation from two individuals would create new combination of variants.
- Sexual reproduction create variation generation after generation, which is useful for survival of species over time.
- The inbuilt tendency for variation during sexual reproduction is the basis for evolution.
Question 5.
What are the functions performed by the testis in human beings?
Answer:
The functions performed by the testis in human beings :
- to produce sperms
- to secrete testosterone.
Question 6.
Why does menstruation occur?
Answer:
When egg is not fertilised, the thick-spongy and highly vascular inner lining of uterus breaks causing menstruation in woman.
Question 7.
Draw a labelled diagram of the longitudinal section of a flower.
Answer:
Flower is the reproductive organ in flowering plants (angiosperms).
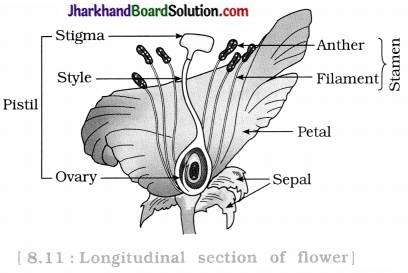
Parts of a flower: Sepals, petals, stamens and pistils. Among these stamens and pistils are reproductive parts.
Stamens : It is a male reproductive part. It consists filament and an anther.
Anther produces pollen grains that are yellowish in colour.
Pistil : It is present in the centre of a flower and is the female reproductive part. It is made up of three parts :
- Ovary : bottom swollen part
- Style : middle elongated part
- Stigma : terminal sticky part.
The ovary contains ovules and each ovule has an egg cell.
Types of flowers on the basis of reproductive parts are as follows :
- Unisexual flowers : When flower contains either stamens or pistil, it is called unisexual flower, e.g., Papaya, watermelon.
- Bisexual flowers : When flower contains both stamens and pistil, it is called bisexual flowers, e.g., Hibiscus, mustard, datura.
Question 8.
What are the different methods of contraception?
Answer:
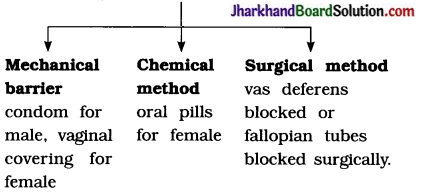
Question 9.
How are the modes for reproduction different in unicellular and multi-cellular organisms?
Answer:
Unicellular organisms multiply by simple cell division, i.e., by fission, budding, multi-cellular organisms have complex body organisation. They need to use more complex ways of reproduction mainly by sexual reproduction.
![]()
Question 10.
How does reproduction help in providing stability to populations of species?
Answer:
Reproduction gives rise to new offsprings of a species. No organism is immortal. High death-rate reduce the size of population. The rates of birth and death in a given population will determine its size.
So, reproduction is the process by which organisms increase their population and help in providing stability to population of species.
Question 11.
What could be the reasons for adopting contraceptive methods?
Answer:
The reasons for adopting contraceptive methods :
- To prevent unwanted pragnancies.
- To control human population.
- To prevent the transmission of sexually transmitted diseases especially by using condoms or vaginal covering.
Jharkhand Board Class 10 Science How do Organisms Reproduce? InText Questions and Answers
Question 1.
What is the importance of DNA copying in reproduction?
Answer:
Importance of DNA copying in reproduction :
- Transmission of hereditary information of parents to offsprings.
- Formation of variations by changes in DNA leads to evolution of species over a period of time.
Question 2.
Why is variation beneficial to the species but not necessarily for the individual?
Answer:
When reproduction takes place, new DNA copies are generated. They may show some amount of variations. The variations may not be beneficial for an individual. But when such variations go on accumulating over a longer time span, they may change the species. This change leads to evolution.
Question 3.
How does binary fission differ from multiple fission?
Answer:
- Binary fission is a type of fission, in which parent cell splits into two cells, example Amoeba, bacteria.
- Multiple fission is a type of fission in which single celled organisms divide into many daughter cells at one time, example Plasmodium.
Question 4.
How will an organism be benefitted if it reproduces through spores?
Answer:
Spores remain coated with protective envelope under unfavourable condition. This helps to survive in adverse conditions. They germinate only after favourable conditions return. Thus organism is benefitted by spore formation.
Question 5.
Can you think of reasons why more complex organisms cannot give rise to new individuals through regeneration?
Answer:
More complex organisms cannot give rise to new individuals due to following reasons :
- Different cell types perform different specialised functions.
- Complex organisms have tissues and organs.
- In complex organisms the regenerative ability is lost due to specialisation of tissues and organs.
- Reproduction in more complex organisms is the function of a specific cell type.
- Specialized cells to carry out regeneration are not present in complex animals.
Question 6.
Why is vegetative propagation practised for growing some types of plants?
Answer:
Vegetative propagation is practised for growing some types of plants because:
- Plants produced by vegetative propagation can bear flowers and fruits earlier than those produced from seeds.
- Plants that have lost their capability to produce seeds can be propagated by this method.
- It helps in retaining useful characters from generation to generation.
Question 7.
Why is DNA copying an essential part of the process of reproduction?
Answer:
DNA copying is an essential part of the process of reproduction because entire genetic information of parents is passed on to next generation through DNA. The DNA in the nucleus of the cell is the information source for making proteins which in turn form the body designs.
Question 8.
How is the process of pollination different from fertilisation?
Answer:
Pollination is the process of transfer of pollen grains from the anther of a stamen to the stigma of a carpel. Fertilisation is the process of fusion of male gamete with a female gamete to form a zygote.
![]()
Question 9.
What is the role of the seminal vesicles and the prostate gland?
Answer:
The secretion of the seminal vesicles and the prostate gland makes transport of sperms easier and provides nutrition to the sperms.
Question 10.
What are the changes seen in girls at the time of puberty?
Answer:
In girls, breast size begins to increase, with darkening of the skin of the nipples and menstruation begins at the time of puberty.
Question 11.
How does the embryo get nourishment inside the mother’s body?
Answer:
The embryo gets nourishment from the mother’s blood with the help of special tissue called placenta. Placenta contains villi on the embryo’s side of the tissue through which glucose and oxygen pass from the mother to embryo.
Question 12.
If a woman is using a copper-T will it help in protecting her from sexually transmitted diseases?
Answer:
No, a copper-T will not help in protecting woman from sexually transmitted diseases because during sexual intercourse fluid of male and female body directly come in contact.
Activity 8.1 [T. B. Pg. 129]
To observe the asexual reproduction method -Budding in yeast.
Apparatus : Test tube, conical flask, cotton plug, cover slip, glass slide, microscope, dropper.
Materials: Water, sugar, dry yeast granules.
Procedure:
- Take 100mL of water in conical flask. Add 10g sugar and dissolve it to prepare sugar solution.
- Take 20 mL of sugar solution in glass test tube. Add little amount of dry yeast granules. Shake the mixture and close the test tube tightly with cotton plug.
- Keep the test tube in warm place for 1 to 2 hours.
- Take one or two drops of yeast solution on the glass slide with the help of dropper.
- Now put a cover slip over it and observe under the microscope.

Questions :
Questions 1.
What is seen under the microscope?
Answer:
Yeast cells are seen under the microscope.
Questions 2.
Explain meaning of Bud.
Answer:
Bud is an outgrowth on yeast cell surface due to cell division.
Questions 3.
Can yeast live in the dormant condition?
Answer:
Yes.
Activity 8.2 [T. B. Pg. 129]
To observe the growth of fungus-Rhizopus on the piece of bread.
Apparatus : Petridish, Magnifying glass.
Material: Wet slice of bread.
Procedure :
- Wet a slice of bread in water. Now put the wet piece of bread in petridish. Keep the petridish in dark, moist and cool environment for a week.
- Now observe the bread slice with help of magnifying glass.
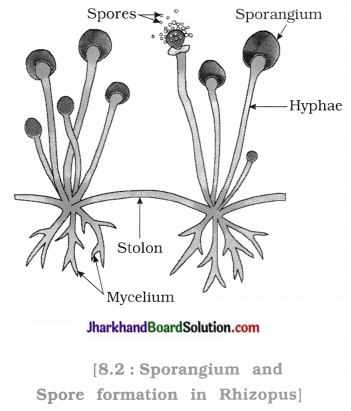
Questions :
Question 1.
What is seen on the slice of bread?
Answer:
Network of white cotton fibres-like structure is seen on the slice of bread.
Question 2.
From where did the fungi arrive on bread?
Answer:
The fungal spores arrived on bread from air.
Question 3.
Which fungi grow on the bread?
Answer:
Rhizopus fungi grow on the bread.
Question 4.
Why do spores of fungi germinate on the bread?
Answer:
Spores of fungi germinate on the bread because on bread moist environment and nutrients are available.
![]()
Question 5.
Reproduction through spore formation is which type of reproduction method ?
Answer:
Asexual reproduction.
Question 6.
Compare the growth of yeast and mould.
Answer:
Yeast is a type of fungus that grows as a single cell. Mould is a type of fungus that grows multicellular filamentous structures called hyphae.
These tubular branches from a single organism have multiple, genetically identical nuclei. The reproduction in yeast occurs by budding. Mould reproduces by formation of sexual or asexual spores.
Activity 8.3 [T. B. Pg. 129]
To observe binary fission in Amoeba. Apparatus: Microscope, permanent slide of Amoeba.
Procedure:
- Observe a permanent slide of Amoeba under a microscope.
- Observe another permanent slide of Amoeba showing binary fission.
- Compare your observations in both the slides.
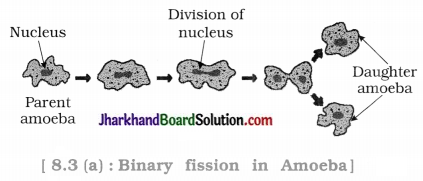
Questions :
Question 1.
Is Amoeba prokaryotic or eukaryotic organism ?
Answer:
Eukaryotic.
Question 2.
Can you give the sequence of binary fission in Amoeba?
Answer:
The sequence of binary fission in Amoeba : Nuclear division → Cytoplasmic division → Cell divides into two daughter cells.
Question 3.
Which unicellular, eukaryotic organisms reproduce through binary fission?
Answer:
Amoeba, Paramoecium, Leishmania. Euglena, etc.
Activity 8.4 [T. B. Pg. 130]
To observe filamentous algae under a microscope.
Apparatus : Microscope, slide, coverslip. Materials : Glycerine, pond water, blotting paper.
Procedure:
- Collect water from a lake or pond that appears dark green and contains filamentous structure.
- Put one or two filaments on a slide.
- Put a drop of glycerine on the filaments and cover it with a coverslip.
- Observe the slide under a microscope.
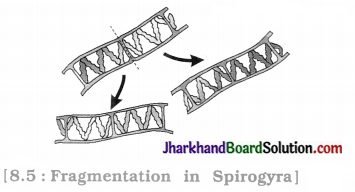
Questions :
Question 1.
State the example of filamentous organism.
Answer:
Filamentous algae : Spirogyra.
Question 2.
Can you identify different tissues in the filaments?
Answer:
No, filament of spirogyra is devoid of tissues.
Question 3.
Why is filament of spirogyra green in colour?
Answer:
A green colour of the filament of spirogyra is due to presence of chlorophyll.
Question 4.
Is spirogyra a prokaryotic or eukaryotic organism?
Answer:
Eukaryotic organism.
Question 5.
How do spirogyra reproduce asexually?
Answer:
Spirogyra reproduces asexually by fragmentation.
Activity 8.5 [T. B. Pg. 132]
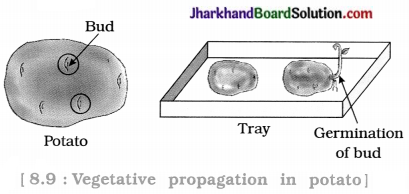
To study the vegetative propagation in potato.
Apparatus : Tray, cotton
Material: Potato
Procedure:
- Take potato tuber and observe its surface.
- Observe the pits on its surface and bud present in the pit.
- Make circle around them with the help of marker.
- Cut the potato into small pieces in such a way that, some of them possess bud.
- Now put wet cotton in the tray and put the potato pieces on it.
- Water for some days in tray, so that cotton remains wet.
- Observe the changes that occur in the potato piece.
Questions:
Question 1.
Is potato tuber root or stem?
Answer:
Potato tuber is stem.
Question 2.
Which other plants except potato produce buds for vegetative propagation?
Answer:
Bulbs of Ginger, amorphophalus, etc. produce buds for vegetative propagation.
Question 3.
Which are the potato pieces, that give rise to fresh green shoots and roots ?
Answer:
Only those potato pieces having bud, give rise to fresh green shoots and roots.
Activity 8.6 [T. B. Pg. 132]
To show vegetative propagation by stem cuttings.
Materials : Money-plant (pothos)
Procedure:
- Select a money-plant. Cut some pieces which contain at least one node of leaf.
- Cut out some other portions between two leaves.
- Dip one end of all the pieces in water.
- Observe over the next few days.
Questions :
Question 1.
Which pieces grow and give rise to fresh leaves?
Answer:
Those pieces with at least one node of leaf can grow and give rise to fresh leaves.
![]()
Question 2.
State your conclusion.
Answer:
Node is essential in a stem cutting for vegetative propagation of money-plant.
Question 3.
Can you give some other example to show vegetative propagation by stem cuttings?
Answer:
Rose, hibiscus, lemon, sugarcane, tamarind, etc.
Activity 8.7 [T. B. Pg. 135]
To observe the different parts of seed.
Materials : Seeds of Bengal gram [chana], water, wet cloth.
Procedure:
- Soak a few seeds of Bengal gram (chana) and keep them overnight.
- Drain the excess water and cover the seeds with a wet cloth and leave them for a day.
- Make sure that the seeds do not become dry.
- Cut open the seeds carefully and observe the different parts.
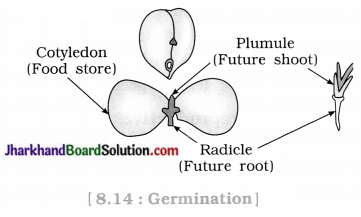
Questions :
Question 1.
What is an embryo of plant?
Answer:
An embryo is a future plant which develops into seedling.
Question 2.
Which are the structures seen in an embryo?
Answer:
A radicle, plumule and cotyledons occur in an embryo.
Question 3.
What is the role of cotyledon in chana?
Answer:
Cotyledons store food nutrients in chana and provide these nutrients during seed germination.
Question 4.
Which parts in seed are known as future root and as future shoot?
Answer:
Radicle is known as future root and plumule as future shoot.
Question 5.
How is an embryo formed from zygote?
Answer:
The zygote divides several times to form an embryo.