JAC Board Class 9th Social Science Important Questions Economics Chapter 1 The Story of Village
I. Objective Type Questions
1. The main economic activity of Palampur village is
(a) Agriculture
(b) Manufacturing
(c) Dairy
(d) All of the above
Answer:
(a) Agriculture
2. What is required for the production of goods and services ?
(a) Land
(b) Labour
(c) Physical capital
(d) All of the above.
Answer:
(d) All of the above.
3. Green revolution took place in India in
(a) late 1980s
(b) late 1970s
(c) late 1960s
(d) late 2000s
Answer:
(c) late 1960s
4. To grow more than one crop on the same piece of land during the years is known as
(a) Multiple cropping
(b) Mixed cropping
(c) Modern cropping
(d) Plantatign cropping
Answer:
(a) Multiple cropping
3. is a common activity in many families of Palampur.
(a) Manufacturing
(b) Dairy
(c) Transportation
(d) Shopkeeping
Answer:
(b) Dairy
II. Very Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
Where is Palampur village located?
Answer:
Palampur village is located in Bulandshahar district of western Uttar Pradesh.
Question 2.
What is the main economic activity of Palampur village?
Answer:
Agriculture is the main economic activity of Palampur Village.
![]()
Question 3.
Write the name of various forms of transport visible on the road from Palampur to Shahpur.
Answer:
Forms of transport seen are bullock carts, tongas, bogeys, motorcycles, Jeeps, tractors and trucks.
Question 4.
Name some non-farming activities.
Answer:
Small manufacturing, shop-keeping, tailoring, carpentery, dairy; transporting, animal husbandary, etc.
Question 5.
What is the aim of production?
Answer:
The aim of production is to produce the goods and services that we want.
Question 6.
Name the factors of production.
Answer:
- Land,
- Labour,
- Physical capital,
- Human capital.
Question 7.
A What is Bigha or Guintha?
Answer:
Bigha or Guintha is the local unit of measuring land in villages.
Question 8
During which season do farmers of Palamphur grow Jowar and Bajra?
Answer:
During the rainy season (kharif) the farmers of Palampur grow Jowar and-Bajra.
Question 9.
In which season wheat is grown in Palampur village?
Answer:
During rabi season (winter), wheat is grown in Palampur village.
Question 10.
What is multiple cropping?
Answer:
To grow more than one crop on a piece of land during the year is known as multiple cropping.
Question 11.
What is the full form of‘HYV’ seeds?
Answer:
HYV stands for High Yielding Variety seeds.
![]()
Question 12.
In which states modern farming was first used?
Answer:
Modem farming was first introduced in Punjab, Haryana and Western Uttar Pradesh.
Question 13.
What is the disadvantage of using chemical fertilisers in modern farming methods?
Answer:
The chemicals kill bacteria and microbes, which are essential for soil fertility.
Question 14.
Which state has the highest consumption of chemical fertilisers in India?
Answer:
Punjab has the highest consumption of chemical fertilisers in India.
Question 15.
Who hires farm labourers?
Answer:
Medium and large farmers hire farm labourers.
Question 16.
Where do farm labourers come from?
Answer:
Farm labourers come either from landless families or families cultivating small plots of land.
Question 17.
From where do most of the small farmers borrow money to arrange for capital in Palampur?
Answer:
Most of the small farmers borrow money from village moneylenders in Palampur.
Question 18.
What are the non-farming activities being carried our in Palampur?
Answer:
Some of the non-farming activities being carried out in Palampur are manufacturing, transport, shopkeeping and computer education.
III. Short Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
There are some requirements for production of goods and services. What are these?
Answer:
There are four requirements for production of goods and services. These requirements are as follows:
- The first requirement is land and other natural resources.
- The second requirement is labour.
- The third requirement is physical capital.
- The fourth requirement is human capital.
![]()
Question 2.
What are the items that come under physical capital?
Answer:
The following items come under physical capital :
1. Fixed capital:
Tools, machines, buildings that can be used in production over many years are called fixed capital. Example Farmer’s plough, generators, turbines, computers, etc.
2. Working capital:
Raw materials and money in hand are called working capital. It is used up during the production activity. Resulting in finished goods and services that are required. Example Yarn used by the weaver, clay used by the potter.
Question 3.
How many kinds of crops are grown in Palampur?
Answer:
Following types of crops are grown in Palampur:
- During the rainy season (Kharif), farmers grow jowar and bajra.
- It is followed by cultivation of potato between October and December.
- In the winter season (Rabi), fields are sown with wheat.
- A part of the land area is also devoted to sugarcane which is harvested once every year.
Question 4.
Throw light on irrigation in the villages across India.
Answer:
Not all the villages in India have high levels of irrigation as Palampur. Apart from the riverine plains, coastal regions in our country are well-irrigated. In contrast, plateau regions such as the Deccan plateau have low levels of irrigation. Of the total cultivated area in the country, a little less than 40 per cent is irrigated even today. In the remaining areas, farming is largely dependent on rainfall.
Question 5.
What was the Green revolution? How did it solve the food crisis in India?
Answer:
Green revolution is the modern technique of using high yielding varieties of (HYV) seeds (Hyvs). increased use of chemical fertilizers and irrigation in agriculture Green Revolution was introduced in India by M.S. Swaminathan.
Green Revolution made India self-sufficient in food grains by improving crop production at a large scale.
![]()
Question 6.
Write any four differences between traditional and modern methods of farming.
Answer:
Four differences between traditional and modern methods of farming are as follows:
| Traditional methods | Modem methods |
| 1. Seeds used are simple. | 1. High Yielding Variety (HYV) sees are used. |
| 2. Fertilizer used is manure from cow dung. | 2. Chemical fertilizers are used. |
| 3. Manual labour is used for all activities. | 3. Modern machinery is used for all activities. |
| 4. Irrigation is done through wells and tanks | 4. Irrigation is done through dams, tubewells and canals. |
Question 7.
Modern farming methods have overused the natural resource base. How?
Answer:
Land is a natural resource. It is necessary to be very careful in its use. But scientific reports indicate that modem farming methods have overused the natural resource base in the following ways:
- Green Revolution is associated with the loss of soil fertility due to increased use of chemical fertilizers.
- Continuous use of groundwater for tubewell irrigation has reduced the water table below the ground. Environmental resources like soil fertility and groundwater are built up over many years. Once destroyed, it is very difficult to restore them.
Question 8.
What are the bad-effects of chemical fertilizers?
Answer:
The bad-effects of chemical fertilizers are as follows:
- Chemical fertilizers provide minerals which dissolve in water and are immediately available to plants but they not retain in the soil for long. This means, some time after, their use, the soil become less fertile than ever before.
- Chemical fertilizers kill useful bacteria and other micro-organisms in the soil.
- Chemical fertilizers pollute groundwater, rivers and lakes.
Question 9.
Explain the distribution of land among farmers in Palampur village.
Answer:
In Palampur village, about one-third of the total of 450 families are landless, i.e., 150 families are landless. 240 families cultivate small plots of less than 2 hectares. There are 60 families of medium and large farmers who cultivate more than 2 hectares of land. A few of the large families have land extending over 10 hectares or more.
Question 10.
What is the need of labour in farming and where does it come from?
Answer:
Farming requires a great deal of hard work for various activities, like ploughing, harvesting, seeding, threshing etc. Small farmers aloi-g with their families cultivate their own fields. Thus, they provide the labour required for farming from their family itself. While medium and large farmers hire farm labourers to work on their fields.
![]()
Question 11.
How do most small farmers arrange the necessary capital for farming?
Answer:
Most small farmers have to borrow money to arrange for capital. They borrow from large farmers or the village moneylenders or the traders who supply various inputs for cultivation. The rate of interest on such loans is very high. They are put to great distress to repay the loan.
Question 12.
What do large farmers like Tejpal Singh do with the capital derived from surplus produce?
Answer:
Like Tejpal Singh, other large and medium farmers sell the surplus farm products. A part of the earnings is saved and kept for buying capital for the next season. Thus, they are able to arrange for capital needed for farming from their own savings. Some farmers might also use their savings to buy cattle, tractors or to set up shops.
IV. Long Answer Type Questions
Question 1.
“Palampur is a well-developed village”. Justify this statement
Or
Provide major evidents to show that Palampur a developed village.
Answer:
Palampur is a developed village due to the following reasons:
1. Palampur is well-connected with neighbouring villages and towns. Raiganj is a big village three kilometers from Palampur. An all-weather road connects the village to Raiganj and further on to the nearest small town of Shahpur.
2. Many kinds of transport are visible on this road, starting from bullock carts, tongas, bogees loaded with jaggery and other commodities, to motor vehicles like motorcycles, jeeps, tractors and trucks.
3. Palampur village has about 450 families belonging to several different castes. The 80 upper caste families have their houses made of bricks and cement plas¬tering.
4. Most of the houses have electric connections. Electricity powers all the tubewells in the fields and is used in various types of small businesses.
5. Palampur has two primary schools and one high school.
6. There is a primary health centre run by the government and one private dispensary where sick people are treated.
This description shows that Palampur has a well developed system of roads, electric¬ity and irrigation facilities, schools and health centres, so, we can say that Palampur is a well-developed village.
Question 2.
What do you mean by the factors of production? Explain.
0r
What are requirements for production of goods and services?
Answer:
Productjpq. is organised by combining land, labour, physical capital and human capital which are collectively known as factors of production. We cart understand about these factors of production with the help of a chart as given below: Factors of Production/Requirements for Production
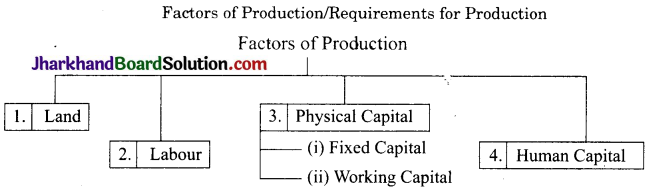
The description of each of them is as follows:
1. Land:
Land is the foremost factor of production. Land includes other natural resources; such as water, forests, minerals etc. which are essential for production.
2. Labour:
Labour is the second factor of production. People who perform work are known as labour. Some production activities require highly educated workers to perform the necessary tasks. Other activities require workers who can do manual work. Each worker provides labour necessary for production.
3. Physical capital:
The variety of inputs required at every stage of production is called physical capital. Physical capital can be categorised into two as follows.
(a) Fixed capital:
Tools and machines range from very simple tools to sophisticated machines, buildings etc. and these are included under fixed capital. This capital can be used in production over many years. The examples of fixed capital are, farmer’s plough, generators, turbines, computers, land, factory etc.
(b) Working capital:
Raw material and money in hand comes under working capital. This capital is used in production. Examples are-yarn used by weavers, clay used by potter, etc. Money is also required during production to make payments and buy other necessary items.
(4) Human capital:
Human capital is required to put together land, labour and physical capital and produce an output either to use yourself or to sell in the market. Knowledge and enterprise are known as human capital.
![]()
Question 3.
How are the farmers in Palampur village able to grow more crops from the same land? Explain.
Answer:
The following points state how the farmers in Palampur village are able to grow more crops from the same land:
- All land is cultivated in Palampur village and no land is left idle.
- Palampur’s farmers follow multiple cropping. They grow at least two main crops. Many of them also grow potato as the third crop.
- There is a well-developed irrigation system in Palampur village that enables the farmers to grow three different crops in one year.
- Electricity has played an important role in transformation of the irrigation system in the village. The previously existing Persian wheels were replaced by electric run tubewells which could irrigate much larger areas of land.
- Previously farmers follow modem farming methods for obtaining a higher yield.
- Green Revolution introduced HYV seeds and modem farming methods. The farmers of Palampur village significantly increased their agricultural produc¬tion by using HYV seeds, chemical fertilizers and pesticides.
Question 4.
What do you know about HYV seeds? Write its merits and limitations.
Answer:
HYV seeds HYV seeds means high yielding variety of seeds. These types of seeds provide much more yield than traditional seeds for the same area under cultivation.
1. Merits of HYV seeds: Compared to the traditional seeds, the high yielding variety of seeds promise to produce much greater amounts of grain on a single plant. As a result, the same piece of land can now produce far greater quantities of food grains than it was possible earlier.
2. Limitations of HYV seeds: High yielding variety of seeds need plenty of water, chemical fertilizers and pesticides to produce best results. Excessive use of these inputs reduces soil fertility over a long time period.
Question 5.
What do you mean by farm labourers? Write some characteristics of farm labourers.
Answer:
Farm labourers come either from landless families or families cultivating small plots of land. Characteristics of Farm Labourers: The chief characteristics of farm labourers are as follows:
- Farm labourers do not have a right over the crops grown on the land.
- They are paid wages by the farmer for whom they work.
- Paid wages can be in cash or in a kind, e.g., crop.
- Sometimes labourers get meals also.
- Wages vary widely from region to region, from crop to crop, and from one farm activity to another.
- A farm labourer might be employed on a daily basis or for one particular farm activity or for the whole year.
- They look for work every day.
- There is heavy competition for work among the farm labourers.
![]()
Question 6.
Mention ary four non-farm production activities of Palampur village.
Answer:
Following are the four main non-four production activites of Palampur village
1. Dairy:
Dairy is a common activity in many families of Palampur village. They keep buffaloes ror supplying the milk to the collection-cum-chilling center at Rani- ganj. The milk i. orocessed further for supply in various town and cities.
2. Manufacturing:
At present, less than fifty people are engaged in manufacturing in Palampur village. Unlike the manufacturing that takes place in the large factories in the towns and cities, manufacturing in Palampur involves very simple production methods and are done on a small scale. They are carried out mostly at home or in the fields with the help of family members and rarely are labourers hired.
3. Shopkeeping:
People involved in trade are not many in Palampur village. The traders of Palampur are mostly shopkeepers wrho buy various goods from wholesale markets in the cities and sell them in the village. Some of them have also opened shops selling eatables near the village bus stand.
4. Transport services:
There are a variety of vehicles on the road connecting Palampur to Raiganj. Ricksha wallahs, tonga wallays, jeep, tractor, truck drivers and people driving the traditional bullock carts and bogeys are people engaged in the transport services. They carry people and goods from one place to another and in return they get paid for it, i.e., the number of people involved in transport has grown over the last several years.